Pain in the ovaries - for an explanation of the causes and treatment of this symptom, women often turn to the gynecologists of our Leib Medic medical center, which is conveniently accessible for treatment from many districts of Moscow. Treatment of pain in the ovaries is one of the specialized areas of our medical center, where experienced responsible doctors of various specialties work, including gynecologists. The cause of pain in the ovaries can be the following diseases, pathologies and conditions that require professional treatment or observation:
- ovarian apoplexy
- polycystic ovary syndrome
- ovarian cyst
- the presence of microbial lesions of the ovaries
- ovarian cancer
- natural causes of ovarian pain
- pain in the ovaries during abortion
- pain in the ovaries when taking birth control pills
- pain in the ovaries during artificial insemination
The female reproductive organ system is represented by the uterus and ovaries. The ability to produce offspring and the health of the unborn child depend on the condition of the ovaries. However, more than 70% of women, especially in cities, suffer from various problems of the reproductive system, including the ovaries. Much of the reason for this is the lifestyle that modern ladies adhere to and especially their clothing. After all, even in severe frosts, women prefer to wear miniskirts instead of warm clothes.
Why do my ovaries hurt, left or right?
Typically, pain in the ovarian area is cramping and stabbing in nature. However, based on these signs, it is impossible to accurately determine that it is the ovaries that are hurting. After all, inflammation of appendicitis, kidney disease and digestive system have the same expression. Therefore, you should not diagnose yourself; you can see a gynecologist at our medical center in Moscow.
In some cases, the pain may be periodic. In this case, the pain manifests itself either in the lower abdomen, then in the kidney area or in the pubic area. At times you may experience leg cramps. Pain in the left ovary is rare and mainly indicates a harmful external influence. If there is pain in the left ovary, most likely it is due to the medications you are taking.
Pain in this area indicates problems with the reproductive system or hormonal phenomena. Both types of illness can lead to complications, so you should not delay the examination. Only an experienced doctor will be able to accurately determine the disease and say exactly why the ovaries hurt.
What kind of prevention should be carried out?
In order for a woman not to suffer the sad fate associated with this pathology, it is necessary to take care of her health. Even if you feel excellent, go to the gynecologist for an examination every six months. If there are gynecological problems, be observed regularly. Patients with adnexitis, oophoritis, polyendocrine syndrome or STDs must definitely treat their disease.
Women who have suffered from ovarian apoplexy should take care to ensure that there is no relapse. One of the preventive measures is complex treatment to normalize the menstrual cycle and improve blood supply.
Patients who have undergone surgery are required to monitor the restoration of hormonal levels and the normalization of blood circulation. They are advised to take nootropics and tranquilizers. Under no circumstances should you refuse such drugs. The use of multiphase oral contraceptives will ensure normalization of hormonal levels and help prevent ovulation. It is better not to plan pregnancy during this period. It is necessary to wait for the body to fully recover and become stronger. Then you can confidently hope for a successful pregnancy and birth of a healthy baby.
Observation by a doctor is considered mandatory.
Treatment of ovarian apoplexy at Life Medic
Ovarian apoplexy is one of the most serious problems. In this case, hemorrhage occurs in the ovary, which poses a threat to the normal functioning of this organ. To understand how this happens, it is necessary to consider the menstrual process in a woman’s body:
1. When an egg matures in a follicle, it must receive sperm.
2. This does not happen and due to the death of the egg, menstruation occurs.
3. The blood of the dead egg filling the follicles is removed from the body.
So at this time, these organs are especially tense, as they are filled with blood, and the risk of damage to blood vessels also increases. When the walls of the ovary cannot withstand it, the blood entering it from the artery spills inside.
Causes of ovarian apoplexy
In general, the right pair is more often susceptible to apoplexy, since it is larger and more blood circulates in it than in the left. Therefore, the right ovary hurts more often. Blood enters the right organ directly from the aorta, and the left one through the blood vessels of the kidney. This also causes increased pressure and tension in the right organ. So, if for some reason the right ovary hurts, then the reason is most likely apoplexy.
