What is torticollis and how is it dangerous for a child?
The most comprehensive and accurate definition of the phenomenon was given by Professor S.N. Popov. According to it, congenital muscular torticollis in children - the child’s head is in an unnatural position due to congenital underdevelopment of the sternocleidomastoid muscle (SCM) or damage to it during childbirth. Torticollis is an anomaly that is accompanied by secondary changes in the spinal column and deformation of the bones of the skull.
What is torticollis in an infant? In the maternity hospital, pathology can rarely be detected: a noticeable deviation from the norm in the first 10 weeks of life is observed only in a small part of newborns. In some cases, the muscle undergoes changes (its fibers thicken, elasticity decreases) up to 2-12 months of life, and then the reverse process occurs. In other children, muscle hypertonicity leads to tissue changes, which further aggravates:
- abbreviation GKSM;
- abnormal head position;
- development of pronounced facial asymmetry;
- decreased motor activity in the cervical spine.
If treatment
If not started as early as possible, the anomaly progresses, and other structures are involved in the pathological process - the spine, nervous and circulatory systems.
Due to lack of nutrition and blood supply, muscles
stop
developing
, shorten, are replaced by fibrous tissue, and by the age of 3-6 years the deformation increases significantly.
It is uncomfortable for a child with torticollis to lie down
, which causes anxiety, sleep disturbances, and tearfulness.
In the future, such children lag behind in psychomotor development
.
In some forms of torticollis, children latch on poorly and suck inactively, which leads to weight loss and slows growth and physical development
.
In some forms of torticollis, an apparently healthy
the child has clinical manifestations of pathology, which worsen with age, so timely detection of disorders and early adequate treatment are necessary.
Torticollis: causes of appearance
Factors that cause the development of torticollis in children vary depending on the type of pathology. The occurrence of the most common form, muscular or myogenic, causes a change
structure and functioning of the GKSM.
The cause of
the phenomenon may lie both in genetic disorders of muscle formation and in injuries received during childbirth. The development of fetal tissue is affected by the condition of the pregnant woman, diseases suffered during gestation, and injuries.
Congenital
Hypertonicity of the neck muscles is provoked by intrauterine intoxication and abnormal position of the fetus, methods of obstetrics. The muscle responsible for tilting and rotating the head changes under the influence of pathogenic factors - it thickens and contracts.
Why does congenital torticollis occur in infants?
There are several recognized theories of the occurrence of congenital
muscular torticollis:
- traumatic - at the site of the formed hematoma, a keloid forms, the muscle
disorder
occurs and, as a consequence, ischemic changes -
the muscle
shrinks, “shrinks out”; - topographic – the abnormal position of the fetus in the uterus leads to prolonged compression of the muscle
, which causes its persistent shortening, and can cause injury during the passage of the child through the birth canal; - inflammatory – penetration of infection into the fetus causes chronic interstitial myositis and muscle
; - discrepancy between the length of the spinal column and the length of the muscles of the neck and shoulder girdle;
- genetic - hereditary anomaly in the synthesis and structuring of collagen fibers, hereditary pathologies - Shereshevsky-Turner, Klippel-Feil syndromes.
Congenital torticollis in newborns is often detected during multiple pregnancies, severe toxicosis in the mother, or the threat of miscarriage.
Pathological pregnancy
causes endogenous and exogenous factors of anomaly.
The main reason
is injury:
- asphyxia when entwined with the umbilical cord;
- ischemia due to malposition;
- hemorrhage in the tissue of the GCM.
Birth injuries can lead to other disorders: congenital
fracture, dislocation of vertebrae, damage to nerve endings.
Statistical data confirm that adequate treatment
carried out in the first 2 months of a baby’s life gives a positive result of 75-85%.
Causes of acquired torticollis
If congenital torticollis occurs due to the action of pathogenic factors on the fetus, then the violation
musculoskeletal system in the postpartum period is called an acquired anomaly.
The reason
why deformation occurs in the postpartum period in newborns is
trauma
caused by:
- mechanical compression or muscle tear when applying forceps or manual torsion of the fetus;
- damage and displacement of the vertebrae during certain types of difficult labor and delivery;
- perinatal injury to the fetus with a narrow maternal pelvis.
