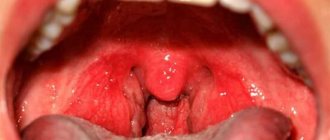
Increased body temperature, painful sensations in the throat, weakness, headache - people usually attribute these symptoms in the spring-winter period to a common cold. However, often such signs indicate the development of a dangerous infectious disease, which doctors call purulent tonsillitis. The disease is manifested by severe inflammation of the tonsils (glands), located in the nasopharynx. The infection primarily affects the parenchyma and lymphoid tissue lining the tonsils. The disease is dangerous due to severe complications that develop when symptoms are ignored and there is no proper treatment.
If you suspect that you have a sore throat and need to consult a doctor, call +7 (499) 653-58-25 - we will definitely help you. Reception is carried out both in the clinic and with a visit to the patient’s home. To register online, fill out the form on the website.
Causes
Inflammation of the palatine tonsils is provoked by infections transmitted by airborne droplets. Less commonly, infection occurs through contact and household contact (through shared dishes, towels, bed linen). The most common causative agent of purulent sore throat is hemolytic streptococcus. However, if a person’s immune system works normally, bacteria of this group die immediately after entering the body. The development of pathology is facilitated by weakened immunity and provoking factors.
Indirect causes of purulent sore throat include:
- severe hypothermia;
- chronic diseases of the upper respiratory tract;
- oral infections;
- alcoholism and smoking history;
- stress, overwork, strong emotional tension;
- living in areas with difficult environmental conditions;
- deficiency of vitamins and nutrients;
- mechanical damage to the tonsils (trauma, surgery).
The disease is diagnosed with equal frequency in adults and children.
Incubation period
The period from the moment the pathogen enters the body until the appearance of the first characteristic symptoms can range from 2 to 6 days. During the first few days, the sick person is still unaware of his condition, becoming a source of infection for others. During the incubation period, the infection is actively transmitted by airborne droplets (through coughing, sneezing, kissing, talking). The onset of the disease is manifested by a feeling of chills, increased body temperature, weakness and headache. The sooner the patient sees a doctor, the easier the treatment is.
Questions
- Which doctor treats follicular tonsillitis in children?
An otolaryngologist is involved in identifying and treating follicular tonsillitis in children. - Is it possible to treat a sore throat on your own?
Independent choice of drugs for follicular tonsillitis in children under 3-4 years of age is extremely undesirable. Due to early age, many medications cannot be used in adequate doses. This leads to incorrect treatment. You can overcome a sore throat at home. However, in all cases, an in-person consultation with an otolaryngologist is required. This will help avoid the development of serious complications. - Does traditional medicine help with follicular sore throat?
Traditional medicine can have a positive effect in the presence of sore throat. However, it must be borne in mind that in case of high body temperature and pronounced signs of intoxication, antibacterial drugs should be prescribed in 100% of cases. It turns out that with follicular tonsillitis you can do without traditional medicine, but you cannot do without antibiotics. Therefore, in most cases, otolaryngologists do not recommend the use of non-traditional approaches due to the risk of losing valuable time. - Are anesthetic sprays harmful to children?
Anesthetic components in antiseptic sprays are contained in minimal doses. They are external anesthetics approved for use in pediatric practice. Therefore, to relieve pain in follicular tonsillitis, such sprays can be used in complex treatment.
Symptoms of purulent sore throat
In most patients, the first signs of purulent tonsillitis appear 2-3 days after the pathogen enters the body. When the patient's immunity is weakened, the clinical picture is most pronounced. In adult patients, the following symptoms are observed:
- the appearance of noticeable white or yellowish spots of pus on the tonsils;
- high body temperature (in the range of 39-40 ° C);
- intense pain in the throat that increases during swallowing;
- significant enlargement of the lymph nodes located under the lower jaw;
- easily removable whitish coating on the tongue;
- severe headaches;
- feeling weak and overwhelmed;
- loss of appetite;
- aching joints.
