DuoTrav are drops that are used in ophthalmology to reduce intraocular pressure.
The components in this drug help accelerate the outflow of fluid from the eyes.
Additionally, the increase in such fluid is inhibited.
Two hours after use, the effectiveness of the drug is observed.
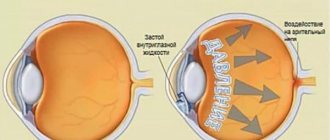
Intraocular pressure is a major factor in the development of glaucoma. Such processes are monitored by an ophthalmologist and determine the treatment method. DuoTrav in such cases shows high efficiency.
More information about the drug can be found here
Azopt
Azopt drops are classified as anti-glaucoma medications. The drug is prescribed to protect the optic nerve and reduce intraocular pressure. The active substance is brinzolamide. Main indications for use:
- normalization of IOP;
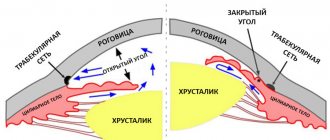
- open angle glaucoma.
Contraindications:
- teenagers;
- pathological changes in the liver;
- hypersensitivity to the composition;
- severe kidney pathologies;
- closed glaucoma.
Adverse reactions occur in the form of blurred vision, changes in taste, and lacrimation. They disappear on their own after a short time. Otherwise, you should inform your doctor. Contraindicated for use during pregnancy and lactation. Price - 650-680 rubles.
Betoptik
Eye drops are used to prevent glaucoma and reduce intraocular pressure. The main substance is betaxolol hydrochloride. Release form: bottles with droppers of 5 ml. Betoptik promotes fluid outflow. This process reduces high and normal intraocular pressure.
The effect of the drug lasts 12 hours. The main component does not reduce blood flow in the optic nerve. Unlike other drops, it does not cause fogginess in the eyes after instillation. During pregnancy, you can take it as prescribed by your doctor. Price - 300 rub.
Xalacom
Xalacom eye drops are a combination drug. Used to reduce intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma, in order to increase ophthalmotonus. The composition contains a couple of strong, active components.
The composition of these drops allows you to reduce intraocular pressure for a long time. Effectiveness is observed 3 hours after instillation. When using other drops, an interval of 5 minutes should be maintained.
Contraindications:
- bronchial asthma;
- individual intolerance to the components in the composition;
- disorders of the cardiovascular system.
Local adverse reactions rarely occur and resolve on their own. Price - 600 rub.
DuoTrav, 1 piece, 2.5 ml, eye drops
General information
Like other topical ophthalmic drugs, travoprost and timolol are absorbed into the systemic circulation. Due to the presence of timolol, which has a beta-blocking effect, in the ophthalmic drug, it is possible to develop the same types of adverse reactions from the cardiovascular system, lungs and other organs as when using systemic beta-blockers.
Heart disorders
In patients with cardiovascular diseases (for example, coronary artery disease, Prinzmetal's angina, heart failure) and hypotension, the appropriateness of using beta-blockers should be critically assessed and the possibility of using other active substances should be considered. Patients with cardiovascular diseases should be assessed for signs of worsening of these diseases and the development of adverse reactions.
Because beta blockers have a negative effect on conduction time, they should be used with caution in patients with first-degree AV block.
Vascular disorders
In patients with severe illness or peripheral circulatory disorders (i.e. severe forms of Raynaud's disease or Raynaud's syndrome), treatment should be carried out with caution.
Breathing disorders
The patient's condition should be monitored before and during timolol therapy.
After the use of certain ophthalmic drugs from the group of beta-blockers, cases of respiratory reactions, including death from bronchospasm, have been described in patients suffering from bronchial asthma.
In patients with mild to moderate COPD, DuoTrav® should be used with caution and only if the expected benefit outweighs the possible risk.
Hypoglycemia/diabetes mellitus
In patients prone to developing spontaneous hypoglycemia, as well as in patients with labile diabetes mellitus, beta-blockers should be used with caution, as they may mask the signs and symptoms of acute hypoglycemia.
Hyperthyroidism
Beta blockers may mask signs of hyperthyroidism.
Muscle weakness
It has been reported that beta blockers may potentiate muscle weakness, which is consistent with certain symptoms of myasthenia gravis (eg, diplopia, ptosis, and generalized muscle weakness).
Corneal diseases
Beta blockers for ophthalmic use may cause dry eyes. In patients with corneal diseases, the drug should be used with caution.
Choroidal detachment
In patients who used drugs that suppress the production of aqueous humor (for example, timolol and acetazolamide), cases of choroidal detachment were observed after fistulizing operations of the organ of vision.
