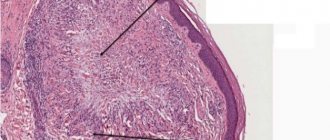
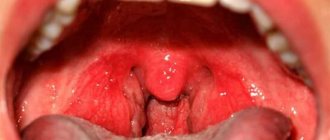
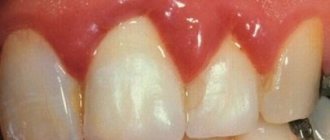
Dental granuloma is an inflammatory formation at the apex of the root. It is a proliferation of granulation tissue. Granuloma is formed as a result of the action of protective mechanisms in which the body localizes the source of infection and seeks to isolate it from other tissues. According to ICD-10, the disease was assigned code K04.5.
Typically, a granuloma is formed against the background of inflammation of the neurovascular bundle - the pulp. If pulpitis is not treated, its root part becomes inflamed, and the infection spreads beyond the boundaries of the tooth, into the peri-root tissue. As a result, a kind of pouch is formed, filled with decay products of dead cells.
A granuloma is considered to be a formation up to 0.5 cm in size, but it can grow, and as it grows, it transforms into a cystogranuloma, the size of which reaches 1 cm. With a diameter of more than 10 mm, we are talking about a tooth root cyst. There is no cavity in a granuloma; it is an area of tissue surrounded by a capsule. Due to the latter, the granuloma is firmly attached to the apex of the tooth root.
Classification of granulomas and forms
In medicine, granulomas are classified according to several criteria: etiology, pathogenesis and morphology. Specific varieties are collected in a separate group. In the group according to the criterion of etiology there are types of established and unidentified etiology: infectious and non-infectious. The latter include dust granulomas, drug-type granulomas and neoplasms around foreign bodies. Pathogenesis group: immune and non-immune. The first type includes epithelioid cell granulomas. Non-immune ones occur due to toxic factors and acute infections. The morphological group is divided into two main groups: mature and epithelioid cell. According to the morphology of granulomas, there is the formation of a diffuse-type granulomatous infiltrate and the formation of tuberculoid-type granulomas.
Main types of granulomas
In medical practice, there are many types of neoplasms of this type. They can be single or multiple. It is not always possible to see the beginning of their formation, since pathogenic cells are located deep in the layers of the dermis. Granuloma in children and adults can appear and disappear without treatment. This should justify the need for gentle therapy in the future. Granulomas of the following type are most often diagnosed in children and adults:
- ring-shaped;
- pyogenic;
- tuberculosis.
Causes and development factors
Granuloma annulare in children can appear for various reasons, which have not yet been fully established. The provoking factor is a focus of chronic infection in the form of rheumatism, tonsillitis. The presence of diabetes mellitus, allergic diseases, and metabolic pathologies increases the risk of development. In children, a lot depends on the immune system. If there is a failure, the development of the neoplasm will be started. Pyogenic granuloma in a child occurs due to a pyococcal infection. The reason for the development lies in skin injuries, due to which infection gets into the wounds. It is localized mainly on the face, legs, fingers and arms. Eosinophilic granuloma is rarely found in young children. The peak incidence occurs between 5 and 10 years. The causes of such granuloma in a child are ambiguous. The question still remains open. Scientists suggest that immunopathological processes are the basis.
Stages of granuloma development
From the moment of inception, the neoplasm goes through 4 stages. At the initial stage, there is an accumulation of cells with a tendency to phagocytosis. At the second stage, the process of their rapid growth begins. The third stage is characterized by the transformation of phagocytes into epithelial cells. At the last fourth stage, granuloma formation occurs directly.
Urgent dental care for the development of purulent inflammation
We already wrote above that dental granuloma develops asymptomatically for a long time and this form is called chronic. But if a person experiences severe stress, catches a cold, a malfunction occurs in the immune system of his body - the granuloma will turn into an acute form, in which purulent inflammation can begin to actively develop. Its signs are excruciating pain that does not subside after taking pharmaceutical painkillers, swelling of the gums and cheeks, and increased body temperature.