Ovarian apoplexy most often occurs in teenage girls and young women. In many ways, it is this group that is at risk, since the reproductive organs most actively perform their function in them. In very rare cases, apoplexy can result from mechanical damage. Other causes of apoplexy
In addition to natural processes, hemorrhage can be caused by:
- overly active sex
- improperly performed gynecological procedure
- excessive stress on muscles
These are all mechanical factors. However, there are also pathogenic factors:
- pathology of the uterus;
- tumors;
- varicose veins;
- improper healing after surgery or injury;
- ovarian inflammation
So pain is a symptom not only of disorders in these organs themselves.
Symptoms of ovarian apoplexy
The main sign of apoplexy in a woman’s body is acute pain in the ovary or lower abdomen, which aches. And usually the right ovary hurts. However, the disease may be accompanied by other signs:
- vomit;
- dry mouth;
- tachycardia;
- stickiness of sweat;
- hypotension;
- pale skin color;
- temperature increase.
Usually, additional symptoms indicate that the accumulation of blood has reached its critical level and an attack of pain may soon occur. When the right or left ovary is pulled, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor, otherwise complications are possible.
Complications
In men, chlamydia causes inflammation of the epididymis (epididymitis), and in women it causes cervical disease, inflammation of the epididymis, and tubal infertility. During pregnancy, chlamydia can cause serious pathology of the fetus. It also leads to Reiter's disease (severe damage to the eyes and joints).
Monitoring the results of treatment for chlamydia, as well as other hidden STIs, should be carried out no earlier than 3 weeks after stopping medication. Symptoms may persist for several weeks or even months after successful treatment. As for resuming sexual activity, this is possible only after a follow-up examination of two partners.
Ureaplasmosis
Ureaplasmas are very small microorganisms that do not have and do not need their own cell membrane. This feature allows them to penetrate the cells of the host body, so very often they are not visible to the protective cells of the immune system. Consequently, ureaplasma can exist in the human body for more than 10 years. Note that ureaplasmosis is more common among women than among men.
Ureaplasmas received this name because of their ability to break down urea - ureolysis. That is why ureaplasmosis is a urinary infection; without urea, ureaplasma cannot survive. Very often, ureaplasmosis is associated with diseases of the urinary system, chronic cystitis, urethritis and pyelonephritis.
Ureaplasma is usually transmitted sexually, but it is also possible for a child to become infected during childbirth. The incubation period is approximately 1 month. The further development of the disease depends on the body’s immunity, the presence or absence of other vaginal diseases, etc.
In most cases there are no symptoms. Sometimes patients may complain of more abundant discharge than usual, a burning sensation when urinating, discomfort in the genital area and intermittent nagging pain in the lower back and lower abdomen.
Ureaplasma and pregnancy
Ureaplasma can lead to a destructive process in the appendages and uterus, thereby contributing to the development of complications that can lead to pathologies during pregnancy. That is why during this period it is imperative to get tested for this infection, and if it is confirmed, then undergo treatment.
Ureaplasma does not cause malformations in the fetus. In most cases, infection of the baby occurs during childbirth during the passage of the fetus through the infected birth canal. In addition, ureaplasmosis can cause miscarriage, premature birth, threatened miscarriage and endometritis (one of the postpartum complications).
Treatment during pregnancy is most often carried out at 18-20 weeks.
Treatment of ureaplasmosis
Treatment of this disease must be comprehensive and long-term. First of all, antibacterial drugs are prescribed, but taking antibiotics alone is not enough, since ureaplasma can easily adapt to the effects of antibiotics during treatment. Also used in treatment are drugs that increase general and local immunity; antifungal drugs, since antibiotics can cause thrush. The drug complex also includes drugs that can protect the intestines from the effects of antibiotics.
As for the need to treat a partner if he does not have an infection, this is a controversial opinion. This issue must be resolved by the attending physician and the partners themselves.
During pregnancy, the choice of drugs is limited. Only those drugs that are approved during this period can be used. Antibiotics include Vilprafen, Rovamycin, and Erythromycin.
