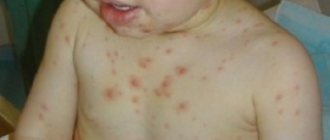
Carbuncle is an acute purulent-necrotic inflammation of several closely located sebaceous glands and hair follicles, caused by Staphylococcus aureus (St. aureus). It mainly affects the back of the neck, interscapular area, skin of the buttocks and face. On the extremities, carbuncles appear much less frequently.
Most often, a carbuncle is formed in patients with blood diseases, diabetes, obesity, and reduced immunity. Predisposing factors may also include oily skin type and poor personal hygiene.
Causes of carbuncle
The appearance of a carbuncle is preceded by an inflammatory process in the soft tissues, which usually begins with an inflammatory disease of the hair follicle - staphylococcal folliculitis, less often - with streptococcal folliculitis.
The development of inflammation can lead to the formation of a boil, which is an acute purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle. When several such boils form in one area of the body, they can merge with each other.
The product of the merger of several boils is a carbuncle. A sharp bursting pain occurs in the area of infiltration. The skin over the infiltrate becomes purple, tense, and swollen. Large amounts of gray-green pus are released from the pustules.
The tissues become necrotic. There are clear signs of general intoxication: tachycardia, nausea, vomiting, severe headache, hyperthermia up to 39-40 ° C, leukocytosis, shift of the blood count to the left, lack of appetite, insomnia. If the carbuncle is localized on the face, the symptoms of intoxication are much more pronounced, even to the point of fainting.
After exfoliation of necrotic tissue and removal of pus, the severity of signs of intoxication weakens significantly.
Risk factors for carbuncle formation:
- the presence of a chronic source of infection in the body;
- lack of vitamins;
- diabetes mellitus and other metabolic disorders;
- exhaustion of the body;
- psychological overload;
- immunodeficiency states;
- recent operations or serious illnesses;
- skin contamination, poor sanitary culture;
- nutritional deficiency;
- obesity;
- prolonged friction of the skin with clothing;
- increased sweating.
Carbuncle mainly affects teenagers and young adults. Men get sick more often than women.
ICD-10 code
Carbuncle belongs to the group of infectious skin diseases with the code - L00-L08 .
It includes:
- carbuncle on the skin ( L02 );
- carbuncle in the facial area ( L02.0 );
- carbuncle of the neck ( L02.1 ) and body ( L02.0 );
- carbuncle of the buttocks ( L02.3 );
- carbuncle of arms and legs (L02.4);
- carbuncle of other ( L02.8 ) or unrefined localization ( L02.9 ).
Symptoms of carbuncle
Clinical signs of a carbuncle are:
- suppuration and wound formation;
- hyperemia of the skin around the lesion;
- severe pain in the entire affected area.
The appearance and development of a carbuncle is usually accompanied by the following symptoms:
- elevated temperature, which often reaches 40 degrees;
- major intoxication;
- vomiting;
- nausea;
- loss of appetite;
- headache;
- general malaise.
These signs are especially pronounced when the carbuncle appears on the face or neck.
There are 3 stages of carbuncle:
Stage 1: infiltrate (folliculitis)
During this period, nodes form under the skin, which will be represented by inflamed hair follicles. The infiltrate contains adipose tissue, pus, lymph and lymphocytes. Nodules rise above the surface of the skin.
Since the nutrition of the dermis is disrupted, it acquires a bluish color. After a few days (from 9 to 12), the infiltrate reaches impressive sizes. It can be about 10 cm in diameter. The skin is swollen, tense, and hot to the touch. The more swelling there is, the more intense the pain will be.
Stage 2: purulent formation
At the stage of suppuration, the carbuncle reaches maturity. Blisters form on it, which are filled with pus. They open, so the surface of the carbuncle resembles a sieve. Through these small holes, pus leaks out, mixed with blood and dead epithelium.
The suppuration stage lasts about 14-21 days. During this period, the patient’s general health deteriorates.
Stage 3: necrosis and tissue rejection
During this period, pus from the carbuncle stops oozing. At the site of inflammation, ulcers are formed that will have rods. They merge with each other, forming one large defect. Tissue damage is very intense and often involves muscles. The affected area is black.
The wound heals slowly, gradually filling with granulations. A scar remains in its place. The necrosis stage lasts about 21 days.
