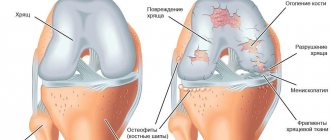
The knee joints are distinguished by a particularly thick and dense cartilage lining - after all, nature intended them to withstand the weight of our body and absorb shocks when walking, running and jumping. And although the average person runs much less than his wild ancestors, this does not make it easier for the joints: they suffer from excess body weight, monotonous loads and even the wrong selection of furniture, due to which the legs do not rest, even if we are sitting. Most sports injuries occur in the knee area.
Doctors warn: gonarthritis (or arthritis of the knee joint) increasingly begins at a young age - starting at 30 years old. What are the symptoms and treatment of knee arthritis? How to treat knee arthritis?
General information about the disease
Inflammation and arthritis of the knee joint is one of the most common diseases. This is due to the peculiarities of the structure, functioning and high loads on the knee joint. Depending on the causes, the disease can manifest itself in the form of damage to one joint (monoarthritis) or several (polyarthritis).
There is no separate code for arthritis of the knee joint according to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10); general arthritis codes are used - M00 - M14.
Like all other joint inflammatory processes, arthritis of the knee joint is prone to chronicity, and therefore often causes disability.
Prevention
- The most important factor in favorable disease control is control of BMI (body mass index), which reduces the axial load on the joints. You should avoid foods rich in starch and sugar (potatoes, sweets, sweet flour products). 2. It is worth adding more vegetables and fruits: apples, sea buckthorn, rowan, black currants, plums.
- Include fatty fish in your diet: tuna, salmon, cod, sardines, trout, herring.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Taking vitamins.
- Hardening.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Maintain an active lifestyle (preferably including regular exercise).
Causes of knee arthritis
Gonarthritis develops after an injury, so it mainly affects children, adolescents and young people. Athletes are at risk. After an open injury, an infection can enter the joint cavity, resulting in an acute inflammatory process.
With a closed injury, acute arthritis of the knee joint can also develop. At first, it is aseptic (without the presence of infection) in nature, and then either recovery occurs, or infection from nearby or distant foci (carious teeth, chronic tonsillitis, boils, etc.) occurs and purulent persecution develops.
The causes of arthritis of the knee joint may be associated with any general infection - gonorrhea, tuberculosis, brucellosis, etc. In such cases, the joint inflammatory process has the characteristics of the infection that caused it.
Another cause of arthritis of the knee joint and a damaging factor is an allergy to the patient’s own tissues (autoallergy). In most cases, there is a hereditary predisposition to these diseases, so people who have close relatives suffering from this pathology (rheumatoid arthritis) are at risk.
Toxic-allergic processes include reactive arthritis of the knee, which develops with certain urogenital, intestinal and nasopharyngeal infections. This arthritis of the knee joints also has genetic roots, which is why signs of knee arthritis appear after an infection. The trigger (triggering factor) in this case is infection. People who are sexually promiscuous are at risk.
Symptoms of knee arthritis
Despite the presence of significant differences in the course of different clinical forms, all patients suffering from arthritis of the knee joints have common symptoms.
The first signs of driving
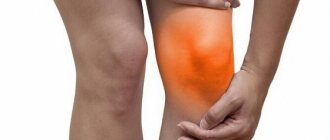
In most cases, the onset of the disease is acute. It begins with an increase in body temperature, general malaise, and headache. At the same time, the soft tissues over the affected joint become inflamed and swollen, the skin turns red, and pain appears.
In some clinical forms of arthritis of the knee joints, the disease initially develops unnoticed, and the course immediately becomes chronic. The pain may be minor at first, but gradually increases. Such pathological processes include tuberculosis.
It is very important to immediately consult a doctor when joint pain first appears: it is much easier to treat any disease at the initial stage.
Obvious symptoms
In acute cases, all symptoms of knee arthritis can increase very quickly. The combination of increasing inflammation, swelling and pain is especially characteristic of acute purulent arthritis and the onset of rheumatoid arthritis.
