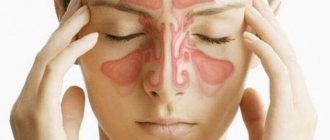
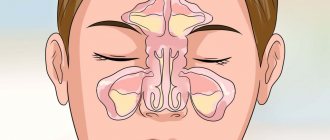
Acute sinusitis is an inflammatory process that occurs in the mucous membrane of the nasal appendages (sinuses), so sometimes the diagnosis of sinusitis is also related to inflammation. This disease is characterized by swelling of the cheeks and purulent discharge, accompanied by an unpleasant odor.
In terms of its symptoms at the onset of the disease, the acute form of sinusitis is very similar to a common runny nose, only the treatment of the disease can be more difficult and lengthy. And the condition itself causes enormous discomfort to the patient and interferes with a full life.
Anatomy of the sinuses
There are 4 types of sinuses in the human skull:
- frontal (in the forehead area);
- maxillary, also known as maxillary (in the area of the cheeks under the eyes);
- ethmoid sinuses, or cells of the ethmoid labyrinth (in the area between the nose and eye);
- wedge-shaped (in the very middle of the skull, behind the eyeballs).
The sinuses are peculiar voids that reduce the weight of the skull, participate in the formation and sonority of the voice, in the process of smell, and also serve as shock absorbers for injuries to the facial skeleton.
They also perform a protective function: when foreign particles and bacteria enter the nasal cavity, the nasal mucosa is irritated, sneezing begins, and the particles are evacuated from the body along with mucus. But if the body’s defenses are weakened, bacteria can enter the sinuses from the nasal passages and cause severe inflammation, which is what we observe during the development of acute manifestations of the disease.
Causes and mechanisms of the disease
Among the main conditions causing inflammation are:
- past viral diseases;
- diseased teeth (caries, pulpitis);
- allergic reactions;
- deviated nasal septum;
- neoplasms and anatomical features of the nasal cavity that interfere with normal breathing through the nose (for example, with enlarged adenoids in children, cysts, polyps);
- the presence of a focus of chronic infection in the body;
- nasal injuries.
The most common cause of the inflammatory process is infection in the sinuses. The acute form occurs, as a rule, under the influence of viruses. The source of chronic inflammation is often bacteria (staphylococcus, streptococcus and others).
In second place are diseases of the nasopharynx. If a patient suffers from frequent runny noses, the mucous membrane is in a constant state of edema, which prevents the release of mucus. As a result, it accumulates and turns into a favorable environment for the proliferation of bacteria, and as a result, inflammation of the sinuses occurs.
People who often suffer from inflammatory diseases of the pharynx also have a constant source of infection in their bodies, so people with chronic tonsillitis always have a high chance of developing sinusitis.
With a deviated septum, air cannot circulate freely in the nasal cavity, and accordingly, the release of mucus is difficult, which is also a common cause of the inflammatory process. Surgery to correct the septum can solve the problem.
The proximity of the maxillary sinuses to the upper jaw made it possible for infection to penetrate from the teeth. Such inflammations are called odontogenic. To avoid them, you need to carefully monitor oral hygiene and treat problem teeth in a timely manner.
Exposure to allergens on the body leads to prolonged runny nose, swelling of the nasal mucosa and narrowing of the channels that remove mucus. As a result, it accumulates and inflammation occurs.
In the absence of proper treatment of the acute form, it develops into a chronic form with characteristic purulent discharge from the nose. To avoid this, it is necessary to carry out therapy at a very early stage.
Why do the maxillary sinuses become inflamed more often?
Among inflammations of the paranasal sinuses, acute sinusitis - inflammation of the maxillary sinuses - is most often diagnosed. And there are several reasons for this:
- the maxillary sinuses are the largest in volume;
- The maxillary sinuses are connected to the nasal cavity using anastomoses - small openings covered with mucous membrane (these openings are quite narrow, and even a slight swelling of the mucous membrane with minor inflammation can make it difficult for mucus to come out of them, and the formed and accumulated mucus in the absence of proper outflow becomes a powerful catalyst, if the inflammatory process develops first in neighboring ones.).
Rating of drugs for the treatment of sinusitis
When compiling the rating, we took into account the results of comparative tests, expert opinions, and customer reviews. They allow you to determine which product will more effectively fight bacteria. Additionally, the following characteristics were taken into account:
- Composition of the drug;
- Release form;
- Duration of treatment;
- Effect speed;
- Side effects;
- Contraindications;
- Price;
- Dosage.
After additional checks of each drug, it was possible to create a rating of medications that can fight sinusitis, eliminate the cause of its occurrence, as well as the consequences.
The best antiviral agents
Types of acute sinusitis
There are catarrhal and purulent forms of sinusitis.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
The name “catarrhal” comes from the medical term “catarrh,” meaning “to flow, drain.” That is, with this form of sinusitis, inflammation of the mucous membrane and its swelling develop quite quickly. Initially, the changes affect only the mucous membrane. Inflammation during sinusitis of this form is accompanied by severe swelling of the mucous membrane - it noticeably increases in size and, as a result, a little later transparent mucus forms. Only thanks to timely treatment, it is possible to prevent the transition of catarrhal forms into purulent sinusitis, which with a high degree of probability can become chronic.