Naturally, with such symptoms, you need to urgently contact the dentist to get emergency help. Treatment will depend on where the pus is located and accumulates:
- If the pus is in the granuloma itself, then assistance to the patient will consist of opening the tooth to ensure the outflow of pus through the root canals;
- If there is swelling on the gum and cheek, this indicates that the pus could go into the mucous membrane or periosteum and then the doctor will have to make an incision in the gum to drain it.
If you go to the dentist with a granuloma of a tooth that is completely destroyed, it would be advisable to remove such a tooth. But at the same time, it is important that the tooth extraction procedure is carried out efficiently and not only the tooth is extracted, but also the granuloma. If the tumor remains in the socket, alveolitis may develop - a rather serious and unpleasant complication.
If you have had a tooth with a granuloma removed, you must properly care for your teeth and oral cavity after this operation. You should:
- Temporarily stop drinking too hot food/drinks, alcohol, smoking;
- Avoid overheating and hypothermia of the body and for this purpose do not visit baths, saunas, swimming pools, be sure to dress according to the weather;
- Eliminate stress and physical activity;
- Eat soft and warm foods for a week, trying not to chew on the side of the jaw on which the extracted tooth was located.
Be sure to take all medications and carry out all procedures prescribed by your doctor! If, within 3-4 days after the removal of a tooth with a granuloma, pain and swelling do not go away, contact the clinic immediately. The persistence of pain and swelling may indicate that the inflammatory process continues for some reason.
After tooth extraction during the treatment of granulomas, prosthetics and dental implantation are carried out no earlier than six months later. Such a pause in treatment is necessary for the complete restoration of all tissues in the area of tooth extraction.
Symptoms and signs
Granuloma annulare in children has different causes, but the symptoms do not change. Mainly affects the bones of the pelvis, skull, and spine. The course of the disease is slow. The symptom of eosinophilic granuloma is pain and swelling at the site of localization. There are cases where there is no discomfort. On the surface of the skin it appears as semicircular intradermal lesions. Granuloma annulare in children of a localized form is usually located on the hands and arms, feet and legs. It is diagnosed mainly before the age of 6 years. Ring-shaped lesions range in diameter from 2 to 5 cm. Giant sizes up to 10 cm are less common.
On the body, a pyogenic granuloma in a child does not exceed 2 cm in diameter. It has a thin surface and can bleed. The structure is fragile. Occurs quickly due to skin trauma. It does not turn pale when pressed. There is a rim of skin around the granuloma or it may be raised on a stalk. Rarely does a rash appear in the affected area. A characteristic symptom that children complain about is itching. Ring-shaped and pyogenic varieties occur in children more often than other neoplasms from the granulomatous group.
When to see a doctor
If papules of red-pink and bluish color appear on the skin, you should contact a dermatologist to confirm the diagnosis at JSC “Medicine” (clinic of Academician Roitberg) in the center of Moscow. Granuloma annulare in children causes and treatment depends on the degree of proliferation of foci and intensity. You will also need the help of a specialist in case of itching. Treating yourself or visiting a doctor is not a conflict of interest. Granuloma in a child may have characteristic causes, but the clinical manifestations can easily be confused with another serious disease. We are talking about lichen, which is sometimes mistakenly self-diagnosed based on external signs. There are a number of other diseases that stand apart, but can be mistaken for granuloma annulare: erythema raising, necrobiotic lesions, rheumatoid nodules.
Granuloma annulare
Granuloma annulare is a benign dermatological disease of an often relapsing nature, in which dense rashes slightly raised above the skin, resembling a ring in shape, appear.
The nodules are usually pink in color, but can be flesh-colored or bluish in color. There are single and multiple. Granuloma annulare of the skin is a fairly rare disease, diagnosed in 0.3% of patients who consult a dermatologist. Most often these are school-age children and young people, less often adults. In men, the disease occurs almost 2 times less often than in women.