Severe pain syndrome prevents flexion and extension of the knee - the first signs of impaired mobility appear. In the future, impaired motor function may increase against the background of a decrease in inflammation due to the destruction of cartilage tissue and the proliferation of connective tissue - ankylosis (immobility of the joint) is formed. At first it is connective tissue ankylosis, and then bone.
To prevent the development of ankylosis, you need to seek medical help in a timely manner.
Dangerous symptoms
Not only is pain, swelling and redness above the knee joint indicative of inflammation, but these symptoms are the main
Dangerous signs of knee arthritis include:
- severe fever and general impairment for several days
may indicate the development of a purulent process; you can’t do without the help of a doctor; - moderate knee pain, lameness, decreased muscle volume (one leg is thinner than the other)
- indicates the presence of a chronic inflammatory process characteristic of tuberculosis; - the development of an inflammatory process in the small joints of the hand and foot against the background of arthritis of the knee joint
- signs of rheumatoid gonitis, requiring the help of a rheumatologist.
Is it possible to do without surgery?
Only certain types of gonarthritis are amenable to conservative treatment: acute infectious, reactive and fresh post-traumatic, not accompanied by massive hemorrhage and damage to joint structures. In the presence of hemarthrosis, rupture of menisci and ligaments, patients require surgical intervention. In this case, arthroscopy is most often performed. With purulent arthritis, patients often require puncture of the knee joint. During the procedure, doctors remove accumulated exudate, wash the joint cavity and administer antibiotics. Rheumatoid, psoriatic and other autoimmune arthritis in the initial stages are treated conservatively. However, with late prescription of drug therapy and high disease activity, patients experience impaired knee function and chronic pain. In this case, there may be a need for endoprosthesis replacement, that is, replacing the knee joint with an artificial endoprosthesis.
How dangerous is the disease?
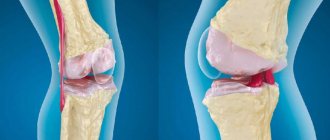
Arthritis of the knee joint is dangerous because it leads to deformation and destruction of the articular surfaces - cartilage and bone tissue. As a result, the function of one of the main joints involved in movement is lost, and the person becomes disabled. The various signs of the disease vary from stage to stage.
Stages of knee arthritis
Any form of arthritis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
See how easily the disease can be cured in 10-12 sessions.
There are 4 stages of disease development with the gradual formation of arthrosis and persistent dysfunction of the joint:
- The initial stage is inflammatory.
Inflammation, swelling, and severe joint pain cause reversible movement disorders. The general condition of the patient is impaired. - Progressive - formation of pannus.
The acute inflammatory process subsides, granulations of loose connective tissue grow in the knee joint, covering the articular surface and destroying the cartilage. Pain during movement is associated with low-grade inflammation and destruction of cartilage tissue. These disorders are also reversible. - Ankylosing - the formation of fibrous ankylosis (immobility of the knee).
The connective tissue becomes dense and fuses with the bone surface, ensuring immobility. The course of the disease has an undulating nature: relapses alternate with remissions. Complete restoration of joint function is problematic. - Deforming - the formation of bone ankylosis and deformation of the knee joint.
In place of the connective tissue, bone grows, the knee is motionless, and it is impossible to restore its function.
Possible complications
Full or partial restoration of joint function is possible at any stage, but if you self-medicate, the consequences can be very sad:
- in acute purulent knee arthritis
- melting of articular tissues, rapid formation of ankylosis, spread of a purulent inflammatory process to surrounding and distant organs and tissues; - in infectious diseases
- a chronic progressive course with the formation of ankylosis, persistent pain and dysfunction of the knee; - in rheumatoid arthritis
- spread of inflammation to small joints with persistent pain, joint deformation and disability.
How do the various clinical forms of knee arthritis occur?
The course of various clinical forms of knee arthritis has its own characteristics.
Acute purulent drive
Symptoms of the disease develop at lightning speed, within a few hours. High fever, chills, muscle pain, headache. The periarticular tissues of the affected knee joint swell, and the skin over it turns red. The pain is very severe, the pain syndrome increases as purulent inflammatory fluid accumulates in the knee.
