The human body is a most complex and at the same time most beautiful harmony, for the preservation of which details are of primary importance. After all, the lack of substances that seem to be necessary in very small quantities can be incomparably more important for the health of our body than their specific weight in the diet. This statement is absolutely true for macronutrients such as potassium and magnesium. The daily need for these substances is measured in milligrams - this is so small that it is sometimes difficult to even consider, but a lot depends on their presence in our body. Therefore, in this publication we will focus specifically on the details that determine health, well-being and excellent mood. What are potassium and magnesium responsible for in our body and why do they always “walk” in an inextricable link? What are the signs of a deficiency of these macroelements and how to replenish it?
Magnesium: heart, muscles and nerves are fine
Magnesium is involved in the work of about 300 enzymes in our body. Thus, magnesium takes part in many processes occurring in the body - this includes energy metabolism, the synthesis of proteins, fats and nucleic acids, and participation in various signaling cascades. Magnesium helps relax smooth muscles, acting as a counterbalance to calcium. At the same time, a fifth of all magnesium in our body is located in the heart, and this alone indicates how important this macroelement is for the functioning of our main motor. Magnesium also plays an important role in protecting the nervous system from destructive stress (Yarosh A.K., 2010). The daily requirement for magnesium for men is 350 mg, for women - 300 mg, and for young people, pregnant and breastfeeding, this figure can increase by another 150 mg. However, the total amount of magnesium in the human body is only about 24 g, most of which is found in muscle and bone tissue. It should be noted that the need for magnesium increases significantly during physical activity, stress, in hot climates, when visiting a bathhouse, alcohol abuse, unbalanced restrictive diets and chronic fatigue syndrome (Nedogoda S.V., 2009).
What foods do we get magnesium from? First, magnesium is found in regular drinking water, but its concentration can vary significantly. In some regions with “soft” water, its level in the water is much lower. In addition, some substances, for example those contained in tea, can negatively affect the absorption of magnesium in the digestive tract. Nuts, dark chocolate and legumes are rich in magnesium, but a significant increase in the consumption of these products can lead to the appearance of a couple of extra pounds due to their high calorie content. Other less nutritious foods include spinach, broccoli and rhubarb, but they do not meet the body's daily requirement for magnesium. In addition, only 30% of the magnesium we get from food is absorbed in the digestive tract. The absorption of magnesium is negatively affected by excess consumption of calcium, sodium, protein or fat from food, which significantly reduces the intake of magnesium in the body due to the formation of its non-absorbable complexes. Thus, the most common cause of magnesium deficiency is precisely insufficient dietary intake. Magnesium deficiency can also be caused by taking certain drugs, for example, diuretics, caffeine, some antibiotics and estrogen-containing drugs (Postnikova S.L. et al., 2007). As a result, magnesium deficiency can occur in 40% of the population (S.V. Nedogoda, 2009).
Foods high in magnesium
The list shows the Mg++ content per 100 product:
- Nuts. It is especially important to consume peanuts (182 mg), hazelnuts (160 mg), pistachios and walnuts (120 mg), and the leaders are pine nuts (251 mg).
- Fruits. Watermelon (10 mg), apricot (10 mg), tomatoes (11 mg), citrus fruits (9-10 mg).
- Vegetables. Pumpkin (590 mg), sesame (540 mg), seaweed (170 mg), dill (256 mg), potato (25 mg).
- Cereals and legumes. Bran (440 mg), buckwheat (250 mg), barley (150 mg), beans (140 mg).
- Beverages. Cocoa (245 mg), milk and dairy products (137 mg).
- Dark chocolate (133 mg).
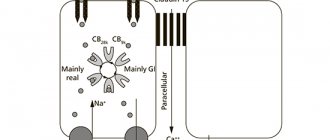
Also pay attention to the infographic:
Magnesium is a microelement that regulates the tone of cardiomyocytes (relaxation), their coordinated interaction in the generation and propagation of impulses.
Role of Mg++
We list the main properties of magnesium:
- It has a protective effect on the endothelium: it protects the inner wall of the artery from damage by turbulent blood flow and during spasm under the influence of stress hormones.
- It has an antiatherogenic effect , that is, it slows down the accumulation of cholesterol on a damaged vessel and the subsequent formation of a plaque, which can transform into a blood clot.
- Disaggregation effect: leads to a reduction in the formation of blood clots due to “thinning” of the blood.
- Vasodilating effect: reduces the tone and general peripheral resistance of blood vessels, which prevents the onset of arterial hypertension and hypertension.
