Sexual diseases in women are serious pathologies, extremely dangerous with serious consequences in the absence of timely treatment. They are provoked by various microorganisms: viruses, bacteria, parasites, fungi. These are not only sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea, syphilis, etc.), but also infections of the genitourinary organs (chlamydia, candidiasis, etc.).
A feature of sexual diseases is the absence of clearly defined symptoms, which is why they are often called hidden. A woman may not even suspect that she is infected for a long time. Symptoms are determined by factors such as the type of infection, the degree of damage to the genitourinary system and the body as a whole. Therefore, the manifestation of symptoms of sexual diseases is very diverse.
Syphilis
The content of the article
Typically, syphilis in women appears 2-4 weeks after infection, sometimes this period is reduced to 9 days or extended to 6 months. Clinical manifestations are divided into 3 stages: primary, secondary and tertiary.
The disease begins with the formation of a syphilitic ulcer - a flat, compacted papule - at the site of penetration of the pathogen:
- on the mucous membrane of the vagina, labia;
- on the nipples of the mammary glands;
- on the oral mucosa;
- in the corners of the lips;
- on the skin of the face.
The formation is painless, so many women do not even suspect its appearance when it is located inside the vagina and hidden from view. For this reason, syphilis is often diagnosed only in the secondary period. Over time, the papule turns from a small formation measuring 1-3 mm into a round or oval red ulcer with a diameter of up to 2 cm.
It has a dense structure and is moist to the touch. In the center the ulcer is dirty yellow in color, which resembles a purulent mass.
Symptoms of primary syphilis:
- enlarged lymph nodes near the sites of syphilitic ulcers (pelvic, submandibular or axillary). This occurs 5-7 days after the formation of hard chancre. They are painless, mobile, and can reach the size of a walnut;
- general malaise of the body: increased body temperature, fever, pain in bones and joints, weakness;
- copious thick discharge with a pus-like consistency and an unpleasant odor, sometimes causing itching and burning;
- menstrual irregularity, characterized by unpleasant sensations during bleeding.
Only 3-4 weeks after the formation of syphilitic ulcers, the RW blood test shows a positive result.
Diagnostics at the MOSMED clinic
Diagnosis of diseases of the reproductive system in women, carried out in a timely manner by highly qualified specialists, is the key to successful and effective treatment of these pathologies. Our clinic “MOSMED” provides all types of diagnostic measures to its patients. These include: primary examination by a gynecologist (history taking, palpation, visual and gynecological examination), colposcopy, smears from the vagina and cervical canal, cytological and histological examination, tissue biopsy, ultrasound, computed tomography, magnetic resonance examination of the pelvic and abdominal organs , blood and urine tests, hysteroscopy, diagnostic laparoscopy and other types of instrumental and laboratory diagnostics.
Symptoms of secondary syphilis
The development of the secondary stage begins 2 months after the formation of compacted papules. The following symptoms may be observed:
- general malaise: headache, tinnitus, dizziness, poor appetite, high body temperature (up to 380C), pain in bones and joints, insomnia, nausea, vomiting, confusion. Speech disturbances and epileptic seizures may occur;
- dysfunction of internal organs (in 25% of cases): damage to the myocardium, liver, stomach, kidneys, membranes and blood vessels of the brain;
- loss of hair, eyelashes and eyebrows. Hair growth resumes after 1-2 months;
- the appearance of condylomas on the genitals and in the anal area;
- the occurrence of rashes on the skin, including the palms and soles of the feet, and mucous membranes.
The following types of rash are distinguished:
- syphilitic roseola - pink or pale pink flat spots from 0.5 to 1 cm in diameter. Localization – trunk and limbs;
- lenticular syphilide - copper-red round formations with a dense structure, rising above the skin;
- meliary syphilide - small dense formations with a diameter of up to 2-2.5 mm. They are brown in color and localized on the skin of the body. As a rule, such papules accumulate and form rings, arcs or plaques;
- coin-shaped syphilide - large red or brown formations with a diameter of up to 2.5 cm, slightly raised above the skin;
- weeping syphilide - eroded formations. They are moist, round in shape, and cause moderate itching. Localization – groin area and axillary folds;
- Condylomas lata are soft, pale pink formations that rise above the skin and are similar in appearance to papillomas. Localization – perineum and area around the mouth;
- pustular syphilide - small purulent formations with a yellowish crust at the end. Localization - on the skin of the trunk, limbs and face.
Usually after 3-5 weeks the rashes suddenly disappear, leaving no trace, even if no treatment was carried out. This period is called secondary latent syphilis. This stage lasts up to 5 years. During this time, relapses of the disease are observed, the rash appears again, but later also disappears on its own.
The course of the first wave of rashes is pronounced: multiple skin lesions, formations of a bright shade. Subsequently, darker elements are observed, often accumulating in groups.
How do gynecological diseases occur in women?
