Pharmacological properties of the drug Ketoprofen
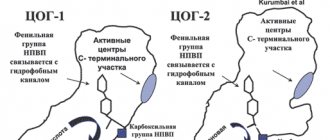
NSAIDs of the group of propionic acid derivatives. It has a pronounced anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effect. Pharmacological effects are due to the ability to disrupt the synthesis of prostaglandins by inhibiting COX activity. Ketoprofen also inhibits the synthesis of leukotrienes, bradykinin activity, and stabilizes lysosomal membranes. In case of articular syndrome, it reduces the severity of arthralgia (at rest and during movement), morning stiffness and swelling of the joints, and helps reduce the degree of their functional insufficiency. Ketoprofen does not have a catabolic effect on cartilage tissue, and at concentrations of 10-4 mol/l it is able to stimulate the synthesis of proteoglycan in cells of immature human cartilage. Antipyretic activity is due to the effect on the thermoregulation center in the hypothalamus. Inhibits platelet aggregation. It is quickly and almost completely absorbed from the digestive tract after oral administration. Simultaneous administration with food or milk slows down absorption, but does not reduce its volume. Bioavailability - approximately 90%, maximum concentration in blood plasma is achieved after 1-2 hours; half-life is 1.1–4 hours (may increase in elderly people and with severe renal failure). With rectal administration, the maximum concentration in the blood plasma is achieved after 4 hours, and with intramuscular administration - after 15–45 minutes. After using retard tablets, the effective concentration is achieved within 45–60 minutes. The therapeutic concentration of ketoprofen lasts longer in synovial fluid than in the blood. Up to 99% of ketoprofen binds to blood plasma proteins. Metabolized in the liver, mainly by conjugation with glucuronic acid. Excreted in urine, mainly in the form of metabolites; Less than 1% of ketoprofen is excreted unchanged. About 1–8% is excreted in the feces.
KETOPROFEN VRAMED GEL TO RELIEF JOINT PAIN
Anti-inflammatory drugs are drugs that suppress the inflammatory process by preventing the mobilization or transformation of arachidonic acid. Anti-inflammatory drugs do not include drugs that can influence the inflammatory process through other mechanisms, in particular cytostatics, “basic” antirheumatic drugs (gold salts, D-penicillamine, sulfasalazine), anti-gout drugs (colchicine), quinoline derivatives (chloroquine). The indications for the use of glucocorticosteroids as anti-inflammatory drugs are predominantly pathoimmune inflammation. They are widely used in the acute phase of systemic connective tissue diseases, arthritis, sarcoidosis, alveolitis, and non-infectious inflammatory skin diseases. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are substances of various chemical structures that, in addition to anti-inflammatory, also usually have analgesic and antipyretic activity. The NSAID group consists of derivatives of salicylic acid (acetylsalicylic acid, mesalazine), indole (indomethacin, sulindac), pyrazolone (phenylbutazone, clofezone), phenylacetic acid (diclofenac), propionic acid (ibuprofen, naproxen, flurbiprofen, ketoprofen), oxicam (meloxicam, piroxicam , tenoxicam) and other chemical groups (benzydamine, nabumetone, niflumic acid, etc.).
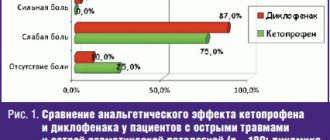
Ketoprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) from the group of propionic acid derivatives, which has an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effect. The main goal of treating most soft tissue injuries (bruised wounds, sprains and ruptures of the ligamentous apparatus of joints, dislocations) is to prevent and reduce swelling. In most cases, there is a need for effective pain relief, for which NSAIDs are most often used. In a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study, oral ketoprofen in 120 patients with tendinitis, bursitis or periarthritis quickly and effectively relieved pain and reduced functional limitations in the joints. The analgesic effect occurred within 30 minutes after taking the drug with tolerability comparable to placebo. More details - ketoprofen for acute soft tissue injury, ketoprofen in postoperative pain relief, the effect of ketoprofen on postoperative complications and reparative processes in bone tissue.