Pathological childbirth, during which stimulation was carried out, the provision of obstetric care, and the use of artificial ventilation of the newborn in 92-100% of cases lead to hemorrhagic-ischemic damage to the GCM and in 61.1% to spinal injuries in the cervical region. The proportion of such injuries is especially high in children with increased or decreased body weight ( children with weak muscle tone
) when using obstetric benefits (32%).
In such children, development
in the first months of life is complicated by the presence of torticollis, with the head tilted to one side (41%), caused by:
- dislocation and subluxation of the vertebrae of the neck (osteogenic);
- flaccid or spastic paralysis with which the muscle reacts to injury (neurogenic).
In addition, a static position of the child in the crib (installation deformity) can cause torticollis in an infant.
In adults and older children, acquired torticollis can be caused by:
- injury;
- infection - with osteomyelitis, syphilis (stage III of development), bone tuberculosis or neuroinfection;
- cerebral palsy;
- gastroesophageal reflux (Sandifer syndrome);
- inflammatory process: in the inner ear, pharynx or nasopharynx (Grisel's disease), perichondritis of the ribs, fibromatosis of the pectoral or cervical muscle;
- paralytic strabismus, development
of ophthalmological unilateral pathologies - as a compensatory reaction; - cicatricial changes in the skin in the chest and neck area - burns, inflammation, surgery;
- spinal tumor;
- hysterical psychosis.
An acquired anomaly is easier to treat. The most common type of torticollis in infants can be prevented by frequently shifting the child to the other side and using special devices to fix the head.
General information
Spasmodic torticollis (cervical dystonia) is the most common form of focal dystonia, a rare pathology accompanied by involuntary contractions of certain muscle groups. According to European researchers, the frequency is 5.7-8 cases per 100 thousand population. Manifestation, as a rule, occurs at the age of 30-40 years. Data on sex distribution are contradictory. Russian scientists believe that women get sick one and a half times more often than men, American authors point to an almost threefold predominance of representatives of the stronger sex.
Spasmodic torticollis
What are the types of torticollis?
Depending on the causes, the following types of torticollis are distinguished:
- myogenic – the most common type
of pathology, in which the GCSM is shortened or thickened; - osteogenic - this type of
deformation causes a congenital disorder of the development and formation of vertebral bodies and joint function in the cervical region (Klippel-Feil syndrome); - neurogenic - this type of
anomaly is caused by dystonic syndrome.
It is characterized by muscle
hypertonicity on one side of the neck and decreased tone on the other; similar disorders of muscle function are observed on the corresponding side of the body; - arthrogenic – caused by displacement of the articular surfaces of the cervical vertebrae;
- dermatogenic – manifested as a consequence of gross scar changes in the skin and soft tissues of the neck;
- reflex – the disorder
causes unilateral reflex muscle contraction; - spastic torticollis is one of the forms of focal muscular dystonia, in which muscle hyperkinesis causes forced deviation of the head;
- hypoplastic – a consequence of hypoplasia of the GCM and trapezius muscle;
- compensatory - an adaptive reaction that compensates for unilateral visual impairment and hearing impairment;
- installation torticollis - incorrect static position of the child in the crib;
- idiopathic – unknown nature.
Treatment
deformations accompanied by organic changes are difficult and surgical intervention is often required to eliminate them.
Depending on the location, the pathology is divided into:
- right-sided - the head is tilted to the left and the face is turned to the right;
- left-sided - the head is tilted to the left, and the face is oriented to the right, the shoulder on the side of the shortened muscle is raised.
Bilateral torticollis is very rare. With this form of the phenomenon, the head is thrown back or tilted forward.
To compensate for the forced pathological deviation of the head, a person takes a forced posture, which leads to deformation of the spine, which causes early osteochondrosis, scoliosis
, pelvic distortion, flat feet, hallux valgus (clubfoot).
What does torticollis look like in a child? photo
For clarity, below are photographs of children with various types of torticollis. Left image
a newborn with congenital left-sided muscular torticollis.
The photo
on the right illustrates right-sided torticollis. It is noticeable that the shoulder on the side of the short GKSM is raised, there is a slight deformation of the skull and asymmetry of the face.
Photo 1. Torticollis in a newborn.
