The benefits of paraffin therapy
The main healing properties of paraffin applications include:
- Compression effect. After hardening, paraffin decreases in volume by approximately 10% - this property indicates a tightening effect; tissue lymph flow is enhanced due to compression.
- Metabolism accelerates, which promotes the rapid removal of harmful substances from the body.
- Anti-inflammatory effect. The lingering and spreading heat deep into the layers of the human body contributes to the rapid relief of painful sensations and the healing of the body, both mono and complex. Paraffin therapy is widely used for the treatment of joints, restoration of muscle tone, for fractures, acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections, and therapy of internal organs.
- Skin renewal (rejuvenation, resorption of scars and scars).
Ozokerite (paraffin therapy)
Ozokerite is a waxy mass from dark brown to black in color - a substance of petroleum origin. Ozokerite contains paraffin, mineral oils, resins and other substances. To free it from foreign inclusions, raw ozokerite is melted and washed with water, and then with acid, and bleached with special bleaching clay (Fuller's earth). Commercial ozokerite is black, green, yellow or white, depending on the degree of bleaching. Purified ozokerite melts at a higher temperature (65°C to 80°C) than paraffin; it consists almost entirely of high molecular weight hydrocarbons. Acids and alkalis have no effect on ozokerite. It holds oils and other additives firmly. Ozokerite is insoluble in volatile alcohols, but soluble in benzene, kerosene and other hydrocarbons.
The term "ozokerite" was first proposed by Glocker in 1833. The first chemical analysis of ozokerite was carried out by the famous French chemist Walter in Paris in 1840.
Clinical experience with the use of ozokerite indicates that the most favorable results are achieved when treating inflammatory and metabolic-dystrophic diseases. Ozokerite applications have a positive effect on inflammatory processes, accelerate recovery processes, increase immune parameters, normalize the tone of the autonomic nervous system, and stimulate blood circulation. The inclusion of ozokerite applications in the treatment complex increases the effectiveness of spa therapy in the treatment of pathologies of the digestive system, urination and metabolism.
The effect of ozokerite on the body consists of temperature, mechanical and chemical factors. In addition, the numerous chemical components of ozokerite and the possibility of their penetration through the skin cause significant changes in the overall reactivity of the body.
Ozokerite is characterized by very low thermal conductivity, high heat capacity and heat-retaining ability. Convection heat transfer in ozokerite is weakly expressed, therefore, when it is applied to the skin, a layer quickly forms, the temperature of which is close to the skin temperature, and the transfer of heat to the body from the overlying layers occurs very slowly. This makes it possible to use ozokerite at high temperatures (60-70 C) without fear of causing a burn.
The mechanical factor of the action of ozokerite is due to its ability, when solidified, to decrease in volume by 10-12%, which is accompanied by slight compression of the underlying tissues (compression effect). This promotes deeper distribution of heat. The compression effect of ozokerite is most pronounced during circular applications, when an area of the body is covered from all sides, for example, on the extremities, while tissue swelling is reduced, because due to the thermal effect, the outflow of tissue fluid and lymph improves.
The chemical effect of ozokerite is due to the presence of biologically active substances in it (having an estrogen-like, acetylcholine-like effect) that can penetrate through intact skin into the body and, entering the humoral channel, cause a parasympathicotonic effect. Ozokerite also contains substances with antibiotic properties. It has been established that ozokerite can have an anti-inflammatory, absorbable, analgesic, antispastic, desensitizing effect, and stimulates regeneration processes.
Indications for use of ozokerite
Diseases of the joints and spine of a dystrophic and inflammatory nature in the acute or chronic stage; consequences of damage to the musculoskeletal system; diseases and injuries of peripheral nerves and spinal cord; diseases of internal organs (chronic pneumonia, pleurisy, hepatitis, cholecystitis, gastritis, colitis, peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum); chronic and subacute inflammatory diseases of the female genital area, secondary infertility; chronic inflammatory diseases of the ear, nose and throat; skin diseases; diseases of peripheral vessels of the extremities in the initial stages, chronic. thrombophlebitis.
Technique of procedures
Ozokerite is heated to the required temperature in electric paraffin heaters or in a water bath. Sterilization of used ozokerite is carried out by heating in a water bath to a temperature of 100 degrees for 10-15 minutes. When reusing ozokerite, 25% of the unused substance is added to it.