Medicines containing ketoprofen:
Ketoprofen Vramed gel, Actron instructions, Artrozilen instructions, Ketolist retard instructions, Ketonal instructions, Ketonal Duo instructions, Ketoprofen-Verte instructions, Knavon instructions, OKI instructions , Oruvel (Oruveil) instructions, Ostofen (Ostofen) instructions, Prontoket (Prontoket) spray instructions, Profenid (Profenid) instructions, Fastum (Fastum) instructions, Fastum gel instructions, Febrofid (Febrofid) instructions, Flamax (Flamax) instructions, Flexen ( Flexen) instructions, Bystrumgel instructions, Bystrumcaps instructions, synonyms of the drug Ketoprofen: Alreumant instructions, Asozal, Dexal, Kefenid, Ketoprosil, Meprofen, Niflam, Reumoquin, Rofenid, Synpofen, etc. For all drugs, the main active ingredient is ketoprofen.
Use of the drug Ketoprofen
Externally, internally, rectally, intramuscularly or intravenously. Orally - during or after meals, 200–300 mg/day in 2–3 divided doses or 1 retard tablet 1–2 times a day. IM - 100 mg 1-2 times a day. Ketoprofen infusions are carried out only in a hospital setting. The average infusion time is 30 minutes - 1 hour, the maximum is no more than 48 hours, and the dose of ketoprofen should not exceed 300 mg. For short-term infusion, 100–200 mg of ketoprofen is dissolved in 100 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution and administered over 30 minutes to 1 hour; the interval between injections is 8 hours. For long-term infusion, 100–200 mg of ketoprofen is dissolved in 500 ml of infusion solution (isotonic sodium chloride solution, Ringer's solution, glucose solution) and administered for 8 hours; the interval between administrations is 8 hours. Ketoprofen can be used in combination with centrally acting analgesics. For combined use, ketoprofen is mixed with morphine in one bottle (100–200 mg of ketoprofen and 10–20 mg of morphine), dissolved in 500 ml of isotonic sodium chloride solution or Ringer’s solution and administered every 8 hours. If necessary, treatment can be continued by prescribing ketoprofen orally or rectally in the form of suppositories. The cream or gel is applied to the skin of the affected area 3-4 times a day.
Ketoprofen Organica, 20 pcs., 100 mg, film-coated tablets
Film-coated tablets
Inside,
during or immediately after a meal, without chewing, with water or milk (the volume of liquid should be at least 100 ml).
Usually the drug is prescribed in 1 tablet. 2 times a day.
Ketoprofen preparations for oral administration can be combined with the use of rectal suppositories, for example, the patient can take 1 tablet. (100 mg) ketoprofen in the morning and administer 1 supp. (100 mg) rectally in the evening. The maximum dose of ketoprofen is 200 mg/day.
It is not recommended to exceed the maximum daily dose of the drug. In order to reduce the risk of developing adverse events from the gastrointestinal tract, patients with risk factors are recommended to simultaneously prescribe proton pump inhibitors.
Capsules
Inside,
during or immediately after meals with plenty of water. Adults and adolescents (15–18 years old) are prescribed 4 caps. of the drug per day, which can be divided into 3 doses (depending on the severity of the pain syndrome), but not more than 2 caps. once. The maximum daily dose should not exceed 200 mg.
Solution for intravenous and intramuscular administration
IV, IM.
To reduce the frequency of adverse reactions, it is recommended to use the minimum effective dose of the drug.
IM administration:
The recommended dose is 100 mg (1 amp.) of ketoprofen 1-2 times a day.
IV infusion:
prescribed only in a hospital setting. The duration of infusion should be from 30 to 60 minutes.
The IV route of administration should be used for no more than 48 hours.