Picture
Below demonstrates the method of manual diagnosis of torticollis. The specialist, comparing muscle tone on different sides of the neck, examining mobility, checking reflexes, and the location of skin folds, makes a preliminary diagnosis.
Photo 2. Physical diagnosis of torticollis in children of the first year of life.
Baby
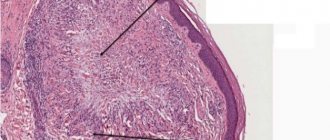
in the next photo, the side is turned towards the viewer, on which the hypertrophied muscle is visible, stretching in the form of a dense protruding ridge from the mastoid process of the skull to the collarbone. Such hypertonicity of the GCM is a diagnostic sign of muscular torticollis.
Photo 3. Appearance of the sternocleidomastoid muscle in torticollis.
Not only an experienced vertebrologist, but also an attentive parent of the child can identify the signs of an anomaly.
Symptoms
Muscle contractions associated with cervical dystonia can cause the head to rotate in various directions, including:
- Chin tilts towards shoulder
- Ear to shoulder
- Chin goes up
- Chin drops straight down
The most common type of twisting with cervical dystonia is when the chin is pulled towards the shoulder. Some people have a combination of poor head postures. Jerky movements of the head may also occur.
Most patients with cervical dystonia may also experience neck pain that may radiate to the shoulder. The disease can also cause headaches. In some patients with spasmodic torticollis, the pain can be intense and debilitating.
Torticollis: symptoms and signs of the disease in children
How can parents understand that a child has torticollis and not miss the moment to start treatment on time? Disease
in the initial stage, it can be determined visually by comparing some characteristics of the child’s physical and psycho-emotional state. With age, torticollis progresses, its signs become more pronounced and more diverse. If you arrange the symptoms and signs of pathology in chronological order, you get the following picture:
- 1-2 months In a supine position, the baby's head is tilted towards the shoulder, and the face is turned in the opposite direction. Attempts to correct the position of the baby's head cause tears. Inspection and palpation of the neck muscles reveals a thickening in the form of a pea or spindle. The skin over the thickening is not changed, there are no signs of inflammation. The body is curved towards the tilt of the head. On this side, the handle can be clenched into a fist and the leg bent. Having laid the baby on his tummy, it is easy to notice tense, convex muscles of the back on one side, and there is an asymmetry in the location of the folds of the body - the gluteal, lower extremities. One of the legs may be shortened due to pelvic displacement. Since lying down is uncomfortable for him, sleep is disturbed, the baby often cries and is restless. Sucks sluggishly, gets tired quickly.
- 3-5 months Psychomotor development is slow - the child reacts poorly to sounds and tactile stimuli. The eruption of baby teeth lags behind, and the spine takes on a C-shape. Deformation of the skull is possible - the affected side becomes flattened, the hairs on it are sparse or “roll out” completely.
- 6-7 months When moving, he does not step on his foot completely - he walks on his toes. Moody, excitable, painful. He often suffers from colds and is prone to allergic reactions. The asymmetry of the face increases; due to the abnormal position of the head and trophic disorders, strabismus may appear. Grows and develops worse than a healthy child.
- 9-11 months The child does not stand well - there is a distortion of the body, and refuses to take steps independently. There are disturbances in grasping movements and orientation in space. Pronounces words indistinctly or refuses to speak - delayed psycho-speech development. There is pronounced distortion of the brow ridges, eyes, and corners of the mouth. Possible muscle atrophy on the affected side of the face, occipital muscles, and flattening of the arch.
With age, S-shaped scoliosis is detected in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine
, the child gets tired quickly, does not assimilate educational material well, verbal memory especially suffers, and attention is unfocused. There may be difficulty in nasal breathing and malocclusion.
Types of disease
As soon as spastic torticollis is identified, treatment is prescribed immediately after clarifying the type of disease and symptoms. There are four types of dystonia anomalies:
- retrocollis - nerve impulses do not pass correctly to the trapezius muscle, and the head falls back;
- antecollis - the defect is observed in the cleidosternal-mastoid region (the head is tilted predominantly forward);
- torticollis - turning and tilting the head to one side;
- laterocollis - the head is tilted towards one of the shoulders.
Methods for diagnosing torticollis in a child
It is also possible to visually detect torticollis, but how to determine at what stage of development the pathology is located cannot be limited only to physical examinations. To differentiate and accurately establish the type of torticollis, the doctor
prescribes instrumental studies.
