27.10.2021
Fetal hypoxia is a syndrome caused by a lack of oxygen or impaired tissue oxygen absorption. This is not an independent disease, but a symptom that indicates a congenital or acquired pathology or a complicated course of pregnancy or childbirth. Oxygen starvation in the early stages of pregnancy can slow down the development of the child and lead to abnormalities, and in the later stages it can lead to damage to the nervous system, cerebral edema, kidney failure and other serious pathologies.
Intrauterine fetal hypoxia is detected, according to various sources, in 4-10.5% of cases of pregnancy and childbirth in our country.
Classification of fetal hypoxia
There are acute and chronic fetal hypoxia. The chronic form is observed for a long time and leads to pathologies in fetal development. The most common causes are diseases of the nervous, cardiovascular, endocrine systems of a pregnant woman, post-term pregnancy, multiple pregnancies, intoxication, and infectious diseases.
Acute hypoxia most often occurs during delivery. It can be caused by short or prolonged labor, premature loss of water, placental abruption, uterine rupture and other factors. Acute hypoxia requires immediate action. If she is observed at a late stage and labor has not yet begun, then doctors induce labor or perform a cesarean section.
Determination methods
Ways to determine fetal hypoxia during pregnancy:
- listening to the fetal heartbeat;
- counting movements (each movement of the fetus is counted for 12 hours, the norm is at least 10 movements during this time);
- Ultrasound examination (especially in early pregnancy);
- intrauterine examination (Doppler);
- cardiotocography (CTG) - ECG of the fetus, recording the heartbeat and movements with a special device for some time (from 20 minutes to 1.5 hours);
- laboratory blood tests.
Signs of fetal hypoxia during pregnancy
The gynecologist will be able to understand that the fetus has signs of hypoxia during the examination. The main manifestation at the initial stage will be a rapid heartbeat and increased respiratory activity. Meconium appears in the amniotic fluid.
If a child has severe hypoxia, then the heartbeat, on the contrary, will be slow. Significant oxygen deprivation leads to intracellular and tissue edema as a result of the blood condensing and plasma leaving the vascular bed. Tissue respiration is disrupted, embryo development slows down, and acidosis develops. Circulatory disorders cause tachycardia followed by bradycardia. Due to the increased fragility of the vascular walls, hemorrhages are possible.
A pregnant woman herself can identify signs of fetal hypoxia in the second and third trimester by changes in motor activity: the child behaves restlessly, moves too often and too much, and with progressive oxygen deficiency, on the contrary, practically stops moving. If such symptoms appear, you should immediately consult a doctor for diagnosis.
If chronic fetal hypoxia is suspected, doctors conduct the following examinations:
- listening to the fetal heartbeat
- Ultrasound, Dopplerography;
- cardiotocography, phonocardiography of the fetus;
- amnioscopy and amniocentesis through the cervical canal;
- laboratory tests of blood and urine in a pregnant woman.
Degrees of oxygen starvation
The degree of hypoxia is diagnosed by the degree of disruption of the blood supply to the placenta and fetus. There are three in total:
1st degree
– compensated – does not lead to complications, when signs appear only occasionally, does not require additional intervention.
2nd degree
– subcompensated – when the mother’s body can no longer cope with the emerging signs of hypoxia on its own.
3rd degree
– decompensated – we are talking about severe oxygen starvation, dangerous to the life and development of the fetus.
Fetal hypoxia during childbirth
Hypoxia of the newborn during childbirth can be caused both by congenital pathologies and unfavorable course of pregnancy, and by problems directly during the birth process. The main danger is oxygen starvation of the brain, which leads to its dysfunction and can even cause the death of the baby.
The baby's condition is assessed in the first minute after birth using the Apgar scale. The following indicators are assessed:
- color of the skin
- breathing rate;
- reflex activity;
- heart rate;
- muscle tone.
For each point, 0 to 2 points are given, resulting in a maximum score of 10. If 6-7 points are scored, then mild hypoxia is observed, if 4-5 points - moderate, 0-3 - severe.
The examination is repeated after 5 minutes. In newborns with mild hypoxia, which is not caused by serious pathologies, by this time the indicators return to normal.
How does a cardiotocograph work and what does it show?
This device has the following sensors:
- Ultrasound, which detects the movements of the fetal heart valves (cardiogram);
- Tensometric, determining the tone of the uterus (tocogram);
- In addition, modern cardiac monitors are equipped with a remote control with a button that must be pressed at the moment the fetus moves. This allows you to assess the nature of the baby’s movements (actogram).
