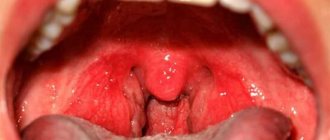
Catarrhal tonsillitis - almost everyone is familiar with this disease. This infectious disease in medicine is called acute tonsillitis. Catarrhal sore throat in adults is a sore throat in the usual sense. This disease proceeds according to the classical scheme, and is quite easy to treat, but only if it is not neglected and you consult a doctor in time, and do not try to prescribe therapy for yourself. Otherwise, even the mildest form of sore throat can lead to serious consequences.
The disease is a disease with a high degree of contagiousness, that is, it is very easy to become infected: just drink from the patient’s cup or use his towel. Moreover, the first symptoms of catarrhal tonsillitis can occur several hours after contact with the patient. On average, the incubation period of the disease lasts from one to four days.
The peak of disease outbreaks occurs in autumn and winter. It is at this time that the body’s defenses decrease, the immune system weakens, and sometimes a slight hypothermia or a stressful situation in combination with the entry of a pathogen into the body is enough to trigger the inflammation mechanism.
Symptoms
Lacunar tonsillitis appears quickly. The obvious and most common symptom is a severe sore throat that gets worse when swallowing.
In addition to a sore throat, lacunar tonsillitis presents symptoms such as:
- Increase in temperature.
- Pain in the head.
- Pain in muscles and joints.
- General weakness of the body.
- Redness on the cheeks.
- Fever, chills in the body.
Atypical sore throats
ICD-10 code
- J03.8. Acute tonsillitis caused by other specified pathogens.
- J03.9. Acute tonsillitis, unspecified
Ulcerative-necrotic tonsillitis (Simanovsky-Plaut-Vincent tonsillitis)
Superficial ulcers form on the palatine tonsil, covered with a dirty green coating with a putrefactive odor.
Etiology
Fusiform stick (B. fusiformis) and Spirochaeta buccalis.
Predisposing factors
Decreased immunity, acute and chronic infections, blood diseases, vitamin deficiency, caries, gum disease, difficulty in nasal breathing.
Clinical picture
Sensation of a foreign body when swallowing, putrid odor from the mouth, increased salivation. General intoxication is not pronounced. Unilateral damage to the tonsil may be accompanied by unilateral lymphadenitis. Pharyngoscopy reveals a gray-dirty coating that does not extend beyond the lymphoid tissue. The plaque is easily removed with a spatula; under the plaque there is a bleeding ulcer-erosion with uneven edges.
Differential diagnosis.
Tumors, syphilis, diphtheria, tuberculosis, blood diseases.
Treatment
- Oral care, oral sanitation.
- Locally: treatment and cleansing of the ulcer surface with antiseptic solutions:
- A solution of 5% potassium iodite;
- An alcohol solution of 1% methylene blue;
- A solution of 10% silver nitrate.
If bacteriological culture reveals coccal flora, then antibiotics are prescribed.
Inflammation of the tonsils caused by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida (usually Candida albicans).
Causes
Lacunar tonsillitis is caused by bacteria (staphylococcus, streptococcus) or viruses, fungi and is an infectious disease. This type of sore throat is transmitted through the air from a sick person to a healthy one. The development of the disease may also continue due to:
- Hypothermia of the body.
- Allergic reactions.
- Chronic diseases of organs and systems.
- Experiences, stress.
- Lack of normal, full sleep.
- Deterioration of immunity.
- Poor, poor quality food.
- Diseases of the ENT organs.
- Advanced dental diseases.
When there is a risk of getting sick
Like any similar infection, the disease is transmitted by airborne droplets. The main cause of catarrhal sore throat is the causative bacteria: staphylococci, streptococci and rhinoviruses. In addition to these bacteria, our oral cavity is inhabited by many microorganisms that are in a passive state and do not cause harm if the person is healthy. They wait for the right moment, and as soon as the body’s defenses weaken under certain conditions, microorganisms begin to become active, and as a result, inflammation of the tonsils and pharynx occurs.
