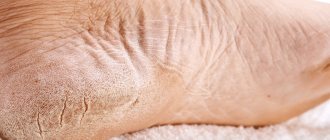
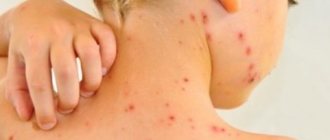
Athlete's foot is a group of fungal diseases that have a common localization and similar clinical manifestations. They are very common and affect people of any age (rarely children), prone to a chronic relapsing course.
Infection occurs in bathhouses, showers, on beaches, gyms, when using someone else's shoes and other household items contaminated with fungal elements.
In the pathogenesis of the disease, the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the skin of the feet, increased sweating, changes in sweat chemistry, metabolic and endocrine abnormalities, injuries of the lower extremities, and vegetative dystonia are of significant importance. Pathogens can remain in a saprophytic state for a long time without causing active clinical manifestations. Athlete's foot has several clinical forms, each of which can be combined with nail damage.
What is mycosis of the feet
Mycosis of the foot is a group of fungal skin diseases, often with simultaneous damage to the nails. These infections cause similar clinical manifestations. They can only be distinguished after a microscopic examination of the skin and nails. Mycosis of the feet is a highly contagious disease. It is transmitted from person to person through household items: rugs in locker rooms, showers and swimming pools, footstools, basins and flooring in baths and saunas. Sharing shoes and socks is dangerous. The surface layer of the skin, which is constantly peeling off, contains a lot of fungi and their spores. Initially, the interdigital folds are affected and skin itching occurs. Subsequently, the infection takes over the entire foot and spreads to the nails. The course of the disease is long-term and requires constant treatment. To prevent mycosis of the foot, in our online store you can buy an effective prophylactic product - Mycospray.
Prevention
Provides, firstly, for the disinfection of floors, wooden flooring, benches, basins, gangs in bathhouses, showers, swimming pools, as well as the disinfection of impersonal shoes; secondly, regular examinations of bath attendants and people working out in swimming pools in order to identify patients with epidermophytosis and their early treatment; thirdly, carrying out sanitary and educational work. The population needs to be explained the rules for personal prevention of athlete's foot: wash your feet every night at night (preferably with cold water and laundry soap), dry them thoroughly; change socks and stockings at least every other day; do not use someone else's shoes; Have your own rubber sandals or slippers for the bath, shower, pool.
To harden the skin of the soles, it is recommended to walk barefoot on sand and grass in the hot season.
Causes of mycosis of the feet
The cause of the disease is microorganisms of the genus Trichophyton, less commonly mold fungi and Epidermophyton floccosum:
- red trichophyton (Tr. Rubrum) causes up to 95% of all cases of the disease;
- approximately a third of patients also have interdigital trichophyton (Tr. Interdigitale);
- inguinal epidermophyton (E. floccosum) causes the disease in 1% of cases.
The likelihood of infection increases in unfavorable external conditions:
- high humidity;
- tight shoes;
- frequent visits to swimming pools, saunas and other wet areas;
- presence of a sick person in the family.
Some internal diseases also contribute to the development of fungal infections:
- sweaty feet;
- immunodeficiency;
- taking corticosteroid hormones orally;
- flat feet;
- Raynaud's disease, atherosclerosis of peripheral arteries, obliterating endarteritis, varicose veins;
- diabetes.
What happens during the disease
Mycosis of the feet rarely develops on healthy skin. Even if the fungus gets to the surface, it will not be able to penetrate the thick layer of intact epithelium. Under the influence of unfavorable external factors, the epidermis accumulates moisture and loosens. Fungi penetrate into the thickness of the skin and begin to actively multiply. This is further facilitated by vascular diseases and immune disorders, which are accompanied by impaired nutrition and local protective mechanisms on the feet. The proliferation of fungi causes damage to the interdigital areas, intense peeling and discomfort. The rejected epithelium ends up in socks and shoes, becoming a source of re-infection. Therefore, during the treatment of mycosis, it is necessary to treat the inner surface of the shoe with Mycospray.
Diagnosis of ringworm
Very often, skin diseases have similar symptoms, but require different treatment. For this reason, the correct diagnosis can only be made by a specialist by taking a sample of the infected nail or skin for culture (culture) or microscopic examination. Culture can determine the type of fungus, but the process takes some time because the fungus develops slowly.
