How to use No-shpu intramuscularly? Let's find out in this article.
The drug "No-shpa" is a drug based on the substance drotaverine, which is produced in the form of tablets and ampoules. The medicine gives an antispasmodic effect and is used in the treatment of spastic syndrome of the digestive tract, reproductive, hepatobiliary and urinary systems. In addition, this medication relieves spasms of cerebral vessels in case of headaches arising from overexertion as a result of depression and neurosis, and of peripheral vessels in case of Raynaud's disease or endarteritis.
The active substance is a derivative of papaverine. The non-proprietary international name of the drug “No-shpa” is “Drotaverine”. According to the clinical and pharmacological classification, it is classified as a myotropic antispasmodic. The properties of the substance are very similar to papaverine, but it has a longer and more pronounced relaxing effect on muscle fibers.
The effectiveness of the pharmacological agent is due to its ability to have an inhibitory effect on the enzyme phosphodiesterase, which, through a series of chemical reactions, can catalyze the inactivation of myosin chain kinase. This kinase phosphorylates myosin and provokes muscle contraction. When it is relieved, muscle relaxation is maintained. The positive properties of the drug also include selective suppression of only the fourth type of PDE, which does not affect the third type enzyme and does not cause negative side effects on the blood vessels and heart.
Drotaverine causes muscle relaxation when spasms of both neurogenic and myogenic origin occur and, regardless of the type of innervation, relaxation of muscle fibers. A significant advantage of this medication is that there is no stimulating effect on the cholinergic system, as a result of which the drug “No-shpa” can be used in people suffering from a disease such as glaucoma. However, some caution must be exercised when taking it, especially in the presence of prostatic hypertrophy, since symptoms of urinary retention may occur due to relaxation of the detrusor muscle in the bladder. So No-Spa is prescribed intramuscularly very often.
Indications for use
Indications for the use of the pharmacological agent “No-shpa” intramuscularly are the prevention and treatment of organ functional disorders and pain caused by:
- spasms of the muscles of the digestive organs of the tract with ulcers, gastritis, dyskinesia, pancreatitis, spastic enteritis, proctitis or colitis, as well as spasms of the pylorus or cardia, irritable bowel, development of flatulence, spastic constipation, tenesmus;
- disruption of the functionality of the hepatobiliary system due to inflammatory processes in the gallbladder or its ducts, hyperkinetic forms of biliary dyskinesia, cholelithiasis;
- excessive excitability of the uterus during pregnancy;
- spasms of the urinary system with the development of kidney stones, pyelitis, urolithiasis, neurogenic bladder, pyelonephritis, cystitis;
- spasms of the uterine pharynx during the birth process;
- prolonged opening of the uterine pharynx;
- postpartum contractions;
- threat of spontaneous miscarriage;
- menstruation.
This is stated in the instructions. “No-spa” is also used intramuscularly when spasms of cerebral and peripheral vessels occur. Effective for postoperative colic due to gas retention, preparation for instrumental studies, postcholecystectomy syndrome.
Use of “No-shpa” injections for children
Children under six years of age are prohibited from injecting the drug intramuscularly. It is important to know that the main substance of the drug is synthesized artificially. In other words, it is not a natural element. Therefore, No-shpu is usually used intramuscularly for children only as prescribed by a specialist.
The medicine is a good antispasmodic, but does not have an analgesic effect like, for example, Analgin and similar drugs. In addition, it has some contraindications for use, which should also be taken into account when treating children.
Instructions for use for No-Spa injections indicate that this medicine is usually prescribed to young patients in the following cases:
- White fever in children, which is accompanied by high fever and coldness of the extremities.
- Spasms due to bronchitis or stenosis, causing severe coughing.
- Spasms causing headache.
- Renal or intestinal colic.
- Excessive painful gas.
- Smooth muscle spasm during pyelitis or cystitis.
- Spasms due to gastritis or colitis.
Contraindications for the use of No-shpa injections for children are:
- age up to 6 years;
- low blood pressure in a child;
- intolerance to drotaverine;
- vascular diseases;
- bronchial asthma;
- suspicion of intestinal obstruction;
- suspicion of acute appendicitis;
- liver and kidney failure.
In accordance with the instructions for use, No-shpy injections can be administered during pregnancy.