As for infectious diseases, especially in an advanced stage, they can provoke acute gynecological pathologies. If the symptoms are erased and were not noticed in time, such diseases often develop into an advanced chronic form.
Tumor pathologies and diseases associated with the endocrine system are distinguished by their duration and the complete absence of direct signs. They can only be identified by examining a gynecologist and undergoing tests.
Women, regardless of their area of work, health or social status, are recommended to undergo a preventive examination every six months.
The medical services of the Confidence Center will help you forget about illnesses and health problems, giving you back a full life.
The reasons for the appearance of pathologies include hormonal disorders, any anomalies in the development of the genitourinary system, as well as external factors. Moreover, the last group is one of the most numerous:
- early sexual activity
- non-compliance with intimate hygiene standards
- frequent change of sexual partners during unprotected sex
- infectious foci
- stress, nervous overexcitation, overwork, insomnia
- uncontrolled and unprescribed use of antibiotics
- weakened immune system
- irregular, unbalanced diet
- frequent esophageal disorders, uncontrolled diets and underweight (excess) weight
- incorrectly selected hormonal contraceptives
- frequent abortions
- various gynecological procedures, including surgical interventions.
Infectious diseases are the easiest to spot. A feeling of discomfort appears, the discharge intensifies, acquiring an uncharacteristic odor and color. This may be due not only to a change in sexual partner, but also to hypothermia, or the use of a new intimate hygiene product.
Other diseases are more difficult to recognize. For example, women may associate a disruption in the menstrual cycle with stress or the absence of a permanent partner, although this symptom may indicate a serious hormonal imbalance. If inconsistent and not abundant bleeding occurs, it is possible to diagnose polyps or ectopia of the cervix.
Symptoms of tertiary syphilis
This type of disease is diagnosed extremely rarely. It develops 4-5 years after infection and is characterized by damage to the skin, mucous membranes, bones and internal organs. Over time it leads to death.
The symptoms are as follows:
- the appearance of brown or red-brown plaques on the skin. They have an uneven outline, rise above the skin, and are covered with ulcers and crusts. Localization – arms, back, face;
- formation in the subcutaneous tissue of an isolated gumma - a hard node the size of a walnut and an ulcer in the center. It usually occurs on the scalp, chest, face, and sometimes on the mucous membranes of the mouth, larynx and nose. In the latter case, tissue destruction and deformation of the palate occurs. Against this background, a number of complications develop:
- the nasal septum is destroyed and the nose is deformed;
- hoarseness and hoarseness appear;
- tongue mobility is impaired.
- damage to the nervous, vascular and skeletal systems, which manifests itself in the form of syphilitic meningitis, hydrocephalus, progressive paralysis;
- deformation and dysfunction of internal organs (liver, kidneys, lungs, heart).
What are the dangers of diseases?
Everyone has long known that any disease, be it the same banal cold, is fraught with serious consequences and complications if they are not treated. The same applies to diseases of the reproductive system in women. The worst complication of these pathologies for a woman is infertility. After all, those organs that are responsible for reproductive function are affected. And if the problem is left unattended, then a woman’s chances of becoming pregnant and bearing a child decrease more and more over time. And even if conception occurs, pregnancy always threatens with some pathological complications, including miscarriage or death of the fetus inside the womb. And the sooner a woman turns to professionals for help, the better for her health and ability to have children.
The first signs of the disease
The first classic manifestation of gonorrhea is discharge. As a rule, they have a thick consistency, yellow or white color, an unpleasant odor, and cause itching. Against this background, women often mistake the disease for thrush or nonspecific colpitis, self-medicate and, thereby, erase the clinical picture.
Pain in the lower abdomen and when urinating may occur, and the urge to urinate may become more frequent. This is also often mistakenly blamed on cystitis or hypothermia.
Gonorrheal cervicitis
When the infection is localized in the vagina, the following symptoms are observed:
- yellowish-white discharge with an unpleasant odor;
- itching, burning and tickling sensation in the perineum and vagina;
- pain during intercourse.
In pregnant women, symptoms are more pronounced.
Inflammation of the appendages and uterus
When infection penetrates higher, the appendages and endometrium are affected. In this case it is observed:
- nagging or sharp cutting pain in the lower abdomen;
- purulent discharge mixed with blood;
- increase in body temperature to 38-390C;
- the appearance of signs of intoxication - weakness, malaise, nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite;
- pain during intercourse.
Urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis
When the urethra is infected, the symptoms are as follows:
- frequent urge to urinate;
- cutting pain and burning during urination;
- swelling and redness of the external opening of the urethra, its palpation is painful, purulent discharge from it is possible;
- the appearance of a false urge to urinate.
- Ascending infection affects the bladder and kidneys.
Gonorrheal proctitis
Gonorrheal inflammation of the rectum causes:
- itching and burning in the anal area;
- mucopurulent discharge;
- painful bowel movements;
- false urge to defecate;
- bloody streaks in stool and discharge;
- purulent plaque on the rectal mucosa;
- redness of the anus;
- filling the folds of the anus with pus.
