An infant almost never gets sick with worms, but with age the baby's curiosity grows. He begins to explore the world and puts everything into his mouth. On the street he pets cats, touches sand, dirty toys, etc. All this is a source of worm infection. Tiny, invisible worm eggs can persist even on the surface of skin, food, and furniture. What types of worms can children have?
Causes of ascariasis in children
Mostly young children become infected with roundworms. The causative agent of ascariasis in a child is the human roundworm (Ascaris lumbricoides), a round worm of white and pink color. Females reach up to 40 cm in length, males - up to 25 cm. Roundworms can parasitize in various organs of the child, but mainly in the small intestine.
The biological host of roundworms is humans, but for a full life cycle, helminth eggs must mature in the soil. Children become infected with mature ascariasis eggs by ingesting them along with contaminated particles of soil and sand from toys, dirty hands, and unwashed fruits and vegetables.
The peculiarity of the development of ascariasis is associated with the life cycle of helminths. Mature roundworm eggs swallowed with dirt turn into larvae. The latter penetrate through the intestinal walls into the bloodstream and enter various organs: liver, gall bladder, right ventricle of the heart, lungs and bronchi. Once in the bronchi, the larvae cause a cough and, together with sputum, are swallowed into the digestive tract. So they again enter the small intestine, where they turn into sexually mature individuals.
It takes 2–3 months from the moment of infection by eggs to adult individuals. At a later stage, adult worms parasitize the child’s intestines. A female roundworm lays up to 240 thousand immature eggs in one day. They are excreted in feces and, once in the soil, can remain viable for several years. Adults live in the body for 12 months and die. Their life cycle ends here. If re-infection with eggs does not occur, the child will spontaneously heal, expelling dead worms naturally from the body. But, waiting for self-healing of ascariasis in children is dangerous, since they cause enormous harm to the child’s body during their stay in the child’s body:
- May cause intestinal perforation with serious consequences;
- They take nutrients from food. This leads to vitamin deficiency, a decrease in the body’s defenses and frequent infectious diseases;
- Promote the development of pulmonary diseases, hepatitis, appendicitis, intestinal obstruction and other pathologies;
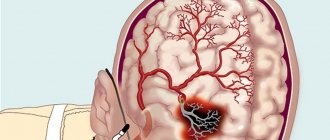
- They can cause hearing loss, vision loss, and damage to areas of the brain.
Treatment methods
Children with ascariasis are hospitalized in a day or 24-hour hospital. Drug treatment is used.
Drug groups
Anthelmintic drugs have an effect mainly on mature roundworms. The effectiveness of treatment is monitored after three weeks. A three-fold microscopic examination of stool is done with an interval of 3 days.
Symptomatic therapy. With a long course, ascariasis leads to impaired intestinal motility and a deterioration in the general condition of the child. The main thing is to optimize the child’s nutrition, introduce a sufficient amount of fiber and liquid into the diet. For the purpose of desensitization, antihistamines are prescribed. If anemia occurs, it is important to provide the child with iron supplements to improve hematopoiesis.
Symptoms of ascariasis in children
How to recognize ascariasis in children, symptoms indicating it? Symptoms of ascariasis appear to a greater or lesser extent and depend on the stage of the disease. In the pulmonary stage, symptoms are as follows:
- temperature rises;
- pain in the chest;
- dry cough;
- sputum with blood.
The period of presence of adult roundworms in the intestines is manifested by symptoms of indigestion, increased gas formation, periodic spasmodic pain in the abdomen, and sudden weight loss. Adult roundworms are excreted along with the feces. The body's reaction to the presence of roundworms can manifest itself in a child with skin rashes (urticaria), which do not respond to conventional methods of treatment.
Symptoms of ascariasis
Symptoms of ascariasis depend on the phase of the cycle, the localization of the pathogen, as well as the intensity of invasion (infection), that is, the number of individuals in the body.
Early phase
At this stage, signs of the disease are associated with the migration of roundworms. The incubation period lasts 1-2 days, then symptoms of general malaise appear: low-grade fever (up to 37-38 ° C) and weakness. The child complains of abdominal pain, nausea, and frequent trips to the toilet. An exanthema appears on the skin in the form of tubercles and areas of hyperemia (redness), and itching occurs.
A dry cough is a sign of damage to the lungs and respiratory tract. Bloody or mucous sputum may appear. In the lungs at this stage, moist rales are heard, as tissue inflammation and the formation of infiltrates (areas of compaction) occur.
When the liver is damaged, hepatitis occurs with all the characteristic symptoms: heaviness in the right hypochondrium, jaundice and indigestion.