The inflammatory process covers the palatine tonsils, or tonsils, as they are commonly called. The tonsils are affected superficially; in the catarrhal form there is no purulent plaque and pus in the lacunae of the tonsils. Despite the fact that catarrhal tonsillitis is the simplest form of tonsillitis, in the absence of proper treatment, it can develop into another, more severe form of the disease.
Factors that provoke the development of the disease include:
- weak immunity;
- the presence of a permanent source of infection in the body (for example, with chronic sinusitis or dental caries);
- unfavorable environmental conditions, gas pollution;
- bad habits, especially smoking;
- unbalanced diet, eating “on the run”;
- stress.
As doctors note, in order for pathogenic microorganisms to have a chance to survive and become more active, it is necessary that the body’s defenses weaken. In other words, for a healthy person, with a strong immune system, who eats well, avoids the negative influence of stressful situations, and does not abuse bad habits, the risk of getting sick is greatly reduced.
Diagnostics
When a patient comes to an otolaryngologist with the first signs of lacunar tonsillitis, the doctor begins an examination. During it, the specialist notices general redness in the throat, as well as enlargement of the tonsils and palate due to swelling. Plaque can be seen inside the tonsils, in their lacunae. Lymph nodes with sore throat increase in size and are easy to feel. They also hurt when touched. After the examination, the doctor sends the patient for tests, which include:
- General analysis.
- A smear from the tonsils to identify the bacteria that caused lacunar tonsillitis.
- Analysis for C-active protein in the blood.
Write to us in online chat
Avoid complications
There are often cases when a patient is careless about his health and decides that “it will go away on its own” or, conversely, tries to try all the advice of traditional medicine on himself. This is the other extreme of negligent attitude towards one’s health. Catarrhal tonsillitis, although it is one of the mildest forms of acute tonsillitis, but in the absence of proper treatment, severe complications can develop, which will be quite difficult to treat.
If tonsillitis is not treated, you may encounter diseases such as chronic tonsillitis (a chronic form of inflammation), rheumatoid arthritis, peritonsillar abscess, myocarditis, kidney disease (glomerulonephritis), laryngeal edema, and even sepsis.
Pregnant women need to pay special attention to their health: the inflammatory process that spreads beyond the palatine tonsils can lead to tonsil intoxication and the threat of miscarriage! Therefore, treatment of catarrhal tonsillitis in adults should be carried out on time and always under the supervision of an ENT doctor.
Treatment
After identifying the causative agent of a sore throat, the doctor will prescribe the patient special medications that will help kill the bacteria. The patient will also need rest and bed rest. To reduce discomfort and get rid of discomfort, doctors advise taking:
- Drugs that lower body temperature and relieve fever.
- Antihistamines.
- Vitamin complexes to improve immunity.
- Medicines to fight viruses.
- Immunomodulators.
The patient should also drink warm drinks and liquids, gargle with antiseptics, and inhale when possible. Often patients are sent for a further course of treatment - physiotherapy. It quickly gives effect and includes ten treatment procedures.
Pathogenesis
In the oral cavity of a healthy person, mushrooms are saprophytic microflora. Reduced immune reactivity and antibacterial therapy cause active proliferation of fungal flora.
Clinical picture
Sudden onset with moderate systemic intoxication in the form of a temperature reaction. Complaints of pain and discomfort in the throat, soreness and dryness. Pharyngoscopy reveals enlarged, swollen, moderately hyperemic tonsils, covered with bright white, loose, curdled islands, spreading to the arches, uvula, root of the tongue, and the back wall of the pharynx. Plaques are easily removed with a spatula, leaving the surface of the mucous membrane unchanged.
Treatment
General treatment
Cancellation of antibacterial drugs
- antifungal drugs
- B vitamins, vitamin C.