Acute purulent arthritis of the knee joint
A general blood test shows signs of an acute inflammatory process; an x-ray shows narrowing of the joint space, foci of destruction of cartilage and bone tissue. Ultrasound reveals an increase in the volume of inflammatory joint fluid. When a joint is punctured, a cloudy exudate with a putrid odor is removed. Acute purulent arthritis of the knee joint can result in complete recovery or be complicated by deforming arthrosis and disability.
The patient's condition may be serious. The patient requires hospitalization and emergency medical care.
Post-traumatic
Chondroprotectors: what are they, how to choose, how effective are they?
Joint pain at rest
The inflammatory process begins with damage to the inner shell of the joint capsule - synovitis. Slight swelling and tenderness in the knee area limit its movement. All symptoms of post-traumatic arthritis appear within a few hours after the injury. The general condition does not suffer. The course of synovitis is favorable if infection does not occur. Infection from the outside through wounds or through blood flow from distant foci contributes to the development of purulent gonitis. X-rays sometimes show widening of the joint space.
Infectious
Arthritis of the knee joint can develop from a variety of bacterial, fungal, viral and parasitic infections. Each of these diseases has its own characteristics:
- Gonorrheal drives.
It begins acutely 14–21 days after a sexually transmitted infection. Fever appears and the general condition of the patient is disrupted. Usually one knee is affected, it swells, the skin over it turns red, and severe pain appears. In the future, in the absence of adequate treatment, the process can take a chronic course with the rapid formation of deformity and ankylosis and disability. With timely treatment, the outcome is favorable - complete recovery. - Tuberculosis drives.
It begins gradually and has a chronic course with exacerbations and remissions. The pain is minor at first, but gradually increases. Redness and swelling of the periarticular tissues are not pronounced and appear only during an exacerbation, at which time fever may appear. Muscle atrophy (decrease in volume) increases - one leg is thinner than the other, and excess hair growth is observed on the affected limb (hypertrichosis). Movement is limited due to pain. In advanced stages - dislocations and subluxations, breakthroughs of discharge from the articular cavity onto the surface of the skin (fistulas). Gradual complete destruction of the joint and disability.
You should know: even severe infectious gonitis can be treated. In the early stages, they can be cured completely; in the later stages, they can suppress the progression of the pathological process and maintain a normal state. Therefore, seek medical help as soon as possible!
Rheumatoid
The disease is associated with autoimmune reactions (allergy to the patient’s own tissues). Damage to one knee joint in rheumatoid arthritis is rare. More often, polyarthritis develops with gonitis and damage to the small joints of the hand and foot. The disease progresses over a long period of time, in waves, with exacerbations and remissions.
The main sign of rheumatoid gonitis is swelling and redness of the tissue in the knee area and severe debilitating pain. Articular deformity and flexion contracture develop very quickly. Over time, knee stiffness and ankylosis develop.
Systematic correct treatment can stop the progression of rheumatoid gonitis.
Reactive
Reactive arthritis of the knee joint develops within a month after a genitourinary, intestinal or nasopharyngeal infection, mainly in genetically predisposed individuals. The knee swells, the skin over it turns red, and the body temperature rises. Often the course becomes chronic and relapsing. If left untreated, permanent impairment of motor function may occur. But more often the prognosis is favorable - complete recovery occurs.
Juvenile idiopathic
This diagnosis is made if it is impossible to determine the cause of the disease. It occurs mainly in childhood and adolescence in hereditarily predisposed children (more often in girls). The long wave-like course of juvenile arthritis with exacerbations and remissions gradually leads to the formation of ankylosis and early disability.
With timely treatment, it is possible to stop the progression of the process and return the child to normal life.
Psoriatic
Psoriatic arthritis of the knee
Drives with psoriasis can develop in one or both knees. Most often, the first signs of articular damage appear against the background of existing skin manifestations. But sometimes pain in the knee appears several years before the characteristic rashes appear. If characteristic lesions of the end joints of the fingers and nails appear simultaneously, then the diagnosis of psoriatic gonitis is beyond doubt. With a long course of gonitis, persistent ankylosis develops. Interestingly, no pannus is formed.
If symptoms of arthritis of the knee joint appear, treatment is prescribed by a dermatovenerologist together with a rheumatologist.