- It helps improve insulin-dependent glucose utilization.
- Strengthens the central nervous system (CNS) and develops immunity to stress. But stress is one of the predictors of the development of cardiovascular diseases), improves performance, relieves fatigue and irritability.
Potassium: the heart's fiery engine
Potassium is the main intracellular cation, maintaining a certain ratio of concentrations in cells and extracellular space is extremely important for the normal functioning of nervous and muscle tissue. Maintaining the required ratio is achieved through the work of an enzyme that transports potassium ions into the cell and sodium ions out of it. And for the normal functioning of this enzyme, magnesium is necessary. Interestingly, the loss of potassium from the extracellular space is quickly compensated for by its supply from the cells, due to which the concentration of this ion in the extracellular space can remain within normal limits for quite a long time. As a result, critical potassium deficiency, fraught with cardiovascular and neuromuscular disorders, often goes unnoticed in standard studies (Lyashenko E.A., 2012). Potassium deficiency mainly develops due to its insufficient intake from food, intense fluid loss (diarrhea, increased sweating, taking diuretics or laxatives), and also, very importantly, magnesium deficiency. In addition, patients with diabetes are at risk for developing potassium deficiency (Lyashenko E.A., 2012).
The role of potassium in human life
The human body contains a lot of potassium. Its weight is about 250 grams. The daily intake of potassium is three to five grams.
A lack of the element means that glucose will not be absorbed and converted into energy, which can lead to poor muscle contraction and possible paralysis.
Together with magnesium, potassium is involved in processes related to the functioning of the heart. Potassium is necessary to normalize pressure in the arteries and normalize heart rhythm and muscle contraction.
Potassium helps get rid of excess fluid, eliminates toxins, and saturates the brain with oxygen.
Potassium is essential in the treatment of allergies. The main signs of potassium deficiency are:
- muscle cramps;
- disturbances in heart rhythm;
- growth slowdown;
- sexual disorders.
A lack of potassium can lead to multiple sclerosis, because... Sodium salts can accumulate in cells. Chronic fatigue is also one of the signs of deficiency of this macronutrient.
Potassium in food table
Having determined the importance of potassium, you should consider where the substance is found.
The best way to get potassium is from animal products because they have the most balanced potassium and sodium content.
Products containing potassium in large quantities are presented in the table.
Product table
| Grocery list | Content in milligrams per 100 grams |
| Mushrooms | 3937 |
| Welding | 2480 |
| Dried apricots | 1715 |
| Soybeans | 1605 |
| Cocoa | 1509 |
| Beans | 1105 |
| Pistachios | 1025 |
| Raisin | 830 |
| Parsley | 800 |
| Peas | 731 |
| Potato | 568 |
| Beef | 241 |
| Fish | 178 |
| Wheat flour | 176 |
| Milk | 127 |
Potassium is found most in dried white mushrooms. The potassium mark per 100 grams of product is 3937 mg/g, which corresponds to 157% of the daily requirement of the substance.
It should be remembered that the amount of potassium exceeding the permissible norms in the human body can provoke various diseases.
Signs of excess potassium
If you consume foods high in potassium in large quantities, you may not only not improve your health, but also harm yourself.
So why is it scary that potassium levels are higher than normal in the body?
Excess potassium can lead to psychological disorders such as:
- anxiety;
- panic attacks;
- insomnia;
- hyperactivity;
- irritability;
- aggression;
- apathy.
Also, excess potassium leads to disruption of muscle function, including the heart. Namely:
- muscle weakness;
- neuromuscular disorders;
- skeletal muscle paralysis.
If you do not monitor the potassium content, you can provoke diabetes.
Potassium + Magnesium = Inseparable couple
The levels of these elements in our body are connected - a deficiency of one negatively affects the level of the other and vice versa. Magnesium prevents the loss of potassium, promoting its fixation in the cell and normalization of its intracellular content (Yarosh A.K., 2010). Magnesium owes these properties to the fact that it participates in the work of the enzyme that “pumps” potassium into the cell. A study of cellular models confirmed the critical role of magnesium in maintaining intracellular potassium levels (Kotova O.V., Ryabokon I.V., 2012). It is worth noting that when replenishing magnesium deficiency, potassium losses are reduced. At the same time, the magnesium content depends on the potassium concentration (Postnikova S.L. et al., 2007). However, most patients with potassium deficiency may also have magnesium deficiency. This makes it advisable to use drugs containing both magnesium and potassium.
