Fibrosis is a diagnosis indicating the formation of scars, pulmonary fibrosis is the formation of scars in the lungs. In patients with this diagnosis, the elastic properties and extensibility of the lung tissue are reduced, and the passage of oxygen through the walls of the alveoli is difficult. The disease is extremely difficult to treat and can lead to irreversible consequences. Pathology is found in most cases in people over 60 years of age.
Symptoms of fibrosis
Among the pronounced symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis:
- shortness of breath, which worsens after physical activity,
- bouts of dry cough,
- persistent pain in the chest area,
- wheezing,
- change in color of lips and limbs,
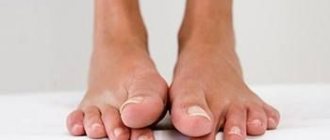
- increase in phalanges,
- weight loss,
- fatigue and general weakness.
Other diseases of the respiratory system also have similar symptoms, so if unpleasant signals appear, it is best to immediately consult a doctor. An accurate diagnosis will help you quickly make the most correct decision on a treatment regimen and begin to implement it.
Reasons for the development of pathology
There are many causes for the development of pulmonary fibrosis. These include:
- Diseases of the respiratory system (COPD, pneumonia, tuberculosis).
- Systemic connective tissue diseases (scleroderma, SLE, rheumatoid arthritis).
- Taking a number of medications (cytostatics, antiarrhythmic drugs).
- Vasculitis of various origins.
- Harmful production factors (asbestos, silicates, etc.).
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is also isolated when the cause of the pathological process cannot be determined.
Causes of the disease
Pathology can be caused by various reasons:
- hereditary predisposition,
- inflammatory processes in the lungs,
- infectious diseases,
- negative impact of the environment,
- work in hazardous industries,
- the effects of radiation therapy,
- chronic autoimmune diseases,
- complication of lung diseases,
- treatment with various drugs.
Bad habits, such as smoking, can also cause dangerous pathology. However, there are cases of the disease developing without any clear cause. Each individual patient must undergo a full examination to identify the factors that influenced the occurrence of the pathology, this will help to choose the right treatment that will significantly improve the condition.
Diagnosis and treatment
To diagnose pulmonary fibrosis, a pulmonologist performs the following tests and studies: general blood test; chest x-ray; computed tomography of the lungs, magnetic resonance imaging of the lungs; lung biopsy; breath tests. Treatment of pulmonary fibrosis is determined by a qualified specialist depending on the characteristics of the disease in a particular person. Glucocorticoids, cytostatics and immunosuppressants are used for severe forms of fibrosis. Lungs affected by fibrosis often become a favorable environment for the attachment of pathogenic microflora and the development of inflammation. To prevent this, antibacterial drugs are prescribed; oxygen inhalation and cardiac glycosides will be useful. For debilitating cough and shortness of breath, bronchodilators are prescribed. Drug treatment of pulmonary fibrosis should be supported by therapeutic breathing exercises, while large physical activities are contraindicated for the patient. It is also necessary to exclude exposure to fibrosis-provoking factors on the body.
Treatment of fibrosis
Treatment of the disease is prescribed by a professional specialist, taking into account the results of the examination and the characteristics of the patient’s disease. There are a number of drugs that help prevent the occurrence of various infections and the development of inflammation. Treatment of fibrosis is supported by therapeutic breathing exercises and the complete exclusion of provoking factors. In case of the total form of the disease, surgical intervention is recommended.
In the early stages of the disease, therapy is used to help reduce scarring. You can consult with a pulmonologist and make an appointment by calling our clinic or using the form on the website.
FIND OUT PRICES
Pulmonary fibrosis: symptoms, treatment and prevention
Zinovenkova Elena Alekseevna
Head of the Department of Occupational Pathology, General Practitioner (family doctor), General Practitioner, Pulmonologist
Pulmonary fibrosis
is the process of formation of fibrous (scar) tissue in the lungs, which leads to respiratory dysfunction. With fibrosis, the elasticity and extensibility of the lung tissue decreases, and the passage of oxygen and carbon dioxide through the wall of the alveoli (pulmonary vesicles in which the inhaled air comes into contact with the blood) becomes difficult.
Causes of the disease
Lung fibrosis can occur due to the development of inflammation in the alveoli of the interstitial lung tissue. As a result, this causes scarring and further tissue growth.
The main reasons for the formation include: • Hereditary factor - the first and main reason • Smoking • Staying in a polluted area or in an industrial area, hazardous production • Complication of diseases such as diabetes, systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis • Complication of lung diseases - such as alveolitis, sarcoidosis, asbestosis, tuberculosis • Prolonged inhalation of particles of organic substances or minerals • Chemical intoxication • Radioactive radiation in the chest area
Types of pulmonary fibrosis
• Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis – when it is impossible to determine the disease that caused it • Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis – when the cause of the disease can be found
Forms
Fibrosis can be unilateral or bilateral, focal (a small area of the lung is affected) and total (spreads to the entire lung).
• fibrosis (pneumofibrosis)
– moderate stringy proliferation of connective tissue, alternating with unchanged lung tissue;
• sclerosis (pneumosclerosis)
– gross replacement of areas of lung tissue with connective tissue with compaction of the lungs;
• cirrhosis of the lungs
– complete replacement of the lung tissue with connective tissue with damage to the bronchi and blood vessels of the lung.
