Vaginal discharge may be normal or indicate an intimate infection.
In a healthy woman, mucus helps moisturize the vagina, it is thick and milky white or transparent and stretchy - it all depends on the phase of the menstrual cycle. All other types of discharge, except menstrual discharge, indicate problems in the intimate area.
Normal vaginal discharge contains 99% lactobacilli, which have a beneficial effect on the bacterial flora of the vagina, and 1% are pathogenic microorganisms such as intestinal bacteria or Staphylococcus aureus. When the balance of the bacterial flora is disturbed and the level of pathogenic microorganisms increases, we can talk about the occurrence of an intimate infection, the most common symptom of which is discharge with an abnormal color and an unpleasant odor.
White vaginal discharge - what does this mean?
White vaginal discharge is completely normal. The problem arises when they acquire a dense consistency that begins to resemble cottage cheese, and numerous lumps appear in them. Such symptoms may indicate an infection of the yeast (fungus) Candida albicans, which colonizes the vagina, perineal area, labia and anus, also causing additional problems.
The most common symptoms of thrush include persistent itching and burning in the intimate area and vagina, redness and swelling of the labia, and a feeling of dryness in the vagina. Usually the white discharge from a yeast infection does not have a bad odor, but sometimes you may notice a yeast-like odor.
White vaginal discharge
How to treat white vaginal discharge? First of all, it is recommended to consult a gynecologist who will prescribe suppositories or ointments with antifungal substances. Most often, the use of both forms of medication is required - suppositories heal the infection in the vagina and restore normal microflora of the genital tract, while ointments applied to the labia and anal area minimize unpleasant symptoms - itching and burning.
About normal discharge
Normally, a woman's vagina should release fluid. But not all discharge is normal. “Good” discharge includes clear, not abundant (from 50 mg per day), odorless mucus. Normal discharge does not cause discomfort, it does not cause itching, burning or irritation of the vagina. If you take a smear for microflora, it should reveal a normal number of leukocytes with a predominance of lactobacilli. Mucus discharge gradually increases in quantity until the day of ovulation (approximately 14 days after menstruation). During this period, the mucus changes its properties. The feeling of moisture in the external genital area at this time is absolutely normal.
But you need to be very careful about brown discharge! A brown, brownish tint to the liquid clearly indicates bloody or bloody additions to the mucus. And this, in turn, may indicate disorders of the female genital area. Further on such violations and their causes.
Is yellow vaginal discharge a cause for concern?
Not every yellow-colored vaginal mucus indicates an intimate infection. Yellowish discharge - cervical mucus - also appears outside the ovulation period. If yellow discharge is not accompanied by any additional symptoms, this is a sign that the bacterial flora of the vagina is in good condition.
Yellow vaginal discharge
In the case of discharge, the occurrence of which is associated with itching, burning in the intimate area, as well as an unpleasant odor, this may indicate the occurrence of cervical erosion.
Yellow and greenish discharge also occurs with trichomoniasis. Other signs of trichomoniasis:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- itching and redness around the vagina and labia;
- frequent urination;
- pain during intercourse;
- Possible menstrual irregularities.
Treatment of this intimate infection requires the use of an antibiotic.
Uterine bleeding
Uterine cancer
Cervical cancer
7510 January 27
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Uterine bleeding: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Every woman and girl can experience abnormal uterine bleeding. They are a signal of dysfunction of the reproductive, endocrine or nervous systems. This condition usually occurs suddenly, so it is necessary to clearly understand what to do if abnormal uterine bleeding develops.
The uterus is an organ of the female reproductive system, consisting of three layers: internal (endometrium), middle muscular (myometrium) and external (perimetry), which is adipose tissue surrounding the outside of the uterus.
The uterus, like other organs of the female reproductive system, undergoes significant changes during the menstrual cycle, which, in turn, is associated with the maturation of eggs in the ovaries.
