Short stature and disproportion of the skull, incorrect body proportions, a very rounded face, pronounced mental retardation - all this speaks of cretinism. Below in the article you will find the causes of the disease; the doctors who treat him; necessary medical procedures for treatment; as well as general information about the disease, its localization, features of diagnosis of diseases and their treatment. However, we advise you to consult a doctor, because self-medication is 90% fraught with complications
Make an appointment and consultation
Cretinism. general information
Cretinism (congenital hypothyroidism) is an endocrine disease characterized by congenital hypofunction of the thyroid gland. Cretinism manifests itself in delayed physical and mental development, dementia.
When treating Cretinism, doctors at the BIOSS clinic use both time-tested and the latest developments and proprietary techniques.
The BIOSS MC employs the best doctors in Moscow who have extensive experience in the treatment of Cretinism
The macroscopic picture reveals asymmetry and microcephaly of the brain, a small number of convolutions, thickening of the soft and dura mater. The cavities of the cerebral ventricles are somewhat dilated and filled with fluid, and the ependyma is thickened. Brain weight is changed. The microscopic appearance of the brain in cretinism is largely unknown. There are often chronic changes in degenerative cell type in the ganglia.
There are no specific histological changes observed in the thyroid gland. Often, degenerative and atrophic processes are detected in the parenchyma of the gland and the proliferation of its connective tissue. Signs of cretinism are presented in the form of facial anomalies and growth disorders that affect both skeletal bones and soft tissues.
Thyroid functions
Many diseases that affect a person’s mental state are organic in nature. Changes occur in the body that cause mental disorders. Hypothyroidism is one of these diseases. Its presence is associated with disruption of the endocrine system.
The thyroid gland is an organ belonging to the endocrine gland system. Its main function is to release hormones into the bloodstream that affect metabolism and organ function.
The thyroid gland is located on the front of the neck, adjacent to the anterior and lateral sides of the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. Weighs about 50 g. It is quite soft, but you can feel it under the skin if you tilt your head forward.
Structure of the thyroid gland:
- right lobe;
- left lobe;
- isthmus.
Thyroid hormones:
- The main hormones are thyroxine and triiodothyronine. They are produced by a special type of glandular cells called A cells, which are found around follicles, microscopic cavities filled with a jelly-like substance. Iodine, necessary for the synthesis of hormones, accumulates in the follicles.
- Calcitonin is a hormone involved in regulating calcium levels in the blood. It is produced by cells of a special type - C cells. They are concentrated in groups at certain points in the thickness of the gland.
- Other biologically active substances. Their production is carried out by B cells, the significance of which is not yet fully understood.
What is the thyroid gland responsible for?
- metabolism
- protein synthesis and breakdown
- breakdown of fat deposits
- energy production for the nervous system and muscles
- blood glucose
- nervous system function
- work of endocrine glands
- supplying cells with nutrients
When the above processes are disrupted, a person experiences mental and physical health problems that lead to cretinism. Cretinism is an endocrine disease associated with dysfunction of the thyroid gland. This delays mental, intellectual and physical development. Researchers noted cretinism as a type of congenital hypothyroidism (decreased production of hormones in the thyroid gland).
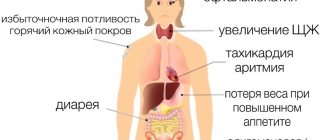
Signs of cretinism in adults
- Changes in size, disproportion of the skull due to disruption of its growth. Despite the fact that the head appears disproportionately large in relation to the body, cretinism is characterized by microcephaly - a decrease in the size of the cranial cavity and brain.
- Short stature. The height of patients with cretinism may vary, but in general it is significantly lower than that of a healthy person.
- Violation of body proportions. In 25% of cases, patients with cretinism have a correct proportional physique. The remaining 75% have imbalances. The arms and legs are shortened in relation to the body and have a large thickness. Due to this, the patient's movements are awkward. The joints are massive, thickened, and often curved. The palms are wide and the fingers are short. The feet are often turned inward, and clubfoot is noted.
- There is impaired mobility in the spine and various joints. Almost all patients have a narrow pelvis.
- With cretinism, the growth of the base of the skull is impaired, so the back of the patient’s nose becomes wide and sunken, and the distance between the eyes is increased.
- The patient's face has a characteristic appearance and is rounded. This occurs due to subcutaneous swelling.
- The forehead is covered with wrinkles, which makes the patient seem older than he actually is.
- Little hair grows on the patient's body; it is coarse and usually dark black in color.
- Other characteristic facial features: high forehead, wide cheekbones, protruding ears, large lips, constantly protruding tongue.
- All patients, to one degree or another, have mental retardation. Sometimes it can occur in the form of idiocy, when the patient is not able to care for himself.
- With cretinism, there is a decrease in size and insufficient function of the gonads. As a result, many patients are infertile.