Late (intestinal) phase
During this period, digestive disorders come to the fore. Children complain of nausea, loss of appetite, and sometimes vomiting. This is accompanied by cramping pain of various localizations: near the navel, in the epigastric and right iliac region. There is diarrhea or, on the contrary, constipation. In some patients these two symptoms alternate. With low localization of the helminth, itching in the anal area is possible.
With a massive infestation by a large number of roundworms, the child's pale skin and weight loss attract attention. This is especially true for young children. They experience delayed physical development and poor absorption of vitamin A, which leads to visual impairment.
From the nervous system and psyche, there is increased fatigue, dizziness, impaired mental activity and attention, headache, irritability. Children complain of poor sleep with nightmares, sometimes they have hysterical fits or convulsions.
Treatment of ascariasis in children
When diagnosing ascariasis in a child, anthelmintic therapy is prescribed. Treatment of ascariasis in children is carried out by a pediatrician. The treatment regimen and its content are prescribed depending on the severity of the disease, age and health status of the child. The most commonly prescribed medications are: Intoxic, Gelmifort, Bactefort, Levamisole, Piperzine, Pirantel. The effectiveness of these anthelmintic drugs is 80–100%. A month after treatment, a control examination of the child is carried out.
Diagnosis of childhood ascariasis
During the consultation, the doctor clarifies the child’s complaints in detail and conducts an examination. Living in areas with a high risk of ascariasis, atypical symptoms of damage to the bronchopulmonary system, coupled with digestive disorders, can prompt an experienced pediatrician to make a diagnosis. But it can only be confirmed using paraclinical methods.
Laboratory and instrumental diagnosis of ascariasis in children:
- A general blood test makes it possible to indirectly identify signs of helminthiasis - an increase in the number of eosinophils in the early phase and anemia in the late phase.
- X-ray of the chest organs. The images clearly show eosinophilic infiltrates, which are characterized by a variety of shapes (oval, round, scalloped, etc.). The shadows do not have smooth contours, and after three weeks they disappear.
- Specific diagnostics. The basis for making a diagnosis of ascariasis is the detection of adults or eggs in the feces (late phase) or larvae in the sputum (early phase). For this purpose, a microscopic examination of the sample is carried out. In cases of intense infestation, eggs can be easily identified even in a regular smear.
If standard diagnostic methods are ineffective, they resort to other methods, for example, examining a smear according to Kato or enriching the material with detergents according to Fulleborn. However, any stool analysis is possible at the stage of intestinal invasion, that is, after the migration period.
Serological methods are less informative - precipitation reaction, indirect hemagglutination, etc. They make it possible to detect antibodies to helminths in the blood, however, antibodies (IgG) are markers of the memory of an encounter with roundworms, and can remain in the blood for a long time, even if the roundworms are no longer present.
Prevention of ascariasis
Infection with roundworms most often occurs in children's groups in the spring and summer during walks and games in nature. The danger of the consequences of this disease cannot be underestimated. Therefore, parents need to teach their children the rules of personal hygiene as early as possible. It is also necessary to monitor the quality of baby food and strengthen general immunity. As a preventive measure, it is necessary to regularly carry out preventive deworming.
Dear parents!
Remember that only a qualified pediatrician can make an accurate diagnosis, determine the causes and nature of the disease, and prescribe effective treatment. You can make an appointment with our specialists or call a doctor at home by calling 8-800-700-31-69 Grow up healthy and happy!
Pathogenesis
Ascariasis is the most common geohelminthiasis in the world, confined to landscape geographic areas, a naturally endemic invasion. The degree of spread of ascariasis depends on the soil and climatic conditions of the area, which determine the possibility of the development of ascaris eggs, as well as the peculiarities of management (growing garden and berry crops), sanitary improvement, which determine the possibility of soil contamination with feces, as well as the sanitary culture and everyday habits of the people living here.
On a global scale, foci of ascariasis, i.e. local ascariasis, do not form only in the tundra zone and in the zone of dry deserts and steppes, where artificial irrigation is not used to moisten the soil. Ascariasis is the most common geohelminthiasis among the population of the Russian Federation; in rural areas the incidence is higher.
Thus, ascariasis is most widespread in the central, western and southern regions of the European part of Russia, in irrigated areas and foothills of Central Asia and Transcaucasia.
The source of infection for ascariasis is only the infected person; children are of primary importance. The eggs released with feces are non-invasive, therefore people infected with roundworms cannot infect others even during close everyday contact.
Helminth eggs excreted in the feces of patients must become infective, developing in the soil. For their development in the soil, favorable conditions are necessary: suitable temperature, humidity and access to air oxygen.
