Dermatovenerologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
9 years experience
Make an appointment
Pityriasis rosea has many names in medicine. It is called roseola exfoliating, Gibert's disease, pityriasis rosea. The disease belongs to the infectious-allergic category of dermatoses, is of an acute inflammatory nature with the appearance of spotty, papular, erythematous-squamous lesions. They are located mainly on the torso and on the surface of the limbs. Most often, Zhiber's pink lichen is diagnosed in women aged 20 to 40 years, as well as in adolescents. In other age categories of people, the disease is extremely rare. The peak of complaints occurs in spring and autumn during the spread of acute respiratory diseases.
Information about pityriasis rosea: causes, symptoms, manifestation
Medicine does not know the exact reasons for the development of lichen deprivation in men and women. Research is being conducted in the field of the influence of herpes viruses types 6 and 7, but a clear etiological agent has not yet been identified. The causes of pityriasis rosea continue to be studied. We only know that a weakened immune system can become a trigger at any time. The causes of pityriasis rosea lie precisely in a decrease in the body's defenses due to bacterial and infectious diseases.
Symptoms and clinical picture of the disease
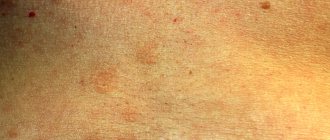
Due to colds, hypothermia, severe emotional states, and stress, a rash may appear on the skin. Symptoms of pityriasis rosea begin to appear from this point. The classic clinical picture is the formation of the main lesion in the form of a medallion with a diameter of 2 to 10 cm. Within 7-14 days after its appearance, the rash spreads in the form of plaques and papules of pink and yellow-brown color. They are smaller than the main lesion - their diameter can be from 0.5 to 2 cm. In appearance, the rashes can be confused with ringworm due to the scaly edge of the rashes. A few days after the rash, the spots turn pale, wrinkle and the stratum corneum cracks. The central part of the plaques remains smooth. Symptoms of pityriasis rosea may be accompanied by itching, fatigue, fever, general intoxication, and enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and chin.
Are you experiencing symptoms of pityriasis rosea?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Types of disease
Pityriasis rosea can have a classic appearance, when the clinical picture develops in stages in accordance with the generally accepted system - from the appearance of a “maternal” plaque to smaller rashes in the chest, back, abdomen, thighs, and on the flexor surfaces of the limbs. In the medical classification, several more forms of the disease are distinguished. Zhiber's lichen occurs:
- urticarial - characterized by the presence not of plaques, but of a rash in the form of blisters. There is severe itching. In appearance it resembles urticaria;
- vesicular - manifested by generalized rashes of vesicles with severe itching. The diameter of bubbles with clear or cloudy liquid is from 2 to 6 mm. They often form “rosettes”;
- papular - rare. It is characterized by the appearance of cavity-free formations above the surface of the skin. Small papules with a diameter of 1-2 mm;
- hemorrhagic – point hemorrhages (bleedings) occur, so the color of the plaques is darker than usual;
- follicular - rashes are grouped into round plaques of follicular papules, which can occur in parallel with classic plaques;
- unilateral;
- hypopigmented - most often occurs in people with dark or dark skin. Lichen inversus is characterized by rashes in the axillary and groin areas and in the popliteal fossae;
- asbestos-like - is extremely rare and appears on the scalp in the form of gray plaques;
- Darier's giant pityriasis rosea - the formation of large diameter plaques from 5-7 cm. In severe cases, they reach the size of the patient's palm;
- ring-shaped ring-shaped pink lichen of Vidal has an atypical location - mainly in the groin or axillary region. The rash appears ring-shaped.
Gender and age characteristics
Women, adolescents and children are susceptible to the occurrence of pityriasis rosea. Different forms of the disease affect specific groups of people. For example, the vesicular form is diagnosed more often in children and adolescents. The papular form is diagnosed in most cases in pregnant women and young children. Unilateral – occurs equally in both adults and children.