Description
Carbuncle is a dermatological disease in which inflammatory, purulent-necrotic damage to several hair follicles and sebaceous glands occurs in the patient’s skin.
The carbuncle received this name because of the black color acquired by the purulent-necrotic masses. After all, translated from Greek, Carbo means coal.
People of all ages can experience carbuncles, however, they are more common in young people. It is worth noting that carbuncles are diagnosed in men approximately 1.5-2 times more often than in women. Moreover, about 50% of all cases of carbuncle are recorded in the summer.
Most often, carbuncles occur on the face, groin, back and buttocks. Treatment of this pathology must be carried out necessarily, otherwise the patient may develop a number of serious complications.
As a rule, there is one carbuncle on the patient’s body, although in some cases there may be several at once.
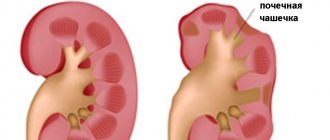
In addition to the usual form of carbuncles, doctors also identify specific ones - anthrax carbuncle, emphysematous carbuncle and kidney carbuncle.
- Anthrax carbuncle (cutaneous form of anthrax) is a special type of disease. When this pathology occurs, patients are isolated from others and anti-epidemic work is carried out;
- Kidney carbuncle is a pathology in which the kidney tissue of a sick person is affected by a purulent-necrotic process. The symptoms of this disease are very similar to pyelonephritis, which occurs in a purulent form;
- Emphysematous carbuncle is an infectious disease of animals in which they develop a fever and swelling appears on the body. The disease progresses very violently and rapidly. As a rule, it causes the death of animals. Cattle are most often affected by the disease.
Pathogenesis
The causative agents of carbuncles are pyogenic bacteria - staphylococci and streptococci. In more rare cases, the disease can be caused by E. coli.
Carbuncle has 2 stages of progression:
- infiltration. At this stage, the infection enters the skin and causes inflammation of several hair follicles. An infiltrate appears at this site, which can reach 10 cm in diameter. In some cases, a carbuncle is the result of an untreated boil. In this case, the pathological process simply moves from already affected tissues to healthy ones. Blood clots may occur in the area where the infiltrate is located, which in turn can lead to necrosis of the skin and adipose tissue. In the center of the pathological process, the skin becomes black (necrosis area). The duration of this stage is 1 week – 12 days;
- purulent spread. At this stage, inflammation intensifies, and pus is actively formed at the site of the pathological process. In this case, the area of necrosis increases. Holes appear on the affected skin, from which pus and necrotic tissue emerge. After the necrotic masses drain, a huge ulcer appears on the human skin, which in some cases can reach the bone tissue. If the carbuncle has reached this stage, patients will most likely be left with rough scars after treatment. This stage usually lasts no more than 20 days.
Causes of pathology
The environment and the individual characteristics of the organism play an important role in the formation of the carbuncle.
The most common causes of carbuncle development are:
- damage to the integrity of the skin, even if it is very minor (for example, squeezing out blackheads or scratching mosquito bites with dirty hands);
- penetration of pathogenic bacteria into areas rubbed with fabric due to prolonged wearing of clothing;
- frequent interaction with machine oil, diesel fuel or fuel oil;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules, as a result of which pathogenic microorganisms enter the pores of the skin and cause inflammation;
- deficiency of vitamins or minerals in the body, unbalanced diet, resulting in a severe decrease in immunity;
- metabolic disorders (diabetes or obesity);
- exhaustion of the body (including nervous exhaustion), decreased hemoglobin levels in the blood, fatigue.
Complications of carbuncle
Most complications arising from a purulent carbuncle are associated with the progression of infection from the lesion to the deeper layers of tissue. So, in some cases, the pathological process can affect not only the skin, muscle and fat tissue, but also the circulatory system.
Most often, these complications are observed in patients who did not treat the disease or treated it incorrectly and have very weak immunity.
Among the main complications of the pathology, one can highlight the development of acute purulent inflammation of surrounding tissues. Penetration of infection to the bone level can cause osteomyelitis.
If the infection affects the veins or blood vessels, the patient may develop inflammation of the vein walls or thrombophlebitis. In this case, bleeding may occur from vessels affected by the pathological process. When the lymphatic system is involved in the pathological process, patients may develop inflammation of the lymph nodes and lymphatic trunks, as well as the tissues that are located near them. In some cases, this is accompanied by their suppuration.