Magnesium preparations
Magnerot
These 500 mg tablets contain magnesium orotate dihydrate . Magnerot is used for a deficiency of magnesium in the body, for arrhythmia associated with such a deficiency, as well as in the treatment of atherosclerosis , endarteritis , chronic heart failure, muscle spasms, myocardial infarction , and metabolic disorders of fats.
Negative effects may include allergic reactions, nausea, diarrhea , and appetite disturbances. Expectant mothers and women during lactation can use the product if they have a normal level of magnesium in their blood.
Contraindicated for use in people with urolithiasis, liver cirrhosis , renal failure, lactase deficiency, and impaired glucose absorption.
Cost – from 330 rubles. for 20 pcs.
Doppelhertz Active
Dietary supplement that combines two microelements. Indications for the use of Doppelhertz Active magnesium + potassium are the same as for the use of Magnerot.
Cost – from 360 rubles. for 30 tab.
Reason to think
Magnesium deficiency manifests itself in a variety of symptoms - from chronic fatigue, decreased mental performance and headaches to arterial hypertension, a tendency to blood clots and cardiac arrhythmias. Increased irritability, depression, anxiety, and sleep disturbances may occur. In addition, spastic contractions of any muscles are possible: skeletal muscle spasms, spastic contractions of the intestines, bronchospasm, increased contractility of the uterus, etc. (Postnikova S.L. et al., 2007). At the same time, additional intake of magnesium in case of its deficiency provides an antiarrhythmic, anti-ischemic effect, helps reduce arterial and intracranial pressure, and has an antispasmodic and anticonvulsant effect. Magnesium is able to normalize blood pressure levels and is effective in therapy for various heart rhythm disorders. In addition, the use of magnesium has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the nervous system and improves sleep. Prevention of magnesium deficiency can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing myocardial infarction (Postnikova S.L. et al., 2007). Potassium deficiency negatively affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system: metabolic disorders and functional insufficiency of the myocardium, arrhythmia, tachycardia, deafness of heart sounds, the occurrence of heart attacks, heart failure, low blood pressure are observed (Kosarev V.V., Babanov S.A., 2012). Potassium deficiency is associated with an increased likelihood of developing arrhythmias and blood pressure levels. Thus, the intake of potassium from food is inversely proportional to the level of blood pressure, and increasing its intake is recommended as a prevention and treatment for arterial hypertension. Also, taking potassium supplements helps to significantly reduce the risk of death from stroke (Lyashenko E.A., 2012).
Signs of excess K+ and Mg++ ions in the body
The pathological basis of hyperkalemia and hypermagnesemia is kidney disease (chronic kidney disease, nephritis), ACS (heart attack + angina) and pathological metabolic changes (gout, diabetes mellitus), or drug overdose.
Important! Rarely does excess ion concentration occur on its own.
Excess K+ Clinic
- Excitation.
- Adynamia.
- Slowing of atrioventricular conduction.
- Pericarditis (uremic).
- Increased urine output.
- Paresthesia of the limbs.
- Sudden death of the heart.
Mg++ excess clinic
An increase in the concentration of magnesium in the blood above normal reduces blood circulation and inhibits the contractility of the heart muscle, resulting in:
- Bradycardia develops - heart rate < 40 per minute and a decrease in contraction of the heart chambers, and therefore - blood flow through the arteries and to the internal organs.
- Disorganization of the impulse conduction between the atrium and the ventricle occurs - extrasystoles occur.
- Arterial hypotension is formed due to relaxation of blood vessels, which will clinically manifest itself as darkening of the eyes, fainting, convulsions, cyanosis of the extremities.
- The risk of sudden cardiac death increases.
- On external examination: red complexion, thirst, severe hypotension, development of a pathological type of breathing, convulsions).
Besides:
- Excess inhibits the functioning of the central nervous system, reducing the activity of nerve cells (lethargy, disturbances in the frequency of respiratory movements, pathological shallow breathing).
- Reduces muscle tone due to inhibition of acetylcholine and, accordingly, the transmission of nerve impulses. Muscular hypotonia is manifested not only by the inability to move, but also, for example, by profuse diarrhea - because. sphincter muscles are unable to hold intestinal contents.
Medical certificate! According to the standards for the treatment of arrhythmias in a 24-hour hospital, all antiarrhythmic drugs are administered in a solution of a polarizing mixture consisting of potassium chloride, insulin and glucose solution; or glucose + insulin + potassium + magnesium. The polarizing mixture promotes high bioavailability of drugs that restore normal sinus rhythm and normalize the functional environment of the PSS.