There are several ways to use ozokerite:
- layering (molten ozokerite t 65-70 C is applied to the skin with a brush);
- ozokerite baths (the limb is coated with ozokerite, and then immersed in a vessel with molten ozokerite at 60-70 C;
- napkin-application (gauze folded in 8-10 layers is immersed in molten ozokerite t 50-55 C, wrung out and applied to the site of treatment, covered with oilcloth, and then with a blanket or quilted pad);
- cuvette-application (molten ozokerite in a layer 1.5-2 cm thick is poured into cuvettes, frozen ozokerite t 48-50-54 C is removed from the cuvette onto an oilcloth and applied together with it to the areas to be exposed).
The latter technique is most often used in practice.
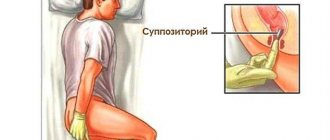
Ozokerite is also used for abdominal treatment in the form of rectal and vaginal tampons at a temperature of 55-60 C. The choice of treatment method is determined by the form of the disease, the localization of the process, the phase and stage of the disease. Usually the procedures are carried out daily or every other day, the duration of the procedure is from 15 to 30-40 minutes, the course of treatment is 10-20 procedures. After the procedure you should rest for 30-40 minutes.
Treatment courses can be repeated at intervals of at least 3-4 months. Ozokerite can be combined (alternating procedures) with galvanization or electrophoresis, ultrasound therapy, light therapy, massage, physical therapy, and general mineral baths. The intervals between ozokerite treatment and one of the listed procedures should be at least 1-2 hours. For the elderly and children, ozokerite is heated to a lower temperature (48-52 C); The duration of the procedure is reduced to 15-20 minutes. In children's practice, preference is given to the napkin-application method (napkins are moistened with ozokerite temperature 48-49 C and a compress is applied).
The use of ozokerite is contraindicated in feverish conditions, decompensation of the cardiovascular system, acute and subacute heart diseases, severe forms, hypertension, emphysema, bronchial asthma, dystrophies, tuberculosis, benign and malignant tumors, a tendency to bleeding, blood diseases, callous and prone to to penetration of stomach and duodenal ulcers, ulcerative enterocolitis, severe liver diseases, gangrenous forms of obliterating endarteritis, acute and subacute thrombophlebitis, thyrotoxicosis, epilepsy, with suppurative processes in the pelvic organs, during pregnancy.
Storage: at a temperature not higher than + 25 C.
Types of paraffin applications
There are several types of procedures, each of which differs in the method of influence and complex properties.
- Cuvette-application;
- Napkin appliqué;
- Layering;
- Paraffin Bath;
- Paraffin-ozokerite;
- Cosmetology;
- Procedures for children.
The cuvette-application method is based on the use of a special container: a cuvette. Melted paraffin is poured onto the bottom of the cuvette, where the oilcloth has already been placed. The cooled but still soft material is removed from the container and placed on the target area of the patient’s body. Cover with a blanket on top.
The napkin-application method involves the use of gauze towels soaked in paraffin. This method is convenient when the area of the body being treated is large.
Layering of the paraffin mass is done using a brush and is used when small areas are treated
Paraffin baths are used to treat the hands or feet. Pre-treated feet or hands are wrapped in film with layered paraffin and lowered into baths filled with heated paraffin.
The procedure is also used in urology and gynecology.
The paraffin-ozokerite method is based on the use of natural material ozokerite. Such applications allow you to relieve inflammation and quickly restore tissue.
For cosmetic purposes, paraffin applications are used for the hands and face. Thanks to their healing properties, paraffin masks and baths smooth the skin, relieve dryness and flaking, eliminate signs of aging, remove waste and toxins, and accelerate blood flow. Paraffin wraps relieve the skin of cellulite, and also bring visible changes in the resorption of scars and scars.
Paraffin therapy for children is widely used in the treatment of acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections. Thanks to the warmth that lasts for a long time, these unique paraffin boots help to cope with frequent respiratory diseases.
