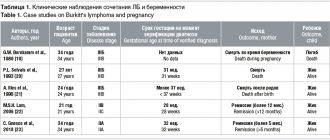
Arthritis
is an inflammatory disease of the joints, which can occur in an acute form or, in the absence of timely treatment, become chronic.
This is an extremely common disease in the CIS, which is especially common in women over 45 years of age
.
According to medical reports, among diseases of the musculoskeletal system, arthritis is one of the most common causes of temporary or permanent loss of ability to work, including severe disability
. Symptoms of arthritis can begin in a person of any gender and age - often even in children. According to statistics, every 100th person suffers from joint inflammation. And in the age group over 60 years, the incidence rate can reach 80%. What are the early symptoms of joint arthritis and the prerequisites for the development of the disease?
Arthritis is an inflammatory disease of the joints
Causes of Arthritis
Arthritis is a consequence of damage to the articular cartilage or the entry of microorganisms into the synovial fluid.
In the first case, the pathology occurs due to degenerative processes in tissues due to injury or osteoarthritis. The causes of inflammatory arthritis are infection and waste products of microorganisms when:
- migration of the pathogen through blood and lymphatic vessels from nearby tissues;
- infectious diseases affecting the entire body - tuberculosis or gonorrhea;
- toxic-allergic effects of by-products of microorganisms;
- an allergic reaction to the body’s own tissues after an infection or in the presence of a permanent focus of inflammation, accompanied by a disruption in the functioning of the immune system;
- injury to the joint and infection through the wound or aseptic inflammation.
The following factors contribute to the occurrence of the disease:
- hereditary predisposition;
- increased load on the musculoskeletal system;
- infectious diseases;
- consuming large amounts of caffeine;
- smoking;
- excess weight;
- allergic reaction;
- metabolic disorders;
- traumatic injury;
- hypovitaminosis and lack of nutrients;
- pathology of the nervous system;
- malfunctions of the immune system;
- improper diet, consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- hormonal disorders;
- stinging insect bites;
- hypothermia of the body.
Folk remedies
Before using traditional methods for arthritis, be sure to consult with your doctor.
- Birch leaves (2.5 teaspoons), stinging nettle leaves (2.5 teaspoons), tricolor violet grass (2.5 teaspoons). Take the infusion 1/2 cup 4 times a day before meals.
- Lubricate the knee with honey, apply mustard plaster and tie it. Hold until a burning sensation appears, then remove the mustard plaster, and wrap the knee with honey, as with a compress, and keep it overnight.
- Mash the ranunculus flowers and apply to the knee for 2 hours, then remove and wrap the sore spot overnight.
- Grate the radish or horseradish on a fine grater. Apply the paste or the juice itself to the painful area. Leave for 40 minutes. The course for arthritis is 10 procedures every other day.
- If salts are deposited in the joint, cut the onion head in half. Pour one drop of tar into the middle of each half and apply to the sore spot.
- Beat the yolk with apple cider vinegar. Apply the application until dry. Use several times a week for a month.
- Garden purslane for arthritis. Grind the grass. Mix with cold water, in a ratio of one spoon per glass of liquid. Place on the fire and boil for ten minutes. Cover the container with a towel and place in a warm place for two hours. Then strain. Take the finished infusion three times a day, one tablespoon.
Classification
Arthritis, depending on the cause and clinical form, is of the following types:
- rheumatoid arthritis associated with malfunctions of the immune system;
- rheumatic, with chronic connective tissue disease with predominant damage to the heart and joints;
- ankylosing spondylitis, or ankylosing spondylitis - inflammation of the joints of the spine;
- infectious, with direct penetration of infectious agents into the joint;
- reactive arthritis - an immune response to a previous infectious disease;
- psoriatic arthritis is a chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disease of the osteoarticular system that develops in patients with psoriasis;
- gouty – occurs due to the deposition of uric acid in the joints;
- inflammation in systemic connective tissue diseases, for example, systemic lupus erythematosus;
- arthritis due to diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, lungs and other organs and systems;
- traumatic, occurring after an injury;
- juvenile idiopathic arthritis in children under sixteen years of age.
Based on the number of joints affected, monoarthritis is distinguished with inflammation of only one, oligoarthritis, if two or three areas are affected, and polyarthritis - a disease of more than three joints.
The process can be acute or chronic. In the first case, it develops rapidly, accompanied by severe pain and inflammation in the tissues. Chronic disease progresses gradually, slowly turning into a serious disease.
Degrees of the disease
The symptoms of arthritis differ in stages by the manifestations of pain and the aggravation of pathological processes. So, if the disease develops into a complicated form, then the symptoms will be more noticeable. Let's look at all four stages of arthritis:
1st degree
The disease does not manifest itself clinically, but X-rays of the joints show the first signs of inflammation. Sometimes there is a slight stiffness of movement and periodic pain during physical activity.