With purulent sinusitis, direct contact of pus with the mucous membrane degenerates it, quite quickly and, what is most dangerous, irrevocably. Thus, with improper treatment or no treatment at all, you can very easily and simply join the army of people suffering from a chronic form of sinusitis.
The cause of the purulent form of sinusitis (acute sinusitis) is bacteria. The secreted mucus contains streptococci, staphylococci, and less commonly pneumococci and fungi, which leads to the appearance of purulent contents in the sinus itself.
Methods for diagnosing sinusitis
Diagnostic procedures for sinusitis are designed to determine the condition of the maxillary sinuses: the degree of swelling of the mucous membrane, the presence and level of fluid in the sinus. For this purpose the following are used:
X-ray of the sinuses
The radiography method of the paranasal sinuses is used most often.
More information about the diagnostic method
MSCT of the paranasal sinuses
A CT scan of the sinuses also uses X-rays. But it allows you to get a more detailed picture of bone structures. This diagnostic method is used, as a rule, for chronic sinusitis.
More information about the diagnostic method
Ultrasound of the sinuses
An ultrasound of the nasal sinuses is usually performed if an x-ray is undesirable (during pregnancy, examination of children, or during a repeat examination). Ultrasound can be performed using the Sinuscan ultrasound diagnostic device.
MRI of the sinuses
MRI of the sinuses is used if it is necessary to evaluate the condition of the sinus mucosa.
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Reasons for the development of sinusitis
Acute sinusitis can be caused by the following factors:
- colds;
- viral infections: ARVI, measles, influenza, etc.;
- allergic reactions;
- damage and injury to the nose;
- untreated teeth, tooth roots entering the cavity of the maxillary sinus, inflammation of the gums.
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish two ways of infection entering the maxillary sinuses: when the infection penetrates from the nasal mucosa into the maxillary sinus or when the infection develops directly in the maxillary sinus through blood flow and general inflammation.
Sinusitis (in addition to bacteria) can be provoked by factors that interfere with normal air circulation and the release of mucous masses from the sinuses. These include:
- deviated nasal septum;
- adenoids;
- cyst;
- polypous formations;
- and etc.
Unfavorable environmental conditions - dust, gas pollution, work in hazardous industries - can also disrupt the process of the release of mucous masses from the sinuses and further treatment.
Is sinusitis contagious?
Sinusitis itself is not contagious. It is not transmitted by airborne droplets. This is an inflammation that occurs inside the maxillary sinuses. But it is worth noting that sinusitis often occurs as a complication against the background of colds and ARVI, that is, on the mucous membranes of the human nasopharynx there is a pathogenic microflora that can be transmitted from a sick person to a healthy one. In this case, a healthy person may become ill with ARVI, but this does not mean that he will develop sinusitis. If the causes of sinusitis were allergies, sinus injuries, deviated nasal septum, diseases of the teeth of the upper jaw, then it is not contagious to others.
Symptoms
Symptoms of acute sinusitis include:
- pain in the cheek area under the eyes;
- pain in the orbital region;
- pressure on teeth and toothache;
- headache;
- pain when tilting the head forward (the pain “radiates” to the back of the head and forehead; the nature of the sensation resembles the pain of a migraine; as a rule, the pain intensifies in the evening);
- difficulty breathing through the nose;
- a feeling of continuous nasal congestion (it may be accompanied by itching, sneezing, dryness);
- the nature of the mucous discharge helps determine the severity of the disease (transparent discharge in a mild form of the disease and thick green discharge in a purulent form);
- bad odor from the nose and mouth (the nose and pharynx are connected to each other; with sinusitis, pus accumulates in the sinuses and causes bad breath; it is difficult to get rid of it, even after brushing your teeth);
- eyes become watery;
- nasality appears in the voice;
- impaired sense of smell;
- high body temperature from 37.5 to 39°C - the body’s response to the presence of infection;
- increased fatigue, decreased appetite, sleep problems;
- swelling of the eyelids, cheekbones, and areas near the nose;
- pain when pressing on the area where the sinuses are located.
Symptoms of sinusitis in an adult
An acute disease is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Unpleasant painful sensations appear around the nose, under the eyes in the cheek area. In the morning the pain is much weaker, but in the evening it intensifies. Pain also appears when turning the head or tilting it to one side.
- The nose is very stuffy. Relief occurs only for a short period of time. Patients notice that their voice begins to sound nasal.
- Greenish nasal discharge. If the nasal passages are completely blocked, there may be no discharge.
- Increased body temperature.
- Lethargy, poor appetite, insomnia are signs of poisoning of the body with waste products of bacteria.
If treatment for the acute form begins late or is chosen incorrectly, the disease can become chronic.
In the chronic form, the signs of the disease are not so pronounced. But persistent nasal congestion, sore throat and cough (since mucus continuously flows down the back wall of the throat), pain under the eyes that occurs with a certain frequency, as well as high fatigue can indicate the presence of chronic inflammation.
Treatment of chronic diseases must also be carried out under the supervision of a competent doctor.
Are complications possible with acute sinusitis?
With delayed treatment or lack of properly selected treatment, acute sinusitis can become chronic and lead to the development of a number of other serious complications.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Chronic inflammation in the sinuses is the most common complication of acute sinusitis. The chronic form requires long-term competent treatment.