How does disease transmission occur?
Research has not given a clear answer to the question of infection. Theoretically, pityriasis rosea is transmitted by tactile contact, but this occurs extremely rarely. There must be provoking factors for infection to occur. We are talking about low immunity, past viral and infectious diseases, and colds. Relapse is possible in people with HIV, oncology and blood diseases.
What does lichen look like in humans?
The external manifestation of the pathology is obvious - lichen is accompanied by a number of signs:
- rash in the form of spots of different colors - red, pink, brownish, yellow;
- itching, burning, unpleasant (painful) sensations;
- scales, bubble formations on spots;
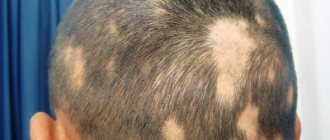
- bald spots on the head in the hairline area (clipping form);
- fever (rare);
- malaise, lethargy.
What you need to know about diagnosis and treatment
Diagnosis of pityriasis rosea is based on taking the patient's medical history. To confirm or refute and analyze complex cases, a number of laboratory tests are prescribed. They include clinical examination of blood and urine. It is necessary to exclude syphilis and mycosis, therefore serological and microscopic studies are additionally carried out. If these methods do not provide enough information to verify the diagnosis, the patient is referred for a biopsy (biopsy histology).
Treatment for pityriasis rosea is not always required. The disease is prone to voluntary self-healing within 5 weeks. However, dermatosis should not be considered harmless. First of all, antipruritic therapy is required. For this purpose, topical glucocorticosteroid drugs and antihistamines are used externally. Ointments, gels, pastes cannot be used without a dermatologist's prescription. Otherwise, the rash may increase the extent of skin damage, covering new areas. Antibiotics and antiviral drugs may be prescribed depending on the indications. Ultraviolet therapy has a good effect.
Ringworm on the skin: treatment
Treatment of the disease is especially effective at an early stage. Ringworm can be cured in all patients, regardless of age. In this case, you need to consult a doctor even with minor manifestations. For diagnostic purposes, a dermatologist conducts a visual or instrumental examination (using a special lamp), prescribes a series of tests - studying urine, blood, as well as immunological studies and skin scrapings.
After establishing the exact cause and type of lichen, treatment is prescribed. Most often it is associated with the use of special ointments externally (antifungal drugs). The course of therapy lasts from 2 weeks to 3-4 months.
Main areas of treatment:
- Etiotropic – the use of drugs that eliminate the cause of the disease. These can be fungicides or antiviral agents (based on Acyclovir).
- Elimination of itching, spots and other unpleasant symptoms.
- Carrying out procedures - UV therapy, physiotherapy, increasing resistance (strengthening the immune system), maintaining personal hygiene.
- In rare cases, it is necessary to disinfect the premises, especially linen, furniture, and personal belongings.
It is not recommended to treat lichen yourself at home. This is dangerous because you can waste time and also infect other people. In addition, the patient often cannot determine which drug to treat the pathology with. For example, a person “prescribes” an antimicrobial ointment while he develops herpetic (viral) lichen. In rare cases, lost time can result in severe consequences such as blindness, arthritis, and other complications.
Help from a dermatologist in Moscow
Diagnosis and treatment of pityriasis rosea is the field of activity of a dermatologist. Depending on the form of the disease and the extent of skin damage, the patient is provided with recommendations. With lichen, the emotional and psychological background of a person is important, so promptly making a correct diagnosis allows you to quickly overcome the disease.
You can make an appointment with a dermatologist at Meditsina JSC (academician Roitberg’s clinic) by phone. You should not self-medicate. The reason is that, according to external signs, skin rashes may turn out to be differential diseases, for example, toxicerma, psoriasis, mycosis, secondary syphilis. In these cases, it is necessary to prescribe another therapy, taking into account the specific clinical picture and medical history of the patient.