Therapeutic use of ozokerite
Ozokerite, a waxy product of petroleum origin, is a natural rock; deposits are found in Turkmenistan, the Fergana Valley, Chimkent, the Carpathian region and some other places. The name "ozo - smelling of wax - comes from the Greek ozo - smell, heros - wax. After processing the rock, it really resembles beeswax in appearance.
Buy products from Pharm-Effect LLC in the Wildberries online store
Ozokerite was introduced into medical practice in 1942 by S. S. Lepsky. In subsequent years, a large number of studies were carried out, which made it possible to clarify its physicochemical properties, some details of the mechanism of its action in the body, to appreciate its medicinal properties in patients with a wide variety of diseases; it is currently widely used in various sanatorium and resort institutions, as well as out-of-resort - hospitals and clinics. M.Yu. Goldenberg (1968) writes that one of the largest well-equipped ozokerite hospitals in our country was built in the resort of Truskavets, famous for its mineral waters. The author points out that the production of medical ozokerite is currently based on its extraction from waste of the oil production and oil refining industries, as well as from the veins mined in ozokerite mines. The process of producing ozokerite using new technology, according to the author, takes place in the following two stages: Stage 1 - preparation of raw materials (semi-finished product). A paraffin plug is loaded into a cold boiler, filled with water, and then a fire is lit in the firebox. The temperature in the boiler is brought to 100°C. Under the influence of heating, the semi-finished medical ozokerite floats to the surface of the water and is collected in a container. The remaining water is drained and mechanical impurities are removed. In another boiler, the vein material is cooked in the same way, which is also cleaned of mechanical impurities.
Stage II - production of the final product. Semi-finished products (vein wax, paraffin petrolatum) are loaded into the boiler. A fire is lit in the firebox. The contents of the boiler melt and pump the finished product container at a temperature of 100–110°C. After cooling to 75°C, ozokerite is poured into molds in which it cools and hardens. The tiles knocked out of the molds are packed in paper. In this form, ozokerite is ready for medicinal use. The ozokerite obtained using the above technology has a dark brown color. Its density is 0.8-0.97 g/m3.
The resulting medical ozokerite complies with the technical specifications of the Committee of Standards MRTU 12N-8-1-6. The composition of ozokerite includes: ceresin, paraffin, mineral oils, petroleum resins, asphaltenes, sulfur compounds, etc., the amount of which may vary slightly for a number of reasons.
Ozokerite, in comparison with all other coolants used in medical practice (silt peat mud, clay, paraffin), has the maximum heat capacity, minimum thermal conductivity and the greatest heat-retaining capacity. Slowly cooling down, it is released into the body over a long period of time. Patients easily tolerate ozokerite even at temperatures of 60-70°C, although experimental and clinical studies show that it should not be used at temperatures exceeding 60°C.
The effect of ozokerite on the body is based on its unique physical characteristics as a coolant, as well as chemical and biological properties. Ceresin, asphaltenes and resins contained in ozokerite have an irritating effect on the skin. Ceresin penetrates into the surface layers of the skin. Biologically active substances show studies by many authors (S. S. Lepsky, 1945; V. V. Efimov, 1946; E. S. Lokishina, 1949; Ch. B. Bayriev, 1972, etc.), penetrate through intact skin into body. It has been established that ozokerite has an effect on the autonomic nervous system, increasing the tone of its parasympathetic department.
Experiments and clinics have revealed the absorbable, anti-inflammatory, analgesic, desensitizing antispastic effect of ozokerite, and its stimulating effect on the regenerative ability of tissues. Ozokerite contains microflora that secretes a substance that has biological activity and antibiotic properties. It can be assumed that due to the peculiarities of the thermal effect, chemical and biological composition of ozokerite, its therapeutic effectiveness is higher than paraffin.
When using ozokerite in medical practice, it must be heated to the required temperature (in a regular water bath, heated on an electric stove or gas stove, in a fume hood).
The methods of ozokerite treatment resemble the methods of paraffin treatment.
I. Layering technique. Molten ozokerite at a temperature not exceeding 55°C is applied with a flat paint brush to the corresponding area of skin, previously lubricated with Vaseline, fish oil or some other indifferent ointment. To apply subsequent layers, ozokerite at a higher temperature is used (After applying the application with a thickness of 1-2 cm, it is covered with oilcloth and wrapped in a blanket).