2nd degree arthritis
The progressive inflammatory process leads to thinning of the tissues of the articular structures and erosion of the heads of the bones. Swelling appears in the area of the affected joints; A local increase in temperature and redness of the skin are often observed, movements are accompanied by crunching.
3rd degree
The third degree of the disease is characterized by the following symptoms:
- X-ray examination shows severe deformity;
- Often a person at this stage is assigned a disability;
- Mobility is limited, it is difficult for the patient to move if the lower part of the body is damaged;
- Hand movements are performed with great difficulty. It becomes difficult for the patient to perform even basic self-care actions. The hands are affected symmetrically;
- Pain haunts a person even when he is at rest;
- Due to muscle spasm caused by pain, the limbs are fixed in the wrong position. This ultimately leads to even greater deformation of the joints.
Arthritis 4 degrees
Leads to almost complete immobility of damaged joints, with severe round-the-clock pain. It is impossible to move independently. Negative changes in the bones are already becoming irreversible. When the knees are affected, muscle contractures form.
Arthritis symptoms
Manifestations of the disease depend on its clinical form and severity of the process. The main symptoms of arthritis include local manifestations of inflammation in the joint - pain, redness and swelling of surrounding tissues, limited mobility, deformation as pathological changes progress. There is also a local increase in temperature, the affected area becomes hot when touched.
Infectious
The course of the disease depends on the type of pathogen. Often there is a sharp increase in temperature, chills, headache, and weakness. Tuberculous arthritis occurs in a chronic form, is difficult to treat and leads to severe dysfunction of the affected joint. With gonorrhea, as a rule, acute serous inflammation develops. Viral lesions go away after the infection is cured.
Gouty
Gout is a metabolic disorder that is accompanied by the deposition of uric acid salts - urates - in the joints. They penetrate the tissues, forming gouty nodes or tophas. The metatarsophalangeal joints of the thumbs are usually affected first, followed by arthritis in other areas. During an exacerbation of the disease, acute inflammation develops with tissue swelling and severe pain. After several attacks of gout, the joint becomes deformed and its function is impaired.
Rheumatoid
An autoimmune reaction develops with damage to the body’s own tissues, including joints. The causes of the disease have not been precisely established, but it is known that inflammation is triggered by infection in the body. At the onset of the disease, there is an increase in body temperature, the patient is worried about morning stiffness - a gradually passing limitation of mobility after waking up, pain and swelling at the site of inflammation. Symptoms may spontaneously disappear for several months, followed by exacerbation and progression of the disease. Damage to the hand and fingers is typical, but there are cases of atypical reactive arthritis with inflammation of the knee or shoulder joint. Gradually, without treatment, articular cartilage is destroyed, connective tissue grows, subluxations and dislocations occur, leading to disability of the patient.
Traumatic
Develops after injury to large joints - hip, knee, shoulder and others. There is pain, swelling and crunching when moving. With a closed injury and aseptic inflammation, spontaneous recovery is possible. With an open wound, the infection penetrates deep into the tissue and can cause purulent inflammation.
Psoriatic
It is characterized by damage to the terminal interphalangeal joints of the fingers and nails with simultaneous asymmetric damage to several other areas. The course of the disease occurs with relapses and remissions.
Reactive
This form is associated with a toxic-allergic reaction to an infection that develops within a week after a bacterial, viral or fungal infection. It occurs acutely, affecting 1-3 large joints. Characterized by pain at the site of inflammation, redness, swelling of surrounding tissues, and limited mobility. Other symptoms of inflammatory damage to the eye mucosa and urinary tract may also be present.
Juvenile idiopathic
Arthritis of unknown cause in children under sixteen years of age. It is believed that the basis is the genetic predisposition of the child. Prolonged exacerbations alternate with remissions and lead to early disability of the patient.
Advantages of the Mama Papa Ya clinic
The network of family clinics “Mama Papa Ya” offers the service of consultation with a rheumatologist and diagnosis of various types of arthritis. An experienced doctor will be able to identify the cause of the disease and explain how to treat arthritis.
Advantages of our clinic:
- working with patients of different ages;
- versatility;
- a network of branches in Moscow for ease of visiting;
- affordable prices for diagnostic procedures and consultations with doctors;
- experienced staff;
- individual approach to each patient, taking into account all the characteristics of his health.
Reviews
Good clinic, good doctor!
Raisa Vasilievna can clearly and clearly explain what the problem is. If something is wrong, she speaks about everything directly, not in a veiled way, as other doctors sometimes do. I don’t regret that I ended up with her. Anna
I would like to express my gratitude to the staff of the clinic: Mom, Dad, and me. The clinic has a very friendly atmosphere, a very friendly and cheerful team and highly qualified specialists. Thank you very much! I wish your clinic prosperity.