In adults, with timely treatment, the acute stage of the disease rarely lasts longer than a week. If the patient does not seek help from specialists, there is a risk of complications.
Complications of sore throat
The reason for the development of complications is often a late start of treatment, incorrect selection of antibiotics and a sharp weakening of the immune system2.
- Streptococcus has an allergenic effect on the body3, creates the preconditions for the development of nephritis (inflammation of the kidneys), myocarditis (inflammation of the heart muscle), rheumatism, manifested by the development of heart defects and inflammation of the joints, systemic connective tissue diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome, systemic vasculitis , scleroderma.
- Aggressive streptococcus can penetrate from the tonsils into the surrounding tissues, causing the formation of paratonsillar and retropharyngeal abscesses, periadenitis (inflammation of the lymph nodes), phlegmon - diffuse purulent inflammation of the tissues.
- The list of complications of tonsillitis includes otitis (inflammation of the middle ear), sinusitis (damage to the paranasal sinuses).
- The infection can enter the blood, spread throughout the body and cause the formation of purulent foci in other organs (septicopyemia).
Sore throat and acute tonsillitis in children should be taken seriously.
Consultation with a pediatrician and ENT doctor is necessary in any case, even if at first glance the patient’s condition does not cause much concern!
Self-medication is fraught with the development of complications - all parents should understand this.
Up to contents
The information in this article is for reference only and does not replace professional advice from a doctor. To make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a qualified specialist.
Stages of disease development
The disease progresses rapidly. This is especially true in children and adults with a weakened immune response. Symptoms depend on the current state of the body, age, concomitant diseases and the stage of infectious tissue damage.
Signs of the development of the disease at different stages from the moment of infection:
- 2-3 days.
This stage is characterized by the maximum severity of the symptomatic picture. The patient's tonsils increase significantly in size and white or yellowish ulcers appear on their surface. The inflammatory process covers the entire surface of the tonsils. The patient notes deterioration in health, weakness, loss of appetite and signs of fever, including an increase in body temperature to 39-40 ° C. The patient also experiences excruciating pain in the throat, which gets worse when swallowing. - Day 4
The ulcers that form on the tonsils begin to spontaneously open, releasing the contents (pus). In their place, lacunae are formed - characteristic depressions. If at this stage the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, the lacunae quickly close. - 5-6 day
. At this stage, patients feel a noticeable improvement in their condition - body temperature normalizes, headaches go away, strength and appetite are restored. - 7-10 day
. The last pathological sign – sore throat – recedes. The size of the lymph nodes located under the lower jaw also decreases. The patient ceases to feel pain and discomfort in this area.
Competent and timely therapy allows you to avoid serious complications.
Classification
Based on the nature of the lesion, the following types of this disease in children are distinguished:
- catarrhal tonsillitis;
- lacunar tonsillitis;
- follicular tonsillitis;
- ulcerative membranous tonsillitis.
It should be noted that in some sources catarrhal tonsillitis is considered as acute pharyngitis.
It is also customary to consider the classification of sore throat in children, based on the type of pathogen:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- fungal.
Catarrhal sore throat
Catarrhal tonsillitis is considered the mildest form of this type of pathology. Characterized by redness and swelling of the tonsils. If treatment is started in a timely manner, complete recovery occurs within a week. Otherwise, the disease progresses to a more complex stage.
Follicular tonsillitis
In this case, a pustular rash forms on the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract. The tonsils become enlarged and swollen. Just as in the case of catarrhal tonsillitis, with adequate treatment, complete recovery occurs in 1–1.5 weeks.
Ulcerative film form
The most complex form of sore throat. It is characterized by a severe clinical picture and is often accompanied by other diseases. The tonsils are enlarged and a loose film forms on them with the accumulation of pus.
With this form of development of the pathological process, general intoxication of the body almost always occurs. Often, the ulcerative film form of tonsillitis becomes the cause of the development of serious complications.