Method of ozokerite baths. The hand or foot is first coated with ozokerite at a temperature no higher than 45-55°C and immersed in an oilcloth bag filled with ozokerite at a temperature of 55-65°C. The bag is tied in a circle with a tightening knot. The limb placed in the bag is wrapped in a warm blanket.
Napkin-application technique (ozokerite compress). Gauze soaked in molten ozokerite, folded in 6-8 layers, wrung out using forceps and spread on oilcloth to cool to the required temperature. An ozokerite compress is made from 2 such multilayer gauze napkins, placing them one on top of the other.
The top is covered with waxed paper or oilcloth and quilted padding. The temperature of the first adjacent gasket should be no higher than 45-50°C, the second (smaller in size) - 60°C. If subsequent wipes are applied, their temperature is increased accordingly. On the external gasket it can be brought to 70-80°C.
When using ozokerite in children, M.Yu. Goldenberg (1968) recommends moistening the pad in ozokerite at a temperature of 70°C and allowing it to cool to 38-39°C. This pad is placed on the child’s body. Subsequent temperatures are applied at 55-60°C. The author does not recommend using the cuvette-application technique in children, according to his observations; children overheat very much in padded jackets and sweat a lot even in winter. The course of treatment consists of 15 procedures. For catarrh of the upper respiratory tract, pads with ozokerite are used on the feet and legs of “boots”. The temperature of ozokerite is 45°C. Such procedures are easily tolerated even by infants.
4. Cuvette-application technique. Molten ozokerite is poured into metal cuvettes onto an oilcloth previously placed there, protruding at the edges by 5 cm. The dimensions of the cuvette must correspond to the area where the ozokerite is applied. Cooling in the cuvette, ozokerite turns into a cake (2-5 cm thick). This cake is brought to the required temperature (50-60°C), removed from the cuvette along with the oilcloth and applied to the skin, a layer of gray cotton wool or a padded jacket is placed on top of it and everything is wrapped up. Unlike ozokerite compresses, ozokerite cakes do not allow the use of ozokerite at high temperatures. Procedures lasting 30-60 minutes are carried out every other day or with a 2-day break on the 3rd day, less often daily. 10-15 procedures are prescribed per course of treatment. After the procedure, the body is not washed with ozokerite; in extreme cases, the remains of ozokerite are removed with cotton wool and Vaseline. Rest after ozokerite applications 60 min.
Vaginal tampons made of ozokerite are used in gynecological practice. Using a forceps, a cotton swab is moistened in sterilized liquid ozokerite, cooled to 45-55°C, and the vagina is inserted through an ebonite speculum, leaving it there for several hours. At the end of the procedure, the tampon is removed. There is no need to carry out subsequent douching. Such vaginal tampons are used either alone or in combination with ozokerite applications to the pelvic area. Ozokerite tampons are prescribed every other day. There are 10 procedures per course of treatment. Reuse of ozokerite for tampons is not allowed.
M.Yu. Goldenberg (1968) developed a technique for applying an ozokerite dressing for long-term non-healing, as well as a technique for treating furunculosis and deep trichophytosis with ozokerite applications.
Ozokerite treatment is prescribed primarily for chronic inflammatory diseases of various locations during septic processes. It is used in arthrology clinics, traumatology and surgery, for diseases of the nervous system, female genital area, in internal medicine clinics, ophthalmology, dental clinics, for a number of skin diseases and in pediatric practice.
Currently, the indications for ozokerite therapy are very wide.
Contraindications are common for heat therapy in general.
Ozokerite produced by Pharm-Effect LLC can be ordered in the WILDBERRIES online store, as well as from our other partners.
Buy products from Pharm-Effect LLC in the Wildberries online store
Application of paraffin in medicine
Paraffin applications and wraps are widely used in medicine and cosmetology. Due to its beneficial properties, paraffin is used to treat various types of diseases. For example, the procedure is used for bone fractures for rapid healing of injury, for ruptured ligaments, neuralgic disorders, chronic bronchitis and pneumonia, for adhesions after operations, for the treatment of female gynecological diseases, and for skin diseases of almost any nature.
Practicing cosmetologists and numerous beauty salons use paraffin to maintain youth and turgor of the skin of their clients, as well as to combat cellulite on the thighs, buttocks and abdomen.