Inflammatory and infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract can pose a great danger to humans. A particularly dangerous pathology is inflammation of the appendix of the large intestine, called appendicitis.
Complications of this pathological process can lead to an extensive infectious process in the body. Inflammation of the appendix can take a chronic form. Chronic appendicitis, the symptoms of which have their own distinctive features, requires surgical treatment.
What is appendicitis?
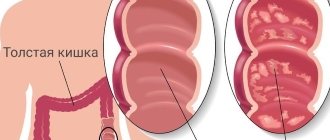
The appendix is the vermiform appendage of the cecum
The human intestine has a considerable extent. Each section of the intestine has its own characteristics, including its functional role and structural features.
The large intestine ensures final absorption of fluid, vitamin saturation and formation of feces. It is within the large intestine that there is a cecum with a vermiform appendix.
The vermiform appendix of the cecum is a kind of hollow, blindly closed pocket containing lymphoid tissue. Normally, food substrates do not pass from the cecum to the appendix, but there are exceptions.
The entry of food and other foreign objects into the appendix causes an acute immunological response, expressed as an inflammatory reaction.
Inflammation of the appendix of the cecum is called appendicitis. This is always an acute disease requiring urgent surgical measures. In rare cases, the disease transitions into a chronic form, when inflammation periodically stops and resumes.
The main danger of the disease is the risk of rupture of the membranes of the appendix. In this case, the inflammatory contents of the appendix end up in the peritoneal cavity and cause extensive inflammation. This complication often leads to death if not treated promptly.
Blind but dangerous
The appendix is a short and thin blind vermiform appendix 7-10 cm long, located at the end of the cecum (the initial part of the large intestine). Like any part of the intestine, the appendix produces intestinal juice, but so little that it does not play a special role in digestion. Therefore, for a long time it was considered a “mistake of nature” and was removed by the patient at the first opportunity. But recently, scientists discovered lymphoid cells in the caecum, the same as in human tonsils. And since these cells have the properties to protect the body from infections, the assumption was born that the appendix is part of the immune system.
However, the number of protective cells in it, as it turned out, is very insignificant and cannot have a strong effect on the immune system. So most experts are still confident that there is no benefit from the appendix, but the harm in case of its inflammation can be significant: acute appendicitis not diagnosed in time can cost not only health, but also life.
Symptoms of appendicitis
Pain as a symptom of appendicitis
The manifestations of appendicitis in each patient are quite variable. It is often difficult for doctors to make such a diagnosis based only on the patient's complaints. There is also an almost asymptomatic course.
Common symptoms:
- Pain in the right abdominal area.
- Diffuse abdominal pain.
- Lack of appetite.
- Diarrhea or constipation.
- Intestinal obstruction.
- Bloating.
- Fever.
- Nausea and vomiting.
Pain with appendicitis can begin with convulsive contractions of the abdominal muscles. Gradually the pain intensifies and spreads to other areas of the abdomen. Sometimes, on the contrary, the pain becomes more localized.
There is a typical body position that is typical for patients with appendicitis. The person takes a lying position and presses his knees to his stomach. This reflex position is adopted to reduce movements that increase pain.
If severe symptoms of appendicitis appear, it is strictly forbidden to take laxatives and cleanse the intestines with an enema. These procedures may result in rupture of the appendix. The appearance of the symptoms described above should be a reason for an emergency visit to a doctor.
Appendicitis in women, elderly and children
Clinical manifestations in females resemble certain gynecological pathologies. The anomaly is associated with the close location of the appendages, and pain syndrome is present:
- with ectopic pregnancy;
- ovarian rupture;
- apoplexy, etc.
To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to pay attention to the presence of gynecological diseases and the menstrual cycle.
Some specific manifestations of appendicitis are present in the elderly, children, pregnant women and with an abnormal location of the appendix.
The following clinical signs are typical for babies:
- diarrhea with frequent vomiting;
- febrile temperature indicators;
- decreased activity - the child loses interest in toys;
- lethargy, moodiness;
- anxiety - with increasing discomfort.
In old age, the symptomatic picture is different:
- temperature rise does not always occur;
- the pulse remains within standard limits - without increasing heart rate;
- there are mild signs of abdominal irritation.