General symptoms
Regardless of the exact subtype of angina, the clinical picture almost always manifests itself the same way. The initial symptoms of sore throat in children are:
- a sharp increase in temperature to 39 degrees;
- a sore throat;
- congestion and pain when swallowing even liquids;
- pain in muscles and joints;
- headache for no apparent reason;
- fatigue, “broken” state;
- the lymph nodes, which are located in the submandibular region and on the neck, are enlarged;
- the tongue is covered with a white coating, sometimes with a gray tint;
- red throat, enlarged tonsils.
In addition, the general clinical picture may be supplemented by the following signs:
- almost complete lack of appetite;
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract - unstable stool, nausea and vomiting;
- a child's hoarse voice;
- capricious state, the child’s sleep is restless.
At the first symptoms, you should immediately seek medical help. It is strongly not recommended to treat this disease on your own, at home, for children under one year of age. A sore throat in a child at this age can cause serious complications.
The danger of this disease also lies in the fact that complications may appear after some time. Therefore, it is better to carry out treatment under the supervision of a doctor in a hospital. It is not recommended to treat a sore throat at home also because you cannot independently diagnose the nature of the pathogen.
Symptoms of a sore throat
Diagnostics
As a rule, children under one year of age are rarely referred for additional diagnostic procedures, since the clinical picture is very clear. If such a need exists, the following additional studies may be carried out:
- general and biochemical blood tests;
- oral swab;
- general urine examination.
Treatment
Clinicians note that it is better to treat sore throat in children under one year of age in a hospital. This infectious disease can cause serious complications even in adults. Due to the fact that a child under one year of age has a weakened immune system, death is no exception.
The main treatment program consists of the following points:
- drinking plenty of warm liquids;
- taking prescribed medications;
- strict bed rest;
- gargling.
Drug therapy includes taking drugs with the following spectrum of action:
- antibiotics;
- antihistamines;
- antipyretics;
- antimicrobial substances.
Antibiotics for sore throat in children are prescribed necessarily. To prevent the immune system from becoming even more vulnerable, vitamin therapy is used at the same time. Please note that antibiotics for sore throat in children should only be prescribed by a doctor. You cannot use any medications on your own, as this may cause the situation to worsen.
In addition to taking medications, you should gargle. Rinsing should be carried out only with warm antiseptic solutions:
- chamomile decoction;
- furatsilin;
- a decoction of sage, calendula and chamomile.
Please note that you can reduce the temperature of a child over 3 years old only if it exceeds 38 degrees. As for infants, the temperature should be lowered already at 38.
Treatment of sore throat should be comprehensive, even if the disease is treated at home. Only in this case can serious complications be avoided. It is unacceptable to use folk remedies alone to treat such a complex infectious disease.
Possible complications
In the case of sore throat in children, complications can be either primary (which arise during the course of the disease itself) or delayed (develop some time after recovery).
The first group includes the following pathological processes:
- laryngitis;
- acute otitis;
- inflammation of the mediastinal organs;
- general body intoxication syndrome;
- meningitis;
- sepsis.
The last two points are only possible if the infection gets into the blood.
Delayed complications include the following ailments:
- damage to small and large joints;
- encephalitis;
- inflammation of the heart valve against the background of an infectious-inflammatory process;
- hemorrhagic vasculitis;
- acute renal failure;
- acute pyelonephritis.
Such serious complications can be avoided if you seek medical help in a timely manner and begin correct treatment. Sore throat should be treated only as prescribed by a doctor.
After completing the course of treatment, the child should be regularly examined by a specialized medical specialist. Also, within a month after the end of treatment, you should avoid vaccinations and Mantoux reactions.
Prevention
Preventing a disease is much easier than treating it. Unfortunately, it is impossible to completely eliminate the formation of sore throat in children. However, if you follow simple recommendations, you can significantly reduce the risk of its development.