An infection from the maxillary sinuses can enter the middle part of the ear and provoke a severe inflammatory process there (otitis media). Otitis is accompanied by sharp pain in the ear, hearing loss occurs, and body temperature may rise.
Diseases of the ternary nerve are associated with sinusitis, since it is located close to the source of inflammation. This condition is characterized by shooting pains in the face. Patients describe the sensations as electric shocks. Such neuritis is extremely difficult to treat.
Complications of sinusitis associated with the eyes are possible. With inflammation, we observe swelling of the eyelids, pain when pressing on the eye socket, and vision may begin to “deteriorate.” Pus entering the eye socket and vein thrombosis can lead to loss of vision and even loss of the eye itself (panophthalmitis).
The worst consequence of sinusitis is inflammation of the lining of the brain (meningitis). A similar complication develops with prolonged and incorrect attempts to independently cure sinus inflammation.
Other common complications of sinusitis in adults: periostitis of the jaw, meningoencephalitis, sinus thrombosis, up to generalized blood poisoning (sepsis).
Remember, sinusitis with complications is much more difficult to treat, so it is very important to promptly seek qualified help from an ENT specialist.
Sinusitis: symptoms
In order to recognize the problem in time and contact an ENT doctor, it is important to be able to recognize the signs of sinusitis.
A distinctive sign of sinusitis is headaches and pain in the maxillary sinuses. The patient experiences pain in the cheek area under the eyes. He feels an unpleasant pressure on the bridge of his nose. By evening the pain becomes much stronger. Discomfort in the sinus area also increases when turning or tilting the head. Painful sensations are explained by the presence of pus in the sinuses. The purulent masses become crowded, and they put strong pressure on the walls of the sinuses. With severe inflammation, pain can radiate to the jaw, temples and other parts of the face.
The disease is often accompanied by nasal discharge. At the initial stage they are transparent, but quickly acquire a greenish tint and become viscous. Green snot indicates a bacterial infection in the nasal cavity. There may be no discharge at all if the sinus openings are completely blocked and the mucus and pus cannot come out.
Many patients experience an increase in body temperature to high levels (38.5°).
The patient also has:
- loss or deterioration of sense of smell;
- swelling in the area of the eyelids, eyes, nose;
- nasal voice;
- nasal congestion;
- weakness, fatigue, lack of performance.
These were the general signs. If you have sinusitis, the symptoms will depend on the type of disease.
Sinusitis happens:
- According to the location of inflammation:
- unilateral (right- or left-sided);
- bilateral.
- According to the nature of the flow:
- sharp;
- chronic.
- traumatic;
- allergic;
- odontogenic;
- rhinogenic;
- hematogenous;
- viral;
- bacterial;
- fungal.
- catarrhal;
- exudative;
- purulent;
- polyposis.
There are many classifications of the disease. Let's look at the most common types of sinusitis and the symptoms of these forms.
Acute sinusitis.
The acute form develops very rapidly. They are very intense and knock the patient out of his usual life. Body temperature rises. It happens that it reaches 38-39°C. This is explained by the fact that pathogenic organisms in the sinus begin to actively multiply, and the human body tries to cope with them on its own.
The second characteristic sign of the disease is pain. The cheeks hurt in the sinus area, the bridge of the nose hurts, and pain in the jaw may appear. If the patient tilts or turns his head, sneezes or coughs, the pain intensifies. In the evening this condition worsens.
In some cases, photophobia occurs. Mucus is discharged from the nose. If bacterial flora is raging in the sinus, the discharge is green, which indicates a purulent process.
It becomes very difficult to breathe through the nose, severe congestion occurs. The patient's eyelids swell. The patient feels overwhelmed, lethargic, and cannot carry out his usual activities.
Chronic sinusitis
The chronic form of the disease occurs if the acute form is not fully treated. Chronic inflammation is a sluggishly developing process that lasts more than a month. The symptoms are blurred and clearly manifest themselves only during an exacerbation.
During an exacerbation, the patient complains of the following symptoms:
- low-grade body temperature (up to 37.5°C);
- nasal congestion, which may go away during the day;
- purulent discharge from the nasal cavity;
- pain not only in the bridge of the nose, but also in the jaw area;
- nasal voice;
- weakness, fatigue.
During the period of remission, the disease is more difficult to recognize. Symptoms are not so intense:
- nasal congestion;
- accumulation of mucus in the throat, which drains from the nasopharynx;
- headache;
- swelling of the eyelids in the morning after sleep;
- impaired sense of smell.
Traumatic sinusitis
The cause of the development of this form of the disease is severe trauma to the skull, which is often accompanied by damage to the nasal septum. Due to heavy bleeding, blood clots can get into the maxillary sinuses. If the problem is not identified in a timely manner, an infection may develop and suppuration may develop. Polyps and growths can form in a sinus that is inflamed after an injury.
The patient's body temperature rises and headaches appear. The inflammatory process can spread to neighboring tissues, causing the formation of phlegmon or abscess (suppuration). Treatment of this form is carried out inpatiently.
With chronic inflammation, a person complains of pain in the sinuses, congestion, and nasal discharge. Swelling of the eyelids and swelling of the cheek on the side of the affected sinus may be observed. A fistula (fistula) may form in the infraorbital region with pus discharged from there. Patients with this diagnosis undergo sinus surgery to remove fistulas and polyps.