The germ cells (cells that are the precursors of the egg) laid down during the intrauterine development of the female fetus are activated and enter into the process of further development every month, but not all at once, but in a strictly defined quantity (about 20–30 cells), while fully maturing only one cell. It leaves the ovary, enters the fallopian tube, through which it gradually moves towards the uterus. If the egg has been successfully fertilized by a sperm, then a zygote is formed - the first cell of the future embryo, which begins to divide and, reaching the uterine cavity, is fixed (implanted) on the surface of the endometrium. If fertilization does not occur, then the egg does not remain in the uterine cavity and is subsequently excreted along with normal menstrual flow. In the process of implantation, the most important role is played by the epithelium lining the uterine cavity from the inside - the endometrium. From the beginning of the menstrual cycle, it grows, thickens and reaches its maximum thickness at the time of ovulation. Next, the endometrium is loosened, which is necessary for successful implantation. If implantation does not occur, then before the start of a new menstruation, endometrial rejection begins, which is preceded by spasm of the uterine arteries. It is the spasm of the uterine arteries that causes the development of pain during the premenstrual period. Next, the arteries relax and become fragile, which leads to the development of bleeding under the endometrium with its further rejection.
Thus, it is the rejected endometrium that is the main component of the discharge from the uterine cavity during uterine bleeding.
Types of Uterine Bleeding
All uterine bleeding can be divided into normal menstrual bleeding and abnormal uterine bleeding. Normal menstrual bleeding is characterized by frequency of occurrence, a certain duration of the menstruation itself (on average from 3 to 7 days) and a small loss of blood (usually about 40-60 ml).
Bleeding that differs in its characteristics from those listed above is considered abnormal in women who have reached reproductive age.
These bleedings are excessive in duration (more than 7 days), volume of blood loss (more than 80 ml), and frequency (including intermenstrual bleeding).
Separately, abnormal bleeding of the pubertal, perimenopausal and postmenopausal periods is distinguished, which is associated with the peculiarities of the functioning of the reproductive and neuroendocrine systems during these age periods.
Possible causes of abnormal uterine bleeding
Identification of the causes of abnormal uterine bleeding formed the basis of the PALM-COEIN classification, widespread throughout the world (many domestic gynecologists also use this classification, indicating this abbreviation in the diagnosis). In accordance with it, the causes of uterine bleeding are divided into organic (structural, accessible to visualization and detection by ultrasound, MRI, etc.) diseases of the female reproductive system and functional, caused by impaired functioning of the reproductive system in the absence of visible changes, as well as those arising from -for disorders of the endocrine system, blood coagulation system, etc.
What diseases cause abnormal uterine bleeding
What diseases are hidden under the abbreviation PALM-COEIN?
- Polyp (polyp) – the presence of polyps, i.e. formations, often benign;
- Adenomyosis (adenomyosis) is a type of endometriosis in which the endometrium grows deep into the wall of the uterus;
- Leiomyoma (leiomyoma, or myoma) is a benign tumor that develops from myometrial tissue;
- Malignancy (malignancy) – malignant (oncological) processes developing from uterine tissue;
- Hyperplasia (hyperplasia) – excessive growth of the endometrium;
- Coagulopathy (coagulopathy) – disorders of the blood coagulation system (for example, hemophilia, von Willebrand disease, etc.), manifested by a tendency to bleeding of various locations (not only uterine bleeding, but also nasal, post-injection, etc.);
- Ovulatory dysfunction (ovulatory dysfunction) – disruption of the functioning of the ovaries, leading to certain changes in the process of egg maturation;
- Endometrial (endometrial dysfunction) – disruption of the functioning of the endometrium in the absence of its visible changes;
- Iatrogenic (iatrogenic cause) – uterine bleeding as a complication in the process of treating a particular disease;
- Not yet classified (not yet classified cause) - other rare or unknown causes of uterine bleeding.
Which doctors should I contact if abnormal uterine bleeding occurs?
Emergency treatment of abnormal uterine bleeding is carried out by an obstetrician-gynecologist. After the bleeding has stopped, the gynecologist continues to care for such a patient, often together with an endocrinologist and mammologist. If abnormalities in the blood coagulation system are detected, the patient is sent for a mandatory consultation with a hematologist (a doctor specializing in blood diseases).