Previously, differential diagnosis in children of the first year of life was limited to physical methods - examination, palpation
, measurement.
Sometimes the examination was supplemented by x-rays
.
Today,
modern methods for studying torticollis disease have come the aid
- Ultrasound;
- MRI
; - CT.
Ultrasound examination makes it possible to identify abnormalities in individual bundles of muscle fibers and tendons, and to suspect disturbances in the structure of the spinal column. The low radiation exposure of MRI and ultrasound, the high information content and reliability of the results obtained have made them the main diagnostic methods. X-rays are used only if pathology of the bones and especially the spine is suspected. MRI and CT can detect brain disorders caused by hypoxia.
The peculiarity of the development of the child’s body makes the ultrasound method the main one. The high hydrophilicity of tissues allows you to clearly see the bone, soft tissue and even circulatory system, and evaluate the strength and speed of blood flow. Improvement of ultrasound methods (ultrasonography) can determine the elasticity of GCSM and the possibility of fibrotic degeneration. Muscle
function and structure are measured and tested.
If an infectious nature of the pathology is suspected, the doctor
orders biochemical tests.
The children's
doctor-
pediatrician
involves specialists in other fields - an ophthalmologist, a neurologist, an orthopedist - in the examination.
An accurate diagnosis
of torticollis is established after a comprehensive examination and
treatment
.
The disease
is most effectively treated when it is diagnosed at an early age.
How is torticollis treated?
Parents should understand that torticollis can be treated, how to correct the pathology? For torticollis, treatment is carried out depending on the type of pathology. If the disease is detected at an early stage and there are no structural changes in the muscles, then conservative treatment
.
And physical therapy (PT) occupies a primary place in the correction of disorders. An integrated
approach prescribed when identifying pathology allows you to achieve:
- improving cellular nutrition;
- balancing muscle tone of affected and healthy muscles;
- restoration of volume of movement;
- prevention of secondary changes;
- correction of psychomotor disorders;
- increasing nonspecific defense of the body.
For correction the following is used:
- massage;
- physical exercises, gymnastics;
- exercises in water;
- treatment with different positions;
- physiotherapy.
Correct
the choice of conservative treatment methods in most cases allows for correction of violations.
The photo shows therapeutic massage
with torticollis.
Photo. Torticollis, treatment with massage.
Baby massage
carried out using gentle manual techniques.
For mild forms of torticollis, the orthopedist
prescribes corrective
treatment
using orthopedic devices.
For the spastic form of the disease, an orthopedist
prescribes drug therapy.
But even the correct
selection of medications does not always give the desired effect and has side effects.
If a course of
conservative therapy does not help get rid of the phenomenon, then
the doctor
may prescribe surgical intervention.
During the postoperative period, the doctor
selects a complex of exercise therapy that helps restore the function of the operated muscle.
Pathology therapy is not a quick process and can take up to a year. You will also need constant monitoring by a doctor - dispensary observation is carried out every 6 months until the age of 14 years.
What are the treatment methods for torticollis and the nuances involved?
The most commonly used correction methods are massage
, exercise therapy, surgical treatment.
No less effective methods are the use of orthopedic devices and
position correction
To increase efficiency, the techniques are combined. Treatment
This position can be combined with the use of a special pillow for torticollis.
A newborn baby spends most of his time lying down, so it’s easy to give him a certain position
.
Pillow
placed with a protruding cushion under the neck, the head is located in the recess.
The pillow
is selected so that the height of the bolster matches the width of the baby's shoulder.
The crib
should be positioned so that the baby faces the light source while awake.
Bright toys are placed in front of the eyes. Thus, the head is fixed in the desired position, the affected muscle
relaxes, muscle tone is equalized, blood circulation is restored, and trophism is normalized.
Treatment
position implies not only the positioning of the head, but also
the correct
vector of the spinal column.
lie
on a semi-rigid mattress so that the body is positioned symmetrically and the spine is on the same axis as the head. To give the desired pose, fabric rolls or bags with filling are placed on both sides from the armpits to the knees.
In this situation
the newborn is laid out 2-3 times a day for 1.5-2 hours.