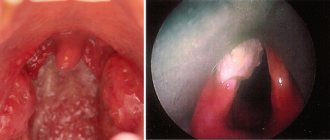
Gonorrheal pharyngitis
Usually hidden under the guise of an ordinary sore throat with characteristic symptoms:
- sore throat (rarely intense);
- pain when swallowing;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling and redness of the tonsils and palatine arches, the appearance of a yellowish-gray coating on them.
However, most often gonorrheal pharyngitis is asymptomatic or manifests itself only as a sore throat and hoarseness.
Gonorrheal stomatitis
It is characterized by the following symptoms:
- inflammation of the gums with the formation of purulent ulcers;
- enlargement of the submandibular lymph nodes.
Gonorrheal conjunctivitis
Infection of the mucous membrane of the eyes causes vivid symptoms:
- swelling of the eyelids, which are literally glued together with purulent discharge;
- redness of the mucous membrane of the eyes;
- in advanced cases - clouding of the cornea and blurred vision.
Chronic gonorrhea
2 months after infection, gonorrhea takes on a chronic form, the clinical picture of which is almost erased. Asymptomatic periods of the disease are replaced by relapses with mild symptoms.
The trigger for an exacerbation can be hypothermia, the onset of menstruation, or termination of pregnancy. Symptoms include discharge and pain in the lumbar region, sometimes spasms can radiate to the legs or abdomen.
Chronic inflammation of the vaginal mucosa due to gonorrhea leads to menstrual irregularities. Bleeding is observed between menstruation, and the cycle itself becomes long and with heavy bleeding. As the disease progresses, adhesions develop in the pelvis.
A distinctive symptom of gonorrhea at this stage is the “morning drop” syndrome: when waking up, a woman may find a cloudy purulent drop at the opening of the urethra.
If left untreated, chronic gonorrhea can lead to infertility.
Trichomoniasis
The incubation period of the disease is 4-14 days, the first signs appear approximately 5 days after infection. Symptoms of trichomoniasis depend on the site of infection (vagina, urethra, and cervix).
Symptoms of “primary” trichomoniasis:
- copious discharge of leucorrhoea from the vagina. They are usually yellowish or greenish in color (may turn gray-green with blood streaks), foaming, and having an unpleasant odor. When combined with gardnerellosis (bacterial vaginosis), a “fishy” odor appears;
- the vaginal mucosa is covered with purulent discharge;
- vaginal discharge upon contact with the skin causes ulcers, irritations and abrasions to appear on it;
- discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse;
- burning and severe itching in the vagina, swelling and redness;
- intermenstrual bleeding from the vagina;
- when the urethra is affected by an infection, frequent urination, burning and cutting pain are observed;
- increase in body temperature to 37.50C;
- general deterioration of health, sleep disturbance;
- rarely – pain in the lower abdomen.
The most common female diseases: symptoms and treatment
Women's health is an important and sensitive topic. Any disease causes discomfort, disrupts the quality of life, and can lead to serious consequences. The situation is complicated by the fact that discussing intimate problems with someone is not always possible. Even when visiting a doctor, women often feel awkward describing their symptoms.
Meanwhile, there is no need to be shy about issues related to the health of the reproductive organs. Most diseases that can cause infertility, the growth of malignant cells and other serious pathologies are easily treated in the early stages. At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor. The specialist will make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Causes of development of female diseases
There are external and internal provoking factors.
External causes of disease development:
- unfavorable ecological environment;
- neuroses, psychological stress, chronic stress and frequent depression;
- promiscuity;
- mechanical injuries of the external and internal genital organs;
- viral and bacterial infections, including STIs;
- early onset of sexual activity;
- incorrect choice of underwear;
- insufficient hygiene of intimate areas;
- local allergic reaction to fabrics, cosmetics;
- frequent and incorrect use of medications, especially oral contraceptives and antibiotics.
Internal provoking factors:
- inflammatory processes in the body that are a source of infection: chronic tonsillitis, sinusitis, pyelonephritis, etc.;
- hormonal imbalance due to gynecological, endocrine diseases;
- anomalies of the anatomical structure of internal organs;
- frequent miscarriages, abortions;
- the presence of systemic diseases (for example, diabetes).
Types of female diseases
According to the etiology of the disease there are:
- Inflammatory. Pathology is caused by the activity of microorganisms: viruses, bacteria, fungi. Diseases such as endometritis, mastitis, colpitis, and thrush are manifested by inflammation.
- Hormonal. Pathologies develop against the background of a hormone imbalance caused by disruption of the glands. This group of diseases is characterized by severe and multiple symptoms. Hormonal changes cause uterine fibroids, endometriosis, menstrual irregularities, and provoke the development of conditional pathologies such as multifollicular ovaries.
- Hyperplastic. The cause of the disease is the growth of a tumor. The tumor can be benign or oncological in nature. Hyperplastic diseases include cervical erosion, cysts, breast cancer, etc.