Allergic sinusitis
The cause of the allergic form of the disease is contact of the sinus mucosa with an allergen (an irritating substance).
The disease resembles a manifestation of classic allergies. The main features of this form are:
- persistent cough that does not go away even after taking antitussive medications;
- impaired nasal breathing;
- nasal congestion;
- mucus from the nose;
- bouts of sneezing;
- swelling;
- itching in the eyes.
Irritating substances can be dust, animal hair, pollen, cosmetics, etc. It is necessary to identify the allergen as quickly as possible and eliminate its effect on the body.
Odontogenic sinusitis
Infection in the sinus can come not only from the nasopharynx. In the odontogenic form, pathogenic microflora penetrates the sinus from the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw. The disease can occur in acute and chronic forms with symptoms characteristic of these types of inflammation. In the case of odontogenic sinusitis, therapy by an ENT doctor alone is not enough. It is necessary to contact a dentist and deal with the “problem” teeth - treat them or remove them.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
Catarrhal sinusitis
The catarrhal form is characterized by inflammation and swelling of the sinus mucosa. The patient has:
- weakness, deterioration of health;
- runny nose;
- nasal congestion;
- slight increase in body temperature (sometimes there is no temperature).
This is the initial stage of inflammation. If it was not possible to diagnose the disease during this period, the catarrhal form easily turns into a purulent form. At this stage, few patients turn to an otolaryngologist, since the disease resembles a cold, and many begin to treat themselves, wasting time.
Exudative sinusitis
With this form, exudate (inflammatory fluid) forms and accumulates in the sinuses. The main symptoms of the disease are:
- pain in the sinuses, headaches that get worse when moving the head;
- thick nasal discharge;
- nasal congestion;
- temperature increase;
- problems with smell;
- deterioration of health.
To prevent the disease from passing into a purulent stage and complications arising, you need to contact an ENT specialist immediately when the first signs of inflammation appear.
Purulent sinusitis
The purulent form of the disease develops when a bacterial infection joins the inflammation. Pus accumulates in the sinuses and cannot come out.
The patient is concerned about the following symptoms:
- high body temperature;
- sinus pain and headaches become very intense;
- loss of smell;
- nasal discharge with an unpleasant odor.
This is a dangerous form of the disease. After all, any concentration of pus near the brain can lead to serious consequences, including death.
Polypous sinusitis
In the polypous form of the disease, changes occur in the mucous membrane of the sinuses. It grows and polyps form, which increase in size and “descend” into the nasal passages. Because of this, the patient begins to have problems with nasal breathing, and he begins to breathe mainly through the mouth. In this case, surgical removal of polyps brings a positive result.
Rhinogenic sinusitis
The most common route for infection to enter the maxillary sinuses is from the nasal cavity. This route of infection is called rhinogenic. Hence the name of this type of sinusitis – rhinogenic.
Rhinogenic sinusitis usually develops against the background of acute rhinitis - inflammation of the nasal mucosa as a complication after influenza, ARVI and other acute respiratory viral diseases.
Hematogenous sinusitis
Hematogenous sinusitis is an inflammatory process in the maxillary sinuses that develops when an infection enters the sinuses through the bloodstream. This type of sinusitis can be a complication of measles, diphtheria, scarlet fever, syphilis, and tuberculosis.
Viral sinusitis
The cause of viral sinusitis is a viral infection in the maxillary sinuses. Most often this happens with acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections. With this form of the disease, the mucous membranes of the nose and sinuses swell, but with proper symptomatic therapy, the inflammation subsides within a couple of weeks.
Bacterial sinusitis
Bacterial sinusitis occurs when bacteria (usually staphylococcal, streptococcal, and pneumococcal infections) become active in the sinuses. As a rule, the inflammatory process debuts in the nasal mucosa - acute rhinitis, or runny nose, develops. If it is not treated in time, conditions favorable for the growth of bacteria appear in the maxillary sinuses. Pathogenic flora begins to lead active life in the sinuses, causing a severe inflammatory process in them.
Fungal sinusitis
The cause of fungal sinusitis is a fungal infection. There is always a certain amount of fungi in the human body that do not manifest themselves in any way and do not affect human health. But under certain conditions they can become active and cause fungal sinusitis. Such provoking factors include:
- uncontrolled use of antibiotics;
- weakened immune system;
- structural features of the nasal cavity;
- hormonal changes;
- foreign object in the nose.
The distinctive symptoms of fungal sinusitis are white, yellow or brown nasal discharge, as well as a bluish tint to the nasal mucosa.
How is diagnosis carried out?
Treatment of acute sinusitis in adults and children must be carried out under the supervision of an experienced otolaryngologist.
At the appointment, the ENT doctor will collect anamnesis and conduct an examination of the nasal cavity. Painful sensations when palpating the area under the eyes at the level of the cheeks will indicate the presence of an inflammatory process in the sinuses.
A reliable diagnostic method is x-ray examination. But young children and pregnant women are not prescribed x-rays. They are shown CT and ultrasound examination of the sinuses - sinus scanning.
To obtain complete information about the disease, rhinoscopy and endoscopy of the nasal cavity and nasopharynx are performed.