Gouty
Knee damage due to gout occurs due to the deposition of uric acid salts in the tissues. In the knee area, such a pathology is rare, but can occur acutely with severe pain, significant tissue swelling and redness of the skin. The leg cannot bend due to severe pain. The attack lasts several days, after which it passes without consequences. But with a long course of gout, gradual, persistent impairment of knee function is possible.
Deforming
Long-term chronic recurrent inflammation in the knee leads to the destruction of the cartilage tissue of the articular surfaces. This contributes to constant injury and proliferation of bone tissue. It can grow in the form of spines and marginal growths, deforming the knee and disrupting its function. Arthrosis-arthritis is gradually formed - a combination of inflammatory and degenerative joint processes. Movements in the knee are painful, especially with loads and prolonged standing. The function of the knee joint may be significantly impaired.
Chronic drives
Any form of gonitis can take a chronic course with exacerbations and remissions. This will inevitably lead to impaired joint function. This is why it is so important to promptly seek medical help if knee pain occurs.
General signs of arthrosis and arthritis
The main manifestation of arthritis and arthrosis is joint pain of varying intensity. The pain intensifies from high activity and decreases as a result of rest, it is worth noting arthrosis. During arthritis, joint inflammation is accompanied by swelling, redness, difficulty moving and constant pain, even at rest.
Let us highlight the most striking symptoms of the disease:
- Regular pain.
- Stiffness, after rest and lack of movement.
- Swelling and tenderness.
- Clicking and crunching in the joint.
- Reduced range of motion.
IMPORTANT! Often forms of arthritis are accompanied by rheumatic diseases, and therefore can cause symptoms affecting different organs. Based on this, the clinical manifestation of pathology in some patients with specific forms of the disease may include swelling of the lymph nodes, weight loss, fatigue, deterioration of well-being, and fever.
In addition to the above symptoms, symptoms of arthritis and arthrosis are quite often accompanied by the formation of Heberden’s and Bouchard’s nodes, which causes significant difficulties in further treatment.
Although they are not always painful, they do significantly limit the movement of the fingers.
Diagnostics
Treatment of knee arthritis is impossible without a preliminary examination and establishment of the etiology (cause) of the disease, since different types of arthritis require different approaches to treatment. As part of the examination, patients may be referred for the following studies:
- laboratory tests of blood, urine, joint fluid
- general clinical, biochemical, immunological, genetic, microbiological; - X-ray of the knee
- bone growths and deformations are identified, the height of the joint space is measured; - MRI of the knee
- changes in soft articular and periarticular tissues are detected; - Ultrasound
– examination of the soft tissues of the knee and determination of the volume of joint fluid; - arthroscopy
– endoscopic examination of the internal articular surface; If necessary, joint fluid is taken for examination.
Sodium hyaluronate
Being a glycosaminoglycan, one of the main components of connective tissues, it plays an important role in the proliferation of cells that determine their division and growth. Most often it can be found in the skin and bones, synovial fluid and intervertebral discs. Hyaluronate is part of the synoval fluid, providing support for knee mobility and reducing friction of the articular surfaces. It is actively used to treat diseases of the musculoskeletal system. It reduces pain and symptoms in general.
According to 2004 statistics, osteoarthritis caused moderate and severe disability in 43.4 million patients. Osteoarthritis of the knee and hip joint ranks 11th out of 291 in the world ranking of evaluated diseases.
Treatment of knee arthritis
Crunching in joints - when to worry
Intra-articular injections of hyaluronic acid
After a complete examination, treatment for knee arthritis is prescribed. It must be comprehensive and individually selected for a specific patient. The complex treatment includes:
- regimen and diet;
- drug therapy;
- non-drug methods for treating knee arthritis;
- folk remedies;
- surgical methods of treatment.
Regime and diet
When exacerbation of gonitis occurs, bed rest with minimal physical activity is applied. In some cases (for example, with purulent gonitis), the joint is immobilized. After the acute inflammation subsides, there is a gradual increase in physical activity. It is also important to regulate sleep and wakefulness patterns.
A special diet is only necessary for gout. Offal, meat of young animals, strong broths, eggs, alcoholic drinks, strong tea and coffee, and chocolate are excluded from the diet.