Due to development, they distinguish:
• fibrosis as a consequence of dust-induced lung diseases (silicosis is an occupational lung disease that develops after prolonged inhalation of silicate dust; asbestosis is an occupational lung disease that occurs after prolonged inhalation of asbestos dust); • drug-induced fibrosis (develops against the background of long-term use of drugs for the treatment of arrhythmia, chemotherapy drugs (for the treatment of tumors)); • fibrosis in connective tissue diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic scleroderma, systemic lupus erythematosus); • fibrosis of an infectious nature (after pneumonia or pulmonary tuberculosis); • idiopathic (primary) fibrosis (occurs for no apparent reason).
Symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis
• The leading symptom is shortness of breath - first during physical activity, and as the disease progresses, at rest. • Cough (dry or with a small amount of sputum). • Paleness, cyanosis (blueness) of the skin. • If the process lasts for a long time – a change in the shape of the fingers (thickening of the fingers, convexity of the nail plate). • With a long course of the process and a large volume of damage, signs of heart failure (the so-called “pulmonary heart”) develop: increased shortness of breath, palpitations, swelling in the legs, swelling and pulsation of the neck veins, chest pain. • Weakness, increased fatigue, inability to perform heavy physical activity.
Treatment of the disease
There is no specific effective treatment for pulmonary fibrosis. Among the main recommendations are the following: • eliminate exposure to damaging factors (occupational hazards); • limited areas of pneumosclerosis that do not manifest themselves clinically do not require therapy; • oxygen therapy (oxygen inhalation using special devices); • surgical treatment: it is possible to remove a functionally defective limited lesion; in the case of total fibrosis (spreading to the entire lung) - a lung transplant.
Today, in the field of medicine, various drugs are being developed that help reduce such scars. Also, some of them, for various types of fibrosis, are able to reduce processes that contribute to tissue scarring. These drugs include corticosteroids, which can suppress the immune system. By suppressing the immune system, lung inflammation and subsequent tissue scarring in the lungs are reduced. In addition, corticosteroids can be taken in combination with anti-inflammatory and other drugs.
Complications and consequences
• Chronic respiratory failure (lack of oxygen to the body). • Pulmonary hypertension. • Chronic cor pulmonale. • Attachment of a secondary infection (with the development of pneumonia).
Prevention of pulmonary fibrosis
• Use of personal protective equipment when working with occupational hazards, compliance with safety regulations. • Timely treatment of inflammatory lung diseases (pneumonia; tuberculosis). • To give up smoking. • When taking drugs that can lead to the development of pulmonary fibrosis (some antiarrhythmic drugs), periodic preventive monitoring of the condition of the lungs.
General practitioner (family doctor), therapist Zinovenkova Elena Alekseevna
Symptoms of the disease
Acute pleurisy results in high fever, chills, and difficulty breathing.
Chronic pleurisy intensifies and accelerates the development of tuberculosis, negative processes in the lungs and chest cavity, promotes shortness of breath, constant weakness, impedes brain activity, and provokes a painful dry cough.
If similar symptoms occur, it is extremely important to contact a clinic where experienced specialists can conduct a comprehensive examination. To establish a diagnosis, in addition to collecting an anamnesis, it is often necessary to undergo an X-ray examination and undergo special blood tests.
The MedicCity clinic employs highly professional therapists and pulmonologists. You can also undergo x-ray examinations and tests to clarify the diagnosis.
Fibrosis of muscles and ligaments
Muscle fibrosis occurs due to mechanical damage or as a reaction to inflammation. Moreover, any strong spasm or muscle tension can be a prerequisite for the formation of an inflammatory focus. As a result of fibrous compaction, muscle tissue loses the ability to contract, conduct nerve impulses and move.
The ligaments themselves consist of dense fibrous tissue, but its hyperplasia leads to impaired joint mobility, pain, and impaired biomechanics.
Other types of fibrosis
Other organs are also susceptible to the pathological process. The most common types of disease include:
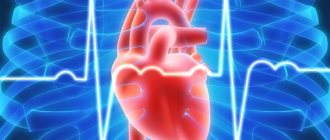
- Cardiac fibrosis
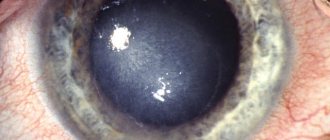
- Fibrosis of the eyeball
- Pancreatic fibrosis, etc.
Cystic fibrosis (cystic fibrosis) is a hereditary disease caused by mutations in the CFTR gene of the father and mother, which is inevitably associated with pathologies of internal organs (lungs and gastrointestinal tract) and in particular is characterized by fibrotic changes.
In cystic fibrosis, diffuse fibrosis, thickening of connective tissue septa, and cysts are found in the pancreas. The pathology also affects the liver, up to the development of cirrhosis.
In the pulmonary or respiratory form of cystic fibrosis, diffuse fibrosis, bronchial damage, and bronchiectasis are detected in the lungs. In addition, signs of emphysema and atelectasis may be detected.
Fibrosis of the liver and kidneys
Most often it is a consequence of chronic liver diseases, such as fatty disease, hepatitis (viral, toxic), or other internal organs (coronary heart disease, diabetes mellitus, cholelithiasis). People who abuse alcohol are also predisposed to liver fibrosis. The process of proliferation of connective tissue and scarring of the organ starts every time the primary disease worsens and the liver is exposed to trauma. Over time, an injured and scarred organ may completely lose its functions, and cirrhosis of the liver develops. A liver CT scan is prescribed in conjunction with other examinations and reliably shows the location, size, and density of fibrosis foci.
Kidney fibrosis leads to impaired renal function and chronic renal failure.