The following rules are good for preventing sore throat in children:
- the child’s immune system should be strengthened;
- Hypothermia and eating too cold food are not allowed;
- all diseases must be treated completely and in a timely manner;
- the use of any medications should be carried out only as prescribed by a doctor;
- At the first symptoms you should seek medical help.
In this case, even if the child gets a sore throat, significant complications can be avoided.
Otorhinolaryngologist L.V. Ledova Literature:
"Practical otorhinolaryngology". Clinical recommendations. Kryukov A.I., Palchun V.T.
“Guide to practical otorhinolaryngology” Palchun V.T., Luchikhin L.A., Magomedov M.M., 2011.
Source: https://gorlonos.com/ushi/otit/opredelit-i-vylechit-naruzhnyj-u-rebenka.html
Forms of the disease
The form of purulent tonsillitis depends on many associated factors and conditions. The most common three forms of development are follicular, lacunar and ulcerative-membranous (necrotic). Each type is characterized by characteristics of the course, specific lesions of the tonsil tissue and varying duration.
Follicular
Follicular tonsillitis is manifested by pinpoint purulent lesions of the parenchyma of lymphoid tissue and follicles of the tonsils. The disease in 85% of cases is caused by group A streptococci. The remaining cases of infection are associated with staphylococcal infection, Haemophilus influenzae, pneumococcus, and adenovirus. This form of pathology is accompanied by a rapid increase in the symptom complex, severe hyperthermia, sweating, loss of sleep and appetite. Intense pain in the throat can radiate to the ear.
Lacunarnaya
This type of disease causes severe inflammatory damage to the tissues of the peripharyngeal ring. The opening of abscesses is accompanied by the formation of specific perforations on the surface of the tonsils - lacunae. The acute phase of the disease is manifested by an increase in the size of the tonsils, up to difficulty breathing. Along with other symptoms, a characteristic sign of the lacunar type of pathology is bad breath. Sometimes doctors note a noticeable change in voice and diction problems. Inadequate therapy can lead to the development of a paratonsillar or retropharyngeal abscess.
Necrotic
Necrotizing ulcerative tonsillitis is rare (about 5-6% of cases). The main cause of the development of this type of disease is fusospirochetous infection. The rapid development of the infectious-inflammatory process causes the formation of histological changes in the tissues of the palatine tonsils. Violations of vascular permeability, associated with the active production of histamine and cytokines, lead to hypertrophy and sometimes tissue necrosis. The first sign of the disease is the feeling of a “lump in the throat.” Later, a sharp, unpleasant putrid odor appears from the mouth and salivation increases.
Symptoms of the disease
Despite the variety of forms, the signs of tonsillitis in children are largely similar. Let us analyze the clinical picture of the disease using the example of the most dangerous streptococcal inflammation1,2.
The incubation period ranges from several hours to 4-5 days - on average 2-4 days3. The onset of the disease is acute - symptoms of infection appear and develop quickly. The introduction of microbes into the tissue of the tonsils leads to their inflammation and the formation of a large amount of toxins. Their absorption causes poisoning of the body and the appearance of general symptoms of intoxication.
General symptoms:
- From the nervous system, weakness, drowsiness, lethargy, tearfulness and headaches are noted. A child of 2-3 years old during a sore throat usually becomes lethargic, begins to be capricious, cry for no reason, goes to bed in the daytime, although he usually refuses to sleep during the day. Older children complain of fatigue.
- Fever occurs as a result of irritation of the thermoregulation center by streptococcal toxins2,4. Sore throat in children is usually characterized by a rapid rise in temperature to 390 C and above, accompanied by chills, pale skin and lips, and cold extremities4.
- Febrile seizures in children (usually under 3 years of age) can occur against the background of a rapid rise in temperature4. They are expressed in twitching of individual muscle fibers or muscles, or in the form of a general seizure, in which the baby’s entire body tenses and bends in an arc.
- Nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain indicate a severe course of the disease1.
- Body aches, muscle and joint pain : Young children may complain of pain in their arms and legs1.
Local symptoms
These are the visible changes occurring in the throat and the sensations they cause. Depending on their nature, catarrhal, follicular, lacunar tonsillitis, as well as necrotic (ulcerative-necrotic, membranous-necrotic) acute tonsillitis are distinguished.
Catarrhal inflammation develops in all cases as the initial stage of the pathological process 1.3. If the immune system is strong and antibacterial treatment of a child’s sore throat is started on time, the disease can stop at this stage and then begin its reverse development3.
The tonsils, arches, soft palate and uvula look red and swollen. There are no raids on them. The baby develops a foreign body sensation, sore throat and sore throat when swallowing, and drooling.
Follicular tonsillitis is characterized by purulent melting of the follicles of the tonsils. Through the inflamed bright red mucous membrane of the tonsils, whitish-yellowish islands, the size of a grain of rice (3-4 mm), are visible. In this case, there is no pus on the surface of the tonsils - it is located inside under the mucous membrane.
In the case of lacunar tonsillitis, yellowish-white pus is secreted from the lacunae onto the surface of the tonsils and covers them with a thin layer, forming easily removable films. The smell from the mouth becomes sweetish-sweet, putrid, the pain in the throat becomes constant, independent of food intake. The baby's appetite decreases and he refuses to eat.
With necrotic sore throat in children, the throat looks uniformly red, large, 1-2 cm in size, areas appear on the tonsils, covered with a “pearly” dirty gray coating. The plaque is tightly bound to the underlying tissues. After its rejection, deep bleeding ulcers form on the surface of the tonsils. The development of necrotic processes indicates a severe course of the disease.
In all cases, streptococcal inflammation spreads to nearby (regional) lymph nodes. They are felt on the neck, below the corners of the lower jaw in the form of painful round formations, the size of which depends on the severity of the disease.
Severity
The disease can occur in mild, moderate and severe forms.
| 1. Light | A sore throat in a child over 5 years old can occur without pronounced symptoms of intoxication with mild weakness, low-grade fever (below 380 C) for 1-5 days, mainly with catarrhal changes in the tonsils, some pain and enlarged lymph nodes up to 1 cm3. This type of flow is considered mild . In children in the first years of life, the disease is often more severe. |
| 2. Medium-heavy | The moderate severity of the disease is indicated by the moderate severity of the general symptoms of angina: temperature above 38.50 C, weakness, headaches and body aches last for 6-8 days3. The tonsils are covered with purulent films and clear no earlier than after 4-6 days3. The lymph nodes are enlarged to 2 cm, but, despite the severity of the condition, there are no complications3. |
| 3. Heavy | A severe course is characterized by the appearance of severe symptoms of intoxication, including vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. A temperature above 39.50 lasts up to 9 days, exhausts the little man, and is often accompanied by febrile convulsions. In the pharynx there is a picture of filmy or ulcerative necrotic tonsillitis. Lymph nodes reach 3 cm in size. The tonsils are cleared after a week or even later. |
Up to contents
Diagnosis and treatment
To make a diagnosis and determine treatment approaches, you need to consult an otolaryngologist. Diagnostics is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- collection of medical history and complaints;
- examination of the pharynx using special lighting (pharyngoscopy);
- general and biochemical blood test;
- bacteriological examination of a smear with the preparation of an antibiogram.
How to treat a purulent sore throat is determined by an ENT specialist. In severe cases, hospitalization is required. General medical recommendations include bed rest, drinking plenty of fluids, taking vitamins and restorative medications.
Specific treatment of the disease is a complex of procedures and medications:
- Drug treatment of the oral cavity.