Use during pregnancy
Among the medications that are widely used during pregnancy, No-spa plays a special role. Being a powerful antispasmodic, this medicine eliminates any pain associated with temporary dysfunction of the digestive tract in expectant mothers. In addition, during pregnancy this medication is absolutely safe and can be used without any fear.
However, even taking into account these properties of the drug, caution should be exercised when using it during this period, since it has certain indications for use, contraindications and negative side reactions.
During pregnancy, No-Spa can be prescribed intramuscularly for hypertonicity of the uterus and the threat of premature birth. At the first symptoms of premature birth or the threat of spontaneous miscarriage, such as nagging pain in the lower abdomen and a feeling of fullness in this area, a single use of No-shpa in most cases completely eliminates uterine hypertonicity and helps maintain pregnancy.
Another indication for the use of this pharmacological drug is spasm of the smooth muscles of the uterus and cervix during childbirth. This situation is dangerous because the child is in a clamped state - excessive tension in the myometrial muscles helps expel it from the uterus, but the contracted cervix prevents its movement through the birth canal. In most cases, one dropper with this medicinal solution is enough to restore the normal birth process. The intramuscular dosage of No-shpa must be strictly observed.
Contraindications
- The main contraindication to the use of this drug, like many other drugs, is the manifestation of severe disorders of the liver, kidneys, and heart, caused by insufficiency of their functions.
- In addition, the drug "No-shpa" is not prescribed during breastfeeding, since drotaverine and other representatives of this pharmacological category can pass into mother's milk.
- The use of the drug is allowed from 6 years of age, but only in tablet form, since studies of the effects of injection solutions have not been conducted, according to which the use of the drug parenterally is contraindicated.
- Taking the medication is contraindicated if you have a high sensitivity to the active element or other substances from its composition.
- This drug can only be used if certain precautions are taken when blood pressure is low due to the high likelihood of collapse, as well as during pregnancy.
What is the dosage of No-shpa intramuscularly?
Dosage regimen and methods of administration
A single dosage of the drug “No-shpa” in the form of solutions for intramuscular, intraarterial and intravenous administration, depending on medical indications, is 1-2 ampoules. The frequency of such injections is 1-3 times a day. How to administer No-shpu intramuscularly is indicated in the instructions.
During labor or after an abortion, administration of the drug in an amount of 80 mg is allowed with a time interval of at least 2 hours. How long does it take for No-shpa to work? Intramuscular and intravenous injection allows you to get the desired result after 5 minutes. That is why injections of this medication have become widespread.
"No-Shpa": composition and other characteristics
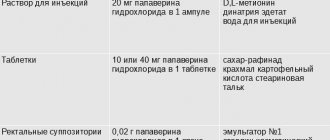
The drug belongs to the category of antispasmodics. Available in the form of tablets (6, 10, 24 pieces in one package) or in the form of injections (25 ampoules of 2 ml each).
The active ingredient is drotavertin (represented as hydrochloride). Each tablet contains 40 mg, each ampoule solution contains 20 mg. In the No-Shpa Forte variety (dosage doubled - 80 mg).
The tablets may have a yellowish, greenish or orange color. The shape of the tablets is round, both surfaces are convex. On one side there is a fault line in the middle, on the other there is a monolithic surface with the inscription “NOSPA”. The solution in the ampoules is also colored in shades of yellow and green.
The shelf life depends on the form of release. Tablets can be stored for 5 years, and ampoules - 3 years from the date of release. The drug is protected from light and stored at room temperature in the range from 15 to 25 degrees.
Attention!
Tablets can be purchased without a doctor's prescription, but injections can only be purchased with a prescription.
Side effects
Negative side reactions that may occur when using this pharmacological drug develop extremely rarely. Most often, its effect negatively affects the nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, blood vessels and heart.
- Nervous system: cephalalgia, dizziness, sleep disturbance.
- Circulatory system: increased or rapid heartbeat, feeling of heat, irregular heartbeat, decreased blood pressure (sometimes to the point of collapse), atrioventricular blockade.
- Digestive system: dyspepsia, nausea, stool disorders.
In addition to the above-mentioned negative effects of this medication, there is some information about side effects such as breathing problems, excessive sweating, and allergic reactions. Local redness or burning sensation may occur. Most often this manifests itself when the dosage of No-shpa injections is not observed.
Side effects from taking No-Shpa tablets
In most cases, no side effects are observed. But with long-term use, as well as due to the individual characteristics of the body and human condition, the following consequences may appear:
- increased heart rate;
- sleep disorders;
- headaches;
- dizziness;
- decreased blood pressure;
- nausea;
- bowel dysfunction (constipation);
- allergic reactions.
