Pharmacological properties
DexaTobropt is a drug with a combined composition that has pronounced antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties.
The antibiotic of the aminoglycoside group, tobramycin, has a wide spectrum of action. Active against: Staphylococci, including strains resistant to penicillin, Streptococci, incl. a number of beta-hemolytic species of group A, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter, most species of Proteus, Haemophilus influenzae, etc.
The glucocorticosteroid dexamethasone is effective as an anti-inflammatory, antiallergic, and desensitizing agent. It actively suppresses inflammatory reactions, inhibiting eosinophils from releasing its mediators, reduces the possibility of mast cell migration, reducing the permeability of the capillary wall. Does not have mineralocorticoid activity.
The time of maximum activity of the drug is 15-20 minutes after its use.
Composition and release form
Dexatobropt eye drops are a suspension that is white in color. The main components contained in the composition are dexamethasone and tobramycin. You can also find additional components in these drops, which include:
- Tiloxapol.
- Sodium sulfate.
- Sodium chloride.
- Benzalkonium chloride.
The capacity of the plastic bottle is 5 ml. You can also find instructions in the dexa.
pharmachologic effect
The main feature of this drug is that it is a combination drug. Tobramycin is an antibiotic that belongs to the aminoglycoside family. Dexamethasone is a glucocorticosteroid that can have anti-inflammatory as well as antiallergic effects.
With its help, you will have a wonderful opportunity to suppress the inflammatory processes that develop in the eye. The maximum activity of these drops can be noticed within 20 minutes after use.
Indications
Instructions for use of Dex Tobrom provide information that drops should be used for treatment:
- Blepharitis.
- Conjunctivitis.
- Keratitis.
- For the treatment of inflammatory processes.
Mode of application
Dexa tobro eye drops instructions contain information that the drops must be used topically. Installation must be carried out every 6 hours, 1-2 drops. Before use, you must consult a doctor who will tell you how to properly use Dexatobropt eye drops.
If you see certain improvements, then remember that in this case the dose must begin to be reduced.
Contraindications
When using Dexatobrom drops, remember that there are the following contraindications:
- Fungal diseases.
- Pregnancy period.
- Age up to 18 years.
- Viral diseases.
- Sensitivity to certain components contained in the composition.
It is also necessary to be careful when choosing a drug while breastfeeding.
Side effects
When using these drops, you can also experience side effects, which include:
- Itching.
- Burning.
- Headache.
- Increased blood pressure.
- Swelling.
If you use these drops for more than 3 months, then you may also experience corneal mycosis, as well as a slowdown in regeneration processes. Sometimes a secondary infection may develop.
Interaction with other drugs
To date, drug interactions with other drugs have not been studied. If you plan to use Dexatobropt with other drugs, then be sure to leave an interval of 5 minutes between uses.
Special instructions and precautions
After each use of the drops, be sure to close the bottle with a lid. Also remember not to touch the tip of the drops with your fingers, as this may introduce bacteria. Before use, you definitely need to consult with specialists who will really help. If you use contact lenses, then it is better to remove them and put them on only 15 minutes after instilling the drug.
During installation, your vision may be impaired and therefore driving is prohibited.
The shelf life of the drops is currently 3 years, but after opening the bottle, the drops must be consumed within 1 month. Attention! The description of the drug on this page is simplified. Before purchasing and using the drug, consult your doctor or pharmacist, and also read the instructions approved by the manufacturer. Information about the drug is provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as a guide to self-medication. ATTENTION! This section is provided for informational purposes only and is not a catalog or price list of our company. To obtain information about the availability of drugs, call + 99871 202 0999 Pharmacy Network Helpline 999.
Contraindications
- Viral eye diseases (including keratitis caused by Herpes simplex and chickenpox).
- Fungal diseases of the eyes.
- Mycobacteria.
- Individual hypersensitivity.
- Damage to the epithelium after removal of a foreign body.
- Childhood.
DexaTobropt can be prescribed with caution in pregnant and breastfeeding women, when strictly necessary and under medical supervision. During treatment, breastfeeding is interrupted.