Other beta blockers
When timolol is used in patients already taking systemic beta-blockers, the effect on IOP or other known effects of systemic beta-blockers may be enhanced. The response to therapy in such patients should be carefully monitored. The use of two beta-blockers for topical use is not recommended (see Interactions).
Skin contact
PGs and their analogues are biologically active substances that can be absorbed through the skin. Women during pregnancy, as well as women planning pregnancy, should take appropriate precautions to prevent direct contact of the contents of the bottle with the skin. If a significant portion of the contents of the bottle does come into contact with the skin (which is unlikely), the area of skin on which the drug has come into contact should be immediately washed with water.
Anaphylactic reactions
The use of timolol in patients with atopy or a history of severe pathological reactions to various allergens may provoke more severe reactions in response to the introduction of various allergens. Such patients may respond poorly to normal doses of epinephrine to relieve anaphylactic reactions.
Effects on the eyes
Travoprost may gradually change eye color by increasing the number of melanosomes (pigment granules) in melanocytes. Before starting treatment, patients should be informed about the possibility of permanent changes in eye color. Treatment of only one eye can lead to permanent heterochromia. The long-term effect on melanocytes and the consequences of this influence are currently unknown.
The change in iris color occurs slowly and may not be noticeable for months or years.
Changes in eye color are predominantly observed in patients with mixed iris colors (blue-brown, gray-brown, yellow-brown or green-brown), a similar effect was observed in patients with brown eyes. In typical cases, brown pigmentation around the pupil extends concentrically to the periphery of the iris, causing the entire iris or parts thereof to become browner. After completion of therapy, no further accumulation of brown pigment was observed in the iris. Darkening of the skin in the periorbital area and/or eyelids has been reported with the use of travoprost.
Travoprost may gradually change the condition of the eyelashes in the treated eye(s); These changes include changes in length, thickness, pigmentation and/or number of eyelashes.
The mechanism of these changes is currently unknown.
The product contains propylene glycol, which may cause skin irritation!
The drug contains macrogol glyceryl hydroxystearate, which may cause skin reactions.
Macular edema has been observed during treatment with PGF2α analogues. Travoprost should be used with caution in patients with neovascular, angle-closure, narrow-angle glaucoma, pigmentary and congenital glaucoma, open-angle glaucoma with pseudophakia, pseudoexfoliation glaucoma, inflammatory diseases of the organ of vision, aphakia, pseudophakia with rupture of the posterior capsule of the lens or anterior chamber intraocular lens, as well as in patients with with risk factors for macular edema, iritis, uveitis.
When using PG analogues, changes in the periorbital region and eyelids were noted. Deepening of the eyelid sulcus was observed only in studies in monkeys, while clinical studies in humans did not provide data on this effect, which allowed it to be considered species-specific.
Anesthesia for surgical interventions
Ophthalmic drugs from the group of beta-blockers can suppress the beta-agonist effects, such as epinephrine. The anesthesiologist should be informed if the patient is receiving timolol.
Contact lenses
Patients should be instructed to remove contact lenses before using DuoTrav® and to wait at least 15 minutes before reusing them.
Influence on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery. Temporary blurred vision or other visual disturbances after taking this drug may affect your ability to drive or use machinery. If blurred vision occurs after instillation of the drug, then the patient must wait until clear vision is restored before driving a vehicle or operating machinery.
Fotil
Fotil - combined eye drops. Used in ophthalmology for the treatment of glaucoma and in the postoperative period of intraocular hypertension.
Indications for use:
- closed and open glaucoma;
- secondary glaucoma;
- increased intraocular pressure during surgery.
Contraindicated during pregnancy, with individual intolerance, bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis. Price - 230 rub.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2100
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
DuoTrav®
General information
Like other topical ophthalmic drugs, travoprost and timolol are absorbed into the systemic circulation. Due to the presence of timolol, which has a beta-blocking effect, in the ophthalmic drug, it is possible to develop the same types of adverse reactions from the cardiovascular system, lungs and other organs as when using systemic beta-blockers.
Heart disorders
In patients with cardiovascular disease (eg, coronary artery disease, Prinzmetal's angina, heart failure) and hypotension, the appropriateness of beta-blocker use should be critically assessed and the use of other active agents should be considered. Patients with cardiovascular diseases should be assessed for signs of worsening of these diseases and the development of adverse reactions.
Since beta blockers have a negative effect on conduction time, they should be used with caution in patients with first degree atrioventricular block.
