Contraindications
Combigan should not be prescribed in case of hypersensitivity to the components of the drops. Prescribing the medication is also contraindicated for:
- Heart rhythm disturbances (bradycardia, 2nd or 3rd degree AV block);
- Changes in heart function (cardiogenic shock, heart failure);
- Increased reactivity of the respiratory tract (bronchial asthma, bronchial obstruction, etc.);
- Simultaneous treatment with MAO inhibitors, tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants;
- Patients under 18 years of age;
- Lactation and breastfeeding period.
Caution is required when prescribing Combigan to patients with:
- Kidney failure;
- Insufficient blood flow through the vessels of the heart or brain;
- Raynaud's syndrome;
- Depression;
- Orthostatic hypotension;
- Diabetes mellitus;
- Thromboangiitis obliterans;
- Metabolic acidosis;
- Pheochromocytoma;
- Simultaneous use of radiopaque substances;
- Metabolic acidosis;
- Intravenous administration of slow calcium channel blockers and lidocaine;
- Use of adrenergic agonists or adrenergic blockers.
When prescribing Combigan to pregnant women, careful monitoring of newborns is required during the first days of life.
Combigan eye drops 2mg/ml + 5mg/ml dropper bottle No. 1
A country
Ireland
Country of manufacture may vary depending on the batch of goods. Please check with the operator for detailed information when confirming your order.
Active substance
Brimonidine + Timolol
Compound
benzalkonium chloride, sodium hydrogen phosphate heptahydrate, sodium dihydrogen phosphate monohydrate, hydrochloric acid, sodium hydroxide, water.
pharmachologic effect
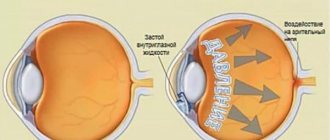
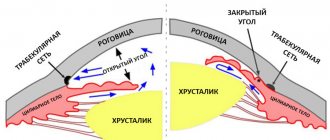
Combigan® is a combination drug that contains 2 active substances: brimonidine, an adrenergic agonist that has a stimulating effect on alpha2-adrenergic receptors, and timolol, a beta-adrenergic receptor blocker. Both active substances reduce intraocular pressure (IOP) through a combined interaction, leading to a significantly more pronounced hypotensive effect compared to the effect of each component separately. Brimonidine is an alpha-adrenergic receptor agonist, and it has 1000 times greater selectivity for alpha2-adrenergic receptors compared to alpha1-adrenergic receptors. Selectivity is expressed in the absence of mydriasis and vasoconstriction of microvasculature vessels. The hypotensive effect of brimonidine is achieved by reducing the formation of intraocular fluid and increasing its outflow along the uveoscleral pathway. Timolol is a non-selective beta-blocker and does not have intrinsic sympathomimetic or membrane-stabilizing activity. Timolol reduces IOP by reducing the formation of intraocular fluid. The exact mechanism of action has not been established; it may be associated with inhibition of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) synthesis and is caused by endogenous stimulation of beta-adrenergic receptors.
Indications for use
- open-angle glaucoma; - ophthalmic hypertension (with insufficient effectiveness of local therapy with beta-blockers).
Mode of application
In adults, including elderly patients: Locally, instill 1 drop into the conjunctival sac of the affected eye 2 times a day with an interval of 12 hours. Combigan® can be used with other ophthalmic drugs to reduce intraocular pressure. If more than 2 drugs are used, then it is necessary to take a 5-minute break between instillations. As when using other eye drops, to reduce possible systemic absorption, short-term (for 1 minute) pressure on the lacrimal sac in the area of the projection of the lacrimal sac of the eye at the inner corner of the eye is recommended. There have been no controlled studies examining the use of Combigan® in pregnant women. Brimonidine There are no data on the use of brimonidine in pregnant women. Animal studies have demonstrated reproductive toxicity at high doses with maternal toxicity. The degree of risk to humans has not been established. Timolol Animal studies have shown reproductive toxicity when using doses of the drug that significantly exceed those recommended for use in clinical practice. Epidemiological studies have not revealed congenital malformations of the fetus, but there is a known risk of intrauterine growth retardation when taking beta-blockers orally. In addition, symptoms characteristic of the group of beta-blockers (bradycardia, decreased blood pressure, respiratory shortness of breath and hypoglycemia) were observed in newborns in cases where beta-blockers were used by the mother until delivery. In this regard, if Combigan® is prescribed during pregnancy until the moment of birth, medical monitoring of the newborn’s condition during the first days of life is necessary. Combigan® can be used during pregnancy only if absolutely necessary. During lactation Preclinical studies have shown that brimonidine and timolol are excreted in breast milk. Breastfeeding should be stopped during treatment. Contraindicated for children under 18 years of age.