Let's look at the most common female diseases.
Inflammation of the uterine appendages
The disease develops when pathogens (gonococcus, streptococcus) or conditionally pathogenic microbes enter the body against the background of decreased immunity. Inflammation of the uterine appendages is often diagnosed after hypothermia, installation of an intrauterine device, or artificial termination of pregnancy.
Main symptoms:
- pain in the lower back and lower abdomen from the inflamed organ, which can radiate to the sacrum or anus;
- copious discharge with an unusual odor;
- weakness due to general intoxication;
- elevated body temperature.
Inflammation can spread to the ovaries and fallopian tubes, become chronic, which is more difficult to treat, and affect one or both uterine appendages. If left untreated, complications arise. According to medical statistics, about 20% of women suffering from infertility previously had inflammation of the uterine appendages and were not treated in a timely manner. The pathology also increases the risk of ectopic pregnancy. In advanced cases, purulent processes develop in the internal genital organs.
For diagnosis, an examination by a gynecologist is sufficient.
Uterine fibroids
Myoma is formed from muscle cells and is a benign tumor. The neoplasm does not degenerate, but increases in size. The growth of uterine fibroids causes discomfort and creates the risk of bleeding. During menopause, due to a decrease in the level of female sex hormones, the formation may decrease in size.
Causes of uterine fibroids:
- hormonal imbalance with an increase in the level of estrogen and progesterone in the blood;
- frequent abortions, curettage of the uterine cavity;
- irregular sex life;
- passive lifestyle.
Myoma has no characteristic symptoms. A woman learns about the presence of a neoplasm during a routine examination by a gynecologist or an ultrasound scan. In rare cases, bleeding that is not associated with menstruation is observed. A large tumor makes it difficult to urinate.
Endometriosis
The endometrium is the inner layer of cells lining the uterus. The peculiarity of the tissue is its ability to respond to changes in hormonal levels during the cycle. During the period of ovulation, when the uterus is preparing for fertilization, the endometrium thickens, grows, and a branched network of blood vessels is formed. If conception does not occur, the cells gradually exfoliate and menstruation begins.
Endometriosis is a pathology that is manifested by abnormal growth of the endometrium outside the uterine cavity. The disease has many causes: hormonal disorders, decreased protective function of the body, hereditary predisposition, etc. Endometriosis of the uterine appendages is accompanied by an enlargement of these organs.
There are no characteristic symptoms of pathology. Tissue proliferation does not manifest itself in any way in the initial stages. As the disease progresses, the following signs appear:
- heavy and painful menstruation;
- cycle disorders;
- weakness, general malaise;
- periodic lower back pain;
- spontaneous bleeding not associated with the menstrual cycle.
Mild forms of endometriosis are treated with conservative methods. In severe cases, laparoscopy is performed.
Cervical erosion
Disorders of the cervical mucosa are often diagnosed in women of reproductive age. The disease itself is not life-threatening, but it must be treated to prevent complications. Cervical erosion develops against the background of hormonal disorders, decreased immunity, inflammation, and endocrine diseases. To diagnose and exclude malignant processes, colposcopy is indicated.
Symptoms of pathology:
- pain during sexual intercourse;
- itching and discharge when infection occurs.
Signs of the disease rarely appear. Usually a woman learns about erosion at an appointment with a gynecologist. There are many modern treatment methods that completely eliminate the pathology without damaging or injuring the cervix.
Colpitis
An inflammatory disease localized in the vagina. Colpitis can be caused by any infectious agent: bacteria, virus, fungus. The disease is more often diagnosed in young women who are sexually active.
Symptoms of colpitis:
- pain in the lower abdomen;
- copious discharge that causes itching and burning of the external genitalia;
- rash on the skin of the perineum;
- dysuria (painful urination, frequent urge);
- swelling of the external genitalia.
The disease in its acute form has pronounced symptoms, the quality of life decreases, and the woman feels constant discomfort.
Chronic colpitis is less pronounced. The only symptoms that may be present are discharge and itching. Periods of exacerbation are followed by remissions.
Thrush
An inflammatory disease caused by the growth of the fungus Candida. These microorganisms are present in the microflora of every person, but do not manifest themselves in any way. In order for the fungus to begin to actively grow and cause disease, provoking factors are needed. The aggressiveness of the pathogen can be provoked by long-term use of antibiotics, decreased local immunity, poor hygiene of intimate areas, hormonal imbalances and other reasons.
According to statistics, about 75% of women have experienced symptoms of candidiasis at least once in their lives:
- leucorrhoea of a cheesy nature with a sour odor;
- burning sensation in the perineum after sexual intercourse;
- soreness, itching in the vagina.
Thrush can occur with acute manifestations or be chronic.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and multifollicular ovaries
The disease is more often diagnosed in women aged 25–30 years. The prevalence of pathology is 2.5–8%.