Anonymous user
Today I had a mole removed on my face from dermatologist I.A. Kodareva. The doctor is very neat! Correct! Thanks a lot! Administrator Yulia Borshchevskaya is friendly and accurately fulfills her duties.
Belova E.M.
Today I was treated at the clinic, I was satisfied with the staff, as well as the gynecologist. Everyone treats patients with respect and attention. Many thanks to them and continued prosperity.
Anonymous user
The Mama Papa Ya clinic in Lyubertsy is very good. The team is friendly and responsive. I recommend this clinic to all my friends. Thanks to all doctors and administrators. I wish the clinic prosperity and many adequate clients.
Iratyev V.V.
We visited the “Mama Papa Ya” Clinic with our child. A consultation with a pediatric cardiologist was needed. I liked the clinic. Good service, doctors. There was no queue, everything was the same price.
Evgeniya
I liked the first visit. They examined me carefully, prescribed additional examinations, and gave me good recommendations. I will continue treatment further; I liked the conditions at the clinic.
Christina
The doctor carefully examined my husband, prescribed an ECG and made a preliminary diagnosis. She gave recommendations on our situation and ordered additional examination. No comments so far. Financial agreements have been met.
Marina Petrovna
I really liked the clinic. Helpful staff. I had an appointment with gynecologist E.A. Mikhailova. I was satisfied, there are more such doctors. Thank you!!!
Olga
Diagnosis of arthritis
Timely detection and treatment of arthritis or arthrosis will help maintain normal joint function and the ability to lead an active lifestyle even in old age.
For successful treatment of the disease, it is important to establish its cause. In addition to analyzing complaints and symptoms, laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods help determine the type of arthritis, as well as the severity of the inflammatory process.
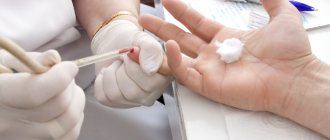
- General clinical blood test. An acute process is characterized by an increase in ESR. When the disease is caused by microorganisms, leukocytosis is observed. In case of an allergic reaction, an increase in the number of eosinophils is possible.
- Blood chemistry. It is carried out to determine the cause of the disease, as well as the severity of inflammation.
- Immunological blood test. It is especially relevant in identifying rheumatoid and reactive forms of the disease. Indicates the presence or absence of specific antibodies to infectious pathogens or the patient’s own tissues.
- General urine analysis.
- Radiography. The main instrumental method for diagnosing arthritis. Allows you to determine the condition of the bones and identify changes caused by the inflammatory process.
- CT scan. Used to assess the condition of soft tissues - muscles, articular discs, ligaments.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. Allows you to more clearly examine the earliest changes in bone structures, articular and adjacent tissues.
- Ultrasonography. In case of arthritis, it helps to determine the degree of damage to large joints, the superficial location of which allows you to examine them from different sides, as well as to identify an increased volume of intra-articular fluid.
- Examination of synovial fluid. In the infectious form of arthritis, bacteriological analysis helps to identify the pathogen and select an effective antibacterial drug for treatment.
- Arthroscopy. An endoscopic method that involves inserting a special sensor into the joint cavity.
- Arthrography. Shows the condition of the cartilage and soft tissues that surround the joint.
Prevention
The best treatment for any type of arthritis is prevention. Preventive measures are primarily necessary for people who are at risk for one of the reasons:
- heredity;
- reduced immunity;
- excess body weight;
- Professional activities involve heavy loads on the joints.
There are two current types of arthritis prevention:
- primary prevention is aimed at preventing the onset and development of the disease, as well as preventing the reasons why it may occur. Involves: timely diagnosis and treatment of various viral and colds;
- quality treatment of chronic infectious diseases;
- the use of measures to strengthen the body's immunity;
- maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
- the use of a course of drug treatment with drugs prescribed by the attending physician;
Timely contact with a professional specialist allows you to promptly identify the disease, determine its degree of development and prescribe the most appropriate treatment.
Self-medication can aggravate inflammatory processes and lead to irreversible consequences, including disability.
Treatment
Treatment of arthritis is aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease and risk factors that contribute to the development of inflammation, relieving symptoms, improving metabolism in the affected joint, and preserving its function.
This can be achieved through the use of medications, physiotherapy, physical therapy and massage. In advanced cases, with purulent processes, dislocations and subluxations, surgical intervention may be required. If the joint is completely destroyed, it can be replaced with an artificial one - endoprosthetics.
Conservative therapy, depending on the form of arthritis, includes the use of tablets, ointments and injections of various groups of drugs:
- antibiotics for bacterial infections;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and hormones;
- chondroprotectors – agents that improve the quality of joint tissue;
- painkillers;
- vitamins, microelements and amino acids.
Author:
Pugonina Tatyana Alekseevna, Therapist