Sinusitis: treatment
Treatment tactics are selected individually, based on the form of the disease and the patient’s condition. At the initial appointment, the otolaryngologist carries out diagnostic measures to confirm the presence of inflammation. For this purpose, rhinoscopy, endoscopy of the nasal cavity, and sinus scanning are performed. If necessary, the patient is sent for an x-ray. An x-ray allows the ENT doctor to draw the necessary conclusions about the condition of the sinuses.
The general treatment regimen includes:
- antibacterial drugs (the drug and dosage are prescribed exclusively by an otolaryngologist. It is important to take the full course of the medicine, even if you feel relief. An untreated disease easily becomes chronic or provokes serious complications);
- antihistamines to relieve swelling of the mucous membrane of the sinuses and nasal cavity;
- rinsing the nose with saline solutions;
- vasoconstrictor drops;
- antiseptics;
- antipyretic drugs.
An important stage of treatment is the rinsing of the maxillary sinuses by an ENT doctor, which allows the sinuses to be cleared of pathogenic contents. There are two methods of washing: vacuum by moving liquid (patients are more familiar with the common name for the procedure - “cuckoo”) and washing with a YAMIK catheter.
It is important not only to thoroughly rinse the sinuses, but also to stop inflammation. Physiotherapeutic procedures do an excellent job of this task, which also improve tissue trophism and enhance the effect of medications:
- infrared laser therapy;
- vibroacoustic therapy;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- photodynamic therapy;
- magnetotherapy.
If the patient’s condition is severe, and no methods help clear the sinuses of pus, the ENT doctor performs a sinus puncture (puncture), combining it with medication and physiotherapy.
Treatment methods for acute sinusitis
The mildest disease does not require the use of any special measures or antibacterial agents for treatment. It is enough to take anti-inflammatory drugs to relieve general symptoms and use vasoconstrictor drops to relieve swelling and facilitate the release of mucus.
Sinusitis with a purulent form is treated with the help of antibiotics (for example, Amoxiclav).
Therapy for the acute form of the disease is best supplemented by rinsing the nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses. The most effective method of treating sinusitis is Proetz lavage, better known as the “cuckoo” method.
Physiotherapeutic procedures and irrigation of the nasal cavity with antiseptic agents will help to consolidate the effect of treating sinusitis.
How to treat sinusitis in adults
The essence of competent therapy is to treat the causes of the disease, and not just relieve the symptoms. As a rule, drug therapy against sinusitis is carried out at home, but subject to strict compliance with all doctor’s instructions. Therapy only with “grandmother’s advice” is unacceptable here. The folk remedy can be used in treatment in parallel with the main methods of therapy, but not instead of them.
The complex of treatment measures usually includes:
- therapy with antibacterial drugs;
- taking antihistamines;
- use of vasoconstrictor drops and nasal rinses;
- taking antipyretic drugs;
- physiotherapy;
- washing the maxillary sinuses using the “cuckoo” method;
- puncture of the maxillary sinus (in particularly advanced cases).
Washing “cuckoo”: description of the method of treating sinusitis
The “cuckoo” method is a painless and, most importantly, effective procedure. Thanks to conservative treatment, purulent masses, mucous secretions along with pathogenic microorganisms are effectively washed out of the sinuses, the mucous membrane improves its function, nasal congestion decreases, and inflammation subsides. In some cases, thanks to Proetz lavage, puncture can be avoided. How is this procedure carried out?
The patient is positioned comfortably, lying on the couch, face up. The ENT doctor carefully pours an antiseptic into one nostril (Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, Miramistin, etc.). And at the same time, with the help of a special metal olive connected by a medical suction device, it sucks out this rinsing solution, but from the other nostril. The manipulation is repeated three times on each side, using a sterile plastic syringe with a volume of twenty ml. The entire procedure lasts about five minutes.
Diagnostics
When making a diagnosis, anamnesis, visual examination, laboratory and instrumental studies are carried out. During rhinoscopy, the lumens of the nasal passages, the condition of the mucous membrane, the nature of the discharge, and the presence or absence of polyps are assessed.
The most informative are instrumental diagnostic methods. X-rays are performed in several projections, sometimes using a contrast agent. To clarify the condition of the sinus walls, computed tomography is used. MRI makes it possible to evaluate changes in soft tissues. In some cases, endoscopy, sinus puncture followed by bacterial culture of the exudate may be required.
Puncture for sinusitis
If all conservative methods of treating sinusitis do not help, the ENT doctor will suggest a puncture of the maxillary sinus. This measure is necessary because pus accumulated in the sinus, as we already know, can lead to serious consequences, including inflammation of the brain.
During the procedure, the otolaryngologist releases the purulent contents of the sinuses and injects medication into the sinus. There is no need to be afraid of a puncture - before the procedure, anesthesia is performed: the ENT doctor inserts a cotton swab soaked in a lidocaine solution into the nasal passage of the patient sitting in a chair. It is completely safe and does not require patient preparation.
As soon as the anesthesia takes effect, the otolaryngologist, using a Kulikovsky needle, carefully inserts it into the sinus through the nasal cavity. Using a syringe, the purulent contents are sucked out. As soon as the purulent masses are completely removed, rinsing is carried out. The sinus should continue to be rinsed for several days after the procedure.
Which brand of sinusitis treatment is better to choose?
When treating sinusitis, you can use different means, but not all of them have a good composition and quickly act on the causative agent of the infection. The rating describes the manufacturers of the best drugs for the treatment of sinusitis:
- Sandoz is a pharmaceutical company that produces drugs for the treatment of infectious, viral and inflammatory diseases. The products do not harm the body and do not put pressure on the cardiovascular system. The company was founded in 1886 in Germany.