A crib
turned towards the light, bright objects, people allows you to interest the baby and keep him from returning to a comfortable position.
is stimulated to turn in the opposite direction
from the abnormal position.
Wearing a special cervical prosthesis
used for bone pathology -
immaturity of the atlas (first cervical vertebra)
, cranial-spinal birth injuries.
Wearing a Shants collar
provides support for the child's head, compensating for
various malformations of muscles and muscle tissue
.
Also, wearing orthopedic devices is indicated after massage
and physiotherapy to stabilize the achieved correction results.
Well
is 1-2 months. The doctor calculates the duration of the child’s stay in the torticollis collar individually. Time can vary from 2-3 hours to a full day.
A good effect is achieved when prescribing classes in the pool. A special inflatable ring is placed on the baby’s neck; the specialist, carefully holding the head, moves the baby from side to side. Turning the baby tummy down and holding it under the chin, move it along the pool. With minimal pressure, stretching and torsion of the vertebrae occurs, eliminating muscle spasm. Gymnastics
in the pool combines the positive effects of exercise therapy, hardening, relaxation, and positive emotions.
Correct
the choice of physiotherapy methods enhances the correction effect.
Procedures in the physiotherapy department
involve the use of:
- electrophoresis with Papaverine, Magnesia, Dibazol;
- paraffin;
- low-frequency pulse therapy;
- magnetic therapy;
- infrared radiation.
Methods allow you to activate blood flow, reflex muscles, soothe inflamed muscle fibers
.
The choice of method for torticollis, how to treat it and the duration of the course of treatment
is made
by the pediatrician
.
The treatment
will not give the desired effect if you do not
carry the baby correctly
. You can carry the baby either facing the parent or with his back, but his shoulders should be level with the mother’s shoulders, and his cheek should support the baby’s head on the affected side in a normal position.
Therapeutic massage, physiotherapy
and other conservative methods allow you to restore
muscle
in 74-83% of cases. As a rule, by the age of 3 their effectiveness is exhausted.
How to do a massage for torticollis in a baby
Massotherapy
effective with early use and mild forms of pathology.
An
infant responds better to
massage
than an older child, and the result obtained is more stable.
The course
and frequency of exposure should
be prescribed
by a specialist, taking into account the severity of the pathology and the individual characteristics of the patient.
The doctor
gives
a massage
, and
help
.
They are taught how to maintain the achieved effect and how to do massage
at home on their own.
The most popular massage method:
- the specialist places the child on a flat surface and stands at the head edge;
- baby’s position – lying down, face up;
- the head is turned to the side of the lesion to achieve maximum relaxation of the muscle;
- movements are directed from the upper edge (below the ear) of the muscle to the lower;
- stroke the affected muscle with your fingertips, gently rub it, use the method of continuous vibration; movements are soft, gentle, so as not to cause discomfort;
- The healthy side of the neck is also massaged, but the technique of kneading and intermittent vibration is added.
Position
the child needs to be changed -
turned
onto his back and continue the massage.
The head
in this position is also turned towards the injury.
Photo Massage for torticollis.
Well
includes passive movements and effects on bioactive points.
How to properly do therapeutic massage
for torticollis,
the video
shows below
Massage
from torticollis begins from the first days of life.
Up to 2 months
, the child experiences hypertonicity of the flexor muscles.
To remove it, use stroking the limbs and rubbing the feet. In a 3-4 month
, hypertonicity disappears and kneading can be introduced.
With age, the duration of the session increases. At 6-10 months,
a reflex effect is added to the exit points of the spinal nerves and feet.
Therapeutic exercises for torticollis
Gymnastics
allows you to consolidate the achieved result, reduces the risk of relapse of the pathology.
The therapeutic
effect of torticollis in a newborn is due to the strengthening of muscles, the creation of a muscle corset, and the formation of the correct stereotype of movements.
To be appointed
the course of exercises should be carried out in parallel with the massage.
Gymnastics
are performed daily or every other day.
The full course is 15-20 lessons. Between courses there are breaks of 1-1.5 months. During this period, the baby needs the help
of his parents; they study at home according to a program developed by a specialist. Up to 2 years of age, parents work with their child daily for 5-15 minutes 3-4 times a day.