Local treatment:
- gargling with miramistin, octenisept;
- treatment of the mucous membrane with a solution of methylene blue 1%, fucarcin, and a solution of silver nitrate 5%.
Symptoms of catarrhal tonsillitis in children
Catarrhal tonsillitis is a disease that develops acutely in 85-90% of cases. After hypothermia or against the background of another respiratory illness, the child may notice the appearance of soreness in the throat area. The nature of this discomfort can vary from a mild tickling sensation to severe pain that makes it difficult to swallow food. Other clinical symptoms of catarrhal tonsillitis in children:
- redness of the throat and enlargement of the tonsils;
- the appearance of pale gray films on the surface of the tonsils, which are easily washed off with saliva or when touched;
- increase in body temperature, but not higher than 38°C;
- pain when swallowing;
- dryness of the tongue and the appearance of a white coating on it;
- slight enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- deterioration of the child’s mood, moodiness.
Despite these symptoms, the patient’s general condition changes slightly. The child continues to play actively, his appetite is preserved.
Complications of acute tonsillitis
You should not self-medicate, as complications often arise with inadequate therapy, incorrect dose selection, or without treatment. For example, the transition of an acute process to chronic tonsillitis, the development of such dangerous conditions as tonsillogenic abscesses (limited accumulation of pus in tissues) of various localizations (peritonsillar, retropharyngeal), phlegmon and mediastinitis - purulent melting of the tissue of the retrosternal space. This dangerous condition can be accompanied by the development of sepsis, symptoms of multiple organ failure and requires treatment in the intensive care unit. Delayed complications in the form of damage to organs and their systems may also occur. The favorite localization of group A B-hemolytic streptococcus is heart tissue. Accumulations of bacteria settle on the valves, destroying them. This can lead to the formation of heart defects, which in turn is dangerous for the development of heart failure. With frequent tonsillitis, the kidneys and joints are affected. In addition, the infection itself can serve as a trigger for the development of autoimmune diseases. Fortunately, with timely treatment and proper use of medications, complications are quite rare.
Up to contents
Expert opinion
As an ENT specialist, I want to say that catarrhal tonsillitis is a very common disease with an increase in incidence in the autumn-winter period. Due to the decrease in air temperature and the spread of respiratory infections, the number of sick children is increasing. However, the pathology responds well to conservative treatment. The main thing is not to ignore the signs of the disease and seek help from a specialist as early as possible. Self-treatment risks progression of the disease and the development of dangerous complications.
Sore throat in infectious diseases
Diphtheria
The increase in incidence is due to the unimmunized population, mostly visitors.
Etiology: diphtheria bacillus (Corynebacterium diphtheriae)
The target organs of diphtheria bacillus toxin are the heart, kidneys, and central nervous system. The mechanism of action is to block protein synthesis in cells, leading to apoptosis.
Classification:
Localized and widespread forms.
- catarrhal
- islanded
- membranous
- hemorrhagic
Depending on the severity, toxic and hypertoxic are distinguished.
Clinical picture
Intoxication comes to the fore, manifested by fever up to 38-39°C, general weakness, loss of appetite, and lethargy. The pharyngoscopic picture corresponds to a sore throat with edematous mucous membrane of the oropharynx, single or multiple fibrinous deposits of grayish-white color, which can spread beyond the palatine tonsils to the palatine arches, uvula, posterior and lateral walls of the pharynx. Severe lymphadenitis is noted. When the heart is damaged, clinical myocarditis develops; the central nervous system develops paralysis of the soft palate, lower extremities and diaphragm).
Diagnosis: bacteriological examination for BL.
Treatment: emergency hospitalization in an infectious diseases hospital and administration of anti-diphtheria antitoxic serum according to Bezredka.
Complications
Inadequate treatment of follicular tonsillitis can lead to purulent complications.