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome at Leib Medic
Polycystic ovary syndrome is one of the main diseases leading to infertility. Cystosis develops very slowly and it is rarely possible to detect it in the initial stages. It is usually diagnosed accidentally, during the next examination. Tingling in the left or right ovary can be a symptom of a similar disease. However, polycystic disease can be expressed by tingling in the right ovary. The disease occurs due to improper formation of the egg. Sometimes due to pathologies of the ovary itself. In both cases, it is difficult for the egg to leave the organ and over time the channels begin to accumulate tissue of residual eggs and polycystic disease develops. Also, a large number of underdeveloped eggs accumulate in the organ itself. Polycystic ovary syndrome mainly occurs in women under 35 years of age. It is especially dangerous for teenagers who are just beginning to menstruate. The presence of cystosis, in addition to periodic pain, causes disruption of the menstrual cycle. So polycystic disease has a direct effect on hormonal functions. This can disrupt hormonal processes, which usually leads to cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, etc.
Causes of polycystic ovary syndrome
The exact reasons for the occurrence of polycystic ovary syndrome have not yet been identified. All patients had the following pathologies, which presumably lead to the development of this disease:
- endocrine system imbalance;
- insulin oversaturation;
- chronic inflammation;
- obesity;
- heredity.
Any of these pathologies can lead to the formation of ovarian cysts.
Symptoms of polycystic ovary syndrome
Doctors identify the following symptoms of cystic disease:
- abnormal menstruation;
- hypertrachia (excessive hairiness);
- skin problems;
- pulling sensation in the ovary area;
- excessive weight.
All these signs are associated with pain that occurs in the lower abdomen.
Symptoms of ovarian inflammation
Symptoms of this disease include:
- aching, nagging pain in the lower abdomen that occurs when the body is overcooled, as well as during menstruation;
- pain during sex.
Later, when the disease develops, the above symptoms are also added such as:
- chills;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- a sharp increase in body temperature to 38-39 ° C;
- intense pain radiating to the lower back;
- copious vaginal discharge that appears clear.
In particularly severe cases, nausea and vomiting may also occur. Chronic inflammation of the appendages contributes to increased pain sensations, as well as their range. Therefore, symptoms of adnexitis (inflammation of the ovaries) may include pain in the lower abdomen, groin, sacrum and vagina.
Chronic inflammation can be accompanied by sexual dysfunction, menstrual disorders, miscarriages and the development of ectopic pregnancy.
Microbes in the ovaries
Of course, the presence and large accumulation of harmful microorganisms in the organs of the reproductive system leads to inflammatory processes and gives rise to pain in the ovary. When the number of such microbes reaches a critical level, thrush and candidiasis develop.
At the same time, thrush indicates a decrease in immunity in a woman’s body, when candidiasis, like a fungal disease, develops as a result of:
- excess sugar in a woman’s body;
- hormonal surges;
- any infectious disease;
- excess antibiotics;
- poor hygiene of the intimate area.
For both thrush and candidiasis, the symptoms are almost identical and are expressed:
- in the presence of unpleasant odors;
- presence of itching;
- pain when urinating;
- inflammation of the genital organs;
- pulls the ovary;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
This disease can be cured with the help of anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents.
Pathogenesis
As an independent disease, oophoritis is extremely rare; it often develops as a secondary form caused by previous infection and the development of inflammatory processes in neighboring structures. The rarity of isolated inflammation of the ovaries is explained by the fact that the ovaries themselves are reliably protected by a dense protein membrane. Since the pelvic organs are compactly located and are a functional whole, there is a high probability of penetration (spread) of infection. It enters through the bloodstream, lymph from anatomically distant organs, from the infected intestines, lungs, genitourinary system, abdominal cavity, but more often there is an ascending route of infection - from the vagina, through the cervix, fallopian tubes.
