Neurology Symptoms Services and prices Specialists Diseases
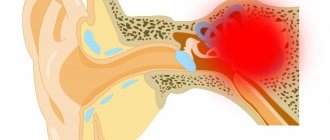
Dizziness is a state of the body characterized by a transient feeling of movement of one’s own body in space or objects relative to the person himself. This symptom is described as the appearance of rotation, because in fact the patient and the objects around him are in a stationary state. Having consulted a doctor, a person often describes his sensations as “everything around is spinning” or “the earth is disappearing from under his feet.” Sometimes the patient complains of fatigue, weakness, anxiety, and unsteady gait. In such a situation, it is important to establish what is actually happening in the body and determine the reasons for what is happening. Classification of dizziness
Such ailment is divided into two types: vestibular or reliable and non-vestibular or imaginary. The vestibular type is considered as dizziness, the source of which is disorders in one or more parts of the vestibular apparatus. Non-vestibular occurs as a consequence of dysfunction of an organ, groups of organs and injuries. It also manifests itself as a consequence of psychological instability and nervous disorders.
Causes of dizziness
This is a common symptom that accompanies a lot of pathological conditions. Dizziness can be both the main manifestation of the disease and a secondary symptom of some diagnoses. Sometimes minor changes in the functioning of the body manifest themselves as such ailments. Often the source is vestibular deviations.
The probable root cause of dizziness is considered to be:
- pathologies of the vestibular analyzer;
- diseases of internal organs;
- diseases of the organ of vision;
- destructive changes in the cervical spine;
- cerebrovascular accidents;
- disorders of the physiological functions of the body.
Dizziness as a consequence of diseases of the internal organs
The appearance of such a symptom provokes the presence of diseases of the cardiovascular system or other organs in a person.
List of common pathologies whose symptoms include dizziness:
- abnormalities in heart rhythm;
- myocardial infarction;
- cardiomyopathy of various etiologies;
- dysfunction of the heart valves (heart defects);
- postural hypotension (a sharp drop in pressure when changing body position);
- excessive pulmonary ventilation due to nervous system disorders;
- anemia;
- diabetes;
- infection of the body;
- use of certain groups of drugs.
Popular medications on the topic
Cerebrolysin Cerebrolysate
For more information about the causes of dizziness, watch the video:
Diagnosis and treatment of dizziness is a difficult task even for an experienced doctor. In every case of a painful, prolonged or sudden attack, consultation with a specialist is required. Only he will determine what the patient should do next, what consultations and examinations she needs.
This article has been verified by a current qualified physician, Victoria Druzhikina, and can be considered a reliable source of information for site users.
Bibliography
1. https://kiberis.ru/?p=50203 2. https://nikio.ru/docs/02-golovokruzhenie1.pdf 3. https://docs.cntd.ru/document/901918942
Assess how much it was useful article
4.4 150 people voted, average rating 4.4
Did you like the article? Save it to your wall so you don’t lose it!
Dizziness as a manifestation of visual pathologies
The organ of vision indirectly maintains balance. Therefore, visual disturbances can cause dizziness.
Eye pathologies accompanying the development of an attack:
- deviation of the visual axis (squint);
- nystagmus (involuntary movements of the eyeball);
- glaucoma;
- cataract;
- weakened vision;
- astigmatism;
- diplopia (double image).
Poor cerebral circulation is a reason for dizziness
The human body is designed in such a way that in situations where the blood supply to the brain is disrupted, compensatory modes are triggered. They work to restore vital processes. In unfavorable circumstances, self-compensation is not possible.
There are several types of cerebrovascular dysfunction:
- Acute condition. Manifests itself in the form of an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke and requires emergency medical attention.
- Acute transient in the form of a transient ischemic attack. In this situation, the body’s compensatory functions are sufficient for self-healing. The duration of the attack is a couple of minutes. Within 24 hours, the person returns to his original state, and his head stops spinning.
- A chronic condition in which the disease progresses slowly.
Physiological dizziness
Not in all cases, dizziness is a manifestation of the disease. Sometimes this is how the body reacts to stimuli. This condition is provoked by:
- A rapid movement in which the body sharply deviates from the horizontal: riding on a swing, jumping from a height.
- Anxiety, panic attacks, fright, during which excess amounts of stress hormones are released into the blood.
- Oxygen starvation, which occurs due to a lack of iron in the blood or for other reasons.
- Hyperventilation of the lungs.
- Hypoglycemia is exhaustion of the body due to a lack of glucose.
- Dizziness as a sign of pregnancy. The monthly physiological state of a woman during the premenstrual period or during menstruation.
- Menopausal syndrome.
Dizziness associated with pathologies
Such diagnoses include:
- Diseases of the inner ear: labyrinthitis, vestibular neuritis, etc. Such conditions lead to disturbances in the conduction of auditory and vestibular signals to the part of the brain that is responsible for recognizing these impulses.
- A cervical hernia compresses blood vessels, preventing proper blood circulation.
- Hypoxia due to stroke, thrombosis or ischemia.
- Migraine and attacks of benign paroxysmal vertigo.
- Brain tumors.
Classification: types of vertigo
Dizziness, depending on the cause and characteristics of the disturbance in the mechanism of maintaining balance, can be true or false.
