Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The main active ingredient is Diphenhydramine . The mechanism of action is based on the inhibitory effect of the drug on central, cholinergic structures, blocking H3-histamine receptors in the brain. Diphenhydramine relieves attacks of itching, tissue edema, hyperemia, prevents spasms of smooth muscle tissue, and has a positive effect on capillary permeability . Taking oral forms causes a short-term feeling of numbness in the mouth. The drug has antiparkinsonian, hypnotic, sedative, and antiemetic effects. By blocking the cholinergic receptors of the ganglia, it reduces blood pressure and can increase existing hypotension . In persons with epilepsy and local brain damage, even low doses of the drug Diphenhydramine can provoke an epileptic attack , and the EEG shows activation of epileptic discharges. The drug is most effective for bronchospasm provoked by taking histamine liberators (morphine, tubocurarine). The drug is least effective for bronchospasm of allergic origin. With repeated doses, the hypnotic and sedative effects are more pronounced. The drug begins to act an hour after entering the body, the effective effect lasts up to 12 hours.
pharmachologic effect
First generation H1-histamine receptor blocker. The effect on the central nervous system is due to the blockade of H1-histamine receptors and m-cholinergic receptors in the brain. Reduces or prevents histamine-induced spasms of smooth muscles, increased capillary permeability, tissue swelling, itching and hyperemia, has local anesthetic, antiemetic, sedative effects, and has a hypnotic effect. Antagonism with histamine manifests itself to a greater extent in relation to local vascular reactions during inflammation and allergies than to systemic ones, that is, a decrease in blood pressure. However, when administered parenterally to patients with a deficiency in circulating blood volume, a decrease in blood pressure and an increase in existing hypotension are possible. In people with local brain damage and epilepsy, it activates (even in low doses) epileptic discharges on the electroencephalogram and can provoke an epileptic attack.
The action develops within a few minutes and lasts up to 12 hours.
Indications for use of Diphenhydramine
Why and for what purpose are tablets and solution prescribed?
The drug is used to relieve allergic reactions, with itchy dermatosis , allergic dermatitis, rhinosinusitis , vasomotor rhinitis, acute iridocyclitis , allergic conjunctivitis. The drug is used for insomnia, chorea, Parkinson's disease, radiation sickness, air sickness, sea sickness, Meniere's syndrome , vomiting in pregnant women. The drug is prescribed as a premedication for extensive traumatic injuries to soft tissues and skin, serum sickness, and hemorrhagic vasculitis .
Interaction with other drugs
Enhances the effect of ethanol and drugs that depress the central nervous system.
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors enhance the anticholinergic activity of diphenhydramine.
Antagonistic interactions are observed when co-administered with psychostimulants.
Reduces the effectiveness of apomorphine as an emetic drug in the treatment of poisoning.
Strengthens the anticholinergic effects of drugs with m-anticholinergic activity.
Contraindications
Diphenhydramine is not prescribed for prostatic hyperplasia, angle-closure glaucoma, epilepsy, bladder stenosis, or stenosing peptic ulcer of the digestive system. For bronchial asthma, breastfeeding, pregnancy, prescribe with caution.
Side effects
Taking the drug can cause tremor, dizziness, numbness in the oral cavity, dry mouth, increased drowsiness, photosensitivity , asthenia, headaches, nausea, accommodation paresis , decreased speed of psychomotor reaction, and impaired coordination of movements. The use of the drug Diphenhydramine in children may be accompanied by a feeling of euphoria , irritability, and paradoxical insomnia.
Pharmacokinetics
Bioavailability - 50%. The time to reach maximum concentration is 20-40 minutes (the highest concentration is determined in the lungs, spleen, kidneys, liver, brain and muscles). Communication with plasma proteins - 98 - 99%. Penetrates the blood-brain barrier. Metabolized mainly in the liver, partially in the lungs and kidneys. Removed from tissues after 6 hours. The half-life is 4 - 10 hours. Within 24 hours, it is completely excreted by the kidneys in the form of metabolites conjugated with glucuronic acid. Significant amounts are excreted in milk and may cause sedation in breastfed infants (a paradoxical reaction characterized by excessive excitability may occur).