The protective effects of “polarity” for cardiomyocytes (nutritional effect of glucose, capture of toxic free fatty acids) have also been described.
replenishing supplies with PANANGIN
One of these drugs, which has been on the market for more than 40 years and has earned the trust of healthcare professionals and patients, is PANANGIN from, which contains potassium and magnesium aspartate. Aspartate is an ion transporter across the cell membrane, facilitating the penetration of potassium and magnesium into the intracellular space. In turn, the presence of endogenous aspartate in PANANGIN promotes a more rapid and efficient entry of potassium and magnesium into myocytes and has a positive effect on myocardial metabolism (Shilov A.M. et al., 2012). The effectiveness of PANANGIN in the treatment of various diseases of the cardiovascular system and the prevention of magnesium and potassium deficiency has been proven by long-term successful experience of use. Thus, combined magnesium and potassium preparations, such as PANANGIN, have shown high clinical effectiveness in the treatment of various types of arrhythmias (Postnikova S.L. et al., 2007). Also, the use of a combination of magnesium and potassium is advisable for ventricular tachycardia and increases the effectiveness of treatment of heart failure and reduces the risk of stroke (Lyashenko E.A., 2012). The role of PANANGIN is no less important for stabilizing electrolyte homeostasis in patients taking diuretics, which sometimes leads to fluctuations in the composition of electrolytes, which can aggravate the course of the disease. Thanks to the combination of magnesium and potassium, PANANGIN is able to provide a whole range of effects that have a beneficial effect on the state of the cardiovascular system:
- reduces blood pressure in patients with arterial hypertension;
- helps maintain the elasticity of the walls of blood vessels;
- reduces the risk of developing arrhythmias;
- improves myocardial contractile function and prevents the development of heart failure;
- improves the function of the vascular endothelium, reduces the risk and rate of development of atherosclerosis;
- reduces blood viscosity and thrombus formation (Lyashenko E.A., 2012).
Thus, PANANGIN is indicated as an additional therapy for chronic heart diseases (heart failure and in the post-infarction period), cardiac arrhythmias, especially ventricular arrhythmias, and also as a supplement for increasing the amount of magnesium and potassium supplied with food. It is recommended for adults to take PANANGIN 1-2 tablets 3 times a day after meals.
Contraindications
Despite the fact that Mg and K deficiency provokes the development of serious diseases, in some cases it is contraindicated to consume foods and preparations containing potassium and magnesium.
If a person has kidney problems, then it is better to limit the intake of potassium and magnesium
In what cases should you limit your consumption of magnesium and potassium-containing products:
- chronic diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands;
- atrioventricular block;
- increased content of K, Mg in the blood;
- severe forms of hypotension – a decrease in readings below 90/60 mmHg. Art.;
- myasthenia gravis;
- acidosis;
- severe dehydration;
- hemolysis;
- disruption of amino acid metabolism.
In older people, when taking antibiotics, potassium-sparing diuretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the risk of developing excess Mg and K in the body increases.
Safe prevention is important
Another argument in favor of using PANANGIN to increase the intake of magnesium and potassium and thus prevent their deficiency is that this drug is available without a prescription. In addition, it is impossible to ignore the fact that, unlike dietary supplements, which are widely used to replenish the diet with biologically active substances, medicinal products are subject to higher registration requirements, including in terms of providing information regarding effectiveness and (which is very important with long-term use) - safety profile. Thus, speaking about the safety profile of the drug, it should be noted that PANANGIN is a non-toxic drug and does not exhibit a cumulative effect (Shilov A.M. et al., 2012). It is characterized by a limited list of contraindications and adverse reactions. In addition, the results of recent studies confirm the successful use of the drug in children (Kryuchkova T.A. et al., 2013). Thus, many years of experience in using the drug PANANGIN has confirmed its high effectiveness and favorable safety profile in ensuring potassium-magnesium balance, as well as in the treatment and prevention of diseases of the cardiovascular system.
Press service of “APTEKA Weekly”
Daily intake of K+ and Mg++ ions for health
The daily need for potassium is 2.5 - 4.5 g , and for magnesium - 350 - 550 mg .
There are conditions when the need for elements increases:
- Pathology of the gastrointestinal tract (peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, gastritis, duodenitis, enteritis).
- Intense physical work, systematic training.
- Chronic stress, intellectual stress;
- Diabetes mellitus and other metabolic disasters;
- Pregnancy
- When working in conditions of high humidity and temperature;
- For acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
Important! An excellent option for replenishing the lack of vitamins and elements is heart paste from Academician Amosov, as well as other mixtures of dried fruits and nuts.
Also watch the video: