Over the course of a lifetime, the average person's skin renews itself at least 950 times. In humans, the dermis is renewed once every 25-30 days, in infants - every 72 hours.
Medicines based on zinc oxide remain one of the most popular over the past decades, despite the presence of a large number of effective analogues. They are available in pharmacies in 2 forms, and not all patients know which is better – zinc ointment or paste. Today’s article will be devoted to this pressing issue.
Zinc paste and ointment: what is the difference between these products
Pharmacies offer customers both zinc paste and ointment. Not everyone knows how zinc ointment differs from zinc paste, but there are differences between these pharmaceutical products. The main difference is the concentration of the active element (the paste contains about 25% zinc oxide, while the ointment contains no more than 10%). These dosage forms differ in their auxiliary ingredients - for the first form - starch (thickener and adsorbent), and for the second - exclusively petroleum jelly.
Paste is a thick consistency based on powdery substances (up to 50-65%).
Features of the mechanisms of action of 2 dosage forms:
- The level of permeability of the pasty mass into the epithelial layer and the main blood flow is insignificant. The risk of developing associated complications or unwanted side reactions in the patient’s body is minimal.
- Powdery components are characterized by a pronounced adsorbing effect. They actively absorb toxic compounds formed on the surface of the skin during serious damage.
- Zinc paste is prescribed for the treatment of acute inflammatory processes accompanied by high vascular permeability.
- The ointment composition quickly penetrates into the deep layers of the dermis, which is important in the treatment of chronic, indolent diseases.
- The ointment does not dry out the skin, which is often observed when exposed to paste.
Depending on the nature and characteristics of the pathological process, dermatologists prescribe zinc oxide in the form of a paste or ointment.
Why do you need salicylic zinc paste?
Some patients, in addition to skin rashes on the face, have acne, blackheads or enlarged pores. In such cases, acne is treated with salicylic-zinc paste. This is the best and completely safe pharmaceutical product, which, according to a number of criteria, is more effective than zinc ointment.
Beneficial properties of salicylic-zinc paste:
- The presence of salicylic acid in the composition of the drug helps to narrow enlarged pores, resolve post-acne and dissolve blackheads.
- The active compounds of the drug normalize the intensity of sweating and dry the skin, which is extremely important for hyperhidrosis.
External local application of the pharmaceutical product neutralizes foci of skin inflammation, stimulates tissue regeneration and disinfects problem areas of the skin.
In 99% of patients, therapy with this drug is not accompanied by any side effects. As an exception, a slight tingling sensation in the affected area and allergic itching are recorded. The drug is contraindicated during pregnancy, lactation, purulent lesions of the skin, as well as hypersensitivity of the body to the components of the composition.
What does salicylic ointment help with?
For the treatment of dermatological ailments (elimination of redness, drying of the skin), salicylic ointment is often prescribed. Its main difference from the zinc paste under consideration is its active ingredients. In the salicylic composition, the main role is delegated to salicylic acid.
The drug has a high concentration of aspirin, so problem areas are treated pointwise, in places where inflammation is localized.
Main indications for use:
- eczema;
- diaper rash in newborns and infants;
- oily seborrhea;
- calluses;
- acne;
- psoriasis;
- pustular dermatitis.
Liniment is widely used in cosmetology. The pharmaceutical product has a pronounced active effect. It is used as an additional component in the preparation of cleansing, rejuvenating masks for the face and body.
Description of drugs
Zinc cream (ointment) is a representative of a large group of universal pharmaceutical preparations intended for external local treatment of affected areas of the epidermis. The medication has pronounced anti-inflammatory, wound-healing and antiviral properties, which is largely due to the activity of zinc oxide, the main active component in the composition.
Zinc ointment is effective against many dermatological diseases
The difference between the paste is the thicker consistency of the pharmaceutical product. The medicine is distributed in darkened glass jars, and the dosage form has a high degree of viscosity. It is used mainly for the treatment of ulcerative formations and weeping eczema.
Pharmacological action and group
Zinc ointment belongs to dermatoprotective drugs with pronounced drying and astringent properties. Ointment and paste are used only locally, externally. The medicinal effect of the drug is due to the activity of the main element of the composition - zinc oxide.
Pharmacological action of the drug:
- After treating the surface of the skin or mucous membrane, a chemical reaction occurs that denatures proteins with the formation of albuminates. These products are quickly removed from problem tissues, thereby activating regeneration processes.
- The pharmaceutical agent stops foci of inflammatory processes and suppresses excessive exudation.
- Zinc ointment is characterized by a whitening and antiseptic effect, thanks to which it is actively used for the treatment of pigmented tumors, scars and scars.
Zinc oxide is one of the most powerful adsorbents. The peculiarity of the chemical compound in question lies in its ability to absorb potentially dangerous toxins, waste, pathogenic microorganisms and related products.
Composition and release form
Having carefully studied the composition and release form of the drug, it is easy to determine what the difference is between ointment and paste.
Composition of paste and ointment:
- zinc oxide – 25%, (10% for ointment);
- potato starch – 25%;
- Vaseline – 50%.
The indicated ratio is not indicated on the packaging. Moreover, the standardized concentration of powders in the composition under consideration is up to 50%. The basis of the drug is medical Vaseline.
Zinc paste, like ointment, is supplied in darkened glass jars, as well as aluminum tubes, with a volume of 50, 40, 30 and 25 g. The dosage form has a light yellow or white tint and a thick consistency. The primary packaging is a cardboard box, which is accompanied by an annotation with instructions.
Indications and contraindications
Treatment of dermatological diseases begins only after consultation with a specialist. A dermatologist determines the etiology of tissue damage and prescribes the appropriate drug. He also develops the most appropriate treatment strategy, based on the characteristics of the pathological process and the patient’s condition.
Zinc ointment (paste) is indicated for the following ailments:
- Pimples, acne, burns, herpes on the lips, dermatitis. The active substance stops inflammation, inhibits the activity of pathogenic microflora, dries problem areas and activates regeneration.
- Dry skin. In combination with other components, it helps to soften the keratinized layer of the dermis, making the skin firm and elastic.
- Pore blockage. The components of the ointment absorb dust, dirt, subcutaneous fat, and prevent the listed substances from clogging pores.
- Shallow cuts and wounds. After application, the paste forms a protective “barrier” that eliminates the possibility of the spread of pathogenic infections in tissues.
- Post-acne, shallow scars and ulcers. The composition activates regeneration at the cellular level, due to which scars quickly resolve and ulcers heal.
The fundamental difference between zinc paste and ointment is that it is prescribed for acute pathological processes (or when the main task is to “dry the problem area”). Liniment has a mild effect, and therefore its use is indicated for chronic ailments.
Since the medications in question do not have a systemic effect on the body, and the composition is monocomponent, they have practically no contraindications. The only exception is individual intolerance to zinc oxide.
Directions for use and doses
Zinc ointment (like salicylic ointment) is used to treat dermatological ailments of non-fungal etiology. The medicine is applied in a thin layer to the affected area of the skin and then evenly distributed over the entire area. Before the procedure, it is important to treat the wound with an antiseptic and also dry it slightly by blotting with a cotton swab. The paste is not applied to open wounds without signs of epithelialization.
Zinc ointment is applied pointwise, externally
Average recommended dosages (the values given are standard, unless prescribed by a dermatologist):
- In cosmetology for the treatment of acne: spot-on up to 6 times a day. The dosage ranges from 0.5 g to 4 g.
- Acne therapy - problem areas on the face are treated with ointment before bedtime, 1 time per day. Average dosage – 1.5 g.
- Treatment of weeping dermatitis and diaper rash - zinc paste is applied 2 to 4 times. Over the next 15 minutes, the treated area is left open. The duration of therapy is determined by the dynamics of the disease process.
- Elimination of herpes (in combination with herpevir) - the paste is applied to the localization of herpes every hour, from the 2nd day - at intervals of 1 time in 4 hours.
Self-medication can be dangerous to the patient’s health, and therefore it is important to consult a doctor before starting treatment. The doctor will help you choose an effective remedy, decide what needs to be treated and how. In some cases, visiting a specialist in advance completely eliminates the likelihood of the disease occurring. The disease begins with the appearance of accompanying symptoms, which only a doctor can “recognize.”
Side effects and special instructions
The medication in question does not cause side effects, since it does not have a systemic effect on the body. Adverse reactions are observed in rare cases, mainly in patients with hypersensitivity to the components of the drug. We are talking about the following allergic manifestations:
- burning;
- itching;
- rash.
At the first signs of adverse reactions, you must stop using zinc paste or ointment and consult a dermatologist to adjust the treatment regimen.
Special instructions:
- Before applying the composition, the skin is thoroughly treated with an antiseptic. The product is used in dosages and multiplicities prescribed in the instructions.
- The medication is not applied to open wounds. Treatment is allowed by applying a cotton swab soaked in the paste.
- The duration of therapy depends on the characteristics of the pathological process.
- The ointment should not be used continuously, especially for patients with dry skin.
Zinc paste can be combined with other dosage forms, but only as prescribed by a doctor and under his supervision.
Topical therapy for skin diseases
N
It is impossible to imagine the treatment of dermatoses without the use of external agents. In some cases, they become of paramount importance, which is why it is so important to navigate the sea of medications that are constantly arriving on the market.
General principles for the use of external agents
Before carrying out external treatment, it is necessary to take into account the stage of the disease, the age of the patient (children, as a rule, are prescribed less irritating drugs in lower concentrations), and tolerability of the drug.
The effect of external treatment is more pronounced if the therapy is carried out comprehensively.
Powders
have a cooling effect on the skin, resulting in calming of burning and itching. During macerations from exposure to sweat, urine, and skin hyperemia, they also have a good effect. Powders are based on plant or mineral powders.
Aqueous solutions of medicinal substances are most often used in the form of lotions, wet-dry dressings and warm compresses
.
A piece of gauze folded in 4-5 layers and soaked in a cooled solution is applied to the affected area of skin. As it warms up, every 15-20 minutes, it is moistened again. This procedure lasts 1-1.5 hours, after which you should take a break for 1-2 hours. Due to the evaporation of water, the lotions
sharply cool the skin and cause a narrowing of blood vessels. This allows the use of lotions for acute inflammatory skin lesions, severely hyperemic, with swelling and weeping.
| Lotions reduce burning, itching and maceration phenomena |
A wet-drying dressing
is applied as follows: gauze folded in 4-5 layers, soaked in an appropriate solution, is applied to the affected area of the skin, covered with a thin layer of absorbent cotton wool and bandaged. The dressing is changed as it dries (usually after 3-4 hours), the slowly evaporating liquid cools the skin, like a lotion, only less actively, helps to subside the symptoms of acute inflammation, which is indicated in the treatment of subacute inflammatory processes accompanied by weeping. Depending on the medications included in the lotion, it has an astringent, disinfectant, drying effect, and in general an anti-inflammatory effect.
Warming compresses
act on the skin with moist heat and are used mainly in the treatment of chronic inflammatory processes. By causing active hyperemia, they increase metabolic processes in the affected area of the skin and help resolve the inflammatory infiltrate.
In addition, various antipruritic, antimicrobial and fungicidal solutions, which can be aqueous or alcoholic, are used externally. Alcohol solutions include solutions of boric and salicylic acids, resorcinol, lapis, iodine, aniline dyes, etc. Ethyl alcohol can cause skin irritation and have an astringent effect, which leads to drying, so its most desirable concentration is 70%.
Shaked suspensions, or “chatterers”
, are used for inflammatory and acute inflammatory (non-wetting) skin diseases (eczema, dermatitis, itchy dermatoses, etc.). Before use, they should be shaken to evenly mix all the ingredients - fine powdery substances that are suspended in water with oil or glycerin. The liquid part of the mash evaporates soon after lubricating the skin with it, and the powdery substances are deposited in a thin layer and are retained on it for a long time. In most cases, chatter is prescribed in equal parts - talc, zinc, glycerin and distilled water when a surface effect is needed. More liquid (up to 50-60%) is added to obtain a cooling effect and, conversely, 20-40% of liquid is taken to create a protective film on the skin. If the patient has dry skin or long-term exposure to the drug is required, it is recommended to prescribe oil suspensions. To speed up drying and enhance the effect, up to 10% alcohol or ichthyol, sulfur, menthol, anesthesin, tar, etc. are usually added to the “talkers”.
Pastes
used when there is a serous crust on the skin (in patients with eczema), for hyperemia (in patients with dermatitis), etc. The paste consists of equal parts of powder and fatty bases, has a dough-like consistency, and penetrates deeper into the skin than powders and mash. Depending on the composition (naftalan, sulfur, tar, lanolin, petroleum jelly), it acts as a cooling, softening and anti-inflammatory agent. The paste protects the skin well against abrasions after acute inflammatory phenomena have subsided.
Ointments
can be official (sulfuric, ichthyol, naphthalan, etc.) or prepared in a pharmacy according to a prescription. Animal and vegetable fats, oils, petroleum jelly, lanolin are usually used as a base, with the addition of various medicines. Ointments can be exfoliating, itching, epithelializing, softening, absorbing, etc.
In addition, medicinal varnishes and plasters
(for the treatment of condylomas, warts, calluses, onychomycosis), made on the basis of collodion, gelatin or lead plaster with the addition of the necessary medicinal substances.
Of course, all the previous well-known ointment products, including the so-called “complex” ones, manufactured to order, have not lost their relevance at all. However, the rhythm of life requires minimal time investment, and ready-made funds are of increasing interest.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
A review of local therapy can begin with drugs used in the treatment of allergic diseases. Allergic dermatoses require the use of different agents at different phases of the disease. In the presence of weeping lesions, lotions are recommended - boron, resorcinol, soda, with tannin - up to 3% - 5% of the active substance, as well as pastes from the above products, with the addition of naphthalan, tar, ichthyol, etc. After the acute weeping processes subside, sequence of ointment forms: flumethasone
(Lorinden), etc.
Among the monocomponent drugs for external use with anti-inflammatory effects, the following drugs have proven themselves well.
Hydrocortisone 17-butyrate
(locoid) - ointment, cream, lipocrem, lotion 0.1% - is an active synthetic non-halogenated glucocorticoid drug for topical use. Has a rapid anti-inflammatory, anti-edematous, antipruritic effect. Used for superficial, non-infected skin diseases - eczema, dermatitis, psoriasis; Apply to affected skin 1-3 times a day. Ointment and lipocrem provide good occlusive and hydrating properties in combination with the cosmetic appeal of the cream. For weeping skin diseases, it is advisable to use dosage forms such as lotion and crelo. The latter, having the properties of cosmetic milk, is especially effective for application to extensive skin lesions, as well as to the scalp.
| Lotions are used for acute inflammatory skin lesions with swelling and weeping |
Elokom - 1 g of cream or ointment contains mometasone furoate
1 mg; in tubes of 15 g; 1 ml of lotion for external use - 1 mg in an aqueous-alcohol solution; in bottles of 20 ml. Has anti-inflammatory, antipruritic effect. Ointment and cream are used for psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, lotion - for lesions of the scalp, rubbing a few drops of lotion once a day.
Betamethasone valerate
(Celestoderm B) - ointment and cream, 15 g each in tubes. Has anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic effects; eliminates swelling, hyperemia, itching at the site of application. Indicated for psoriasis, eczema, nodular prurigo, dermatitis, discoid lupus erythematosus, insect bites, generalized erythroderma. The effect of the drug can be enhanced by covering the treated surface with an occlusive dressing. The product is applied to the affected area 2-3 times a day until improvement, then used 1-2 times a day.
When the course of dermatoses is complicated by a secondary infection
I use products with antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Of the ready-made drugs, aerosols Oxycort T (hydrocortisone + oxytetracycline), Polcortolone (triamicilone + tetracycline), Oxycyclosol (prednisolone + oxytetracycline) provide invaluable assistance for dermatoses complicated by secondary infection.
Diprogent
— 1 g of ointment or cream contains betamethasone dipropionate 0.5 mg (0.05%) and gentamicin sulfate 1 mg (0.1%) in tubes of 15 and 30 g. It has anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, antiallergic, antibacterial effects. Inhibits the growth of gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms, including staphylococci resistant to penicillin, Proteus, E. coli, salmonella, etc. Indicated for psoriasis, contact and atopic dermatitis, eczema (including microbial), dyshidrosis, itching of the anus and external genitalia organs.
Celestoderm B with garamycin
— 1 g of cream or ointment contains 1 mg of betamethasone valerate and 1 mg of gentamicin sulfate, in tubes of 15 and 30 mg. It has anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, antiallergic, antibacterial effects. Used for infected inflammatory and allergic dermatoses: contact, seborrheic, intertriginous dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis, neurodermatitis, anogenital and senile itching. Apply a thin layer to the affected areas of the skin 2 times a day, if necessary, longer use is possible.
In the treatment of chronic dermatoses characterized by severe infiltration and peeling (psoriasis, seborrhea, chronic eczema), agents that combine an anti-inflammatory (betamethasone) and keratolytic (salicylic acid) substance - ointments and lotions Diprosalik, Belosalik - are highly recommended.
In addition to the certainly positive effect of corticosteroid ointments, it is necessary to mention general contraindications for their use: viral skin infections, primary fungal and bacterial skin lesions, undesirability of long-term use due to the risk of skin atrophy.
In this regard, it is advisable to pay attention to effective products without corticosteroid components: a series of Skin-cap preparations based on zinc pyrithioneate
(aerosol, ointment, shampoo) and nizoral shampoo, which have a good effect in the treatment of psoriasis, seborrhea (especially the scalp).
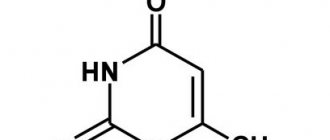
To improve the processes of epithelization, gels and ointments Actovegin, solcoseryl, dexpanthenol (Bepanten), also not containing hormones, are indicated.
Antifungal drugs
Drugs with antifungal effects have been well known for a long time. In addition to the already known terbinafine
(Lamisil), the spray is very successful due to its convenient form of application.
Exoderil
- 1 g of cream or 1 ml of solution for external use contains naftifine hydrochloride 10 mg; cream in tubes of 15 and 30 g, solution in bottles of 10 ml. It has an antifungal (fungicidal effect against dermatophytes, mold fungi, causative agents of sporotrichosis), antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, antipruritic effect. Effective in the treatment of mycoses of the hairy areas of the body and skin with hyperkeratosis, indicated for dermatomycosis and onychomycosis. Apply to the affected surface and adjacent areas, cleaned and dry, 1 time per day for 2-8 weeks, for onychomycosis 1-2 times per day, course up to 6 months.
Lotrimin - 1 g of cream contains clotrimazole
10 mg, in tubes of 15 g. Has antifungal (broad-spectrum), fungicidal, antibacterial effects.
Indicated for athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (caused by Candida albicans
), pityriasis versicolor (caused by
Malasseria furfur
). The required amount of cream is applied with rubbing movements to the affected area and surrounding skin 2 times a day. The itching usually goes away within the first week. The course of treatment for dermatomycosis is 3-4 weeks, for erythrasma and pityriasis versicolor - 3 weeks.
Pimafucin - 1 g of cream contains 20 mg of natamycin
, in tubes of 30 g;
1 ml of suspension for topical use contains 25 mg of natamycin, in 20 ml bottles with a pipette. It has an antifungal, fungicidal effect, and is active against many pathogenic yeast fungi (especially Candida albicans
), dermatophytes. Indicated in the treatment of mycoses of the skin and mucous membranes, otomycosis, candidiasis of the skin and nails. The drug is applied once a day or more often.
In the treatment of combined skin pathologies, external agents that combine anti-inflammatory, antifungal and antimicrobial effects are used with great success.
Triderm
— 1 g of ointment or cream contains 0.5 mg of betamethasone dipropionate, 1 mg of gentamicin sulfate and 10 mg of clotrimazole, in tubes of 15 g. It has a local anti-inflammatory, vasoconstrictor, antipruritic, antibacterial, antifungal effect. Used for various forms of bacterially infected eczema, as well as dermatomycosis, candidiasis, especially when lesions are localized in the groin area and large folds of the skin. A small amount of the drug is applied to the affected areas, lightly rubbing, 2 times a day; the duration of treatment is determined individually. The recommended duration of treatment for dermatomycosis of the feet is 2-4 weeks.
Pimafukort
- 1 g of cream or ointment contains natamycin 10 mg, neomycin 3.5 mg and hydrocortisone 10 mg; in tubes of 15 g; 1 g of lotion - natamycin 10 mg, neomycin 1.75 mg and hydrocortisone 5 mg; in dropper bottles of 20 ml. Action: local antibacterial, antifungal, anti-inflammatory. Used for superficial dermatoses complicated by bacterial or fungal infection, otomycosis. Apply to affected areas of the skin 2-4 times a day for 2-4 weeks.
Acne treatment products
The products used in the treatment of acne deserve special mention. For mildly expressed processes, sinerite
- erythromycin-zinc complex, has a bacteriostatic effect on microorganisms that cause acne;
skinoren
is an ointment based on azelaic acid, the therapeutic effect of which is due to its antimicrobial effect, as well as a decrease in the content of free fatty acids in skin lipids and the normalization of disrupted keratinization processes in the skin follicles.
In the case of poorly resolved inflammatory and infiltrated elements, drugs such as Retin-A gel, Airol ointments and lotions, and Lokacid are indicated to accelerate their maturation and resolution. These products are based on trans-retinoic acid.
, a natural metabolite of retinol. Enhances cell proliferation in the papillary layer of the skin, reduces the adhesion of cells involved in the formation of acne vulgaris. When treating closed acne, it promotes their transition to open acne, which then heals without scarring after removing the keratin plug.