Genital lesions in LP
Therapy for genital lesions with LP is fundamentally similar to treatment tactics for lesions of the oral mucosa. The main goal of therapy is to prevent or minimize the formation of scarring, synechiae, vaginal stenosis in women and phimosis in men. TGCS are used as the first line of therapy, while standard antipruritic drugs are used to relieve itching. Initially, an intensive regimen is used, usually clobetasol 2 times a day for 1-2 months to limit the inflammatory process, followed by a transition to a maintenance regimen - using the drug 2-3 times a week. The above treatment tactics are appropriate in the treatment of lichen sclerosus, and their effectiveness has been confirmed in a number of clinical case reports. To relieve friction and pain, it is possible to use intravaginal applications of emollients. If the anal area is affected, topical corticosteroids in the form of foam or suppositories can be used. In case of disease refractory to therapy, as well as severe damage to the genitals, systemic oral corticosteroids can be used in a course with a gradually decreasing dosage and transition to topical maintenance therapy. Topical retinoids have a pronounced irritant effect and are usually poorly tolerated in the erosive form of the disease. There are a number of retrospective studies and case reports with successful use of topical calcineurin inhibitors. Despite a burning sensation when applied to erosive lesions, topical calcineurin inhibitors are better tolerated than topical retinoids and are widely used in the treatment of LP affecting the genitals.
Follicular form of LP
The goal of therapy for the follicular form of LP (lichen planopilaris) and its variants is to stop the inflammatory process as early as possible to minimize the death of epithelial stem cells of the hair follicle through inflammation-induced apoptosis, as well as control of concomitant symptoms of the disease until the spontaneous occurrence of clinical remission. Strong and very strong topical corticosteroids are used as the first line of therapy in clinical practice. Intralesional administration of corticosteroids is practiced by many specialists, despite the lack of sufficient data in favor of this technique, as well as the risk of developing scalp atrophy with prolonged use of drugs. Many doctors prefer twice daily use of strong and very strong topical corticosteroids for 6-8 weeks, with a gradual transition to use 3 times a week or as required. With an aggressive, rapidly progressive course of the disease, systemic corticosteroids (30-80 mg/day in terms of prednisolone) are often prescribed, and in some cases, systemic cyclosporine (3-10 mg/kg/day), although there is insufficient data on the effectiveness of drugs in these groups. In the presence of pronounced inflammatory changes, in addition to topical therapy, a course of prednisolone with a gradual dose reduction (starting from 40 mg/day) may be prescribed, and hydroxychloroquine may be prescribed simultaneously. It is believed that the latter helps to reduce the immune response to self-antigens and also modulates T-cell-mediated gene expression. Its immunomodulatory effects as well as its good safety profile may be useful in the treatment of follicular LP, making hydroxychloroquine a preferred treatment option for lichen planopilaris. In case of intolerance to hydroxychloroquine or if there are contraindications to its use, tetracycline antibiotics, which are second-line drugs, can be used. Also, second-line drugs include mycophenolate mofetil and cyclosporine.
Nail damage
Despite significant functional and cosmetic impairments associated with nail lesions in LP, evidence-based data are currently insufficient. The goal of therapy is to prevent or minimize permanent scarring (as with the follicular form of LP), and it is also important to stop the inflammatory process at the earliest possible stage to achieve optimal results. Topical and systemic corticosteroids are used as the first line of therapy, as well as their intralesional administration; systemic use of drugs is indicated when several nail plates are affected. According to the literature, the use of alitretinoin appears to be effective. For many dermatologists, including the authors of the article, the use of systemic corticosteroids (in the form of pulse therapy or a short course with a gradual dose reduction) is preferable to intralesional administration of corticosteroids, due to the convenience and effectiveness of this technique. Also, there is evidence of an increase in the effectiveness of topical therapy with strong and very strong topical corticosteroids when applied under occlusion.