For other types of arthritis of the knee joint, during the treatment of exacerbations, a nutritious diet is recommended with the exception of foods that cause tissue irritation. These are onions, garlic, radishes, hot seasonings, fried, cooked, canned foods. It is also recommended to limit sweets and confectionery.
Drug therapy
The question of how to treat arthritis of the knee joint is decided by the attending physician. The general condition of the patient, features of the course of joint pathology, the presence of concomitant diseases, individual intolerance to drugs, etc. are taken into account. In this case, the doctor must adhere to common clinical recommendations for the treatment of certain types of gonitis. Prescribed:
- medications from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). They relieve symptoms of exacerbation of knee arthritis well: inflammation, swelling and pain, improve the general condition of the patient (Diclofenac, Nise, Miloxicam - in the form of injections, oral tablets or ointments);
- for severe swelling and pain that cannot be relieved by NSAIDs, glucocorticoid hormones are prescribed: a course of oral prednisolone, short courses of intravenous drip infusions of methylprednisolone (pulse therapy) or intra-articular injections of Diprospan;
- reduction of tissue swelling is achieved by the use of antihistamines - Erius, Claritin;
- for reactive arthritis against the background of a urogenital infection, long-term (up to a month) courses of antibacterial therapy are prescribed;
- Antibacterial therapy and washing the knee joints with antiseptic solutions are prescribed for the treatment of purulent arthritis of the knee joint;
- in order to restore cartilage tissue, chondroprotectors are prescribed - Dona, Structum;
- to suppress autoimmune processes, basic drugs are prescribed - Sulfasalazine, Methotrexate, Leflunomide, as well as biological substances or agents (MabThera),
Drugs for the treatment of knee arthritis
Non-drug methods
These treatments for knee arthritis include:
- physiotherapy - at the acute stage of the disease these are electrophoresis procedures with medicinal solutions, then magnetic and laser therapy, mud therapy, etc.;
- physical therapy (physical therapy) with a gradual increase in active physical activity during the period of remission;
- massage – during the period of remission, it allows you to restore blood circulation and stimulate metabolic processes in the knee;
- reflexology - influencing acupuncture points on the body, reflexively associated with the knee area; allows you to relieve pain, swelling, restore biological balance in tissues.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for the treatment of knee arthritis can only be prescribed by a doctor. You cannot use them on your own, since different arthritis requires the use of different remedies. An infusion of medicinal herbs will be beneficial to one patient, but harmful to another. Most often, doctors use folk remedies to reduce the drug load on the patient’s body and limit the side effects of drugs.
Surgical methods of treatment
The help of a surgeon is required when conservative therapy does not help:
- in the treatment of purulent arthritis of the knee joint, therapeutic arthroscopy is performed with washing the diseased joint with aseptic solutions, constant drainage of the joint;
- in case of severe swelling and severe pain, a synovectomy operation is sometimes performed - removal of the most inflamed part of the synovial membrane;
- in case of deforming arthritis, the appearance of areas of bone tissue growth, in order to increase functionality, arthroplasty is performed - partial removal of bone growths and parts of the bones; in some cases, destroyed bone structures are replaced with implants;
- endoprosthesis replacement is a surgical intervention to replace a destroyed joint with an artificial one.
Surgical treatment of knee arthritis
Approach to treating the disease in our clinic
The Paramita clinic has developed a unified approach to the treatment of knee arthritis. It includes:
- Mandatory preliminary examination of the patient using the latest instrumental methods, including MRI.
- Individual approach to the treatment of each patient.
- Using two opposing approaches to treatment:
- Western
- based on the achievements of modern medicine with high results in the treatment of pathologies of various organs; this is the use of modern medications and treatment regimens, PRP therapy - stimulation of regenerative processes in the joints by administering the patient’s own platelet-rich plasma, diagnostic and therapeutic arthroscopy, etc.; - Eastern
- the traditional approach of doctors from China and Tibet, who consider the human body as a single whole, and the disease as an imbalance in the body; restoring balance leads to the elimination of pathology and overall improvement of the body; courses of acupuncture, moxotherapy, pharmacopuncture, herbal medicine, etc. are prescribed.