The phenomenon of multifollicular ovaries itself is not a pathology. However, the process of follicle maturation and ovulation is disrupted. Gradually, the ovary becomes covered with multiple formations (non-ovulated follicles) - polycystic disease is formed. Among the causes of the disease are a genetic predisposition to increased levels of androgens and obesity.
Symptoms of PCOS:
- painful menstruation;
- the appearance of acne on the face;
- fluctuations in blood pressure both up and down;
- depressed state, depression;
- alopecia of certain areas or, conversely, excess hair growth (for example, mustache);
- skin pigmentation.
The most characteristic symptom of polycystic disease is irregular menstruation. The duration of the cycle can be several months.
Menstrual irregularities
Failure to menstruate is not a disease - it is a symptom of other pathologies. Normally, menstruation lasts from 3 to 8 days and repeats every 3-5 weeks. A cycle that is too long or too short, heavy or scanty discharge should be considered a symptom of the disease. A doctor's consultation is required. The absence of menstruation during childbearing age is a serious pathology.
The causes of menstrual irregularities are various:
- thyroid diseases, diabetes mellitus;
- hormonal disorders due to dysfunction of the ovaries and pituitary gland;
- chronic fatigue, stress;
- gynecological diseases with acute or chronic course;
- unfavorable ecological environment;
- irregular and/or unhealthy diet;
- malignant neoplasms.
To find and eliminate the cause of menstrual irregularities, a woman is prescribed a comprehensive laboratory and instrumental examination.
Mastitis
The disease develops in the mammary gland. Mastitis is an inflammation of the ducts or functional tissues of the breast. More often, the pathology is diagnosed in nursing women. The vast majority of cases occur in first-time mothers.
The main reason for the development of mastitis is stagnation of breast milk. Liquid is an ideal breeding ground for bacteria. The development of infection causes characteristic symptoms:
- feeling of fullness, tightness, pain in the mammary gland;
- redness and swelling of the skin on the side of inflammation;
- increase in body temperature.
Lack of treatment threatens the appearance of an abscess and sepsis. Timely consultation with a doctor allows you to quickly and completely get rid of mastitis.
Mammary cancer
Cancer is a malignant tumor. In different regions of the world, the prevalence of the disease ranges from 10 to 30%. Breast cancer affects women of all ages, including teenage girls. After 65 years, the risk of developing a malignant tumor increases several times compared to the group of patients under 30 years of age.
The cause of breast cancer can be genetic predisposition, radiation, refusal of breastfeeding after childbirth, lack of pregnancies or too frequent abortions, bad habits, poor environment, endocrine diseases, hormonal imbalance.
Malignant formation in the early stages has no symptoms. You can detect cancer yourself by palpating the breast - small nodules and lumps are detected. Women over 40 years old undergo mammography, which is also an effective method of early diagnosis.
Symptoms of breast cancer are nonspecific:
- frequent mastopathy and breast tenderness;
- menstrual irregularities;
- enlarged axillary lymph nodes;
- swelling of the breast.
At later stages, visible changes appear on the skin of the diseased mammary gland. A so-called lemon peel is formed. The skin changes color and becomes wrinkled. The progression of the disease causes retraction of the nipple, spread of the tumor into the armpits, the appearance of metastases, and ulcerations on the surface of the mammary gland.
Treatment of female diseases
When the first symptoms appear, you should consult a gynecologist. The specialist conducts an examination and takes a swab from the vagina. If necessary, the patient is prescribed additional tests, ultrasound, and other research methods.
Treatment is carried out comprehensively. Therapy is aimed not only at eliminating symptoms, but also at combating concomitant diseases.
Depending on the diagnosis, the patient is prescribed:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The drugs help eliminate inflammation and alleviate the patient’s condition with urinary tract infection. Medicines also have an analgesic effect for menstrual irregularities.
- Antibiotics, antiviral drugs, antiseptics, antimycotics. Medicines with broad or targeted action eliminate the causative agent of the disease. The type and dosage of medications is selected by the doctor after diagnosis.
- Hormonal agents. An effective remedy for restoring the menstrual cycle, treating tumors, inflammation, and concomitant diseases. Hormones are prescribed for recovery after surgical treatment, to prevent unwanted pregnancies, normalize hormonal levels and treat infertility.
- General strengthening drugs. After treatment, a woman needs to take care of her immunity. A course of vitamins is an adjuvant to the main therapy. Additionally, your doctor may prescribe iron supplements, for example, after heavy menstruation or bleeding.
Physiotherapy is actively used in the treatment of gynecological diseases. The procedures are carried out in courses of several days. In cases of severe chronic disease, surgical intervention is indicated. Treatment is carried out in a hospital using modern gentle methods. For example, after laparoscopy, the patient can go home 2–4 days after the operation; there are practically no scars left on the skin.
An important factor in maintaining women's health is regular medical examinations and preventive examinations by a gynecologist.