In the presence of several unfavorable factors, complications of the carbuncle can be supplemented by erysipelas.
Of all the carbuncles, the most dangerous are those found on the face. This is due to the fact that the blood vessels of the face are located close to the brain, as a result of which an infection through the bloodstream can quickly spread to the brain and cause purulent meningitis.
Once in the blood, the infection can also cause another serious disease - sepsis (blood poisoning), which in turn often leads to death.
If a patient, despite treatment, develops such complications as blood poisoning, meningitis or bleeding in a short period of time, then the carbuncle that caused these complications is called malignant.
What is the difference between a carbuncle and a boil?
If a patient experiences severe inflammation of the hair follicle, and tissue necrosis occurs in the affected area, this indicates the presence of a boil. If there are many such affected areas on the skin of the body, but they are located in different places, we are talking about furunculosis. With this disease, the patient experiences severe pain, his skin turns red, and a purulent core forms.
The difference between a carbuncle and a boil is that a carbuncle is an accumulation of several boils in one area. It is characterized by a larger area of inflammatory damage, and after opening, ulcers remain in its place. A skin carbuncle requires longer and more complex treatment than a boil.
Disease prevention
Prevention of carbuncle involves maintaining personal hygiene, proper nutrition, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and strengthening the immune system.
If symptoms indicating a carbuncle occur, you should contact a dermatologist, and in advanced cases, a surgeon.
Methods for diagnosing carbuncle
Carbuncle is diagnosed based on clinical symptoms.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with the following pathologies:
- rupture of an epidermal cyst;
- hidradenitis (if the carbuncle is localized in the perineum or armpit);
- anthrax;
- chronic ulcerative herpes.
Laboratory diagnostics
Microscopy of the smear reveals staphylococci. Bacterial culture allows identification of the pathogen and assessment of sensitivity to antibiotics.
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.
Treatment methods for carbuncle
Small carbuncles that occur without noticeable intoxication and deterioration of the patient’s general condition are treated on an outpatient basis.
In cases where
- the patient is severely intoxicated,
- the carbuncle is large and localized on the face,
- the patient suffers from uncompensated diabetes mellitus or other serious diseases,
treatment is carried out in a hospital.
Conservative treatment
If treatment of the carbuncle was started at the stage of its maturation, then conservative methods are used, which in most cases leads to regression of the disease, that is, resorption of the infiltrate.
Antibacterial drugs with a broad spectrum of action are indicated for oral administration to the patient.
At the same time, the carbuncle itself is injected with antibiotics. To reduce pain, analgesics (Novocaine, Lidocaine) are used.
The surface of the carbuncle is treated with ethyl alcohol or other alcohol-containing antiseptics. An aseptic dressing is applied. Syntomycin or streptomycin emulsions are also used.
Surgery
If the carbuncle enters the necrotic stage, then this is an indication for surgery, which is performed while using antibiotic therapy.
The operation consists of dissecting the carbuncle and removing necrotic tissue from it.
Then a tampon with a hypertonic sodium chloride solution and proteolytic enzymes is inserted into the wound.
To clean the postoperative wound and completely remove necrotic tissue, the dressing is changed daily.
Physiotherapy
At the maturation stage, as well as in the postoperative period, UHF therapy and local ultraviolet radiation are prescribed.
To stimulate the body's defenses, intravenous laser and ultraviolet irradiation of blood can also be performed.
More information about the treatment method
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
Folk remedies
Photo: fittedmagazine.com
You should not use local methods (lotions, compresses) on your own, because choosing treatment methods without taking into account the severity and stage of development of the abscess can cause severe complications. At home, it is recommended to use safer general remedies:
- Brewer's yeast . The high content of amino acids, vitamins B and D helps the body fight infection and eliminate toxins faster. Yeast is taken before meals 3 times a day in the amount of 1 teaspoon.
- Chicory . It has an immunostimulating effect, contains useful vitamins and minerals, and has antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects. Pour 2 teaspoons of chicory root into a glass of boiling water, leave for 2 hours, then consume a third of a glass 3 times a day.
To increase immunity, rose hip tea, cranberry juice, infusion of ginger and lemon, infusion of sea buckthorn with lemon and honey, and a decoction of bay leaves are useful. Before using any folk recipe, you should consult your doctor to rule out contraindications.
The information is for reference only and is not a guide to action. Do not self-medicate. At the first symptoms of the disease, consult a doctor.