More detailed information about treatment methods at the clinic can be found on our website.
This approach to treatment allows the patient to quickly relieve pain, suppress the progression of the disease and restore joint function.
We combine proven techniques of the East and innovative methods of Western medicine.
Read more about our unique method of treating arthritis
Physiotherapy
Phonation
Vibroacoustic therapy involves the transmission of sound microvibration using a special medical device. It creates microvibrations that, with their physical characteristics, are identical to those created by muscle tissue under maximum static physical tension. In short, this therapy is a direct alternative to exercise.
Vitafon.
Phoning Effects:
- Improving lymph flow in the area of influence, which promotes accelerated tissue cleansing, has an anti-inflammatory effect.
- Improves blood flow and, accordingly, nutrition of the treated area.
- Has a beneficial effect on nerve pathways with prolonged exposure.
- Promotes the release of joint lubrication.
Galvanization and electrophoresis
The essence of the procedure is to activate the blood supply to joint tissues in chronic arthritis . Vasodilation occurs in the area of influence, increasing blood supply and improving recovery processes.
Electrophoresis.
UHF therapy
The affected joint is exposed to a continuous or pulsed electric field. For the knees, low-thermal doses are used at a current power of 20-30 W.
The procedure is aimed at reducing swelling, activating regenerative processes in the joint, improving nutrition and blood supply. The method allows you to achieve long-term remission.
Infrared laser therapy
Using a laser applicator, they act on biologically active points located along the lateral surfaces of the joint. The procedure activates blood flow, reduces pain sensitivity, and stimulates healing processes.
Ultrasound therapy
The method optimizes and accelerates the biochemical processes occurring in joint tissues, accelerates healing processes, and reduces swelling.
Hydrogen sulfide and radon baths, peloid therapy, massage, and manual therapy have also proven themselves well.
General clinical recommendations
Patients suffering from gonarthritis are recommended:
- avoid heavy physical activity and heavy lifting;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- do therapeutic exercises, swim;
- eat properly regularly;
- do not smoke, do not abuse alcohol;
- regularly carry out anti-relapse treatment courses recommended by your attending physician;
- promptly treat any acute and chronic diseases, foci of infection.
Prevention of knee arthritis
It is especially important for people at risk to follow preventive measures:
- athletes - avoid knee injuries, wear special knee pads;
- persons who have relatives suffering from rheumatoid, reactive, psoriatic, gouty arthritis should be attentive to their health and, if knee pain occurs, immediately seek medical help;
- promptly identify and treat all foci of infection - carious teeth, tonsillitis, sinusitis, etc.
Frequently asked questions about the disease
What is the difference between arthritis and arthrosis of the knee joint?
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease in which the tissues over the joint become red and swollen. Arthrosis is a metabolic disease accompanied by pain and joint deformation.
Best ointment for knee arthritis?
Many patients prefer Voltaren emulgel.
Which doctor treats knee arthritis?
Depends on the clinical form of arthritis. Purulent arthritis is treated by a surgeon, rheumatoid arthritis by a rheumatologist, psoriatic arthritis by a rheumatologist together with a dermatovenerologist.
The knee joint can be affected by any type of arthritis. Treatment of gonarthritis should begin as early as possible, before irreversible changes occur in the joint. But even if this happens, contacting the specialists of the Paramita clinic will relieve you of pain, stop the destruction of the joint and restore the joy of life.
Literature:
- Alekseeva L.A., Chichasova N.V., Mendel O.I. Results of using the drug Arthra for gonarthrosis // Scientific and Practical Rheumatology No. 5, 2005.
- Alekseeva E. I., Zholobova E. S. Reactive arthritis in children // Issues of modern pediatrics. 2003, vol. 2, no. 1, p. 51–56.
- Eid K.A. Injuries to the knee joint in children. Diagnosis and treatment using arthroscopy. Author's abstract. diss. Candidate of Medical Sciences – M. 2003. – 26 pages.
Themes
Arthritis, Joints, Pain, Treatment without surgery Date of publication: 10/20/2020 Date of update: 04/03/2021
Reader rating
Rating: 5 / 5 (1)