Information from these sensors enters the cardiac monitor, where it is processed and displayed on an electronic display in digital equivalent, and is also recorded by a recording device on thermal paper. The speed of the tape drive differs among different types of fetal heart monitors. However, on average, it ranges from 10 to 30 mm per minute. It is important to remember that there is special thermal paper for each cardiotocograph.
example of a CTG tape: above - fetal heartbeat, below - uterine tone values
Consequences of hypoxia in a newborn
A mild degree usually does not have serious consequences. Severe hypoxia can lead to damage to the central nervous system, cerebral edema, convulsions, and areflexia. Damage to the respiratory system leads to pneumopathy and pulmonary hypertension. Problems with the cardiovascular system can be heart and vascular defects.
You can tell that a newborn is suffering from hypoxia by frequent regurgitation, vomiting, and enterocolitis. The consequences of severe perinatal hypoxia are DIC syndrome and secondary immunodeficiency.
How is cardiotocography done?
In order for this study to be informative, the following rules must be adhered to:
- CTG recording is carried out for at least 40 minutes.
It is during this time that certain patterns of rhythm changes can be traced. - A pregnant woman should lie on her side during the examination.
If a pregnant woman lies on her back during CTG registration, unreliable results may be obtained, which is associated with the development of the so-called inferior vena cava syndrome. This condition develops as a result of pressure from the pregnant uterus on the abdominal aorta and inferior vena cava, which may result in disruption of uteroplacental blood flow. Thus, if signs of hypoxia are obtained on CTG performed with the pregnant woman lying on her back, it is necessary to redo the study. - The sensor that records the fetal heartbeat must be installed in the projection of the fetal back.
Thus, the location of the sensor’s fixation depends on the position of the fetus in the womb. For example, with a cephalic presentation of the baby, the sensor must be installed below the navel, with a pelvic presentation - above the navel, with a transverse or oblique presentation - at the level of the umbilical ring. - A special gel must be applied to the sensor
to improve the conduction of the ultrasonic wave. - The second sensor (strain gauge) must be installed in the fundus of the uterus.
It is important to know that you do not need to apply gel to it. - During the study, the woman must be given a remote control with a button that must be pressed when the fetus moves.
This allows the doctor to compare rhythm changes with the baby’s motor activity.
Treatment and prevention of intrauterine hypoxia
The most common causes of intrauterine hypoxia are placental insufficiency, fetal malformations, umbilical cord compression and maternal hypoxia. It is very difficult to help a fetus with hypoxia in utero - before birth you can only monitor the condition and carry out delivery in a timely manner.
One of the main recommendations for the prevention of intrauterine hypoxia for expectant mothers is to spend as much time as possible in the fresh air. Doctors recommend evening walks, preferably not in the city, where the air is polluted and the oxygen content in it is reduced, but in nature. An alternative or additional way to cope with hypoxia is to use an oxygen tank. Just a few breaths are enough to increase the oxygen level in the blood of mother and child. The cans are compact and lightweight, you can carry them with you to work or store them in your car. An additional advantage is that oxygen therapy procedures strengthen the immune system and help cope with toxicosis, relieving nausea, dizziness, and weakness.
The PRANA company offers wholesale purchase of oxygen cylinders of various sizes with delivery throughout Russia. As a manufacturer, we have set minimum prices for oxygen-containing products and guarantee the quality of cylinders.
Main causes of hypoxia
There are four main causes of oxygen deficiency in the fetus: pathologies during pregnancy (for example, a conflict of Rh factors), illnesses of the mother, her bad habits and harmful environmental influences.
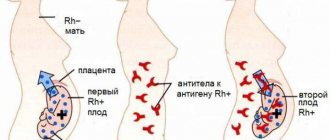
Pathologies during pregnancy . Hypoxia can be caused by postmaturity, entanglement with the umbilical cord, Rh conflict between the blood of mother and child, disturbances in the development of the umbilical cord and placenta, as well as pathologies of the fetus itself:
- intrauterine trauma;
- genetic abnormalities;
- developmental defects;
- hemolytic disease.
Mom's illnesses. The range of pathologies is very wide. One of the most common causes of hypoxia in this case is iron deficiency anemia.
Oxygen deficiency in the fetus can also result from:
- pyelonephritis;
- diabetes;
- diseases of the urinary and respiratory system;
- arterial hypertension;
- endocrine diseases;
- kidney diseases;
- diseases of the immune system.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the consequences of STIs (herpes, chlamydia, gonorrhea, mycoplasmosis, bacterial vaginosis, candidiasis and trichomoniasis), malnutrition, exhaustion and severe toxicosis in the mother.
Drinking alcohol and smoking. Why does the mother’s bad habits often result in fetal hypoxia? It’s all about the effect that the listed substances have on the inner surface of the alveoli of the lungs.
The alveoli have a special lubricant that ensures rapid delivery of oxygen to the blood. Alcohol vapor dilutes this lubricant, causing it to perform its function worse. This is just one of many other harmful effects of drinking alcohol during pregnancy.