- Pliva is a Croatian pharmaceutical company and is a major global manufacturer of drugs for the treatment of viral and respiratory diseases. It began actively creating medicines in 2008 and supplies medicines to many European countries.
- Sofartex is a French company founded on June 11, 1970, it has a capital of 850 thousand euros. Every year he creates high-quality medicines for the treatment of diseases of the nose, oral cavity, eyes, and many body systems.
- JSC "Biosintez" is a pharmaceutical company that produces medicines of various types, intended for the treatment of purulent and inflammatory diseases. In 2015, the company passed a quality test.
- Teva is a company founded in 1901 in Israel; it creates drugs for immunity, to maintain health, the functions of organs and systems. Medicines are exported to different countries, the company is known in Europe and America.
- Aurena Laboratories ABC is a Swiss company that produces medicines for the treatment of viral and infectious diseases. She uses new technologies that allow her to create universal products for adults and children.
- Novartis is a large pharmaceutical company that produces drugs in various fields. Created in 1971, it supplies medicines to 140 countries and is a full member of the European Federation of the Pharmaceutical Industry.
- Reneval is a pharmaceutical company that produces drugs aimed at eliminating health problems. The medicines were created using new technologies and contain useful components to maintain immunity and improve the functioning of the patient’s organs and systems.
- Berlin-Chemie AG is a German pharmaceutical company that is part of the Italian company Menarini. Founded in 1890, from the first year it began actively developing medicines and collaborating with companies from different countries and cities.
- ALSI Pharma is a pharmaceutical plant in Kirov, the company's main office is located in Moscow. The company creates medications for the treatment of viral and chronic diseases. During the production process, all international standards are taken into account.
"ENT clinic of Doctor Zaitsev"
Our clinic specializes in the treatment of ear, nose and throat diseases. The most modern equipment, our own techniques and experienced specialists are the three components that will allow you to treat acute sinusitis quickly, safely and effectively. Regular clients of our clinic notice that our prices remain at the 2013 level!
When the first signs of sinusitis appear, please do not delay visiting a doctor. Call and make an appointment - we are always ready to help you!
Prevention of sinusitis
General strengthening measures help to avoid the development of sinusitis. You should pay attention to chronic ENT diseases and get medical help in a timely manner.
And in order to prevent complications, it is important to complete the course of therapy and not self-medicate. Some drugs, such as Sinupret®, can be taken without consulting a doctor, others, especially antibiotics, should only be prescribed by a specialist.
Important: if symptoms of sinusitis appear, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment of sinusitis at Dr. Korenchenko Clinic
See also Treatment of ENT diseases Sinusitis Sinusitis in a child Operation maxillary sinusotomy
Dr. Korenchenko’s ENT clinic is a specialized medical center with modern high-quality equipment. We use progressive treatment and diagnostic regimens, giving preference to minimally invasive, highly effective techniques. Surgeries on ENT organs in our clinic are performed endoscopically; if necessary, other technologies are also used.
Endoscopic ENT operations do not require general anesthesia (anesthesia), do not violate the integrity of the bone walls of the sinus, do not provoke pronounced swelling and subsequent severe scarring, and are practically bloodless. This reduces rehabilitation time and quickly restores nasal breathing.
The use of endoscopy allows our specialists to effectively identify and treat sinusitis, reducing the risks of complications and relapses.
Treatment of chronic maxillary sinusitis
Treatment of chronic sinusitis is carried out comprehensively; conservative treatment of the disease is often supplemented by surgical interventions. This approach allows you to eliminate the current infectious and inflammatory process, cope with complications and prevent relapse.
In most cases, outpatient treatment is sufficient. Hospitalization is indicated in case of complications or severe disease.
Conservative therapy includes lavage of the nasal cavity, puncture and lavage of the maxillary sinus (the most important thing!), the use of antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, local vasoconstrictor and mucolytic drugs. Outside the active exacerbation phase, physiotherapy can be used.
Treatment with antibiotics
Treatment of chronic sinusitis with antibiotics is aimed at suppressing bacterial infection. In order to select a suitable antibiotic that acts specifically on the microbe that caused the disease, a bacteriological culture of the discharge from the maxillary sinus is carried out. If it is impossible to obtain material for culture, antibiotics are selected based on the clinical picture and the doctor’s experience.
Most often, for chronic sinusitis, broad-spectrum antibiotics are used in order to act on the maximum possible number of microorganisms that could cause the disease.
Also, for chronic sinusitis, nasal drops are used that have a vasoconstrictor or anti-inflammatory effect. These include drugs containing ephedrine, dimethindene with phenylephedrine, xylometazoline, naphazoline and others (Otorhinolaryngology: national manual / edited by V.T. Palchun. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008.).
It should be remembered that only a doctor can select a specific antibiotic for the treatment of chronic sinusitis, since in each patient inflammation is caused by different microorganisms that have a certain sensitivity and resistance to various antimicrobial drugs. Only a doctor can choose the correct course duration and dose of antibiotic.