So, the diagnosis is established on the basis of clinical and epidemiological information, including the results of laboratory examinations. In laboratory examinations, the material used is hair, skin scrapings, scales and crusts from peripheral or infected areas that have not been treated.
During microscopic examination, the pathological material is placed in a Petri dish or on a watch glass and filled with a 10 percent sodium hydroxide solution, after which it is placed in a thermostat for 15-20 minutes or slightly warmed up and split with dissecting needles. The required volume of material is applied to a glass slide in a drop of glycerol (50%), covered with a glass slide and examined under a microscope.
Microscopic examination reveals Trichophyton fungi in the form of straight mycelial hyphae with septa. The spores are oval, round, unicellular, located at the base in chains or clutches.
Microsporum fungi are single-celled round spores located randomly on the surface of the hair or inside it.
Achorion mushrooms, in the form of thin mycelium, consist of rectangular cells with two contours. The spores are multifaceted or round, arranged in groups or chains.
In the differential diagnosis of dermatomycosis, the luminescent method is widely used. If necessary, inoculations are made from the original raw material onto agar.
Symptoms
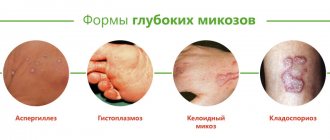
Conventionally, the following forms of mycosis of the feet are distinguished, which are presented in the photo:
- Squamous: unilateral peeling and mild itching in the arch of the foot. This form often goes unrecognized.
- Intertriginous: the folds between the toes are affected, then the process moves to the back of the foot. Weeping cracks appear, accompanied by itching. A bacterial infection may accompany the development of erysipelas.
- Dyshidrotic: on the arch of the foot, vesicles with light and then cloudy contents form, merging with each other. They open with the formation of painful erosions. This type is accompanied by itching and pain.
Mycosis of the skin of the foot in the acute period can be accompanied by fever, poor health, headache, and enlarged inguinal lymph nodes. When infected with trichophyton, the nail of the 1st or 5th finger is affected, and subsequently the process spreads to all nail plates. First, yellow spots appear at the free edge of the nail, then it thickens, loosens and crumbles. Therefore, to treat foot fungus, you need to use complex action products, for example, Clotrimazole lotion for skin and nails.
Symptoms of fungus
The course and development of the disease is influenced by the physiological characteristics of the skin of the feet, increased sweat production, disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine system, and leg injuries. Fungal pathogens can remain dormant for a long time without showing symptoms. If there are disturbances in the body, they can become active. Athlete's foot is characterized by the presence of several forms of the disease, which can be supplemented by damage to the nail plates.
Fungal infection can be determined if several symptoms are present:
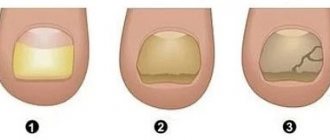
- the nail plate changes its natural color: usually yellow or dark color is fixed, but the nails can even become white or completely black;
- tissue keratosis under the plate: outwardly it looks as if a hard growth has appeared under the nail;
- thickening and delamination of the plate;
- deformation of the nail: protrusion, growth to the side, ingrowth into the skin;
- fragility of the nail plate: parts of it may break off.
Treatment of mycosis of the feet
Therapy is carried out in 2 stages. First, it is necessary to eliminate acute inflammation and remove horny deposits on the feet. Warm foot baths with potassium permanganate and lotions with a solution of boric acid are shown. After removing the dense epithelium, creams containing anti-inflammatory hormones and antibiotics are used. After the inflammation subsides, these creams are replaced with similar ointments. At the second stage of treatment, antifungal ointments and creams (for example, Clotrimazole) are used. They should be applied to clean, dry skin 1 – 2 times a day, lightly rubbing. Not only the affected area is treated, but also the surrounding surface of the foot. The course of treatment takes about a month. Mycosis of the foot is successfully treated with the drug Clotrimazole lotion for skin and nails, which is offered in our online store for residents of Moscow and all regions. Its advantages:
- high activity against the fungus that causes mycosis of the feet;
- safety;
- hypoallergenic;
- affordable price.