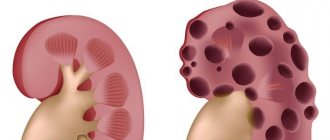
Ovarian cyst - treatment in Moscow, Life Medic clinic
Ovarian cyst is a common disease that occurs in women, and specialists from the Moscow medical center Life Medic assist patients in treating ovarian cysts using specialized techniques. Unlike polycystic disease, when tissue of underdeveloped eggs accumulates in this organ, when a cyst forms under the ovary, usually the right one, the cortical ovary swells pouch. This happens due to the accumulation of yellow cell fluid in it, which is actively released during the post-ovulation period. However, yellow cells are not always to blame. So:
- a cyst may be an accumulation of dead ovarian tissue, leading to the development of cancer;
- a thick-walled cyst usually results from epidermal deposition;
- a capillary cyst is usually a manifestation of natural organic processes;
- a multi-chamber cyst is a consequence of the accumulation of various tissues, including fluids, which also leads to cancer.
The exact reasons for the formation of cysts in women have not yet been established. Many experts argue that the main causes may be hormonal pathologies. In addition, there have been cases where the formation of a cyst was accompanied by chronic inflammatory processes. Usually, it is not possible to detect the presence of a cyst by observing external manifestations, because the formation of a cyst does not have any symptoms. Most cases are detected during a routine examination by a gynecologist. With excessive physical exertion or very intense sexual intercourse, pain may be felt in the right ovary.
Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is detected in older women up to 70 years of age. In more than thirty percent of cases it leads to death. Basically, such malignant formations in the reproductive system are divided into the following groups:
- initial, when a cancerous tumor arose in the ovary itself for no apparent reason;
- secondary, when cancer causes the death of benign cells;
- Metastatic cancer appears due to cancer cells entering the ovaries from another organ through the blood.
The causes of cancer cells in the body are still unknown. Doctors attribute most cases to age and heredity. In addition, hormonal processes are of no small importance.
The signs of a malignant tumor are quite obvious. So in cancer there are:
- a feeling of discomfort reminiscent of a digestive tract disorder;
- persistent feeling of fatigue;
- constant feeling of the presence of a foreign object in the abdomen.
The growth of the tumor causes pain in the left ovary or in the right and difficulty urinating. In addition to a decrease in the amount of menstrual flow, the woman is attacked by apathy and depression does not leave her.
Natural causes of ovarian pain
It is not necessary that a certain pathology be present in the body if there is pain in the lower abdomen. During the week before menstruation, a feeling of discomfort in most women is considered normal. At the same time, the ovary hurts before menstruation. This is a manifestation of natural physiological processes. In addition, the ovary hurts during menstruation for the same reasons.
Another category of natural causes of pain in the lower abdomen is associated with the natural expansion of the uterus and the accumulation of yellow cells due to a woman’s pregnancy. Typically, abdominal pain is felt in the first trimester. But they are not frequent or regular, but appear in isolated cases. However, during pregnancy, the fact that the ovary hurts on the right or left may be the result of some other reasons that will lead to complications and harm the woman’s body and the fetus. These include:
- inflammatory processes;
- infectious diseases;
The most dangerous form of inflammatory processes is inflammation of the ovaries themselves. This disrupts the formation of yellow bodies, which leads to underdevelopment of the fetus at the initial stage of pregnancy. In this case, the left or right ovary colitises, since the inflammation primarily affects it.
Diagnosis
Recognizing oophoritis is a complex process, because Its manifestations are similar to many diseases. To establish the transition of inflammation to the ovaries, the gynecologist:
- Interviews the patient - interested in past illnesses, birth history, presence of abortions, symptoms, duration of course.
- Conducts an examination - palpation, manipulation with a mirror.
- Refers for laboratory testing - analysis of vaginal secretions, blood, urine, urethral smear, bacterial culture.
- Uses instrumental methods - hysterosalpingography, ultrasound OMT, fallopian tubes (USGSS).
- He resorts to additional methods - tuberculin diagnostics, PCR analysis, ELISA, laparoscopy.