To avoid irreparable pathologies
, the rehabilitation program must be drawn up by a specialist. Most programs include the following exercises:
- Tilts (Fig. 1).
- Circular movements of the head (Fig. 2-3). While performing this exercise
, the baby lies on his back.
The mother fixes his shoulders with her hands. The doctor takes a position
at the head end of the table and carefully turns his head with his hands, supplementing the effect with light vibration.
turn
first to
the side
where there is damage, and then in the opposite direction. - From the same position, perform flexion and extension of the neck in the vertical direction.
- head
rises from the side-lying position and also when hanging from the couch.
Then the child must be turned
to the other
side
and the action repeated (Figure 5-6-7).
The resistance exercise His arms are extended forward so that he can lean on him.
Photo. Gymnastics for the correction of torticollis.
When the child grows up, gymnastics is also performed in a sitting position.
In what cases is surgery performed for torticollis?
Surgical methods for correcting pathology
shown if:
- the pathology was detected late and its form
is severe; - the use of conservative methods did not lead to complete regression of the condition;
- there is severe
scoliosis with an asymmetrical position of the shoulder blades and shoulder girdles; - progression of the disease leads to facial asymmetry and skull deformation;
- movements in the cervical spine are severely limited or impossible.
To be appointed
Surgery can be performed in children over 2 years of age or with rapid progression of the pathology, regardless of age.
Correction is carried out using the operation:
- myotomy according to S.T. Zatsepin, in this case the fascia of the neck is dissected and the fibrously changed area of the GCSM is partially or completely excised;
- myoplastic elongation of the GCSM.
For torticollis, the operation is performed under general anesthesia. Modern methods include endoscopic treatment of torticollis. Access to the affected muscle is made through small incisions, which reduces rehabilitation time and makes the operation less traumatic and safer. After treatment, immobilization of the neck using a Shants collar is indicated for a period of 6-7 months. With timely surgical intervention, the muscle can restore its function.
In case of torticollis in adult patients, surgery does not completely eliminate the pathology, secondary disorders persist, and the disease can recur.
Treatment of torticollis with medications
Some forms of torticollis in the initial stage are amenable to drug treatment. Modern methods of treating spastic torticollis include a complex of physiotherapeutic procedures and the administration of botulinum toxin A - “Dysport”. The effect of the drug lasts only 4-6 months, after which the injection must be repeated. Treatment is carried out throughout the patient's life.
Medicines
used in the treatment of spastic form:
- tranquilizers from the group of benzodiazepines;
- centrally acting muscle relaxants;
- L-DOPA preparations;
- anticonvulsants;
- anticholinergics.
Tablets are also prescribed
and injections that improve trophism and increase blood supply to muscle tissue.
If the anomaly is infectious in nature, drug treatment for the underlying cause is prescribed. The effectiveness
of drug therapy is high if it is carried out in combination with other conservative or surgical methods.
Is it possible to cure torticollis at home?
Self-medication of torticollis in newborns can lead to dangerous complications, disability, and missed opportunities for timely treatment. Traditional methods can help
in the treatment of muscle inflammation, pain relief.
Spastic torticollis is treated by placing a load on the affected side in the form of bags with filler (sand, small cereals) sewn to the lining of clothing in the shoulder area. The method helps provided
, if its use has been agreed with a doctor.
Home
is not the place to treat acute forms of the disease. Even massage and exercise therapy performed uncontrollably can lead to complications.
Features of therapy
It is possible to return the affected muscle to its previous normal state. Special exercises can help with this. But a doctor should select them so as not to aggravate the patient’s condition. Such exercises are performed very carefully and extremely carefully. At the Noosphere clinic they are carried out under the supervision of a specialist, a kinesiotherapist. He will always tell you whether the patient is performing the exercise correctly and, if necessary, show how it should be done.
To get rid of torticollis, our clinic uses the kinesiology method. The doctor uses his hands to reset the displaced vertebrae to their original places, thereby eliminating this arthrogenic disease. This method of treatment has a softer, more gentle effect compared to manual therapy. It does not injure the body and is suitable for children suffering from torticollis.
Kinesiology includes methods such as:
- physiotherapy;
- hirudotherapy;
- reflexology.
Due to this, blood supply to the affected muscle area improves. To eliminate unpleasant spasms and thereby relieve the patient from spastic torticollis, massage is added to complex therapy.