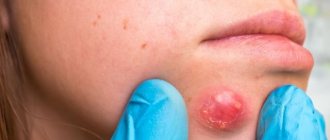
The first place in frequency is paratonsillar abscess - the formation of an abscess in the soft tissues surrounding the tonsil. With this disease, fever persists for a long time, and opening the mouth is so painful that the patient even refuses to take fluids. Surgery is often required. Purulent lymphadenitis and other pathological processes associated with the spread of bacterial infection and the need for surgical drainage of a purulent focus also occur.
3-5 weeks after an acute streptococcal infection, signs of delayed infectious and allergic complications may appear. Possible damage to the myocardium and valve apparatus, which is accompanied by pain in the heart, rhythm disturbances, and shortness of breath. There is swelling of the joints, pain when moving, and a feeling of stiffness.
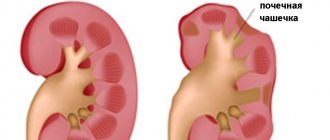
The development of glomerulonephritis is possible - kidney damage with decreased diuresis, fluid retention, and arterial hypertension. These conditions require consultation with specialists - a cardiorheumatologist and a nephrologist, respectively.
Follicular tonsillitis
Treatment of acute tonsillitis
Depends on the severity of the patient’s condition and the stage of development of the disease. Hospitalization is necessary in cases of disruption of the functioning of other organs and systems (lower back pain, changes in urine, arrhythmia, heart failure, suspicion of a heart defect), in case of moderate and severe disease, if a child is sick, as well as social indications (closed groups , boarding schools).
Clinical recommendations for the treatment of acute tonsillitis in adults include non-drug treatment methods: bed rest, isolation of the patient if possible, a gentle diet excluding cold, hot, and solid foods. A diet of plant and dairy products (porridge, stewed vegetables) is preferable. Drinking plenty of fluids is necessary. Frequent ventilation and humidification of the air in the room where the patient is located has a beneficial effect. During treatment, the patient is provided with separate dishes and hygiene items.
Local therapy of acute tonsillitis occupies a special place. In combination with other drugs, it speeds up recovery, relieves discomfort in the throat, and is applicable when systemic therapy is contraindicated7. Methods of irrigating the pharynx with various solutions, for example Hexoral ® spray, can be effective. Its action is based on the suppression of the oxidative metabolism of microbes (thiamine antagonist). The drug can fight many bacteria and fungi, in particular the pathogenic fungi Candida, and Hexoral ® also inhibits the growth of Proteus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. In addition, the active substance Hexetidine has an analgesic effect on the mucous membrane4. An important method of local therapy is rinsing the tonsils with antiseptic solutions (Hexoral ®, Chlorhexidine, chamomile infusion and others). Also tested are Hexoral ® Tabs Extra5 and Hexoral ® Tabs Classic6 lollipops, which contain antimicrobial components and antiseptics. The active components of Hexoral ® Tabs destroy the walls of bacteria, fight infection, thereby helping to reduce sore throat. They should be kept in the mouth until completely dissolved. It is important to remember that after local treatment it is better not to eat or drink for at least 1 hour.
To reduce inflammation, pain, and in order to reduce high fever, analgesics, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic drugs (ibuprofen, paracetamol and others) are prescribed.
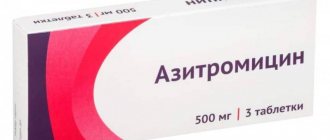
In severe cases, medical treatment includes systemic antibiotics. Remember that self-prescribing antibiotics can be dangerous to your health.
Treatment of sore throat in a child must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor! Diphtheria is especially dangerous for children.
Patients with diphtheria should be hospitalized in the infectious diseases department.