Instructions for use of Diphenhydramine (Method and dosage)
Diphenhydramine tablets, instructions for use
30-50 mg one to three times a day, duration of therapy 10-15 days.
For insomnia, 50 mg is prescribed half an hour before bedtime.
For postencephalic, idiopathic parkinsonism, 25 mg three times a day is initially prescribed, subsequently the dosage is gradually increased to 50 mg 4 times a day.
For motion sickness, you need to take 25-50 mg tablets every 6 hours.
Instructions for use of Diphenhydramine in ampoules
A solution of Diphenhydramine is administered intravenously 20-50 mg of the drug, having previously dissolved in 100 ml of 0.9 sodium chloride, intramuscular injections of 10-50 mg are administered once.
Instructions for the use of rectal suppositories with Diphenhydramine
Rectal suppositories after a cleansing enema are administered twice a day.
Using drops with Diphenhydramine
In ophthalmology, 2 drops of solution (0.2-0.5%) are instilled into each conjunctival sac 3 times a day.
In allergology, 0.05 g of the drug is administered intranasally.
Diphenhydramine-Belmed solution for IV and IM administration 10 mg/ml in 1 ml ampoules No. 5x2
Product description
Diphenhydramine-Belmed.
Release forms
Solution.
INN
Diphenhydramine.
FTG
H1-histamine receptor blocker.
Description
Transparent colorless solution.
Compound
For one ampoule: active substance: diphenhydramine hydrochloride – 10 mg excipient: water for injection.
Pharmacotherapeutic group
Antihistamines for systemic use. Diphenhydramine. ATC code: R06AA02.
pharmachologic effect
The effect on the central nervous system is due to the blockade of H1-histamine receptors in the brain and the depressive central m-anticholinergic effect (can cause both depression and excitation of the central nervous system). It has pronounced H1-blocking activity, reduces or prevents histamine-induced smooth muscle spasms, increased capillary permeability, tissue swelling, itching and hyperemia. Causes local anesthesia (when taken orally, a short-term numbness of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity occurs) - only in high doses, blocks m-cholinergic receptors in the central nervous system, has sedative, hypnotic, antiparkinsonian and antiemetic effects. In people with local brain damage and epilepsy, it activates (even in low doses) epileptic discharges on the electroencephalogram and can provoke an epileptic attack. Sedative and hypnotic effects are more pronounced with repeated doses. The maximum effect develops 60 minutes after application, the duration of action is from 4 to 6 hours.
Indications for use
Diphenhydramine in injection form is effective in adults and in pediatric patients, except premature infants and newborns, for the following conditions when oral diphenhydramine is inappropriate. As an antihistamine: to reduce the intensity of allergic reactions to blood or plasma products, in anaphylaxis, as an adjunct to epinephrine and other standard measures after control of acute symptoms, in other uncomplicated immediate allergic conditions when oral therapy is not possible or contraindicated. As a hypnotic: insomnia (for short-term treatment of situational insomnia in patients who have difficulty falling asleep).
Directions for use and dosage regimen
Intravenously or intramuscularly. For adults and children over 14 years of age, 1-5 ml of solution (10-50 mg) intravenously or intramuscularly 1-3 times a day. The maximum daily dose is 200 mg. For children aged 7 months to 12 months, 0.3-0.5 ml (3-5 mg), from 1 year to 3 years, 0.5-1 ml (5-10 mg), from 4 to 6 years 1-1.5 ml (10-15 mg), from 7 to 14 years 1.5-3 ml (15-30 mg) if necessary every 6-8 hours. Diphenhydramine in injection form is indicated when oral administration is inappropriate. The parenteral dosage form should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to use whenever the package is opened. Dosage should be individualized according to the patient's needs and response.