Diagnosis and treatment of female diseases in Moscow
MedEx Personal Medicine Clinic provides the opportunity to consult a gynecologist and undergo the necessary examinations in one place and in the shortest possible time. Don’t put off visiting a doctor—women’s diseases are best treated at an early stage.
Chlamydia
Chlamydia is an insidious disease, since in 6% of cases it is asymptomatic, which does not mean safety. The incubation period is 2-4 weeks, after which symptoms may appear:
- itching and burning on the genital mucosa;
- white or yellowish mucopurulent discharge with a sharp, unpleasant odor;
- increase in body temperature to 37-37.50C;
- minor or intense pain in the lower abdomen, in the lumbar and groin areas, intensifying before menstruation, with sudden movements and physical activity;
- when the mucous membrane of the urethral canal is infected: frequent urination, pain, itching and burning during urination, cloudy urine;
- discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse;
- slight bleeding during or after sexual intercourse;
- erosion of the cervix, small ulcerations on it and spotting;
- in advanced cases - a violation of the endocrine function of the ovaries and the ovarian-menstrual cycle, as a result of which menstruation becomes irregular, painful, rare, abundant or, conversely, scanty.
Often, with a long asymptomatic course, the only sign of the disease is infertility.
Actinomycosis
This disease is quite rare. At the initial stage, the symptoms of actinomycosis are mild and often resemble an inflammatory process.
Observed:
- increase in body temperature up to 400C;
- sharp or aching pain in the lower abdomen and iliac region.
As the disease progresses, dense, painless infiltrates form. All pelvic organs are involved in this process, deformation changes occur in the uterus, appendages, intestines, rectum with hyperemia of the mucous membrane and smoothness of the vascular pattern. Large dense infiltrates can compress the intestines and disrupt the functions of the urinary tract.
At the next stage of the disease the following is observed:
- the formation of fistulas with purulent discharge, spreading to the retroperitoneal tissue, bladder, thigh and rectum. In this case, the secreted pus has no odor;
- disturbances of menstrual (acyclic bleeding, absence of menstruation) and reproductive function.
In the chronic form of the disease, adhesions and scars appear.
Uterine fibroids
Uterine fibroids are one of the most common benign tumors in women. It often occurs precisely at the most active flowering age - after 30-35 years. The proliferation of cells that form a myomatous node occurs for various reasons. This may be a hereditary predisposition, hormonal imbalance. Myoma can occur in response to a negative impact, for example, after a serious inflammatory process.
The tumor forms “quietly”, without any special symptoms. Only a doctor can detect it during a gynecological examination. To clarify the diagnosis, it is necessary to perform an ultrasound; sometimes CT and MRI are used. After the examination, the doctor determines the further treatment strategy. Most often it is non-operative and combined.
An indication for surgery may be the “term” of fibroids: a tumor over 12 weeks must be removed. Tumors that grow too quickly, cause excessive bleeding, and therefore can cause anemia, are also surgically removed.
It is important to remember that the presence of fibroids can affect the ability to bear a child: it is more difficult for a fertilized egg to attach to the wall of the uterus.
Mycoplasmosis
In 10-20% of cases, this disease is asymptomatic until it is activated by various stress factors: abortion, hypothermia, nervous strain, etc. The incubation period ranges from 5 days to 2 months, with the first signs appearing approximately 7-14 days after infection.
Mycoplasmosis does not have clearly defined specific symptoms; they depend on the clinical form of the disease. The pathology can occur in the form of vulvovaginitis, cervicitis, endometritis, salpingitis, oophoritis, adnexitis, urethritis, cystitis, pyelonephritis.
The following clinical picture is observed:
- if the vagina and cervix are affected: yellow or gray mucous discharge, itching and burning during urination, discomfort and pain during or after sexual intercourse;
- with damage to the uterus and appendages: nagging pain in the lower abdomen and lower back, intermenstrual bleeding, menstrual irregularities;
- when the urethra is infected: frequent urination, pain and burning during it, false urge to urinate, increased body temperature up to 38.50C, cutting pain in the lower abdomen, pain in the lower back;
- with intestinal damage: pain during defecation, false urge to defecate, sometimes - an admixture of mucus in the stool;
- if the respiratory system is affected (does not apply to sexual diseases, but can become a complication of genital mycoplasmosis): sore throat, nasal congestion, inflammation of the ligaments, bronchitis, fever, weakness, sweating, long-lasting cough with sputum.
Women's diseases: types and symptoms
Gynecological diseases are conventionally divided into three large groups:
- Inflammatory diseases;
- Hormone-dependent pathologies;
- Diseases of hyperplastic, dystrophic and tumor nature.
Among the gynecological diseases of an inflammatory nature, the following are distinguished:
- Purulent-inflammatory Vulvitis, colpitis, endometritis, adnexitis, pelvioperitonitis, etc.;
- Sexually transmitted diseases Gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chlamydia, ureaplasmosis, candidiasis;
- Viral Genital herpes, papillomavirus infections, cytomegalovirus infection, HIV infection.