DexaTobropt, 1 piece, 5 ml, eye drops
Some patients may experience hypersensitivity reactions to topical aminoglycosides. Hypersensitivity reactions (allergic reactions) can be of varying severity and range from local to generalized reactions, including erythema, pruritus, urticaria, rash, anaphylaxis, anaphylactoid reactions or bullous reactions.
If hypersensitivity develops during use of the drug, treatment should be discontinued.
It is possible to develop cross-hypersensitivity to other aminoglycosides. Patients hypersensitive to topical tobramycin may also be sensitive to other topical or systemic aminoglycosides.
Serious adverse reactions, including neurotoxicity, ototoxicity, and nephrotoxicity, have occurred in patients receiving systemic aminoglycoside therapy. Caution should be exercised with simultaneous local and systemic use of aminoglycosides.
Caution is required when using the drug in the treatment of deep stromal keratitis caused by Herpes simplex; Also, with this herpetic lesion of the eye organ, frequent biomicroscopy is necessary.
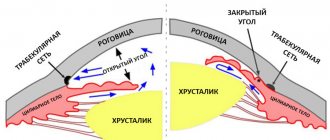
Long-term use of GCS for local use in ophthalmology, exceeding the maximum recommended duration of therapy - 24 days, can lead to an increase in intraocular pressure and the development of a glaucoma symptom complex, including damage to the optic nerve, decreased visual acuity and narrowing of the boundaries of the visual fields; to the formation of posterior subcapsular cataracts. Therefore, in patients who have been using drugs containing corticosteroids for a long time, intraocular pressure should be measured regularly and frequently.
The risk of increased intraocular pressure and/or cataract formation due to the use of corticosteroids is higher in patients with a predisposition (for example, with diabetes mellitus).
In predisposed patients, including children and patients receiving ritonavir, Cushing's syndrome and/or adrenal suppression may occur after intensive therapy or continuous long-term therapy due to systemic absorption of dexamethasone when administered locally. In these cases, the drug should not be discontinued immediately, but gradually.
GCS can reduce resistance to bacterial, viral or fungal infections and promote their development, as well as mask clinical signs of infection.
The appearance of non-healing ulcers on the cornea may indicate the development of fungal invasion. If fungal invasion occurs, GCS therapy should be discontinued.
Long-term use of antibiotics such as tobramycin can lead to increased growth of resistant organisms, including fungi. If superinfection develops, use of the drug should be discontinued and appropriate therapy should be started.
The use of a fixed combination of dexamethasone and tobramycin in the treatment of acute purulent infections of the organ of vision is possible only in the case of previous local antibiotic therapy, since the use of dexamethasone during this period can aggravate the course of the infectious process. Abrupt cessation of therapy due to the possibility of resumption of symptoms of infectious or inflammatory damage to the organ of vision is undesirable. GCS, when applied topically, can slow down the healing process of the cornea. Topical NSAIDs also slow healing. Concomitant use of topical NSAIDs and topical corticosteroids may increase the likelihood of impaired healing.
In diseases that cause thinning of the cornea or sclera, perforations may occur as a result of the use of topical corticosteroids. When therapy lasts more than 2 weeks, the condition of the cornea should be monitored.
In the case of topical use of tobramycin simultaneously with aminoglycoside antibiotics for systemic use, the general blood picture should be monitored.
When treating inflammatory eye diseases, it is not recommended to wear contact lenses. This product contains benzalkonium chloride, which may cause eye irritation and change the color of soft contact lenses. Contact of the drug with soft contact lenses should be avoided. If patients are allowed to wear contact lenses, they should be instructed that before using the drug, soft contact lenses should be removed and reinserted no earlier than 15 minutes after instillation of the drug.
Effect on fertility
No studies have been conducted on the effect of the drug on animal or human fertility. Clinical data to assess the effect on fertility in men or women is limited.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and machinery
Temporary blurred vision or other visual disturbances after using the drug may affect the ability to drive vehicles and machines. If blurred vision occurs after instillation of the drug, then before starting to drive vehicles and machinery, the patient must wait until vision clarity is restored.
special instructions
DexTobropt solution is not intended for injection.
When using DexTobropt suspension with other ophthalmic drugs topically, it is necessary to leave a five-minute interval between their applications.
No adverse effects of DexTobropt solution on the ability to drive vehicles have been reported. However, given that after applying the solution, a temporary loss of clarity of vision is possible, immediately after instilling the drug, it is not recommended to drive or start working with complex mechanisms.