Side effect
From the cardiovascular system: decreased blood pressure, palpitations, tachycardia, extrasystole. From the respiratory system: dryness of the mucous membrane of the nose and throat, increased viscosity of sputum, a feeling of constriction in the chest or throat, sneezing, nasal congestion. From the nervous system: headache, sedation, drowsiness, dizziness, loss of coordination, weakness, confusion, anxiety, agitation, nervousness, tremor, irritability, insomnia, euphoria, paresthesia, neuritis, convulsions. From the senses: impaired visual perception, diplopia, vertigo, tinnitus, acute labyrinthitis. From the digestive system: dryness of the oral mucosa, epigastric pain, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation. From the genitourinary system: frequent or difficult urination, urinary retention, early menstruation. From the hematopoietic organs: hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis. Allergic reactions: urticaria, drug rash, anaphylactic shock, photosensitivity. If the above adverse reactions or adverse reactions not listed in these instructions for medical use of the drug occur, you should consult a doctor.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to diphenhydramine, other antihistamines with a similar chemical structure, breastfeeding, pregnancy, childhood (newborn period and prematurity), closed-angle glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy, stenosing ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, pyloroduodenal obstruction, bladder neck stenosis, bronchial asthma, pheochromocytoma, epilepsy, congenital long QT syndrome or long-term use of drugs that can prolong the QT interval, bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmias, porphyria. Injections should not be used as a local anesthetic (risk of local necrosis). Concomitant use with other drugs containing diphenhydramine, including oral and topical drugs.
Overdose
Symptoms: dry mouth, respiratory depression, persistent mydriasis, increased intraocular pressure, facial flushing, depression or excitation of the central nervous system, depression, confusion, hyperkinesia, convulsions, delirium, tachycardia, including torsade de pointes, arrhythmia. A case of the development of rhabdomyolysis after an overdose of diphenhydramine has been described. Treatment: symptomatic and supportive therapy with careful monitoring of respiratory function and blood pressure. Epinephrine and analeptics are not allowed. Intravenous drip administration of plasma-substituting fluids, oxygen therapy. As an antidote for an overdose of diphenylhydramine hydrochloride, physostigmine (0.02-0.06 mg/kg body weight) can be prescribed if anticholinergic symptoms increase. In cases of physostigmine overdose, atropine is recommended. With the development of convulsions, hyperthermia and symptoms of central nervous system excitation, parenteral diazepam is prescribed.
Precautionary measures
With prolonged uncontrolled use of diphenhydramine, tolerance, physical and mental dependence develop. After discontinuation of the drug, withdrawal syndrome may develop with sleep disturbances, anxiety, and agitation. When treating insomnia, do not use for longer than 7-10 nights without consulting a doctor. UV radiation and ethanol should be avoided during treatment with diphenhydramine. It is necessary to inform your doctor about the use of this drug: the antiemetic effect may make it difficult to diagnose appendicitis and recognize symptoms of overdose with other drugs. Cases of local necrosis associated with the use of diphenhydramine injection solution subcutaneously or intravenously have been described. Do not administer subcutaneously due to irritant effects. Pediatric Use: Diphenhydramine should not be used in newborns or premature infants. In pediatric patients, antihistamines, especially in overdose, may cause hallucinations, convulsions, or death. As in adults, antihistamines can reduce mental alertness in children. In young children, diphenhydramine may cause agitation. The safety and effectiveness of diphenhydramine for the treatment of insomnia in children younger than 12 years of age have not been studied. There is a risk of overdose and toxicity (including death) in children younger than 2 years of age receiving concomitant medications containing antihistamines, antitussives, expectorants, and decongestants, alone or in combination, to relieve symptoms of an upper respiratory tract infection. Evidence of the effectiveness of these drugs in this age group is limited; appropriate doses have not been established. Therefore, it is not recommended to use such drugs in children under 2 years of age. Due to the high risk of overdose and toxicity, these drugs are not recommended for use in children under 4 years of age. If necessary, you should strictly adhere to the dosage of diphenhydramine and avoid the use of cold medications. Use in the elderly (around 60 years of age and older): Antihistamines are more likely to cause dizziness, sedation, and hypotension in older patients. Diphenhydramine has atropine-like effects and should therefore be used with caution in patients with asthma, increased intraocular pressure, hyperthyroidism, cardiovascular disease or a history of hypertension. Use with caution in patients with lower respiratory tract diseases, including asthma. Diphenhydramine may cause drowsiness and has additive effects with alcohol. Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, effects on fertility: Long-term animal studies have not been conducted to determine mutagenic and carcinogenic potential.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Pregnancy: category B (according to FDA classification). Reproducible studies were conducted in rats and rabbits at doses up to 5 times higher than human doses and found no evidence of impaired fertility or fetal harm associated with diphenhydramine hydrochloride. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproductive studies do not always predict human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if truly needed.