At an older age, the clinical manifestations of appendicitis resemble a neoplasm located in the area of the cecum. During pregnancy, the pain syndrome is localized over the iliac region - due to the upward elevation of the intestines against the background of an enlarged uterus.
Causes of the disease
Chronic appendicitis can have different causes
The etiology of chronic appendicitis is no different from the causes of the acute form of the disease. The main cause of inflammation of the appendix is obstruction of the lumen of the appendix.
In most cases, obstruction of the appendix occurs due to the proliferation of internal lymphoid tissue.
The lymphoid tissue of the appendix, in turn, grows due to primary infectious and inflammatory bowel diseases, such as Crohn's disease, gastroenteritis and amebiasis.
Another common cause of appendicitis is obstruction of the appendix by fecal matter. Parasites and foreign bodies can also enter the appendix.
Indications for appendectomy
Surgery to remove the appendix is used for chronic or acute forms of appendicitis. In addition, appendectomy is performed if there is an appendiceal infiltrate, as well as if neoplasms are detected in the appendix.
Emergency appendectomy is usually performed no later than one hour after diagnosis. In case of chronic appendicitis or appendicular infiltrate, surgery to remove appendicitis is performed as planned.
Features of chronic appendicitis
Chronic appendicitis: Ultrasound diagnosis
A chronic course is extremely uncharacteristic of appendicitis, since inflammation of the appendix usually has an explosive nature due to the abundance of lymphoid tissue in the appendix.
However, there are cases of a mild course of the inflammatory process. In this case, appendicitis remains undiagnosed until a sudden exacerbation.
Chronic appendicitis has the same symptoms and causes as acute appendicitis. However, symptoms of the chronic form may be less pronounced or absent altogether.
The most common manifestation of the chronic form of the pathology is rare aching abdominal pain.
Providing first aid for appendicitis
If you suspect appendicitis, you should immediately seek help from a clinic. When the slightest hints appear related to disturbances in the functioning of the organ, thoughts should only be about calling an ambulance, since movement carries a potential danger for the patient. The capacity of the bladder, which is filled with pus, expands to its limit and bursts, which leads to damage to the abdominal cavity. But while waiting for a doctor, it is better to think about providing first aid. Following these steps will help combat pain and prevent harmful consequences.
- First, call your doctor. If you feel very unwell, you can entrust this request to relatives or dial the ambulance number yourself.
- Many patients make one mistake - they use painkillers. Despite the fact that appendicitis causes pain, any medications will interfere with determining the correct diagnosis and the danger to life.
- Consumption of food and liquid is strictly not recommended. In case of severe thirst, a maximum of two sips is allowed.
- The most dangerous actions include eliminating pain with a heating pad. Due to the heat, the inflammation will intensify and the appendicitis may rupture. This risk is unjustified.
- Before help arrives, you should take care to ensure peace and assume a horizontal position. If the pain goes away, do not postpone your visit to the clinic.
By performing this series of actions, you can reduce the symptoms appendicitis to maintain health and life. They must be followed by adults and children. Appendicitis can be caused by various reasons, so it is important to monitor your well-being and focus on emerging symptoms .
Diagnostics
Chronic appendicitis: surgical treatment
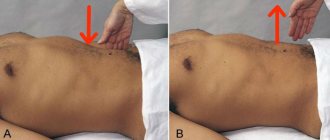
Diagnosis of appendicitis always begins with identifying complaints and examining the patient. The doctor will look for tenderness in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen. In a pregnant woman, pain may occur slightly above the standard area.
With perforation, the abdomen will be slightly distended and tense. There are several diagnostic tests for appendicitis. First, the doctor will order a complete blood test, the results of which will determine the presence of a bacterial infection.
Further actions will depend on the result of the analysis and the patient’s condition. Other laboratory tests:
- C-reactive protein test.
- Liver and pancreas tests.
- Urinalysis (to exclude urinary tract pathology).
- HCG analysis (exclusion of early ectopic pregnancy in women of childbearing age).
- Test for uric 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA).