Egg development can occur at temperatures ranging from + 12 to + 36°C. At an optimal temperature of +24°C, with sufficient soil moisture not lower than 6 - 8%. The formation of an invasive larva in an egg occurs in 10 - 12 days. At temperatures below +12 °C, egg development stops, but their viability remains for a long time. At a temperature of -20°C, mature roundworm eggs remain viable for up to 20 days. And only temperatures below -30°C kill eggs after 24 hours. High temperature has a detrimental effect on roundworm eggs. At a temperature of + 50°C, eggs die quickly, at boiling temperature - instantly.
The third necessary condition for the development of roundworm eggs is access to a sufficient amount of oxygen. In oxygen-free cesspools, eggs do not develop, but remain viable. The survival time of roundworm eggs in soil is 7-12 years.
The formation and maintenance of ascariasis foci in rural areas is facilitated by the nature of the population’s occupations (gardening, strawberry plantations) and the custom of fertilizing vegetable gardens with non-neutralized feces.
During the period of expansion of individual farming, development of suburban garden farms, berry plantations in the dacha villages of citizens, not provided with sanitary soil protection measures, in the absence of latrines, leads to fecal contamination and contributes to the spread of geohelminthiases, primarily ascariasis.
Human infection with ascariasis occurs as a result of ingestion of invasive roundworm eggs when eating unwashed berries (strawberries), vegetables (carrots, radishes, onions, cucumbers, tomatoes, etc.), table greens (lettuce, dill, etc.).
During children's games in the garden, playgrounds, sandboxes, when working in the garden, in the flower garden, their hands become contaminated with soil containing roundworm eggs, which also leads to infection through any food taken with dirty hands.
Infection with ascariasis can occur throughout the year, but mainly in the temperate climate zone in the autumn period of the year, when berries and vegetables ripen. Considering the presence of greenhouses, as well as the preservation of vegetables in cellars, infection is possible in winter conditions.
Due to the peculiarities of the development of roundworms in the human body, the highest infestation of sexually mature helminths is detected in winter. The duration of the season of mass infection of people varies in different climatic zones. In the middle zone it leaves 6-7 months (from April to October).
Ascariasis infection
occurs orally. During the development of roundworm in the body, it goes through two phases: migratory and intestinal. The pathological basis of the migratory, or early, phase is the sensitization of the body by metabolic products of larvae migrating in the blood and tissues and the decay of dead ones. Metabolic products of roundworm larvae are strong parasitic allergens. They cause allergic hypersensitivity reactions, both general and local; eosinophilic infiltrates in the lungs, granulomatous hepatitis, skin rashes, hypereosinophilia in the blood, etc. Traumatization of tissues by larvae during migration, the formation of hemorrhages, and sometimes extensive hemorrhages are also important.
In the intestinal phase of ascariasis
the allergic factor is less pronounced, although the phenomena of allergic toxicosis also occur.
Adult roundworms cause mechanical injuries due to the elasticity of their bodies and mobility. To a certain extent, these mechanisms play a role in reflex dysfunction of the stomach and intestines, the development of spastic intestinal obstruction, injury to the wall of the small intestine, up to its perforation. Severe surgical consequences are caused by the penetration of roundworms into the liver and respiratory tract. The presence of roundworms in the intestines greatly complicates the course and outcome of surgical interventions for various pathologies.
An important role in the pathogenesis of ascariasis is played by a negative effect on vitamin metabolism. This is evidenced by a deficiency of pyridoxine, retinol, ascorbic acid, and a violation of intestinal eubiosis. The immunosuppressive effect of roundworms has been proven; in children, the production of antibodies to diphtheria toxoid is weakened.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of the early phase of ascariasis
caused by the migration of roundworm larvae in the bloodstream, vary in severity. Often, with low-intensity infection, this phase is subclinical or asymptomatic.
In clinically pronounced cases, complaints of general weakness, malaise, headaches, fatigue, loss of ability to work, sometimes fever, and the appearance of itchy rashes such as urticaria prevail on the skin. Less commonly, usually with intense infections, a picture of pulmonary pathology appears in the form of cough, sometimes with sputum mixed with blood, with an asthmatic component, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Auscultation reveals wheezing, pleural friction noise, and phenomena of exudative pleurisy. X-ray examination reveals eosinophilic infiltrates in the lungs, characterized by variability in their size, configuration, and position - “volatile infiltrates.” As a rule, focal infiltration of the lungs is accompanied by blood eosinophilia, sometimes the number of blood eosinophils reaches 35 - 60%.