Impact on the ability to drive a car and potentially dangerous mechanisms
Patients should refrain from all activities that require increased attention, rapid mental and motor reactions.
Interaction with other drugs
Enhances the effect of ethanol and drugs that depress the central nervous system. Monoamine oxidase inhibitors enhance the anticholinergic activity of diphenhydramine. Antagonistic interactions are observed when co-administered with psychostimulants. Reduces the effectiveness of apomorphine as an emetic drug in the treatment of poisoning. Strengthens the anticholinergic effects of a drug with M-anticholinergic activity. Diphenhydramine potentiates the effects of local anesthetics. When used with analeptics, there is a risk of developing seizures. The use of diphenhydramine along with antihypertensive drugs may increase the feeling of fatigue. Concomitant use of drugs that prolong the QT interval and cause hypokalemia (for example, thiazide diuretics) should be avoided.
Storage conditions
In a place protected from light at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Best before date
3 years. Do not use after the expiration date stated on the packaging.
Package
1 ml in USP-1 glass ampoules in package No. 10 or in blister packs No. 5×1, No. 5×2.
Release from pharmacies
On prescription.
Buy Diphenhydramine-Belmed solution for IV and IM administration 10 mg/ml in ampoules 1 ml No. 5x2 in the pharmacy
Price for Diphenhydramine-Belmed solution for IV and IM administration 10 mg/ml in 1 ml ampoules No. 5x2
Instructions for use for Diphenhydramine-Belmed solution for IV and IM administration 10 mg/ml in 1 ml ampoules No. 5x2
Diphenhydramine overdose
Taking high doses causes depression of the nervous system, paresis of the digestive organs, dry mouth, dilated pupils, and depression. A specific antidote has not been developed; intravenous administration of plasma-substituting fluids and the use of drugs that increase blood pressure are required. It is unacceptable to use analeptics, epinephrine .
In case of severe overdose, death, injury, heart attack, and paralysis are possible.
special instructions
The medication has a negative effect on activities that require increased concentration, control of complex mechanisms, and driving vehicles. During therapy, it is necessary to avoid drinking alcoholic beverages and limit exposure to the sun and ultraviolet radiation to a minimum. The antiemetic effect of the drug can mislead the doctor in the differential diagnosis of acute appendicitis , recognizing the symptoms of overdose, and intoxication.
International name (INN) of Diphenhydramine: Diphenhydramine.
The Pharmacopoeia contains a description under FS 42-0232-07.
Described on Wikipedia under the name Diphenhydramine.
It is often necessary to know the name of a drug in Latin. Here, for example, is the recipe in Latin:
Rp.: Dimedroli 0.05 D. td N 10 in tabul. S.
Sticks with Diphenhydramine in Latin: baculi cum dimedrolum.