- Hearing and speech impairment. They can be very pronounced, even to the point of deaf-muteness.
- Apathy, lethargy, drowsiness, mental disorders to varying degrees.
Complications
The main danger of a long-term course of severe myxedema in the absence of treatment is the onset of myxedema coma. At risk are elderly patients and people with a weakened immune system due to acute infections, hypothermia, long-term hypothyroidism and chronic diseases. The list of symptoms of coma includes a drop in body temperature, intestinal obstruction, slowing of the pulse and breathing, heart failure, confusion. The probability of death for patients in this condition reaches 80%.
Blood test for hormones
If cretinism is suspected, two groups of hormones are examined in the blood:
- thyroid hormones;
- pituitary hormones.
Changes in the levels of various hormones in cretinism:
| Thyroid hormone levels | Pituitary thyroid-stimulating hormone level | |
| Healthy man | fine | fine |
| Primary hypothyroidism | demoted | Promoted |
| Secondary and tertiary hypothyroidism | demoted | Demoted |
This condition is known as transient, or temporary, hypothyroidism. The level of thyroid hormones decreases temporarily and then recovers again; cretinism does not develop. In this case, there is a slight decrease in the level of thyroid hormones in the blood and a slight increase in the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland. This result is considered doubtful, so the study is repeated after some time. Many clinics conduct screening studies, that is, blood is taken from every newborn for analysis. Where screening is not carried out, in maternity hospitals blood is taken for analysis from children who have at least two symptoms of the disease after birth. In sick children aged 4–6 months, the level of fats and cholesterol in the blood increases. This may also be indirect evidence of the presence of the disease. To identify pathological changes, a biochemical blood test is performed. When performing a general blood test, some patients are found to have anemia.
Treatment of cretinism in children and adults
Treatment of cretinism and any type of hypothyroidism in a child should begin from the moment the diagnosis is made. The earlier therapy is started, the more favorable the prognosis. In case of insufficiency of thyroid function, so-called replacement therapy is carried out. The patient is prescribed hormones that should restore impaired functions. These drugs are effective for all types of hypothyroidism, except those caused by impaired tissue sensitivity to thyroid hormones. Sometimes the clinic’s capabilities do not allow you to immediately take tests and make an accurate diagnosis. If there are external signs of cretinism, then treatment is carried out without test results, and then they act based on how the patient’s condition changes during therapy. If treatment is started in the first month of life, then the disease can be controlled: the child develops completely normally. If therapy is prescribed later than 4–6 weeks, then there is a high probability of mental retardation and other complications. Drugs used to treat cretinism in children :
| Drug name | Description | Dosages |
| L-thyroxine | The drug is a synthetic analogue of thyroid hormones. It creates an artificial hormonal background in the blood and restores impaired functions. How does a doctor monitor the effect of therapy?:
|
The dose is selected according to the level of thyroid-stimulating hormone in the blood. Subsequently, treatment is carried out for life. |
| Vitamin A (syn.: Retinol, Axerophthol, Vitadral, Alfasterol). | Patients with cretinism experience skin problems that are helped by vitamin A (retinol). | The dosage is determined by the attending physician, depending on the severity of the condition. |
| Vitamin B12 (syn.: Cyanocobalamin, Dodex, Neurobene, Ankermann) | Main effects of Cyanocobalamin:
| The drug is available in ampoules. The solution can be administered intramuscularly, intravenously, or subcutaneously. The dosage and method of administration are determined by the attending physician. |
| Piracetam (syn.: Nootropil, Cerebril) | Main effects of piracetam:
| The drug is available in tablets. Dosages:
Treatment with Piracetam is carried out for a long time, in courses of 1 month or longer. |
| Cerebrolysin | The drug is a protein obtained from the brain of cattle. Main effects:
| Cerebrolysin is administered intravenously. The dosage of the drug is determined by the attending physician. |
| Lipocerebrin | The drug is a phospholipid (a type of fat essential for nerve tissue) obtained from the brain of cattle. | Lipocerebrin is available in tablet form. Dosage: Prescribed 1 - 2 tablets 3 times a day. |
| Encephabol (syn.: Pyriditol) | Main effects of the drug:
| The drug is available in tablet form. It is taken 2-3 times a day after meals. Dosages for children and adults are selected by the attending physician. For adults, the course of treatment lasts from 1 to 3 months. For children - from 2 weeks to 3 months. |
| Pantogam | Main effects of the drug:
| Pantogam is available in tablet form. Dosages:
The course of treatment lasts from 1 to 4 months. After a break of 3–6 months, it can be repeated. |
| Attention! The information in the Treatment section is presented for informational purposes only and cannot serve as a guide for taking medications independently, without medical supervision. Self-medication can lead to negative consequences. |