Once you have started a course of antibiotic therapy, you should never stop it as soon as you feel better. In the middle of the course of treatment for chronic sinusitis, the number of bacteria decreases sharply, and only those that are more resistant to this antibiotic survive. If treatment is stopped, it is these bacteria that will multiply again, causing a new exacerbation. And at the same time, resistance to antibiotics will be passed on to the next generations of microbes, and it will be very difficult to find an effective treatment.
Those who ask whether chronic sinusitis can be cured with antibiotics should remember that although they kill bacteria, they do not clear the tissue of the effects of fighting the disease (damaged cells and toxins). The broad-spectrum antibiotics used, entering the blood and accumulating in the tissues, affect the entire body. Just read about the contraindications and side effects of their use and then a lot will become clear. Therefore, the long-term result of using chemicals is unpredictable.
A surgical operation - a puncture or in other words a puncture, as well as rinsing with antiseptics, cleans the sinuses and the surface of the mucous membranes, but not the adjacent tissue of the sinuses and nose. Also, during puncture, the bone septum is punctured, and this also causes damage and death of cells that must be properly and quickly disposed of.
If painkillers are used during treatment, this can lead to a partial disruption of the innervation of the nerve pathways and the brain will not receive enough signals from the problem area, which can lead to a weakening of the immune response, and, accordingly, the necessary cleansing of the pathological area.
The use of vasoconstrictor drugs disrupts the self-regulation of blood supply, which leads to a deterioration in cell nutrition and a decrease in the effectiveness of immune reactions.
The goal pursued when using such drugs is good - to reduce swelling and ensure the supply of oxygen to the nasal canals, since oxygen kills anaerobic pathogenic bacteria. But as a result, the disease only gets worse. Drug removal of edema is a deterioration in the process of recycling damaged cells. Therefore, it is not recommended to take such drugs for more than 3-5 days, since then negative systemic reactions of the body begin to develop (for example, addiction), the elimination of which will also require appropriate and difficult treatment.
As a result, our modern medicine and pharmacology are largely focused on quickly getting rid of unpleasant symptoms of diseases and removing threats to life, rather than on eliminating the underlying causes of diseases and long-term health promotion.
The question remains, is it possible to cure chronic sinusitis forever?
How and with what to treat chronic sinusitis in adults is still a controversial issue. Currently, despite the rich arsenal of drugs, the prescription of drugs in most cases is a “trial and error” method, since there is no comprehensive approach. According to the fair statement of V.S. Agapov and his co-authors (Infectious inflammatory diseases of the maxillofacial region / Edited by Agapov V.S., Artyunov S.D., Shulakova V.V. - M.: MIA, 2004) chemotherapy and Antibiotics are included in the body's metabolism, which often leads to allergic and toxic reactions. And as a result – to the development of violations of the body’s natural defenses.
No matter how surgically the sinuses are cleaned, no matter what antibiotics kill pathogenic bacteria, damaged and dead cells will still remain in the adjacent tissues of the sinuses - the results of the body’s fight against infection.
These problems encourage scientists and doctors to search for new methods of treating chronic sinusitis and other diseases of the ENT organs. One of these methods includes physiotherapy, namely the phonation method (exposure to the Vitafon medical device).
How to treat and cure chronic sinusitis (sinusitis)?
Comparison of different treatment methods
| Type of treatment | When is it carried out? | Indications for the treatment of chronic sinusitis | Contraindications | Possible complications | Temporary disability during treatment |
| Puncture | During exacerbation | Exacerbation, severe pain in the sinus, ineffectiveness of other therapy | Acute infectious diseases, severe somatic diseases, early childhood | Bleeding, air embolism, damage to the sinus wall, infection in other sinuses | 8-10 days |
| YAMIK therapy | During exacerbation | Chronic sinusitis, including in childhood | Sinus polyps, hemorrhagic vasculitis, bleeding tendency | Bleeding | No |
| Balloon sinuplasty | During exacerbation | Chronic sinusitis, including in childhood | Acute infectious diseases, serious condition | Bleeding, damage to the mucous membrane | 24 hours |
| Maxillary sinusotomy | During exacerbation | Polyps, cysts, formations in the sinus, foreign bodies, ineffectiveness of other therapy | Severe somatic diseases, blood clotting disorders | Bleeding, tooth damage, poor wound healing, secondary infection | From 3-5 with endoscopic to 10-14 days with radical maxillary sinusotomy |
| Conservative treatment (antibiotics) | During exacerbation/in remission | Chronic bacterial sinusitis | Drug intolerance, liver and kidney dysfunction | Allergic reactions, toxic damage, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, lack of effect, development of resistance to treatment | No |
| Phonation (Vitafon) | In remission (symptoms weakening) | Treatment of chronic sinusitis in remission | Malignant neoplasms, acute infectious disease | No | No |
According to the National Guide to Otorhinolaryngology (Otorhinolaryngology: national guide / edited by V. T. Palchun. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2008.) several basic methods of treating chronic sinusitis and sinusitis are practiced in medicine, in particular:
- Puncture (puncture) of the maxillary sinus;
- YAMIK-procedure;
- Balloon sinuplasty;
- Maxillary sinusotomy (radical and endoscopic);
- Conservative therapy with antibiotics.
In addition, physiotherapy methods, less commonly hirudotherapy and acupuncture, can be used.