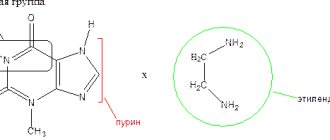
Structural formula of the active substance:
Is Diphenhydramine a drug?
In fact, the medication is not a drug, but in combination with alcoholic drinks and in large doses it causes hallucinations, as well as addiction if used frequently.
Can I take Diphenhydramine in ampoules?
In general, it is possible, but the concentration of the active substance in ampoules is less than in tablets.
Analogs
Level 4 ATC code matches:
Benadryl
Clemastine
Sungmil
Donormil
Tavegil
Analogues are Kalmaben , Dramina .
Diphenhydramine price, where to buy
The price of Diphenhydramine tablets is 3-6 rubles per pack of 10 pieces. How much do tablets cost in Ukraine? The package can be purchased for 6-8 hryvnia.
You can buy Diphenhydramine in ampoules at a price of 25-30 rubles for 10 pieces in Russia and for 15-18 UAH in Ukraine.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Diphenhydramine (amp. 1% 1 ml No. 10) Biosynthesis OJSC
28 rub. order - Diphenhydramine (amp. 1% 1ml No. 10) BZMP
39 RUR order
- Diphenhydramine tablets 50 mg No. 20DHF JSC
13 rub. order
- Diphenhydramine (amp. 1% 1ml No. 10 (5x2)) Belmedpreparaty
27 RUR order
- Diphenhydramine (amp. 1% 1ml No. 10) DHF JSC
30 rub. order
show more
PaniPharmacy
- Diphenhydramine ampoule Diphenhydramine solution d/in.
1% amp. 1ml No. 10 Ukraine, Health of the people LLC 17 UAH. order - Diphenhydramine ampoule Diphenhydramine solution d/in. 1% amp. 1ml No. 10 Ukraine, Darnitsa ChAO
23 UAH order
- Diphenhydramine ampoule Diphenhydramine solution d/in. 1% amp. 1ml No. 10 Ukraine, Galichfarm JSC
14 UAH order
show more
Buy Diphenhydramine solution intravenously and intramuscularly 1% 1ml No. 10 in pharmacies
Instructions for use Diphenhydramine Buy Diphenhydramine solution 1% 1ml
Dosage forms: solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration 10 mg/ml, solution for injection 1%, solution for injection 10 mg/ml Manufacturers ICN October (Russia), ICN Polypharm (Russia), Allergen Stavropol (Russia), Belvitamins (Russia) ), Belgorodvitamins (Russia), Belmedpreparaty (Belarus), Biomed (Russia), Biosynthesis OJSC (Russia), Biostimulator (Ukraine), Veropharm Belgorod branch (Russia), Veropharm Voronezh branch (Russia), Voronezh-Vremya Pharm Production Company (Russia) ), Voronezhkhimpharm (Russia), Dalkhimfarm (Russia), Darnitsa Pharmaceutical Company (Ukraine), Public Health - Kharkov Pharmaceutical Enterprise (Ukraine), Immunopreparat (Russia), Microgen NPO (Allergen) Stavropol (Russia), Microgen NPO (Biomed Perm NPO) (Russia), Microgen NPO (Immunopreparat) Ufa (Russia), Moskhimfarmpreparaty im. ON THE. Semashko (Russia), Organika OJSC (Russia), Samson-Med (Russia), St. Petersburg Research Institute of Vaccines and Serums and Bacter Preparations Production Enterprise (Russia), Tallinn Pharmaceutical Plant (Estonia), Ufavita (Russia), Enzyme (Russia), Endokrininyai Preparatai (Lithuania) Group H1-histamine receptor blockers Composition Active ingredient - diphenhydramine. International nonproprietary name Diphenhydramine Synonyms Diphenhydramine-Vial, Diphenhydramine-UBF, Diphenhydramine hydrochloride, Psilo-balm Pharmacological action Pharmacological action - antihistamine, antiallergic, anticholinergic, antiemetic, sedative, hypnotic, local anesthetic. Blocks histamine H1 receptors and eliminates the effects of histamine mediated through this type of receptor. Reduces or prevents histamine-induced smooth muscle spasms, increased capillary permeability, tissue swelling, itching and hyperemia. Causes local anesthesia, has an antispasmodic effect, blocks cholinergic receptors of the autonomic ganglia (lowers blood pressure). Blocks H3 histamine receptors in the brain and inhibits central cholinergic structures. It has a sedative, hypnotic and antiemetic effect. It is more effective for bronchospasm caused by histamine liberators (tubocurarine, morphine, sombrevin) and, to a lesser extent, for allergic bronchospasm. When taken orally, it is quickly and well absorbed. Most of it is metabolized in the liver, a smaller part is excreted unchanged in the urine. It is well distributed in the body and passes through the BBB. Excreted in milk and may cause sedation in infants. Maximum activity develops after 1 hour, duration of action - from 4 to 6 hours. Indications for use: Urticaria, hay fever, vasomotor rhinitis, pruritic dermatoses, acute iridocyclitis, allergic conjunctivitis, angioedema, capillary toxicosis, serum sickness, allergic complications during drug therapy, transfusions blood and blood-substituting fluids; complex therapy of anaphylactic shock, radiation sickness, bronchial asthma, gastric ulcer and hyperacid gastritis; colds, sleep disorders, premedication, extensive injuries to the skin and soft tissues (burns, crushes); parkinsonism, chorea, seasickness and air sickness, vomiting, incl. during pregnancy, Meniere's syndrome; local anesthesia in patients with a history of allergic reactions to local anesthetic drugs. Contraindications Hypersensitivity, breastfeeding, childhood (newborn period and prematurity). Restrictions on use: Angle-closure glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy, stenosing gastric and duodenal ulcers, pyloroduodenal obstruction, bladder neck stenosis, pregnancy. Side effects From the nervous system and sensory organs: general weakness, fatigue, sedation, decreased attention, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, impaired coordination of movements, anxiety, increased excitability (especially in children), irritability, nervousness, insomnia, euphoria, confusion, tremor, neuritis, convulsions, paresthesia; visual impairment, diplopia, acute labyrinthitis, tinnitus. From the cardiovascular system and blood: hypotension, palpitations, tachycardia, extrasystole; agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, hemolytic anemia. From the gastrointestinal tract: dry mouth, numbness of the oral mucosa, anorexia, nausea, epigastric distress, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation. From the genitourinary system: frequent and/or difficulty urinating, urinary retention, early menstruation. From the respiratory system: dry nose and throat, nasal congestion, thickening of bronchial secretions, tightness in the chest and heavy breathing. Allergic reactions: - rash, urticaria, anaphylactic shock. Other: sweating, chills, photosensitivity. Interaction Hypnotics, sedatives, tranquilizers and alcohol enhance (mutually) the depression of the central nervous system. MAO inhibitors enhance and prolong anticholinergic effects. Method of administration and dosage Intramuscularly - 10-50 mg, maximum single dose - 50 mg, daily - 150 mg, intravenous drip - 20-50 mg (in 75-100 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution). Overdose Symptoms: dry mouth, difficulty breathing, persistent mydriasis, facial flushing, depression or agitation (more often in children) central nervous system, confusion; in children - the development of seizures and death. Treatment: induction of vomiting, gastric lavage, administration of activated charcoal; symptomatic and supportive therapy against the background of careful monitoring of breathing and blood pressure levels. Special instructions Not recommended for subcutaneous administration (irritating effect). Use with caution in patients with hyperthyroidism, increased intraocular pressure, diseases of the cardiovascular system, and in old age. Should not be used during work by vehicle drivers and people whose profession involves increased concentration of attention. During the treatment period, you should avoid drinking alcoholic beverages. Storage conditions List B. In a place protected from light, at room temperature.