False vertigo occurs due to overwork, malnutrition, anemia or hypotension. With false dizziness, patients complain of instability and weakness. You may also experience blurred vision or darkening.
True dizziness, depending on the cause, can be:
- Central
is caused by causes related to the central nervous system. This could be a brain injury or tumor, stroke, multiple sclerosis, and so on. - Peripheral
vertigo occurs due to dysfunction of the vestibular apparatus. Factors that provoke dizziness are ear diseases, damage or injury to the spine, decreased sensitivity of vestibular apparatus receptors, and so on.
Dizziness is also classified into the following types:
- systemic;
- non-systemic (physiological).
A feature of systemic vertigo is that it occurs as a result of disturbances in one of the systems responsible for maintaining balance (visual, muscular, vestibular).
Physiological vertigo occurs as a result of excessive irritation of the vestibular apparatus. Unsystematic dizziness can occur due to overwork, lack of glucose (fasting), riding a carousel, traveling by transport, swinging in the sea, and so on.
Situations that require immediate medical attention
If dizziness is aggravated by the following symptoms:
- Attacks of nausea and vomiting.
- Severe headache.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Rapid heartbeat, chest pain, trembling in the limbs, sweating, lack of full breath.
- A sharp loss of sensitivity. Weakness in half the body, face, arms or legs.
Such manifestations of the disease are highly likely to indicate an emergency condition and the need for urgent treatment.
Definition and Features
It is necessary to distinguish between true dizziness, in which there is a feeling of objects moving in space. Such symptoms may be normal if they occur after prolonged rotation around its axis (on a carousel), but in other cases they indicate a malfunction of the vestibular apparatus. The difficulty in diagnosing this condition is that the doctor has to rely only on the patient’s testimony. Many people also mean other symptoms by this term: impaired visual acuity, headaches and others. In reality, dizziness should be understood as a feeling of movement of environmental objects in relation to a person, while the body position is felt as stable. Most often these are circular movements (objects rotate around a person’s axis), but they can also be linear (a feeling of falling or rising in height, various shocks).
Diagnosis of dizziness
To get a diagnosis, see a doctor. The profile of the specialist has been discussed above. In such situations, health workers act by elimination, so you will need to do a number of studies:
- Ultrasound of the great vessels of the head and neck;
- examination by an ophthalmologist;
- ENT examination, audiogram if necessary;
- X-ray, CT or MRI of the spine and brain (the specific diagnostic procedure is recommended by the doctor);
- laboratory tests (tests).
Treatment is prescribed only based on the results of a comprehensive examination.
A condition in which dizziness is a common occurrence. You should not ignore the problem or tolerate it. Dizziness is not uncommon as a sign of serious health problems. Timely measures are the key to a successful resolution of the situation. If the examination does not reveal any organic pathologies, maintenance therapy will be prescribed.
Preventive measures
To reduce your risk of dizziness, follow these tips:
- watch your diet, give up exhausting diets and hunger strikes;
- choose comfortable clothes without tight collars, which can compress blood vessels;
- if you have heart or vascular diseases, monitor your blood pressure;
- if you get motion sickness in transport, take special tablets or mints;
- try not to stand up suddenly or make sudden movements of your head;
- eat foods rich in iron.
Dizziness can occur for various reasons, but only a doctor can determine the true cause and prescribe effective treatment. Do not self-medicate. Remember that vertigo may indicate the development of serious diseases of the brain or spinal cord.
Treatment of dizziness
Diagnoses vary. And while some conditions can be treated conservatively, others require emergency or planned surgical intervention.
Conservative treatment is prescribed by a specialist who deals with the problem indicated by laboratory and instrumental studies.
Dizziness is not an independent diagnosis, but a manifestation of an underlying disease. Therefore, symptomatic and etiotropic treatment will be required, aimed at eliminating both the cause of the disease and its consequences. The first thing they do is try to influence the symptom that brought the patient to the walls of the medical facility: do everything to stop the dizziness. Then they delve into the original source, affecting the epicenter of the disease.
The doctor will select the necessary medications and procedures, and at the same time give recommendations on physical activity, nutrition, etc. Treatment methods are aimed not only at stabilizing the patient’s condition, but also at long-term prevention of relapses of dizziness attacks.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the timeliness of diagnosis, the qualifications of the attending physician and the patient’s responsible attitude to the recommendations received. Take care of yourself and be healthy!
First aid
If severe vertigo occurs, a person must be put to bed. It is necessary to provide a flow of fresh air. The patient is not recommended to close his eyes.
You need to focus on some subject and try to regain your balance. It is allowed to take 8-10 drops of atropine.
If dizziness is caused by overwork, you need to ensure rest; if there is a lack of glucose (often happens during diets), you need to drink warm sweet tea or eat candy.
To help get rid of dizziness:
- tea with ginger;
- tea with mint or lemon balm;
- tea with linden blossom;
- carrot and beet juice.
For anemia, it is recommended to drink pomegranate juice. Sea kale powder, which is rich in iodine and phosphorus, will help restore the functioning of the vestibular apparatus.
If you experience frequent dizziness, you should not self-medicate. Contact your doctor and get examined.