Migrating roundworm larvae can cause severe pulmonary phenomena - acute pneumonia and bronchitis. In severe pneumonia of ascariasis etiology, accompanied by allergies, extensive hemorrhages caused by the rupture of the lung capillaries by migrating larvae play an important role in the development of the disease with the subsequent development of inflammatory phenomena.
These clinical manifestations of the early phase are supplemented in some patients by symptoms of dysfunction of the cardiovascular system and liver. The second is the intestinal phase of ascariasis
- is also characterized by a variety of pathologies and severity. Invasion can occur with mild symptoms or even asymptomatic. In clinically pronounced cases, gastrointestinal pathology and often asthenic syndrome prevail. Frequent complaints of patients are: disorder of appetite, decreased appetite, “capricious appetite” in children, nausea, increased salivation, “saliva rolls in a cloud”, often in the morning on an empty stomach. In some cases, there is a tendency to diarrhea or constipation; more often they alternate; progressive enteritis is less common. In children, dyspeptic symptoms predominate, accompanied by abdominal pain, often cramping and quite severe, occurring spontaneously or upon palpation. Functional and morphological disorders in the small intestine are detected x-ray in the form of changes in the relief of the mucous membrane, etc. Sometimes there is an unpleasant sensation of something moving in the intestine, bloating.
Pain on palpation of the abdomen during the intestinal phase of ascariasis is not uncommon, and in children it is most often diffuse, in adults it is local - in the midline above the navel, and to the right of the midline. Gastric secretion in infected people is often reduced.
In almost all cases of ascariasis in children, symptoms from the nervous system are observed, asthenic manifestations such as weakness, poor health, irritability, headaches, often absent-mindedness, memory loss, restless sleep, night terrors, twitching, less often hysterical and epileptic seizures, symptom complex Meniere's, decreased intelligence. Sometimes it is these asthenic phenomena that prevail over the others.
In the phase of intestinal ascariasis, sometimes, as in the first phase, allergic phenomena are observed, such as a rash like nettle fever, eosinophilia, although less pronounced. In the blood, especially in children, a frequent companion to ascariasis is moderate hypochromic anemia. From the cardiovascular system, a decrease in arterial and venous pressure was noted.
In the intestinal phase of ascariasis, both intestinal and extraintestinal complications can occur. Most of them are associated with increased motor activity of adult roundworms: intestinal obstruction, perforated peritonitis, ascariasis of the liver, ascariasis of the pancreas, respiratory tract, etc.
Ascariasis infestation in the obstetric clinic also does not remain without consequences. The negative effect of ascariasis on the course of pregnancy has been proven. In infected pregnant women, toxicosis and fetal development disorders are more often recorded, and the course of childbirth and the postpartum period becomes more complicated.
A frequent complication of ascariasis
is intestinal obstruction
, which is caused by the closure of the intestinal lumen with a ball of roundworms or due to a violation of the neuromuscular regulation of intestinal tone. When palpating the abdomen in patients with similar complications, one can feel a round, doughy consistency tumor-tangle of roundworms, which can be localized in any part of the intestine. In some cases, with a thin abdominal wall, it is possible to palpate the bodies of individual helminths in the intestinal lumen.
A severe complication of ascariasis is the penetration of helminths into the bile ducts and gallbladder
. In these cases, severe pain occurs that is not relieved even by narcotic analgesics. Against the background of these attacks, vomiting often occurs, and helminths are sometimes released with the vomit. In cases of cholangiohepatitis and mechanical blockage of the common bile duct by roundworms, jaundice occurs. The temperature during the development of complications can be of a septic nature with shaking chills. As a result of the addition of a bacterial infection, purulent cholangitis and multiple liver abscesses often occur, which in turn can be complicated by peritonitis, purulent pleurisy, sepsis, and abscesses in the abdominal cavity.
Penetration of roundworms into the pancreatic ducts
causes acute pancreatitis. If they enter the vermiform appendix, it causes appendicitis or appendicular colic without inflammatory manifestations. In some cases, roundworms, ascending the digestive tract, reach the pharynx and from here crawl into the respiratory tract, which causes death from asphyxia.
In rare cases, roundworms are found in the genitourinary organs, nasolacrimal canal, eustachian tube, middle ear, external auditory canal, and perinephric tissue.
Infestation by roundworms aggravates the course of various infectious and non-infectious diseases and disrupts immunogenesis in infectious diseases.