Up to contents
Treatment of follicular sore throat
The need for hospitalization for acute tonsillitis is determined by the severity of the general condition. As a rule, follicular purulent tonsillitis is treated at home. Until the end of the fever, it is recommended to observe bed rest, then gentle rest, i.e. the patient should stay at home and avoid physical activity. A sufficient amount of liquid (warm teas, fruit drinks, juices) helps relieve fever and eliminate bacterial toxins. You need to eat according to your appetite - do not force yourself to eat, but give preference to light, low-fat dishes.
Etiotropic treatment is of key importance - the prescription of drugs that suppress the pathogen. For bacterial infections, antibiotics are indicated for follicular angina - protected penicillins, cephalosporins of the 1st-2nd generation, in case of intolerance to beta-lactam antibiotics - macrolides or lincosamides. For a fungal pathological process, antifungal drugs are indicated - fluconazole, ketoconazole, etc. Herpetic tonsillitis requires the prescription of acyclovir. It is critical to maintain the full course of etiotropic therapy, and not stop taking medications when the first relief occurs. An incomplete course contributes to the formation of microflora that is resistant to medications - more aggressive and difficult to treat.
To eliminate the immunopathological process, the use of antihistamines is indicated. During the period of fever, antipyretic therapy (ibuprofen, paracetamol or nimesulide in appropriate dosages) is recommended.
Local treatment to reduce pain in the throat is prescribed in the form of sprays or gargles. It is necessary to keep in mind the risk of aspiration when resolving tablets and laryngospasm when using the spray in young children. Mechanical removal of plaque is contraindicated.
During the period of convalescence, physical therapy is possible as prescribed by the attending physician.
Causes
The pathogen enters the body, covering the tissue of the palatine tonsils. Gradually, microbes spread through the bloodstream, causing the development of intoxication. Local immunity is immediately activated by producing a large number of leukocytes. Blood rushes to the tonsils, causing them to become red and swollen.
The main route of penetration of the pathogen is airborne. Children become infected through shared toys and close bodily contact. The infection begins to spread when the body is weakened and hypothermic. Adults become infected through droplets of saliva or household items.
Diagnosis of acute tonsillitis
To clarify the diagnosis and prescribe treatment, consult a specialist. The diagnosis of tonsillitis can be made by a doctor based on anamnesis, complaints, examination data, and clinical picture.
Laboratory studies include bacteriological (detection of the growth of pathogenic flora in biomaterials from the oropharynx, for example, group A β-hemolytic streptococcus) and serological (determination of antibodies to streptococcal antigens in the blood serum or other media being tested).
There will also be changes in the patient’s blood (leukocytosis, increased ESR, in more severe cases anemia, thrombocytopenia); protein and red blood cells may be detected in the urine if the kidneys are damaged.
If there are plaques on the tonsils, diphtheria should be excluded, especially in unvaccinated individuals. The plaque of diphtheria is characteristic: it is dense, dirty white or yellow, and appears by the second day of illness. The film cannot be rubbed with a spatula; it requires effort to remove it; if you lower the film into a vessel with liquid, it will sink.
Body temperature during diphtheria is often subfebrile (no more than 38 degrees), which does not correspond to the severity of the condition, which progressively worsens. Muscle pain, general weakness, and difficulty breathing appear.
The diagnosis is also confirmed by bacteriological examination of samples taken from the tonsils. The test material is placed on a nutrient medium. With this method, diphtheria bacilli can be detected in 80% of cases.
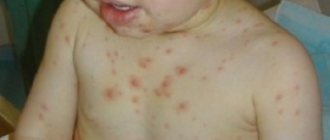
Differential diagnosis of acute tonsillitis is carried out with the aim of carrying out etiotropic therapy (impact on the cause of the disease). With scarlet fever and measles, tonsillitis will be accompanied by the appearance of a rash; the epidemiological history is also characteristic; children are mainly affected. With infectious mononucleosis, a distinctive feature will be changes in the blood test: namely, the presence of atypical mononuclear cells, with agranulocytic tonsillitis - a decrease in leukocytes and granulocytes in the blood, and with leukemia - the presence of blast cells.
Up to contents