Instrumental studies play an important role in the diagnosis of appendicitis:
Contraindications for laparoscopic appendectomy:
- late stages of pregnancy;
- severe blood clotting disorders;/li>
- undergone operations on the abdominal organs;/li>
- severe cardiovascular and respiratory failure;/li>
- abnormal location of the appendix;/li>
- old age;/li>
- pronounced adhesive process;/li>
- widespread peritonitis requiring sanitation and drainage of the abdominal cavity;/li>
- dense appendicular infiltrate;/li>
- gangrenous appendicitis./li>
Treatment methods
Diet after appendicitis is necessary!
Treatment of acute and chronic appendicitis is almost always limited to surgical methods, since conservative therapy does not eliminate the source of inflammation. The type of surgical intervention depends on the course of the disease and the characteristics of the patient.
If an abscess that has not yet ruptured is detected, the doctor may first prescribe antimicrobial drugs. The doctor then drains the appendix cavity by placing a special tube into the abdominal cavity.
After drainage and treatment of the infection, the patient will undergo an appendectomy, during which the appendix will be completely removed. Draining the appendix and treating infection before surgery helps avoid the risk of abdominal infection during surgery.
A ruptured abscess requires an emergency appendectomy. In this case, every hour matters. An open operation will be performed, since laparoscopy for peritonitis is less effective.
In rare cases, a patient with appendicitis recovers without surgery. Such cases include the chronic form of appendicitis. If normal test results are revealed, treatment will be limited to antibiotics and a strict diet. However, you should not rely on the possibility of non-surgical treatment.
You can learn how laparoscopic surgery for appendicitis is performed from the video:
Treatment of appendicitis at SM-Clinic in Ryazan
The only treatment for appendicitis is surgery - appendectomy.
Surgical intervention for resection of the appendix is performed using an open or endoscopic method.
Highly qualified surgeons who have extensive practical experience operate at SM-Clinic. The surgical department is equipped with all the necessary medical equipment that allows high-precision operations to be performed.
SM-Clinic doctors use a modern and minimally invasive method - endoscopic appendectomy. The operation is performed through small punctures using an endoscope, which even allows the use of local anesthesia.
If appendicitis had no complications, the patient can leave the clinic on the second day. In case of perforation of the appendage or rapid peritonitis, the recovery period can take up to 7 days. During this time, SM-Clinic patients are accommodated in a comfortable hospital and are surrounded by the caring attention of medical staff. Antibiotic therapy can be used to avoid infectious complications.
If you are worried about pain and have alarming symptoms of appendicitis, make an appointment at the SM-Clinic in Ryazan.
Advantages of performing an appendectomy at Euromed Clinic:
- Euromed Clinic is a full-service clinic. Before the operation, if necessary, we will arrange for you consultations with a therapist, cardiologist and any other specialist;
- Our own laboratory allows you to take the necessary tests at once and quickly get results;
- all surgeons at Euromed Clinic are experienced and qualified specialists;
- the operating room is equipped with modern medical equipment;
- use of the latest generation of anesthesia;
- own hospital with modern comfortable rooms;
- experienced surgeons at the clinic use the most modern dressing and suture materials and disposable instruments;
- All reusable metal instruments undergo a three-stage sterilization system and are then placed in vacuum packaging to ensure the sterility of the instrument.
You can make an appointment at a convenient time with a surgeon at Euromed Clinic by calling + 7 812 327 03 01 or online.
Preparing for an appendectomy:
In acute appendicitis, preparation for appendectomy is carried out promptly; as a rule, the condition of the patient's cardiac and respiratory systems is assessed.
For a planned operation , the results of blood tests, urine tests, fluorography, and an electrocardiogram are required. Women need to be examined by a gynecologist to rule out inflammatory processes that can lead to complications.
You should not take food or water for at least six hours before surgery. In case of laparoscopic surgery, it is necessary to first perform an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
Recovery after laparoscopic appendectomy
After appendectomy using the laparoscopic method, restoration of work capacity and return to a normal lifestyle occurs faster. As a rule, after 1–2 days the patient is discharged from the hospital. After the operation, the surgeon will prescribe antibacterial therapy and give recommendations on diet and physical therapy to quickly restore the body.
At Euromed Clinic, surgeons perform both open and laparoscopic appendectomies.