Abortion as a cause of pain in the ovaries
An incorrectly performed abortion procedure can cause pain in the ovaries due to infections or damage to the ovaries when the fetus is removed. Both ovaries can hurt at the same time. This is one of the few reasons why the left ovary hurts, since in most cases the pain radiates to the right. Typically, such symptoms appear exclusively in the first week after the procedure. In addition, the abortion procedure can lead to disruption of menstrual processes and the functioning of endocrine organs. But most of all, the organs of the woman’s reproductive system suffer from this procedure, mechanically or otherwise. Therefore, after an abortion, the risk of infertility is very high.
Treatment
Severe forms are treated in a hospital. Therapy is conservative, long-term. The course is selected individually. The range of measures taken usually includes:
- drug therapy - antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunomodulators, vitamins, eubiotics;
- hot douching, ichthyol suppositories, Longidaza;
- physiotherapy – mud, diathermy, ultraviolet irradiation, inductothermy, massage.
Indications for surgery include pain, purulent inflammation, adhesions, and peritonitis.
Pain in the ovaries when taking birth control pills
More than half of the world's women prefer to avoid unwanted pregnancy by using oral contraceptives. However, most of them have no idea what exactly the effect of such pills on the body entails. Thus, most of these drugs accelerate or inhibit hormonal processes. This is mainly a consequence of the need to increase the production of estrogen, which activates the menstrual process and prevents pregnancy. If, along with the right one, the left ovary hurts, then the reasons are precisely this effect on the uterus. Typically, ovarian colitis occurs in 90% of such patients in the first three months after starting medication. This is normal if, along with the right one, the left ovary colitises. However, if the pain does not go away longer than this, then perhaps due to a hormonal imbalance, a cyst or something else has formed in the ovary.
Causes
Depending on the etiology of inflammation of the ovaries, they are divided into 2 groups:
- Specific processes - occur against the background of tuberculosis, mycoplasmosis, venereal disease (most often it is gonorrhea, genital herpes, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, and their combinations are also found).
- Nonspecific inflammation - caused by the penetration of opportunistic organisms, septic diseases, appendicitis. The main culprits: Escherichia coli, staphylo-, strepto- or pneumococci, enterococci, microorganisms of the genus Candida, clostridia, etc.
Predisposing factors for the development of oophoritis include childbirth, abortion, increased sexual activity, intrauterine contraception, and other interventions on the uterus.
The list of factors that provoke exacerbation of existing inflammation includes:
- general hypothermia of the body, swimming in cold water;
- inadequate or insufficient nutrition;
- prolonged stress;
- severe fatigue;
- weakening of the immune system.
What to do if your ovaries hurt?
So, what to do if your ovaries hurt. When pain occurs in the pelvic area, rest is necessary. It is necessary to limit yourself from stress, both physical and emotional. It is also worth reconsidering your diet; you may need to go on a diet. In your diet, you should limit yourself from salty and excessively fatty foods. It is recommended to consume more dairy products, fresh fruits and vegetables.
Folk remedies for such a symptom are absolutely not advisable. But after consulting a doctor, you can take mud baths and salt baths. Medicinal decoctions should also be taken in consultation with your gynecologist. An experienced doctor will also tell you what to do if your ovaries hurt.
If acute pain occurs, you must call an ambulance. You should not try to figure out the reasons on your own, even if this has been observed and successfully eliminated before.
The role of the ovaries in the female body
In size, they are no larger than a peach pit. When there are no pathologies in the body, the left one is always somewhat smaller in size compared to the right one. This organ is a composite organ and is represented by a cortex and connective tissue. Disruption of these components causes general malaise and problems with the functioning of other organs of the female body.
Reproductive function of the ovaries
This paired organ plays a major role in the process of reproduction. After all, they are the ones who produce eggs, which, after fertilization by male sperm, give rise to the birth of a new embryo. They are located on both sides of the uterus, in the pelvic region. Immediately after fertilization, the ovulation process stops and the ovaries begin to produce a temporary protective layer for the future fetus - yellow bodies. However, this layer disappears after the formation of the uterine placenta. Usually replacement occurs after the first 20 weeks of pregnancy.