Vascular disorders
In patients with severe impairments or diseases of the peripheral circulation (i.e. severe forms of Raynaud's disease or Raynaud's syndrome), treatment should be carried out with caution.
Breathing disorders
The patient's condition should be monitored before and during timolol therapy. Cases of respiratory reactions, including death from bronchospasm in patients suffering from bronchial asthma, have been described after the use of certain ophthalmic drugs from the beta-blocker group.
In patients with mild to moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), DuoTrav® should be used with caution and only if the expected benefit outweighs the possible risk.
Hypoglycemia/diabetes mellitus
In patients prone to developing spontaneous hypoglycemia, as well as in patients with labile diabetes mellitus, beta blockers should be used with caution, as they may mask the signs and symptoms of acute hypoglycemia.
Hyperthyroidism
Beta blockers may mask signs of hyperthyroidism.
Muscle weakness
It has been reported that beta blockers may potentiate muscle weakness, consistent with certain symptoms of myasthenia gravis (eg, diplopia, ptosis, and generalized muscle weakness).
Corneal diseases
Beta blockers for ophthalmic use may cause dry eyes. In patients with corneal diseases, the drug should be used with caution.
Choroidal detachment
In patients who used drugs that suppress the production of aqueous humor (for example, timolol and acetazolamide), cases of choroidal detachment were observed after fistulizing operations of the organ of vision.
Other beta blockers
When timolol is used in patients already taking systemic beta-blockers, the effect on intraocular pressure or other known effects of systemic beta-blockers may be enhanced. The response to therapy in such patients should be carefully monitored. The use of two beta-blockers for local use is not recommended (see section Interactions with other drugs).
Skin contact
Prostaglandins and prostaglandin analogues are biologically active substances that can be absorbed through the skin. Women during pregnancy, as well as women planning pregnancy, should take appropriate precautions to prevent direct contact of the contents of the bottle with the skin. If a significant portion of the contents of the bottle does come into contact with the skin (which is unlikely), the area of skin on which the drug has come into contact should be immediately washed with water.
Anaphylactic reactions
The use of timolol in patients with atopy or a history of severe pathological reactions to various allergens may provoke more severe reactions in response to the introduction of various allergens. Such patients may respond poorly to normal doses of epinephrine to relieve anaphylactic reactions.
Effects on the eyes
Travoprost may gradually change eye color by increasing the number of melanosomes (pigment granules) in melanocytes. Before starting treatment, patients should be informed about the possibility of permanent changes in eye color. Treatment of only one eye can lead to permanent heterochromia. The long-term effect on melanocytes and the consequences of this influence are currently unknown.
The change in iris color occurs slowly and may not be noticeable for months or years.
Changes in eye color are predominantly observed in patients with mixed iris colors (blue-brown, gray-brown, yellow-brown or green-brown), a similar effect was observed in patients with brown eyes. In typical cases, brown pigmentation around the pupil extends concentrically to the periphery of the iris; as a result, the entire iris or parts thereof acquire a browner color. After completion of therapy, no further accumulation of brown pigment was observed in the iris.
Darkening of the skin in the periorbital area and/or eyelids has been reported with the use of travoprost.
Travoprost may gradually change the condition of the eyelashes in the treated eye(s); These changes include changes in length, thickness, pigmentation and/or number of eyelashes.
The mechanism of these changes is currently unknown.
The product contains propylene glycol, which may cause skin irritation!
The drug contains macrogol glyceryl hydroxystearate, which may cause skin reactions.
Macular edema has been reported during treatment with prostaglandin F2α analogues.
Travoprost should be used with caution in patients with neovascular, angle-closure, narrow-angle glaucoma, pigmentary and congenital glaucoma, open-angle glaucoma with pseudophakia, pseudoexfoliation glaucoma, inflammatory diseases of the organ of vision, aphakia, pseudophakia with rupture of the posterior capsule of the lens or anterior chamber intraocular lens, as well as in patients with with risk factors for macular edema, iritis, uveitis.
When using prostaglandin analogs, changes in the periorbital area and eyelids were noted. Deepening of the eyelid sulcus was observed only in studies in monkeys, while clinical studies in humans did not provide data on this effect, which allowed it to be considered species-specific.
Anesthesia for surgical interventions
Ophthalmic drugs from the group of beta blockers can suppress the beta-agonist effects, such as epinephrine. The anesthesiologist should be informed if the patient is receiving timolol.
Contact lenses
Patients should be instructed to remove contact lenses before using DuoTrav® and to wait at least 15 minutes before using them again.