Complex therapy necessarily includes gargling with antiseptic solutions. For this purpose, solutions of furatsilin, manganese, hydrogen peroxide, sea salt, and natural herbal decoctions (chamomile, calendula) are used. This procedure is aimed at removing pathogenic microorganisms from the throat and mouth. - Taking systemic antibacterial drugs.
A full course of antibiotic therapy allows you to get rid of pathogenic flora. Antibiotics and their dosages can only be determined and prescribed by a doctor. The most commonly used drugs are from the groups of penicillins, macrolides and cephalosporins. - Symptomatic therapy.
To alleviate the patient’s condition during the acute stage, the specialist prescribes symptomatic treatment in the form of antipyretics, antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs. Sometimes it is recommended to undergo physiotherapeutic procedures during the recovery period.
Correctly selected treatment helps to avoid serious consequences and ensures healing of the affected tissue areas without visible defects.
Diagnosis of sore throat
If you suspect a child has a sore throat, parents should immediately seek advice from a qualified specialist.
An experienced doctor will help determine the type and stage of the disease and, accordingly, select the optimal treatment. At the initial appointment, the doctor listens to the complaints of the little patient and his parents, examines the child’s oral cavity using a laryngeal speculum or pharyngoscopy (visual examination of the pharynx using artificial light), palpates the lymph nodes, and also asks about contacts with patients. Based on the medical history, the doctor makes a preliminary diagnosis, after which he refers the patient for additional studies to confirm the initial assumption. The following methods are used in diagnosing angina:
- Bacteriological examination of a throat smear to determine the type of pathogen and determine sensitivity to antibiotics.
- Clinical blood test.
- Blood test for C-reactive protein, ASL-O, rheumatoid factor.
The method of treating acute tonsillitis will depend on the results of laboratory and instrumental studies.
Purulent sore throat in children
If the disease develops in a child, in addition to the main symptoms, digestive disorders often appear - diarrhea, nausea, vomiting. Children may complain of abdominal pain caused by intestinal spasms. The follicular type of pathology is especially difficult for children aged 5-10 years, causing inflammation of the meninges. Young patients often experience fainting, dry cough and complaints of a feeling of a foreign object in the throat.
If parents ignore the symptoms, the pathology becomes chronic. Pediatricians call this condition chronic tonsillitis, exacerbations of which occur 2-3 times a year.
Angina
CAUSES OF SOLISH
The cause of sore throat is pathogenic bacteria, usually streptococci, which are present in the pharynx in a conditionally pathogenic state and usually do not cause disease, but under unfavorable conditions (hypothermia in autumn-winter and spring, temperature changes) are activated and become pathogenic , as a result, an inflammatory process develops.
THE FOLLOWING MOMENTS CONTRIBUTE TO THE ACTIVATION OF SOLISH CAUSES ON THE MUCOSA:
- Past influenza or other acute respiratory infections;
- Predisposition of the body to sore throat;
- The presence of a purulent inflammatory process in the nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, oral cavity or pharynx (rotten teeth affected by caries).
CLASSIFICATION OF ENGINES (PHARINGOSCOPIC SIGNS ACCORDING TO B.S. PREOBRAZHENSKY):
- Catarrhal tonsillitis (there is hyperemia of the palatine tonsils, the edges of the arches and the soft palate; the tongue is coated, dry);
- Follicular tonsillitis (inflammation occurs in the area of lymphadenoid follicles with their suppuration and subsequent opening);
- Lacunar tonsillitis (appearance of exudate or plaque at the mouths of lacunae);
- Fibrinous tonsillitis (plaques take on a fibrinoid character and completely cover the tonsil);
- Herpetic sore throat is characterized by herpetic rashes on the tonsils, soft palate and arches;
- Phlegmonous tonsillitis develops when pyogenic bacteria penetrate into the tissue behind the tonsil with the formation of an abscess, both in the tonsil itself and behind it;
- Mixed forms.
To select the correct treatment tactics, an otolaryngologist needs a routine examination, but in some cases laboratory tests are required.