The causative agent of parasitic infection is pinworm
Enterobiasis is caused by the pinworm parasite. This helminth is a roundworm belonging to the class of nematodes. It has some features in appearance. Females grow to a length of 9-12 mm, they have a “tail” - a pointed end. It severely injures the intestinal mucosa when the worm is in the body. Males are 2-3 times smaller than females, and their “tails” are curved in a spiral. Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2306321/ JP Caldwell Pinworms (Enterobius Vermicularis) Can Fam Physician. 1982 Feb; 28: 306–309.
Adult helminths live in the cecum and at the end of the small intestine. At night, females crawl out of the cecum through the anus. At this time, the person’s anal sphincter is relaxed, so nothing interferes with the worms. When the female pinworm emerges, she lays eggs in the perianal folds. There are a lot of eggs - up to 15 thousand. Having laid them, the female dies. The entire cycle of her life is about a month. The eggs are resistant to environmental factors and can remain viable for up to 3 weeks. They stain clothes and bedding.
After a few hours, the embryo from the egg becomes a larva, which itself begins to parasitize. This is how enterobiasis spreads. Pinworms can penetrate the thickness of the intestinal mucosa, causing the formation of granulomas. Sometimes worms crawl into the vagina, uterus and ovaries. Because of this, the female organs become inflamed.
How to take a stool test for ascariasis?
No special preparation is required. But some recommendations will have to be taken into account:
- Before collecting stool for ascariasis, both children and adults need to go to the toilet and urinate.
- Then you need to take a clean, dry container (pharmacies sell special plastic containers designed for collecting feces, as they look like in the photo). If you don't have any on hand, any empty bottle with a lid will do.
- To determine ascariasis, it is necessary to place a volume of material equal to two teaspoons in a container.
- It is necessary to take samples from different sides of the feces (side, bottom, inside).
- After immersion in the container, the material is tightly closed with a lid.
- It is important to stick a piece of paper on the container with the inscription of the last name, first name and date of collection of the analysis.
In order to make an accurate analysis of stool, the material cannot be stored in a container for a long time (ideally, the time difference between collection and laboratory examination should be no more than 45 minutes). If necessary, you can delay the time for five to six hours, but for this it is best to put the feces in the refrigerator.
Traditional medicine methods demonstrate good effectiveness in treating ascariasis. Particularly popular is the juice obtained from pumpkin seeds. It is recommended to drink it daily on an empty stomach. You can also take garlic diluted with milk.
Dietary recommendations for the treatment of helminthiasis
Excessive consumption of sweets and dairy contributes to the proliferation of worms. Therefore, during treatment it is necessary to exclude sweets, chocolate, cakes, and milk from the child’s diet. Fermented milk products are useful - kefir, fermented baked milk. It is extremely important to get more fiber in your diet, which has a beneficial effect on intestinal function. It is found in sufficient quantities in foods such as wholemeal bread, fruits, and vegetables. The diet also includes foods containing vitamins A, B, C. These are liver, especially sea fish, egg yolk, cream, butter, fish oil, peas, walnuts. The fruits of sea buckthorn, rose hips, black currants, and red pepper contain large quantities of vitamin C.
Among plant products, garlic, strawberries, apricot kernels, ripe melon juice grown without chemicals, raw carrots and their seeds, watermelon and pumpkin seeds, walnuts, pomegranate juice and St. John's wort tea have good anthelmintic properties. This will help get rid of worms, in addition to the special tablets that the pediatric gastroenterologist will prescribe.
When treating giardiasis, whole milk and foods containing gluten (baked goods and pasta, all cereals except rice, buckwheat and corn) are excluded from the child’s diet. Sour drinks (cranberry, lingonberry fruit drinks, tea with lemon, kefir), boiled meat, fish, vegetable side dishes are recommended.
Preventive actions
So, you need to wash your hands every time after walking, visiting the toilet, and before eating. In addition, the child must have trimmed nails, a neat appearance, and clean underwear. Each person must have their own bed and their own towel. It is also necessary to thoroughly wash vegetables and fruits, and heat process meat and fish.
It is recommended that all family members be periodically examined by a doctor and regularly carry out preventive deworming for pets.
Treatment or drug prophylaxis will be prescribed by a pediatric gastroenterologist. The basis for prescribing any drug to a child of any age should be test results and a conversation with parents.
Services and prices
Primary appointment (examination, consultation) with a gastroenterologist
2,200 rub.
Repeated appointment (examination, consultation) with a gastroenterologist
2,100 rub.
Fecal occult blood test
390 rub.
Stool examinations: Stool analysis for protozoa and helminth eggs
440 rub.
Stool tests: Test for enterobiasis
440 rub.
Giardia Lamblia, cal
410 rub.