A disease such as torticollis can be corrected if you contact our Noosphere clinic in time. In this case, it will be possible to restore the impaired function of the affected muscle.
Torticollis in adults - treatment features
In adult patients, acquired torticollis is usually diagnosed. Cause pathology:
- injuries;
- occupational pathogenic factors;
- age-related changes in the spinal column;
- inflammation
; - infectious diseases;
- spinal tumors and other causes.
The older you are
patient, the more difficult the treatment.
Often the main diagnosis
is complicated by secondary changes that remain even after the anomaly has been eliminated or by concomitant diseases.
Adult
the patient suffers from the same types of torticollis as the little patient.
Photo. Types of spastic torticollis depending on the position of the head.
However, an adult
the patient practically does not respond to conservative methods of therapy, due to the physiological characteristics of the body and age-related changes.
Most often, surgery
, but it does not guarantee complete regression and does not eliminate the risk of relapse of the pathology.
Consequences and complications of torticollis
In the absence of treatment or an incorrectly chosen strategy, torticollis tends to progress, and therefore will develop
and violations.
The relevance of early treatment of torticollis is due to the fact that under certain conditions the anomaly can develop into a severe
destructive process involving bone and muscle structures,
the development
of which will lead to neurological and somatic complications:
- Chronic oxygen starvation of the brain leads to a slowdown in the maturation of cortical structures, which leads to the following disorders:
- hearing and vision;
- speech development;
- verbal memory and attention;
- cognitive function;
- paresis;
- scoliosis;
- early osteochondrosis;
- disruption of vertebral growth due to damage to their growth zones;
- facial asymmetry;
- malocclusion;
- underdevelopment of the jaw;
- asymmetry of the paranasal sinuses;
- curvature of the nasal septum;
Progressive scoliosis
accompanied by a violation of the location of the pelvis, which leads to gynecological, urological diseases, disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and hepatobiliary system.
Severe, untreated form
of torticollis in infants leads to disproportion of the limbs, chest and other bony structures of the skeleton.
The pathology requires treatment - it will not resolve on its own, especially in adulthood. Refusal to undergo surgery can lead to “shrinkage” of the muscle, severe consequences of oxygen starvation of the brain and the whole body.
Self-medication is no less dangerous. Without the help of professionals, degenerative disorders progress much faster, and the consequences of a frivolous attitude towards one’s health can lead to permanent disability. Most changes are irreversible and cannot be eliminated even after successful correction of the condition. In addition to physical complications, torticollis leads to psychological suffering, loss of self-confidence, decreased self-esteem, and depression. Often such pathologies require not only treatment by an osteopath, vertebrologist, neurologist or surgeon, but also psychological rehabilitation.
What is the prevention of torticollis?
There are no methods for preventing congenital torticollis in infants. But older children can avoid the appearance of pathology. An acquired anomaly can also be prevented if:
- lead a healthy lifestyle, undergo timely examinations and treat infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- choose the right
sleep mode - choose bedding that provides support for the spine and relieves stress on the cervical spine;
the pillow
should not be too voluminous, and the mattress should not be too soft; It has been established that spastic and acute muscular torticollis often manifests itself after sleeping on an uncomfortable bed; - harmful working conditions also affect the condition - prolonged exposure to a forced position, drafts, work injury
, vibration cause torticollis;
changing
working conditions or profession will help eliminate the disease; - a set of exercises, exercises, and rational physical activity help strengthen muscles and normalize their tone, which reduces the risk of developing pathology;
- In infants at risk, torticollis can be prevented by a health
massage, frequent changes of position in the crib, and gymnastics for newborns and children in the first year of life.
Important condition
health of the musculoskeletal system and prevention of torticollis -
the correct
choice of posture during study or work, ergonomic workplace equipment, lighting.
Complications
Long-term course of spastic torticollis leads to the development of secondary pathological processes in the spine. Patients suffer from cervical spondylosis and spondyloarthrosis, which contributes to compression of the spinal nerves and the occurrence of radicular syndrome. There is a decrease or complete loss of ability to work, the ability to self-care suffers, household activity decreases, and the quality of life deteriorates. The pathology is often complicated by mental disorders: social phobias, depression, and increased anxiety.