Interaction
No special studies have been conducted to study drug interactions with Combigan®. However, one should take into account the possibility of enhancing the effect of drugs that depress the central nervous system (alcohol, barbiturates, opium derivatives, sedatives, general anesthetics) when used simultaneously with Combigan®. Timolol may exacerbate compensatory tachycardia and increase the risk of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure when used with general anesthetics. It is necessary to warn the anesthesiologist about the use of the drug Combigan® before the upcoming operation. With the simultaneous use of timolol and epinephrine, the development of mydriasis is possible. Beta-blockers may enhance the hypoglycemic effect of hypoglycemic drugs. They may also mask hypoglycemia. The hypertensive reaction to abrupt discontinuation of clonidine may be exacerbated by the use of a beta blocker. An increase in the hypotensive effect (for example, a decrease in heart rate) when timolol is used together with quinidine is possible due to the fact that quinidine slows down the metabolism of timolol through the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme, CYP2D6. The combined use of beta-blockers with drugs for general anesthesia may hide compensatory tachycardia and increase the risk of a pronounced decrease in blood pressure, therefore the anesthesiologist must be warned about the patient's use of the drug Combigan®. Cimetidine, hydralazine, ethanol can increase the concentration of timolol in the blood plasma. It is necessary to use with caution drugs that affect the metabolism and absorption of circulating catecholamines, for example, chlopromazine, methylphenidate, reserpine. Concomitant use of MAO inhibitors is contraindicated. For patients receiving MAO inhibitors, treatment with Combigan® can be prescribed 14 days after discontinuation of the MAO inhibitor. Potentiation of the effects of combined use of eye drops containing timolol and ingested calcium channel blockers, guanethidine or beta-blockers, antiarrhythmic drugs, cardiac glycosides or parasympathomimetics has been reported, which was manifested by a pronounced decrease in blood pressure and/or severe bradycardia. After using brimonidine in very rare cases (Side effects) The most common side effects were hyperemia of the conjunctiva of the eye (about 15% of patients) and a burning sensation of the mucous membrane of the eye (about 11% of patients). In most cases, the severity of these symptoms was mild, discontinuation of therapy was required only in 3.4% and 0.5% of cases, respectively.During clinical trials of the drug Combigan®, the following side effects were reported, taking into account the frequency of occurrence: very often (>1/10); often (>1/100, 1/1000, From the organ of vision: very often: hyperemia of the conjunctiva of the eye, burning sensation. often: acute burning or stabbing pain, allergic conjunctivitis, corneal erosion, superficial keratitis, itching of the skin of the eyelids, conjunctival folliculosis, blurred vision, blepharitis, epiphora, dry mucous membrane of the eye. , discharge from the eye, pain, irritation of the mucous membrane of the eye, foreign body sensation.uncommon: decreased visual acuity, conjunctival edema, follicular conjunctivitis, allergic blepharitis, conjunctivitis, floating precipitates in the vitreous, asthenopia, photophobia, hypertrophy of the papillary muscles of the eye, eyelid pain , pallor of the conjunctiva, corneal edema, corneal infiltrates, vitreous rupture. Mental disorders: often - depression. From the nervous system: often - drowsiness, headache; uncommon - dizziness, syncope. From the cardiovascular system: often - increased blood pressure; uncommon: congestive heart failure, palpitations. From the respiratory system: uncommon: rhinitis, dry nasal mucosa. From the digestive system: often - dryness of the oral mucosa; infrequently - perversion of taste. From the skin and subcutaneous fat: often - swelling of the eyelids, itching of the skin of the eyelids, redness of the skin of the eyelids; uncommon - allergic contact dermatitis. Other disorders: often - asthenic conditions. Laboratory indicators: often - increased activity of liver enzymes. The following side effects have been additionally reported since the introduction of Combigan® on the market: From the cardiovascular system: Frequency unknown - arrhythmia, bradycardia, tachycardia, decreased blood pressure. Side effects that were observed when using one of the active ingredients, the possibility of which cannot be excluded when using the drug Combigan®: Brimonidine On the part of the visual organ: iridocyclitis, miosis. Mental disorders: insomnia. From the respiratory system: inflammatory diseases of the upper respiratory tract, shortness of breath. From the digestive system: taste perversion, dyspepsia. Other: systemic allergic reactions. Timolol On the part of the organ of vision: decreased sensitivity of the cornea, diplopia, ptosis, rupture of the choroid (after filtration surgical treatment), changes in refraction (due to the abolition of miotic therapy in some cases). Mental disorders: insomnia, nightmares, decreased libido. From the nervous system: memory loss, worsening symptoms of myasthenia gravis, paresthesia, cerebral ischemia. On the part of the hearing organ: tinnitus. From the cardiovascular system: complete transverse heart block, cardiac arrest. Vascular disorders: cerebrovascular accident, intermittent claudication, Raynaud's syndrome, cold extremities. From the respiratory system: bronchospasm (mainly in patients with a history of broncho-obstructive diseases), shortness of breath, cough, respiratory failure. From the digestive system: nausea, diarrhea, dyspepsia. From the skin and subcutaneous fat: alopecia, psoriasis-like rash or exacerbation of psoriasis. From the musculoskeletal system, connective and bone tissue: systemic lupus erythematosus Other: peripheral edema, Peyronie's disease, chest pain.
Contraindications
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug; - increased reactivity of the respiratory tract, including bronchial asthma and episodes of bronchial obstruction, incl. history of severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; - sinus bradycardia, II-III degree atrioventricular block without an implanted artificial heart pacemaker, heart failure, cardiogenic shock; - concomitant therapy with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), antidepressants - tricyclic and tetracyclic (including mianserin); — age up to 18 years; - period of breastfeeding. With caution: - renal/liver failure (the use of the drug has not been sufficiently studied in this group of patients); - depression, cerebral or coronary insufficiency, Raynaud's syndrome, orthostatic hypotension, thromboangiitis obliterans; — severe cardiovascular diseases of an unstable course; - diabetes mellitus, episodes of hypoglycemia (in the absence of therapy); — pheochromocytoma (without previous treatment); - metabolic acidosis; - simultaneous use of radiopaque agents; - intravenous administration of lidocaine, blockers of “slow” calcium channels (verapamil, diltiazem) due to the risk of inhibition of atrioventricular conduction, development of bradycardia, heart failure and lowering blood pressure; - simultaneous prescription or change in the dose of drugs taken from the groups of adrenergic agonists (isoprenaline) and adrenergic blockers (prazosin), as well as other drugs that affect adrenergic transmission - due to their possible interaction with the active components of the drug or changes in their therapeutic potential.
Overdose
Brimonidine Overdose when applied topically: loss of consciousness, decreased blood pressure, bradycardia, hypothermia, cyanosis and apnea. Overdose due to accidental ingestion: After accidental ingestion of brimonidine, clinical manifestations included: CNS depression, transient confusion, loss of consciousness or coma, decreased blood pressure, bradycardia, hypothermia and apnea; which resulted in the need for urgent hospitalization in the emergency department; in some cases, tracheal intubation was performed. Full functional recovery was reported in all reported cases within 6 to 24 hours. In case of overdose caused by drugs of the alpha2-adrenomimetics group, the following symptoms were reported: decreased blood pressure, asthenia, vomiting, drowsiness, sedation, bradycardia, arrhythmias, miosis, apnea, hypothermia, respiratory depression, convulsions. Timolol Symptoms of a general overdose of timolol: bradycardia, decreased blood pressure, bronchospasm, headache, dizziness, cardiac arrest. A clinical study showed that timolol is not completely eliminated during hemodialysis. If an overdose is diagnosed, symptomatic therapy is carried out.