Diagnosis and examination of abnormal uterine bleeding
Diagnosis of the cause of abnormal uterine bleeding begins with a detailed interview of the patient in order to identify risk factors for a particular disease and clarify the circumstances of the development of bleeding. The dates of the last normal menstruation must be specified, and pregnancy is excluded (in the laboratory) using a blood test for hCG (human chorionic gonadotropin).
Green vaginal discharge is a bacterial infection
Vaginal discharge with a characteristic greenish color often indicates a bacterial infection (vaginosis), which can be caused, for example, by pathogenic microorganisms of the species Gardnerella vaginalis.
Gardnerellosis is most often accompanied by burning and itching of the perineum, swelling of the labia, pain when urinating, as well as a characteristic fishy odor from the vagina. If these symptoms appear, consult a gynecologist, as ignoring them can lead to serious health problems - bacteria can enter the cervical canal.
Burning and itching of the perineum
Green vaginal discharge may also indicate atrophic vaginosis, which affects women during menopause and when estrogen levels in the blood are low.
Diagnostics
When consulting a doctor about such discharge, a detailed examination is necessary:
- detailed questioning and examination of the woman,
- gynecological examination on a chair,
- examination in mirrors, colposcopy,
- taking a smear for flora, a smear from the cervix for atypical cells,
- carrying out blood and urine tests for general analysis,
- blood and smear for antibodies to infections,
- Ultrasound of the genital organs,
- blood for hormones.
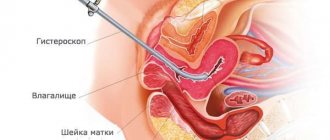
If it is necessary to exclude serious diseases of the genital area, hysteroscopy and hysterography, biopsy and diagnostic curettage of the endometrium, and, if necessary, MRI and laparoscopy are indicated.
Brown vaginal discharge - what to be afraid of?
Not all brown vaginal discharge is cause for concern. Very often, this type of spot appears just before the start of menstruation. Vaginal discharge can also occur during ovulation or during the first stage of pregnancy when the embryo implants into the uterine lining.
However, sometimes brown vaginal discharge can be a sign of health problems if it is a symptom of bacterial vaginosis or pelvic inflammatory disease.
Brown spots may appear after taking birth control pills. In general, this is not a cause for concern - the body reacts to hormones in this way. However, if the problem persists for more than 2-3 days, you should seek help from a doctor, who will determine whether the vaginal discharge is a symptom of a more serious condition.
Self-medication for any type of discharge is prohibited, as you can do more harm to the body than good.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
Prevention of brown secretions between periods
Experts say that there is no universal remedy for preventing the rejection of intermenstrual secretions, because the causes of this problem are different. Despite this, a number of simple rules can be identified to reduce the risk of brown mucous fluid appearing between menstruation to a minimum:
- Moderation in physical activity.
- Careful selection of contraceptives.
- Maintaining a daily routine.
- Balanced diet.
- Having a permanent sexual partner.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules, especially during menstruation.
Doctors recommend going for a gynecological examination once every 6 months. This procedure will not help prevent brown discharge in the middle of the cycle without pain and odor, but it will allow you to diagnose possible pathological processes in time and begin comprehensive treatment.
Endometriosis
Brown or bloody discharge are also the main symptoms of endometriosis of the cervix or uterine body. This does not necessarily cause pain. Endometriosis of the cervix is nodular, small cystic formations or growths in the form of red or purplish-blue stripes. Dark bloody and brown discharge may appear from individual lesions. Endometriosis of the uterine body is the growth of endometrial cells in the myometrium (the muscular layer of the uterus). Pathological discharge decreases in size after menstruation, and its color becomes lighter.
Make an appointment
Discharge associated with pregnancy
Brownish leucorrhoea in the middle of the cycle may indicate the beginning or end of pregnancy (miscarriage). Why is this happening?
When a fertilized egg attaches to the uterus, the endometrial vessels may be slightly damaged. The released blood stains the mucus. Sometimes mild spasms may occur.
Heavy discharge, which is accompanied by severe pain, nausea and cycle disruption, can be a symptom of an ectopic pregnancy.
If the fertilized egg detaches from the endometrium (due to the non-viability of the fetus or the presence of scars and adhesions in the uterus), a miscarriage occurs, which is accompanied by slight bleeding (duration - up to 48-72 hours).