Most often, antibiotic therapy is used to treat chronic sinusitis. And if it is ineffective, puncture the sinus and wash it out. A modern alternative to puncture is the YAMIK procedure and balloon sinuplasty, which allow you to do without surgery and its attendant complications. But, unfortunately, these methods are not yet widespread enough and are not available in many cities.
You can find information about all modern methods of treating sinusitis here.
Treatment with puncture
In the treatment of chronic sinusitis (sinusitis) in adults, puncture treatment is often used, which in our country is considered the “gold standard”. It is used when the patient is in serious condition, conservative therapy is ineffective, or there is severe pain in the sinus.
Contraindications to puncture are:
- Exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- Infections (including acute respiratory viral infections and influenza);
- Childhood;
- Anomalies of sinus development.
The puncture is performed after preliminary anesthesia. To carry out the procedure, a Kulikovsky needle is used - a long metal rod, hollow inside, with a pointed end. It is inserted through the nose, after which a puncture is made through the wall of the sinus at a distance of about 2 centimeters. In this place its wall is thinnest.
The needle is immersed into the sinus about half a centimeter and the puncture is checked to ensure that the puncture is performed correctly. The needle should not rest against the opposite wall of the sinus, and should be inside the cavity. After this, the maxillary sinus is washed with solutions containing antiseptics, the pathological contents are removed, and antimicrobial drugs and other medicinal substances are administered.
YAMIK-procedure
The YAMIK procedure is carried out using a special YAMIK catheter, which is a system of balloons and tubes. Before the procedure, the inner surface of the nose is numbed. They also use drugs that constrict blood vessels to remove swelling and make communication between the sinus and the nasal passage freer.
One of the catheter balloons is located in the nasopharynx, and the second in the nasal passage. Both balloons are inflated with air, resulting in an isolated cavity. After this, the air is pumped out using a syringe attached to the catheter, creating negative pressure. This allows pus and other contents to be removed from the sinus. After this, it is filled with antiseptic drugs or antibiotic solutions.
In this video you can see how one of the authors of the method is Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor V.S. Kozlov. performs the YAMIK procedure:
The YAMIK procedure is painless, does not require surgical intervention, and in most cases is well tolerated by patients. Contraindications to its implementation are polyps and other formations in the sinus cavity and hemorrhagic vasculitis. Changes in pressure in the sinus can damage the polyp and even lead to its rupture, and vascular disease increases the risk of bleeding and hemorrhage.
Balloon sinuplasty
Balloon sinuplasty is a modern, low-traumatic method of treating chronic sinusitis.
After preliminary local anesthesia, under endoscopic control, a thin catheter is inserted into the maxillary sinus through a natural opening. The balloon, located on the catheter, is gently inflated, expanding the canal connecting the sinus with the nasal passage. After this, the doctor, by inserting a thicker catheter, can remove the pathological contents and pus, rinse the sinus and dry it. The catheter is then removed and the patient can go home the same day.
This operation is performed if conservative therapy does not have an effect, or instead of it. The balloon sinuplasty method was created in 2006, and registered in Russia in 2012, and until now only a small number of medical institutions use this procedure. The lack of devices, consumables and trained specialists so far reduces the importance of this method of treating sinusitis for the population.
Radical and endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy
Maxillary sinusotomy is a small operation during which an artificial opening is created in the maxillary sinus. It is performed for polyps, cysts, various formations and foreign bodies that are located in the maxillary sinus. This method is also used when more gentle methods of treating chronic sinusitis are ineffective.
With microsinusrotomy (endoscopic maxillary sinusotomy), a hole is created above the roots of the 4th tooth, located approximately in the middle of the sinus itself. After this, an endoscope is inserted into the resulting hole, with which the surface of the sinus is examined and, depending on the results of the examination, therapeutic manipulations are performed. If necessary, polyps and formations that interfere with the communication of the maxillary sinus with the nasal passage are removed.
With a radical maxillary sinusotomy according to Caldwell-Luc, an incision is made through the soft tissue and bony wall of the sinus, located from the 2nd to the 5th tooth. This allows you to create a hole sufficient for therapeutic manipulations.
Contraindications for surgery are blood clotting disorders, which can lead to bleeding, severe concomitant diseases, and exacerbations of somatic diseases.
Conservative treatment
Those who are afraid of surgical interventions have a question about how to cure chronic sinusitis without surgery completely.
According to the manual for doctors (Clinical otorhinolaryngology: A guide for doctors / V. I. Babiyak, J. A. Nakatis. - St. Petersburg: Hippocrates, 2005) the principles of non-surgical treatment of chronic sinusitis are:
- Complete restoration of drainage of the maxillary sinus through the opening associated with the nasal passage;
- Removing pus and other contents;
- Use of medications (antibiotics, anti-inflammatory, other drugs);
- Physiotherapy;
- Increasing the body's immune resistance;
- Elimination of complications.
It is extremely important to ensure and maintain nasal breathing and avoid prolonged nasal congestion, as this leads to thickening and drying of mucus, which, in turn, reduces the protective function of the mucous membranes and, accordingly, leads to the development of infection in the sinuses and its spread further along the respiratory tract.
To maintain nasal breathing, it is necessary to ensure:
- regular and abundant drinking;
- indoor air temperature is around 18-20 C;
- indoor air humidity in the range of 50-70%;
- regular ventilation and wet cleaning of the premises.
Such recommendations are given by the famous doctor E.O. Komarovsky.