Most frequently asked questions from patients
What causes pityriasis rosea?
There is no clear answer to this question. Research continues. Presumably, the cause may be herpes virus type 6 or 7. When immunity decreases, it becomes more active, which triggers the process of various types of rashes (plaques, vesicles, blisters). The disease can be triggered by stress, poor ecology, hormonal fluctuations, and chronic diseases.
Is pityriasis rosea contagious?
Pityriasis rosea in humans is considered non-contagious, but rare cases of the disease affecting entire families are known. Much depends on the state of the immune system and the body’s defenses, which can resist viruses, bacteria and infections.
Is it possible to sunbathe with pityriasis rosea?
One type of therapy for this dermatological disease is light therapy. Moderate exposure to ultraviolet radiation has a positive effect on the condition of the skin, stimulating its regeneration. Combustion must not be allowed. This will lead to increased itching in the area of the spots.
Symptoms of lichen
What symptoms indicate that you have contracted lichen planus? It should be noted that lichen affects not only the skin of the body, but also mucous membranes, nails and even human hair. As a rule, any type of this disease begins with the appearance of the following symptoms:
- minimal increase in body temperature;
- the appearance of chills, mild headache, and sometimes nausea;
- later the temperature rises, and itching appears in certain places (face and body, less often - limbs);
- after a few hours, bubbles will appear at the site of redness, which soon burst and only a crust remains.
Routes of infection
The causative agent of microsporia enters the body when a healthy person comes into contact with a carrier of the disease. An alternative way is to interact with objects covered with fungal spores. Ringworm is most often detected in children aged 5-10 years; in boys, microsporia is diagnosed five times more often than in girls. The pathology almost does not affect adults due to the presence of organic acids in their hair structure, which suppress the growth of fungal mycelium.
The reasons for the development of ringworm are microtraumas of the skin and its dryness. Spores get into cracks, scratches or open calluses. Healthy skin becomes an insurmountable barrier to fungus. The pathogen does not survive contact with personal hygiene products - thorough hand washing after contact with spore carriers eliminates the possibility of infection.
The risk group includes people who regularly come into contact with the ground and wild animals. The active growth of the fungus is facilitated by disturbances in the functioning of the sebaceous glands due to changes in the chemical composition of their secretions. Microsporum spores can remain viable for three months when left in open ground.
Rating of remedies for lichen
Taking into account the cause of occurrence, 7 types of pathology are distinguished. The most dangerous are considered viral infections, which are characterized by rapid spread and long-term treatment. Therapy is aimed at alleviating symptoms, increasing immunity, and eliminating the irritant. The rating of the best treatments for lichen in an adult or child is based on the results of comparative tests of the following characteristics of the drugs:
- Pharmacological group;
- Release form;
- Indications;
- Presence and type of side effects;
- Packaging volume;
- Availability;
- Active substance;
- Number of contraindications;
- Impact on human psychomotor reactions;
- Terms of Use;
- Interaction with drugs from other pharmaceutical groups;
- Best before date.
The price/package volume ratio was taken into account. This indicator often determines the need for additional purchase of funds for a course of treatment. All top drugs are divided into 3 categories based on the release form. Each section provides a description, pros and cons of the medication according to reviews from doctors and patients.
The best antiviral agents
Causes of pityriasis
Despite the fact that Gibert's disease is very common, the mechanism of the disease is not fully understood. The following factors are believed to play an initial role:
- Exposure to viruses (type 7 herpesvirus, etc.), bacteria and other infectious agents. This is confirmed by tests that prove the presence of pathogens in the body. Very often, skin disease appears against the background of influenza, acute respiratory infections and other infections.
- Attachment of allergic reactions.
- Bites from bedbugs, lice and other blood-sucking insects.
- Reduced immune defense.
- Frequent hypothermia and stress.
- Violation of gastrointestinal functions and metabolism.
- Introduction of vaccines.