Clotrimazole lotion can be used to treat other skin diseases:
- pityriasis versicolor;
- skin candidiasis;
- erythrasma;
- secondary bacterial infection against the background of mycosis.
The medicine is used 2 times a day, gently rubbing it into the affected areas. The skin must first be washed with soap and dried well, especially between the fingers. The course of treatment lasts until the symptoms of the disease disappear and for another 2 weeks. The drug is well tolerated. Only occasionally does it cause skin irritation. It has the only contraindication – the first trimester of pregnancy. Of course, clotrimazole is not used if you are hypersensitive to it. One of the advantages of clotrimazole lotion is the excellent penetration of the drug into the nail plates, which distinguishes it from cream or ointment. Regular use of this drug provides excellent results for mycosis of the feet and nails without the use of additional agents. Nail damage requires oral antifungal medications:
- itraconazole;
- fluconazole;
- griseofulvin;
- terbinafine
At the same time, medicinal varnishes are used, which are applied to the nails 1 – 2 times a week until complete healing.
Treatment of foot fungus
For successful therapy, you need to pay a lot of attention to the treatment of lesions.
A person affected by fungus should take foot baths every day with potassium permanganate. It is necessary to get rid of the crusts, puncture the blisters and remove the “fringe” along the boundaries of the erosive areas and the covers of the festering blisters.
After the bath, you need to apply medicinal bandages soaked in an aqueous solution of copper sulfates (0.1%) and zinc (0.4%) or a 1% solution of resorcinol to the affected areas. After the weeping areas have begun to heal, dermozolon, mycozolon are used, and then alcohol solutions based on fungicide and fucorcin. If necessary, the kit is supplemented with fungicidal ointments.
Obtaining the desired result does not depend on the drugs used, but on the correct sequence of their use according to the current situation with inflammatory processes.
Additional treatment plays a huge role after the end of the fight against the lesions, because it helps prevent relapses. The skin of the feet is wiped with 2% salicylic alcohol or 1% thymol, and the use of 10% boron powder is also required. To get rid of and prevent the appearance of fungi in shoes, you need to wipe them from the inside with a formaldehyde solution, wrap them in thick fabric for a couple of days, and then dry them in the fresh air. For socks, tights and stockings everything is simpler - you just need to boil them in this solution for 10 minutes.
If a complication occurs with pyococci, then antibiotics are used - methicillin, cephaloridine and others. Bed rest is mandatory.
Preventive methods
Treatment of a fungal infection takes a long time. Mycosis of the feet requires the use of drugs, the cost of which is quite high. Prevention of the disease is especially important in people with risk factors for the disease. Athletes, swimmers, and hot shop workers are recommended to regularly use antifungal and antibacterial drugs, for example, Mycospray. This product is safe, does not damage the skin and does not cause irritation. With its regular use, the likelihood of becoming infected with foot fungus is sharply reduced. Mycospray is useful for preventing re-infection. To do this, the drug must be sprayed monthly on the inner surface of the shoes. Mycospray is safe even with long-term use. It should be applied to dry, clean skin of the feet before each visit to the pool and other similar places. There are no contraindications to the use of this drug. It should be used with caution only by pregnant and breastfeeding women. It is necessary to eliminate the external causes of the disease:
- wear boots and shoes that fit;
- use high-quality sports shoes made from natural materials;
- wash your feet daily and treat your nails on time;
- fight sweaty feet;
- When visiting a bathhouse, swimming pool, or beach, it is better to use lightweight silicone or rubber slippers.
General strengthening of the immune system, treatment of diabetes and vascular diseases are necessary.
Infection with dermatomycosis
This infectious disease is quite common. If you identify and begin to eliminate the disease in a timely manner, and follow all the doctor’s recommendations, then such effective therapy will give positive results. However, it may also happen that when the disease is advanced, its chronic form develops.
Infection with dermatomycosis occurs through direct contact with a sick person, or through contaminated objects. Such objects may include towels, shoes, and carpets. Some types of fungus live on damp surfaces, such as the floor of a locker room, bathhouse, or shower. The fungus can be contracted from pets suffering from ringworm (ringworm).
The causative agent of the disease is a fungus of the genera Microsporum, Trichophyton, Achorion.