special instructions
Do not touch the tip of the bottle to any surfaces to avoid infection of the eye and the contents of the bottle. Like all ophthalmic drugs used topically, Combigan® can be absorbed systemically. If allergic reactions occur, treatment with Combigan® should be discontinued. In patients with severely impaired renal function undergoing hemodialysis, treatment with timolol is accompanied by a pronounced decrease in blood pressure. While taking a drug from the beta-blocker group in patients with agonic manifestations and severe anaphylactic reactions to various allergens in history, there may be a decrease or lack of effectiveness from the administration of epinephrine in usually used doses. Beta blockers may also mask symptoms of hyperthyroidism and worsen Prinzmetal's angina, vascular disease, both peripheral and central, and hypotension. Signs indicating acute hypoglycemia, in particular tachycardia, palpitations and sweating, may be masked during beta-blocker therapy. If it is necessary to discontinue therapy with Combigan®, as well as in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases with systemic beta-blockers, therapy is discontinued gradually to avoid the development of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial infarction and/or sudden death, the risk of which increases with abrupt discontinuation of drugs this group. The excipient benzalkonium chloride contained in Combigan® may have an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the eyes. Before installing Combigan®, contact lenses must be removed; they can be put on again after 15 minutes. The shelf life of the drug after the first opening of the dropper bottle is 28 days. After the specified time has expired, it is recommended to throw away the dropper bottle, even if it still contains a residual amount of the drug. This is necessary in order to avoid the risk of infection. Patients are advised to write down the date the bottle was opened on the cardboard packaging. Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery Combigan® has an insignificant effect on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery. During treatment with Combigan®, transient visual impairment (blurredness) and the development of episodes of weakness and drowsiness are possible, which may have an adverse effect if the patient’s work is associated with potentially hazardous activities. If these symptoms occur, you should refrain from performing hazardous activities.
Dispensing conditions in pharmacies
On prescription
Side effects
When using Combigan eye drops, local side effects may develop, including burning, hyperemia of the mucous membrane, pain, conjunctival folliculosis, decreased vision, superficial keratitis, dryness, epiphora, irritation, conjunctival edema, asthenopia, precipitates in the vitreous, vitreous rupture .
Systemic effects of the drug include depression, drowsiness, syncope, headache, increased blood pressure, rhinitis, dry mouth, eyelid swelling, asthenia, insomnia.
Ganfort
Antiglaucoma drops are used, 1 drop per day. If a dose is missed, the amount of the drug is not doubled. The medicine causes the growth of eyelashes, changes in the color of the iris, the skin around the eyes, and reduces visual acuity. The cost of Ganfort is from 800 rubles.
It is important to pay attention to the expiration date before using medications. It is necessary to strictly observe sterility and not touch the tip of the bottle to the mucous membrane of the eye.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2100
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 2 ratings, average: 4.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Interactions
When used simultaneously with substances that depress the central nervous system, this effect may be enhanced.
When used with systemic anesthetics, tachycardia and hypotension may occur.
Mydriasis develops when Combigan and epinephrine are used together.
The hypoglycemic effect of drugs for diabetes mellitus may be enhanced when patients are treated with Combigan.
Do not use together with drugs that inhibit MAO. Treatment with Combigan can be prescribed only 14 days after discontinuation of drugs from this group.
Pilocarpine
Drops improve the outflow of intraocular fluid, resulting in a decrease in intraocular pressure. When instilled, side effects are possible, which manifest themselves in the form of:
- burning, redness;
- pain;
- weakened vision in the evening.
In case of an overdose, the heartbeat slows down and nausea occurs. Only a doctor, taking into account the specific health conditions, prescribes the dosage and duration of use of Pilocarpine.
Cheap domestic drug costing from 28 rubles.
special instructions
Do not touch the tip of the dropper to any surfaces, as the solution may become contaminated.
If it is necessary to discontinue Combigan, this should be done gradually so as not to provoke cardiovascular disorders.
Benzalkonium chloride can negatively affect the mucous membrane of the eye, so contact lenses should be removed before instillation.
During treatment with drops, the ability to drive a car may slightly decrease, as transient blurred vision, weakness or drowsiness occurs.
Betoptik
Fast-acting antiglaucoma drug. 30 minutes after instillation, a decrease in IOP is observed, the maximum decrease is achieved after 2 hours. Betoptik has no effect on the blood supply to the optic nerve. The recommended dose is 1 drop 2 times a day.
In rare cases, tearing and other uncomfortable sensations occur after instillation. If the patient wears lenses, they must be removed before using the drug and put on 15 minutes after administering the drops. Sold in pharmacies from 235 rubles.