If an injection is administered, a local reaction (redness, foreign sensations) may additionally be observed.
Special Recommendations
There are also special instructions that should be strictly followed when using the No-Spa medication:
- Increased caution is required when treating patients who suffer from atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries or low blood pressure.
- The medicine is approved for use in the complex therapy of hypertensive crisis.
- The issue of driving a vehicle while using the drug is decided on an individual basis, especially if its negative effects occur. In this case, it is advisable to refrain from driving and activities involving the use of complex mechanisms when using an antispasmodic in injection forms. If dizziness occurs after administration of No-shpa, it is prohibited to perform these types of work intramuscularly.
- According to clinical studies, this medication does not have embryotoxic or teratogenic effects. However, it is necessary to remember the possible risk to the fetus and use the medication only for strict medical indications and with caution. The use of medication during pregnancy in the form of injections is undesirable.
- The use of an antispasmodic during labor can cause the development of postpartum atonic bleeding.
- The pharmacological agent contains metabisulfite (sodium disulfite) as an auxiliary element, which must be taken into account in the presence of hypersensitivity to it.
- When administering this medication parenterally, patients suffering from hypotension should take a horizontal body position due to the high likelihood of collapse.
What else does the instructions for “No-shpe” (intramuscular) tell us?
special instructions
No-Shpa contains lactose, so patients with impaired absorption of glucose and galactose should take the tablets with caution and only after the doctor’s approval.
If the solution is administered intravenously, the patient should lie down for several minutes at rest. If you have high blood pressure, use is allowed only in consultation with your doctor.
The injection solution contains sodium metabisulfite, which can cause an allergic reaction. In rare cases (especially in the presence of bronchial asthma, chronic allergies), bronchospasm and the onset of individual signs of anaphylactic shock are possible.
Drug interactions
Drotaverine, like other papaverine derivatives that inhibit PDE enzymes, can reduce the antiparkinsonian properties of levodopa, as well as increase muscle rigidity and tremor. With simultaneous therapy with other antispasmodic medications, mutual potentiation of antispasmodic effects may be observed. This pharmacological drug in injection form enhances the decrease in blood pressure caused by the use of antidepressants, quinidine or procainamide. This is confirmed by the instructions for use of No-shpa injections intramuscularly.
This medication reduces the spasmogenic effectiveness of morphine. When using phenobarbital, the antispasmodic effect of the drug “No-shpa” increases. Taking into account the high level of binding to plasma proteins (more than 80%), the possibility of competition of this drug with medications that have the same feature cannot be ruled out. Taking this fact into account, if a combination of such drugs is used, the toxic effect of the medications taken may be enhanced.
Analogs
The medical product "No-spa" in the form of injection solutions has many analogues that have the same composition, but different bioequivalence and bioavailability. These medications include:
- “Nosh-bra” is a medicine from the category of myotropic antispasmodics. In terms of pharmacological properties and chemical structure it is close to papaverine, but has a longer and stronger effect. Reduces the level of calcium ions entering smooth muscle cells (suppresses phosphodiesterase, promotes the accumulation of intracellular cAMP). Reduces muscle tone of organs and peristalsis, dilates blood vessels. It has no effect on the autonomic nervous system and does not penetrate the central nervous system. The presence of a direct effect on smooth muscles allows the use of this drug as an antispasmodic in situations where medications of the M-anticholinergic class are contraindicated (prostatic hyperplasia, angle-closure glaucoma).
- “Spazmol” is a medicine that is an antispasmodic with myotropic effects. A distinctive feature of this pharmacological drug is the presence of a long-lasting effect. The medicine affects not only the smooth muscles of internal organs, but also the walls of blood vessels. It can be taken to prevent the development of spasms or their presence in colitis, cholelithiasis, to eliminate spasms of the gastrointestinal tract, brain, to reduce the tone of the uterus, dilate blood vessels, and reduce peristalsis in the intestines.
- “Spakovin” is an antispasmodic with myotropic effectiveness, similar in properties to papaverine, but superior to it in effectiveness and duration of action. Reduces the tone of internal organs, their motor activity and has a vasodilating effect.