Short IV infusion:
100–200 mg (1–2 amp.) of ketoprofen, diluted in 100 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution, is administered over 0.5–1 hour.
Continuous IV infusion:
100–200 mg (1–2 amp.) of ketoprofen, diluted in 500 mg of infusion solution (0.9% sodium chloride solution, lactated Ringer's solution, 5% dextrose solution), is administered over 8 hours; re-administration is possible after 8 hours.
The maximum daily dose (including all dosage forms) should not exceed 200 mg of ketoprofen.
The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor.
Ketoprofen can be used in combination with centrally acting analgesics; it can be mixed with opioids (including morphine) in the same vial.
If necessary, treatment can be supplemented with the use of oral forms (tablets, capsules), rectal suppositories or external dosage forms of ketoprofen.
Special patient groups
Elderly age.
In elderly patients, treatment with Ketoprofen Organica should be started with a low dose of ketoprofen and maintenance treatment should be carried out with the minimum effective dose of the drug.
Kidney failure/dialysis and liver failure.
In patients with renal failure with creatinine Cl less than 20 ml/min and with chronic liver disease (with reduced serum albumin levels), the dose of ketoprofen should be reduced.
Warning
Pharmaceutically incompatible with tramadol solution due to precipitation.
Infusion bottles should be wrapped in black paper or aluminum foil because ketoprofen is sensitive to light.
Side effects of the drug Ketoprofen
Dyspepsia (12% of cases), nausea/vomiting, abdominal pain, heartburn, diarrhea, constipation, flatulence (3–9%), gastritis, hemorrhoidal bleeding, peptic ulcer, upper gastrointestinal bleeding, intestinal perforation (less than in 1% of cases), urticaria, maculopapular rash (1–3%), purpura, bullous rash, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, photosensitivity (extremely rare), headache, dizziness, drowsiness, insomnia, depression, increased excitability (1–3%), peripheral edema (2%), worsening of congestive heart failure and peripheral vascular disease (less than 1%), hemorrhages and retinal pigmentation (less than 1%), jaundice, hepatitis, cholestatic hepatitis (less than 1%), increased activity of liver enzymes (15%), hematuria, proteinuria, papillary necrosis, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome (extremely rare).
Drug interactions Ketoprofen
To avoid the formation of sediment, do not mix ketoprofen and tramadol solutions in one bottle. The frequency of side effects from the digestive tract, primarily hemorrhagic, increases when ketoprofen is taken simultaneously with other NSAIDs, ethanol, indirect anticoagulants, and corticosteroids. Preparations of garlic, onion, and ginkgo biloba potentiate the antiplatelet effect of ketoprofen and may increase the risk of developing hemorrhagic complications. When administered concomitantly with cidofovir, potentiation of nephrotoxicity is possible; ketoconazole should be discontinued at least 7 days before cidofovir is prescribed. Co-administration with probenecid may increase the concentration of ketoprofen in the blood plasma. The concentration of lithium and its toxic effects may increase when used simultaneously with ketoprofen, so they should be monitored. The simultaneous administration of ketoprofen and digoxin may cause an increase in the concentration of the latter in the blood plasma, especially in patients with renal failure. Ketoprofen inhibits the synthesis of prostaglandins in the kidneys and may potentiate the nephrotoxicity of cyclosporine. When used simultaneously with ketoprofen, the clearance of methotrexate may be reduced. Ketoprofen helps reduce the diuretic, natriuretic and antihypertensive effect of diuretics; simultaneous use of potassium-sparing agents (triamterene, spironolactone) can cause the development of hyperkalemia. Ketoprofen can reduce the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs (beta-adrenergic receptor blockers, ACE inhibitors) due to disruption of the synthesis of prostaglandins in the kidneys. When used simultaneously with alendronate, the risk of developing gastropathy increases significantly.
List of pharmacies where you can buy Ketoprofen:
- Moscow
- Saint Petersburg