Disturbances in the body's endocrine system lead to pathologies of puberty (delayed or premature sexual development, sexual hermaphroditism, menstrual irregularities, abnormal development of the genital organs). This also includes diseases such as pathologies of the menstrual cycle (premenstrual syndrome, amenorrhea, algomenorrhea), ovarian dysfunction, lack of ovulation, dysfunctional uterine bleeding, etc.
The third group includes such serious diseases as benign and malignant neoplasms in the genital organs, fibroids, hyperplastic and dystrophic changes in the cervix, in particular erosions and pseudo-erosions.
Ureaplasmosis
In 70-80% of cases, there are no clinical manifestations of this disease, therefore, as a rule, it is detected during the diagnosis of another disease. Ureaplasmosis has no specific symptoms and during periods of exacerbation it manifests itself as an inflammatory process. The incubation period can last from several days to several months.
The symptoms of the disease are as follows:
- urethritis (inflammation of the urethra): pain and burning in the urethral area, while the pain increases sharply when urinating, inflammation of the mucous membrane of the external urethral os, frequent urination;
- mucous discharge from the vagina and urethra. They are usually quite scanty, odorless and colorless. If the inflammatory process has already started, the discharge may become greenish or yellowish and take on a sharp, unpleasant odor;
- painful and uncomfortable sensations during and after sexual intercourse;
- bloody discharge from the vagina after sexual intercourse;
- aching or nagging pain in the lower abdomen. If the disease has caused complications in the appendages and uterus - pain in the lower abdomen of a cutting nature;
- in acute form: increase in body temperature to 37-37.50C; weakness, fatigue, decreased performance;
- in the chronic form: infertility, spontaneous miscarriage, pathological course of pregnancy, treatment-resistant urethritis, vaginitis, endocervicitis, adnexitis.
If the infection occurs during oral sex, ureaplasmosis can be hidden under the “mask” of a sore throat: plaque appears on the tonsils (tonsils), painful sensations in the throat, it is difficult and painful to swallow, etc.
CLASSIFICATION OF INFLAMMATORY PROCESSES DEPENDING ON THE LOCALIZATION OF THE PATHOLOGICAL PROCESS.
| Definition | Localization | Decoding |
| Vulvitis | external genitalia (vulva) | “Vulva” (lat.) |
| Vulvovaginitis | Inflammation of the vagina and vulva | Simultaneous inflammation |
| Bartholinitis | Inflammation of the Bartholin glands (glands of the vestibule of the vagina) | The glands were named after the anotome who discovered them. |
| Colpitis , or vaginitis | Inflammation of the vaginal mucosa | “Vagina”, “colpos” (Latin, Greek) – vagina |
| Metroendometritis | Post-abortion or postpartum inflammation of the uterus | Same as endometritis |
| Pelveoperitonitis | Inflammatory process in the pelvic peritoneum | “Pelvis” (Latin) - pelvis, “peritoneum” (Greek) - peritoneum |
| Salpingitis | Inflammation of the fallopian (uterine) tubes | Salpinx” (Greek) – trumpet |
| Salpingoophoritis , or adnexitis | Inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes (uterine appendages) | “Adnexa” (Latin) – appendages “salpinx” – tube, “oophorum” (Greek) – ovary |
| Endometritis | Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the uterine | Metra, in Greek uterus, endometrium - the inner mucous layer of the uterus |
| Endocervicitis | Inflammatory process in the mucous membrane of the cervical canal of the uterus | “Cervix” (lat.) – neck, “endo” – inside |
Inflammatory diseases, depending on the nature of the pathogen, are divided into nonspecific and specific. Genital infections are specific processes of inflammation (they are caused by Trichomonas, gonococci, Treponema pallidum, mycoplasma, chlamydia, ureaplasma, gardnerella). Inflammation can be simultaneously caused by several microorganisms (combined microflora), caused by bacteria, fungi and viruses. Such inflammation is considered to be specific (syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, tuberculosis, chlamydia, etc.). Inflammation of a nonspecific nature is associated with opportunistic microorganisms (strains that are dangerous under certain conditions), for example: gardnerella (it causes bacterial vaginosis or gardnerellosis), Candida fungi (causes thrush or candidiasis), enterococci, E. coli, streptococci, staphylococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus, Klebsiella. The symptoms of nonspecific and specific inflammatory processes are no different.
Gardnerellosis
The incubation period of the disease is 4-10 days. The first signs of infection are:
- the appearance of a “rotten fish” smell from the vagina. This specific odor is caused by the breakdown of waste products of the infection;
- slight whitish-gray or yellowish vaginal discharge.
- With the development of the disease, the clinical picture is supplemented by symptoms:
- feeling of irritation, itching and burning in the vagina;
- frequent urination;
- pain in the lower abdomen, which indicates an increase in the inflammatory process;
- increasing discomfort and pain during sexual intercourse;
- creamy discharge flowing down the walls of the vagina into the perineum.