DescaTobropt solution contains benzalkonium chloride, which is a preservative and can cause discoloration of soft contact lenses. Therefore, before using the drug, it is recommended to remove the lenses. They can be inserted again after a quarter of an hour after instillation.
Before using the solution, the bottle should be shaken vigorously.
After use, the bottle cap must be screwed on tightly.
Store Dexa Tobropt in a dark place at room temperature. Protected from children.
After opening the bottle, the suspension is good for 4 weeks.
Dexatobropt
Some patients may experience hypersensitivity reactions to topical aminoglycosides. Hypersensitivity reactions (allergic reactions) can be of varying severity and range from local to generalized reactions, including erythema, pruritus, urticaria, rash, anaphylaxis, anaphylactoid reactions or bullous reactions.
If hypersensitivity develops during use of the drug, treatment should be discontinued.
It is possible to develop cross-hypersensitivity to other aminoglycosides. Patients hypersensitive to topical tobramycin may also be sensitive to other topical or systemic aminoglycosides.
Serious adverse reactions, including neurotoxicity, ototoxicity, and nephrotoxicity, have occurred in patients receiving systemic aminoglycoside therapy. Caution should be exercised with simultaneous local and systemic use of aminoglycosides.
Caution is required when using the drug in the treatment of deep stromal keratitis caused by Herpes simplex;
Also, with this herpetic lesion of the eye organ, frequent biomicroscopy is necessary.
Long-term use of GCS for local use in ophthalmology, exceeding the maximum recommended duration of therapy - 24 days, can lead to an increase in intraocular pressure and the development of a glaucoma symptom complex, including damage to the optic nerve, decreased visual acuity and narrowing of the boundaries of the visual fields; to the formation of posterior subcapsular cataracts. Therefore, in patients who have been using drugs containing corticosteroids for a long time, intraocular pressure should be measured regularly and frequently.
The risk of increased intraocular pressure and/or cataract formation due to the use of corticosteroids is higher in patients with a predisposition (for example, with diabetes mellitus).
In predisposed patients, including children and patients receiving ritonavir, Cushing's syndrome and/or adrenal suppression may occur after intensive therapy or continuous long-term therapy due to systemic absorption of dexamethasone when administered locally. In these cases, the drug should not be discontinued immediately, but gradually.
GCS can reduce resistance to bacterial, viral or fungal infections and promote their development, as well as mask clinical signs of infection.
The appearance of non-healing ulcers on the cornea may indicate the development of fungal invasion. If fungal invasion occurs, GCS therapy should be discontinued.
Long-term use of antibiotics such as tobramycin can lead to increased growth of resistant organisms, including fungi. If superinfection develops, use of the drug should be discontinued and appropriate therapy should be started.
The use of a fixed combination of dexamethasone and tobramycin in the treatment of acute purulent infections of the organ of vision is possible only in the case of previous local antibiotic therapy, since the use of dexamethasone during this period can aggravate the course of the infectious process. Abrupt cessation of therapy due to the possibility of resumption of symptoms of infectious or inflammatory damage to the organ of vision is undesirable. GCS, when applied topically, can slow down the healing process of the cornea.
Topical NSAIDs also slow healing. Concomitant use of topical NSAIDs and topical corticosteroids may increase the likelihood of impaired healing.
In diseases that cause thinning of the cornea or sclera, perforations may occur as a result of the use of topical corticosteroids. When therapy lasts more than 2 weeks, the condition of the cornea should be monitored.
In the case of topical use of tobramycin simultaneously with aminoglycoside antibiotics for systemic use, the general blood picture should be monitored.
When treating inflammatory eye diseases, it is not recommended to wear contact lenses. This product contains benzalkonium chloride, which may cause eye irritation and change the color of soft contact lenses. Contact of the drug with soft contact lenses should be avoided. If patients are allowed to wear contact lenses, they should be instructed that before using the drug, soft contact lenses should be removed and reinserted no earlier than 15 minutes after instillation of the drug.
Effect on fertility
No studies have been conducted on the effect of the drug on animal or human fertility. Clinical data to assess the effect on fertility in men or women is limited.