Other analogues of the drug “No-shpa” are:
- "Drotaverine hydrochloride";
- "Papaverine";
- "Drotaverine Forte";
- "Spazgan";
- "Kuplaton";
- "Niaspam";
- "Spazmolysin";
- "Disflatil";
- "Kidakol";
- "No-h-sha";
- "Spasmomen."
Buy No-spa solution intravenously and intramuscularly 40mg/2ml 2ml No. 5 in pharmacies
Instructions for use No-spa solution IV and IM 40 mg/2 ml 2 ml No. 5
Dosage forms injection solution 20mg/ml 2ml
Synonyms Droverin Nosh-bra Spazmol Spazmonet Group Antispasmodics - isoquinoline derivatives International nonproprietary name Drotaverine Composition Active substance - Drotaverine. Manufacturers Hinoin (Hungary), Hinoin Pharmaceutical and Chemical Products Plant A.O. (Hungary), Hinoin Pharmaceutical and Chemical Products Plant CJSC (Hungary) Pharmacological action Antispasmodic, myotropic, vasodilator, hypotensive. Quickly and completely absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract. It is evenly distributed throughout the tissues and penetrates smooth muscle cells. Excreted by the kidneys. Pronouncedly and for a long time expands the smooth muscles of internal organs and blood vessels, reduces blood pressure, and increases cardiac output. It has virtually no effect on the autonomic nervous system and does not penetrate the central nervous system. Side effects: Feeling of heat, dizziness, arrhythmias, hypotension, palpitations, sweating (more often with parenteral administration), allergic dermatitis. Indications for use Spasm of smooth muscles of internal organs (cardio- and pylorospasm), chronic gastroduodenitis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, cholelithiasis (hepatic colic), chronic cholecystitis, postcholecystectomy syndrome, hypermotor dyskinesia of the biliary tract, spastic intestinal dyskinesia, intestinal colic due to gas retention after surgery, colitis, proctitis, tenesmus, flatulence, urolithiasis (renal colic), pyelitis, spasm of cerebral vessels, coronary and peripheral arteries, the need to weaken uterine contractions and relieve cervical spasm during childbirth, smooth muscle spasm during childbirth time of instrumental interventions Contraindications Hypersensitivity, glaucoma. Overdose AV blockade, cardiac arrest, paralysis of the respiratory center. Interaction Enhances (especially with intravenous administration) the effect of other antispasmodics (including m-anticholinergics), hypotension caused by tricyclic antidepressants, quinidine, novocainamide. Phenobarbital increases the reliability of eliminating spasms. Reduces the spasmogenic activity of morphine and the antiparkinsonian properties of levodopa. Special instructions Restrictions on use. Prostate adenoma, severe atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries. Storage conditions List B. In a place protected from light at room temperature.
Reviews of No-shpy injections
Reviews about this drug are mostly positive. This is due not only to the high effectiveness of the drug, but also to the fact that it has been known for several decades as a good antispasmodic agent for various disorders in the body.
Patients say that No-Spa is one of the remedies that is always available in the home medicine cabinet. After taking it, the painful sensations associated with the development of spasms quickly disappear, and patients observe this effect within approximately 20 minutes. It was used by patients who left reviews, most often with the development of intestinal colic, cephalalgia of vascular origin, and pain in the right hypochondrium associated with impaired outflow of bile.
Experts also characterize this pharmacological drug as a highly effective antispasmodic, time-tested, and indicate its high safety, which helps to use this medicine even when treating pregnant women. However, they do not recommend using intramuscular injections without medical indications and recommendations, since this must be done very carefully. At home, as a rule, the tablet form of this medication is used.
We reviewed the instructions for use of No-shpe intramuscularly.
Instructions for use "No-Shpa"
Dosage and rules of administration depend on the form of the drug and the age of the person:
- The daily dosage of the active substance for an adult is in the range of 120-240 mg, which corresponds to 3-6 tablets of the regular drug and 2-3 tablets of the “Forte” variety. In this case, it is allowed to consume no more than 40 mg at a time, i.e. maximum 2 tablets.
- For children under 11 years of age inclusive, the optimal dose is 80 mg - this amount is taken 2 times a day.
- For older children, a dose of 160 mg is indicated, divided into 2-4 times.
The general course of therapy (with self-treatment) is no more than 2 days. If during this time your health does not improve, you need to contact a specialist for a possible replacement of the drug and diagnostics. If No-Shpa is used as an additional medication as part of complex therapy, then the course without consulting a specialist can last up to 3 days.