Smoking also provokes the development of fetal hypoxia: the tars in tobacco smoke “clog” the alveoli, due to which lubrication is not produced in the required quantity. Smoking contributes to chronic hypoxia - both for the mother and the unborn child.
Environmental factors . Living in an ecologically unfavorable area, working in a hazardous industry, or in the presence of toxic substances in the air can also cause fetal hypoxia. A similar effect is caused by constant stay in rooms with poor ventilation, when the air contains too much carbon dioxide and too little oxygen.
What to do if CTG indicators are borderline between normal and pathological?
When registering a CTG and receiving a questionable result, you must:
- Conduct additional research methods (ultrasound, study of blood flow velocity in the uteroplacental system, determination of the biophysical profile).
- After 12 hours, repeat the CTG study.
- Avoid taking medications that may affect the baby's heart rate.
- Carry out CTG with functional tests:
- Non-stress test - consists of studying the heart rate in response to fetal movements. Normally, after the baby moves, the rhythm should speed up. The lack of acceleration after movements is an unfavorable factor.
- Stress test - characterized by a change in heart rate after administration of 0.01 units of oxytocin. Normally, after this drug enters the body of a pregnant woman, the fetal rhythm accelerates, there is no deceleration, while the basal rhythm is within acceptable limits. This indicates the high compensatory capabilities of the fetus. However, if after the administration of oxytocin the fetus does not experience accelerations, but, on the contrary, heart contractions slow down, then this indicates intrauterine hypoxia of the baby.
- A mammary test is an analogue of a stress test, but instead of administering oxytocin, the pregnant woman is asked to massage her nipples for 2 minutes. As a result, the body releases its own oxytocin. The results are evaluated in the same way as in a stress test.
- Physical stress test - a pregnant woman is asked to climb the stairs of the 2nd floor, immediately after this a CTG recording is performed. Normally, the fetal heart rate should increase.
- Breath-hold test - while recording a cardiotocogram, the pregnant woman is asked to hold her breath while inhaling, while the baby’s heart rate should decrease. Then you need to hold your breath as you exhale, after which the fetal rhythm should speed up.
How is CTG scored?
To ensure that the interpretation of CTG results is not subjective, a convenient system for assessing this type of study has been developed. It is based on studying each CTG indicator and assigning certain points to it.
For ease of understanding of this system, all characteristics of CTG are summarized in the table:
| 2 points | 1 point | 0 points | |
| Basal (basic) rhythm | From 120 to 160 | From 100 to 180 | Less than 100, more than 180 |
| Amplitude | From 6 to 25 | 3-5 | < 3 |
| Variability | > 6 | 3-6 | < 3 |
| Number of acceleration episodes in 40 minutes | >5 | 1-4 | none |
| Decelerations | Not registered | Short-term | Long, heavy |
| Fetal movements | >3 | 1-2 | No |
The interpretation of the results is assessed as follows:
- CTG is considered good if it scores 9-12 points;
- A score of 6-8 points indicates signs of hypoxia; in such situations, daily monitoring and treatment are required.
- Less than 5 points is extremely unfavorable.
Important!
Pronounced pathological changes on CTG may indicate a terminal condition of the fetus. Of course, in such situations, it is absolutely impossible to carry out any functional tests. In these cases, emergency delivery may be required, since delay is very dangerous.
conclusions
{banner_banstat10}
Cardiotocography is rightfully one of the most widely used studies in obstetrics. However, like any other technique, it is effective only if it is applied correctly (in accordance with all standards), as well as with proper interpretation of the results obtained.
Unfortunately, there are still disputes and different interpretations of some complex and dubious cases. For this reason, we should not forget that there are also additional research methods that can either confirm or refute possible concerns.
In addition, CTG results remain relevant and informative for no more than 1 week, which means that the key to a favorable pregnancy is regular monitoring of the condition of the fetus.
How does CTG influence medical tactics?
{banner_banstat9}
The results of the study must be taken seriously. The doctor who evaluates the CTG bears great responsibility. It is for this reason that each film recording cardiac activity must be evaluated by the responsible physician, certified by his signature indicating the time of the study and pasted into the birth history.
A normal cardiotocogram is a sign of correct and careful management of labor.
When receiving a questionable CTG, the doctor has no more than 40 minutes to correct labor activity. At this stage, it is necessary to eliminate all risk factors leading to hypoxia:
- Stop administering “oxytocin” and prostaglandin-based drugs;
- Explain to the woman how to breathe correctly during contractions;
- Determine the position of the fetus and exclude compression of the umbilical cord;
- Perform an ultrasound to exclude incipient placental abruption;
- Administer drugs that improve the rheological properties of blood.
Poor CTG is a good reason to change delivery tactics in favor of emergency cesarean section,
or eliminate the causes of acute hypoxia. Ignoring pathological CTG is absolutely unacceptable, because this can cause fetal death.
In other words, CTG is a serious tool in the hands of an obstetrician.