After sexual intercourse, the symptoms become more pronounced, since sperm, having an alkaline reaction, serves as a favorable environment for the proliferation of gardnerella bacteria.
Candidiasis (thrush)
The first signs of candidiasis (thrush) appear already 4-5 days after infection or activation of the vagina’s own opportunistic microflora. The clinical picture of this disease is as follows:
- pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse: the vaginal mucosa is destroyed by Candida fungi, becoming inflamed and painful;
- burning and itching in the genital area. These symptoms are worse after urinating or washing;
- swelling and redness of the genitals;
- white coating and copious “curdled” discharge with an unpleasant sour odor. The discharge is mucus with many white dense lumps (a type of curdled mass or curdled milk);
- pain and discomfort when urinating;
- the appearance of a rash on the labia. With thrush, the formation of small burgundy pimples-vesicles with liquid contents inside - vesicles - is often observed. After 1-2 days they burst and small erosions and crusts form in their place;
- general deterioration of condition. The listed symptoms cause nervousness, attacks of bad mood, and sleep disturbances (the burning sensation intensifies at night). Their manifestation is especially intensified after a long walk and during menstruation.
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
The forms of manifestation of the papilloma virus in women are different: genital warts, flat warts, dysplasia, bowenoid papulosis, precancerous condition and cervical cancer. Usually, papillomavirus occurs latently and is detected during a routine examination. Pathological changes in the skin are usually detected 1–6 months after infection.
The incubation period and the main manifestations of symptoms depend on the type of papillomavirus, its quantity (viral load), immune activity and concomitant diseases (sexually transmitted infections).
The following are the main symptoms of HPV in women:
| Symptom | Condylomas acuminata | Dysplasia | Cervical cancer |
| Pain in the lower back, lower limbs and pelvis | No | No | Eat |
| Intermenstrual bleeding | No | Eat | Eat |
| Minor bleeding after intercourse | Eat | Eat | Eat |
| Discharge | Transparent or yellowish-green color with an unpleasant odor | With an unpleasant odor | With an unpleasant odor |
| Itching and burning in the genital area | Eat | Eat | Eat |
| Pain during and after intercourse | Eat | Eat | Eat |
The clinical picture can be supplemented by general signs:
- chronic fatigue;
- periodic weight loss;
- decreased appetite;
- swelling of the lower extremities.
Prevention of gynecological diseases
Prevention of gynecological diseases includes:
- protecting the health of girls from the period of intrauterine development;
- timely treatment of infectious and other diseases;
- timely treatment of the consequences of birth injuries;
- healthy lifestyle, giving up bad habits, hardening;
- compliance with the rules of general hygiene and genital hygiene.
In gynecology, there are several mandatory principles for effective work for the benefit of women. Timely consultation in gynecology is necessary to avoid serious problems in the future, because female diseases, like all others, are treatable the better the earlier they are identified.
Herpes infection (cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex)
Primary herpes
Primary herpes occurs in 5 periods:
- Incubation . Lasts from 2 to 14 days, there are no symptoms;
- Prodromal . General and local manifestations increase: malaise, muscle pain, accompanied by swelling and weakness, increased body temperature to 37-37.50C, possible chills, enlarged inguinal lymph nodes. There is also itching and burning in the genital area, leucorrhoea, painful urination with pain and burning;
- Rash period . The duration of the period is from 7 to 10 days. The appearance on the vaginal mucosa of rashes in the form of bubbles with a diameter of 2-3 mm with liquid contents - vesicles. They accumulate in groups, forming a painful, itchy area. Periodically, the number of rashes increases. General symptoms are mild, local manifestations in the form of itching, burning, swelling and pain persist. They lead to nervousness, attacks of bad mood, sleep disturbances;
- Stabilization period . Lasts about 2-3 weeks. At this stage, the vesicles become cloudy, open and form weeping erosions that are prone to fusion. Sometimes ulcers up to 1 mm deep appear in their place. The affected areas are painful, purulent plaque is possible, there is no bleeding;
- Healing period . Lasts about 2-3 weeks. Local and general symptoms subside. The affected areas dry out, a thin crust forms, under which a new epithelium forms. After a while, the crust disappears, and in its place there is redness, which goes away after complete healing.
The rash is usually localized near the external opening of the urethra, at the vaginal opening, on the labia, on the cervix, in the anus or buttocks.
The total duration of primary herpes is 5-7 weeks.
Recurrent herpes
Recurrent herpes can occur in typical and atypical forms. The typical form is characterized by the same symptoms as primary herpes. Only the total duration is 7-10 days.
The atypical form can be presented in various ways:
| Option | Predominant symptoms |
| Hydropic | Diffuse swelling and redness of the vulva |
| Itchy | The appearance of deep, poorly healing cracks, severe itching of the vaginal mucosa |
| Abortive | Absence of some stages of the disease, regression of rashes in 2-3 days |
| Subclinical | Presence of microsymptoms (itching, superficial cracks) or absence of clinical manifestations |