DIAGNOSIS OF SOLISH. METHODS.
- Clinical examination. Includes a survey and examination of the patient with palpation of the lymph nodes, examination of the oropharynx and tonsils, and listening to the lungs. Based on the data obtained, a preliminary diagnosis is made.
- Pharyngoscopy (examination of the oropharynx using a spatula under artificial bright light.
- Bacteriological analysis.
- Nasal cavity test.
- General blood analysis.
When a sore throat becomes chronic or severe, complications are diagnosed:
- Laboratory blood test.
- Echocardiogram.
- Radiography.
CLINIC OF SOLISH
Sore throat, as a rule, begins acutely.
SYMPTOMS OF SOLISH
- General symptoms: weakness, malaise, “heavy” head, increased body temperature to 39-40°C, chills, a feeling of weakness in the body with joint pain and pain in the muscles of the extremities;
- Dryness, rawness, soreness, burning in the throat and pharynx;
- A feeling of narrowing, tightness, squeezing in the throat, making breathing difficult;
- Hoarseness;
- Pain when swallowing (may radiate to the ear, temple);
- Redness of the tonsils, with severe damage, the appearance of purulent plaque on them.
COMPLICATIONS OF SOLISH
With incorrect diagnosis and inadequate treatment of angina, serious complications are possible, such as peritonsillar abscess, retropharyngeal abscess, neck phlegmon, postanginal sepsis (Lemierre's syndrome), streptococcal meningitis, acute rheumatic fever, glomerulonephritis, pyelonephritis, polyarthritis, etc.
TREATMENT OF SOLISH AT THE CLINIC ENT CENTER
Mainly local and systemic antibacterial therapy, anti-inflammatory therapy are carried out, in severe cases - steroid, detoxification therapy, etc.
A frivolous attitude towards sore throat is unacceptable, especially independent treatment. Treatment must be carried out under the supervision of an otolaryngologist. Only timely and correct comprehensive treatment of sore throat will protect the patient from serious complications.
PREVENTION OF SOLISH
- Indoor air humidification. The humidity of the air in which a person is located must be at least 45%, otherwise the mucous membranes dry out and become susceptible to inflammation.
- To give up smoking. Cigarette smoke impairs blood circulation in the mucous membranes and destroys the protective mechanisms of the upper respiratory tract.
- Breathing is not through the mouth (with cooling and drying of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx), but through the nose. The nasal mucosa absorbs many foreign bodies before they enter the throat, warms and humidifies the air.
- Maintaining a gentle voice regime.
- Hardening the body.
Complications and consequences
The advanced form of the disease leads to inflammatory damage to other organs, including the heart, kidneys, and joints. The most dangerous complications include:
- mediastinitis
– inflammation of the mediastinal tissue; - chronic bronchitis
- inflammatory damage to the bronchi; - sepsis –
spread of infection through the bloodstream; - arthritis -
inflammation of the joints; - glomerulonephritis is
a dangerous kidney disease; - purulent meningitis -
damage to the meninges; - peripharyngeal abscesses
- suppuration of the lymph nodes and tissue of the peripharyngeal space.
Timely access to a medical facility allows you to avoid negative health consequences.
Prevention
By paying attention to preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of developing the disease. Effective prevention includes:
- avoiding hypothermia (wearing warm clothes, monitoring microclimatic indicators in the room);
- regular preventative visits to the dentist to identify the early stages of caries and stomatitis;
- giving up bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol);
- moderate physical activity, regular walks in the fresh air;
- normalization of diet, sleep and wakefulness;
- compliance with hygiene standards and requirements, maintaining cleanliness in the home and workplace;
- limiting contacts with unfamiliar people during periods of unfavorable epidemiological conditions.
Strengthening the immune system based on leading a healthy lifestyle helps to avoid infection and make it easier to endure purulent sore throat.
If you have a sore throat, call us and we will definitely help you!