Available diagnostic methods
At JSC “Medicine” (academician Roitberg’s clinic) near the Mayakovskaya metro station, you can comprehensively examine the health of adults and children. The latest equipment (ultrasound, MRI, CT) and advanced diagnostic methods, specially equipped rooms - everything is there to confirm or refute granuloma annulare in children. In the early stages of development, neoplasms cannot be detected. Symptoms appear when lesions appear on the surface of the epidermis. A diagnostic examination by a dermatologist is carried out when there are complaints of skin changes. Only after this do they turn to laboratory and histological analyzes of skin biopsies from lesions in case of suspicion of deep forms of lesions.
Should I treat or remove a tooth for granuloma?
In most cases, a tooth with a granuloma can be saved - for this purpose in modern dentistry there are a lot of effective techniques, most of which we discussed above. But it is natural that treatment should be done without extreme measures - it should not be postponed until the pain in the tooth becomes unbearable, and the cheek swells from swelling.
If you want to keep your teeth intact and healthy, you must remember one very simple rule - even the slightest pain, slight discomfort that occurs in the teeth when eating or on its own is already a serious reason to see a dentist! The sooner a granuloma is diagnosed, the higher the chances of saving your tooth!
Methods of treating the disease
Granuloma annulare in children requires restrained treatment. The characteristics of the body allow us to expect spontaneous resolution. According to statistics, in 75% of cases, granulomas regress within 2 years. A granuloma may reappear on the skin of a child in 40% of patients. It is important that recurrent tumors behave benignly. For painful symptoms, corticosteroid ointment with a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antiallergic effect is used. Another treatment method is superficial scarification. How to treat granuloma annulare in a child without harm to health is an important topic. The methods are based on the use of physiotherapeutic procedures: PUVA therapy, ultraviolet irradiation and phototherapy, pulsed laser. The treatment of pyogenic neoplasm is characterized by excessive proliferation of blood capillaries. With this diagnosis, it is recommended to be treated by excision, curettage, liquid nitrogen and electrocoagulation. Granuloma annulare in children is treated within a month. The need for manipulation and use of ointments is determined individually.
Features of diagnosis and treatment of dental granuloma
The basis for making a diagnosis is an X-ray examination of the patient in the area of the suspected problem. In order to cure a dental granuloma, the doctor must know its size, and also take into account the individual anatomical and physiological characteristics of the individual patient. If technical equipment is available in the dental clinic, radiovisiography may be prescribed for diagnosis.
With radiovisiography or an x-ray, the doctor sees a darkened formation, usually round in shape, located near the root of the tooth. During the diagnostic process, the dentist differentiates from other diseases that have similar symptomatic signs, for example, periodontitis.
Prevention in children
Any granuloma in a child is treated only after consultation with a dermatologist. There are no special methods of prevention. Granuloma annulare in children has variable causes for the development of the disease. Taking into account the influence of immunity on the occurrence of formations, it is necessary to undergo timely treatment. It is necessary to take into account the infectious nature and metabolism in the body. Any disease should receive therapy to reduce risks. This is what prevention consists of – eliminating factors that can provoke the disease.
Complications after granuloma at the site of an extracted tooth
Lack of timely treatment and hope that the disease will go away on its own is fraught with serious consequences. Among the most common complications it is worth highlighting:
- development of periodontitis and further formation of a fistula;
- the occurrence of alveolitis is a consequence of the presence of an inflammatory process;
- formation of purulent flux;
- suppuration of the perimaxillary tissue;
- entry of pathogenic bacteria into the lymph nodes, from where they penetrate the cardiac system and internal organs (kidneys, liver and brain);
- development of facial asymmetry;
- the emergence of new foci of infection;
- infection of the body due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the blood vessels.
Timely removal of granuloma is a guarantee to avoid unpleasant health consequences.
How to make an appointment with a dermatologist
You can make an appointment with a dermatologist using the special form “Make an appointment with a doctor” - just enter your data so that the administrator can call you back and coordinate the time of the visit. During the consultation, the doctor will examine the clinical picture, prescribe tests if necessary, and select treatment. You can make an appointment with a dermatologist using the number. JSC "Medicine" (clinic of academician Roitberg) has a convenient location at the address: 2nd Tverskoy-Yamskaya lane, building 10. Nearby there are metro stations: "Mayakovskaya", "Tverskaya", "Novoslobodskaya", "Belorusskaya", "Chekhovskaya" .