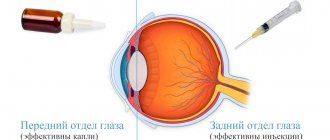
There are contraindications, consultation with a specialist is required
In any health food store, pharmacy or cosmetics section of the supermarket, you can find a variety of products containing aloe extract - from skin care products to medicines, from dishwashing liquid to yogurt.
From this article you will learn what benefits aloe brings to the immune system and not only, because this amazing plant also has other beneficial properties.
All types of aloe, and there are more than five hundred of them, have similar characteristics. Most species grow in small endemic populations and, with the exception of Aloe vera, are listed as endangered.
Researchers are interested in the question of the reasons for the global dominance of aloe vera: whether this is due to evolutionary differences from other species or due to historical factors.
The results of the study showed that the aloe vera species originated in the Arabian Peninsula. This is the northernmost natural habitat of aloe, where conditions are very hot and dry. Moreover, aloe vera’s composition is not very different from its counterparts growing in this region.
Therefore, scientists highlight the historical reasons for the popularity of aloe vera. The Arabian Peninsula is close to ancient trade routes between Asia and the Mediterranean. Most likely, people pragmatically chose a local plant with large, succulent leaves and saw no need to test similar species from other places. So aloe vera simply happened to be in the right place at the right time.
Composition and release form
| Liquid | 100 ml |
| juice from biostimulated leaves or “children” of aloe vera | 80 ml |
| ethanol | 20 ml |
in dark glass bottles of 50 ml; 1 bottle in a cardboard pack.
| Syrup | 1000 g |
| freshly prepared 20% solution of ferrous chloride | 135 g |
| food grade citric acid | 4 g |
| diluted hydrochloric acid | 15 g |
| aloe vera syrup | up to 1000 g |
in dark glass bottles of 100 g; 1 bottle in a cardboard pack.
| Liniment | 1 ban. |
| Aloe vera juice | |
| Eucalyptus oil | |
| Castor oil | |
| excipients: emulsifiers |
in dark glass jars of 30 g; in a cardboard pack 1 jar.
| Film-coated tablets | 1 table |
| crushed preserved aloe vera leaf | 0.05 g |
in a blister pack 10 pcs.; 2 packs in a cardboard box.
Contraindications and precautions for taking products with honey and aloe
For all their positive effects, drinks made from aloe juice and honey can cause side effects. If you are allergic to honey, exclude this component from the aloe drink. And you can use raw sugar or natural syrup as a sweetener.
Aloe gel is generally safe. Caution must be exercised with the green part of the leaf, which is highly toxic:
- causes cramps and diarrhea;
- reduces the effectiveness of drugs;
- causes allergies;
- leads to impaired kidney function;
- sharply reduces blood glucose levels.
The study found that consumption of aloe extract that contained the upper parts of the leaf was associated with the development of intestinal cancer in male and female rats.
Researchers are not entirely sure what caused the risk, but suggest that it is due to anthraquinones found in the waxy part of the leaves.
In particular, they identified the compound aloin as a potential cause of cancer. However, the rats drank water daily containing aloin, 6 times higher than the norm for humans. Therefore, with moderate use there is no danger to humans. However, as a result of this study, many aloe juice manufacturers began to indicate the aloin content in the product.
pharmachologic effect
Pharmacological action - general tonic, adaptogenic.
Aloe juice enhances bile secretion, the secretion of digestive glands, has a laxative effect and bactericidal activity against pathogens (internally), anti-inflammatory, wound-healing effect (externally).
Aloe syrup with iron contains easily digestible iron for the formation of hemoglobin and normal hematopoiesis, replenishes the lack of iron in the body associated with poor absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, blood loss, malnutrition, increased need for iron (pregnancy, active growth in children and adolescents).
Aloe liniment accelerates epithelization, increases skin tolerance to X-ray irradiation, has an analgesic effect, reduces burning sensation and tightness. In experiments on rabbits, it was found that when used prophylactically, it reduces the reaction and significantly shortens the healing time of radiation damage to the skin.
Aloe coated tablets are used as a biogenic stimulant.
Aloe juice benefits
What are the benefits of aloe for the body? Treating Constipation
Aloe juice is known as a natural laxative. This effect is exerted by the outer part of the plant, which contains anthraquinone and aloin. However, at the moment there are no studies revealing the presence of side effects when using the plant as a laxative.
Lowering Sugar Levels
According to a 2016 study, aloe may be beneficial for people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes.
The experiment was conducted on volunteers who consumed various aloe vera preparations, including juice. Adding aloe juice helped lower blood sugar levels. Prevention of gastrointestinal diseases
Aloe juice helps improve digestion, relieves heartburn and is a good preventative for stomach ulcers.
This is facilitated by the anti-inflammatory compounds and antioxidants found in aloe juice, such as vitamin C. Source of Vitamin C
This vitamin is vital to human health, from reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease to improving immune system function.
Having enough vitamin C increases the body's ability to absorb iron from plant foods. Reduces gum inflammation
Research has shown that rinsing with aloe juice helps reduce gum inflammation after treatment or preventative procedures.
Scientists suggested that the antimicrobial and antibacterial properties of the plant helped achieve the results. Treatment of skin diseases
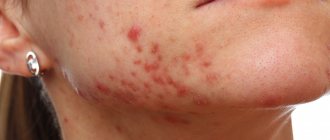
Aloe creams soothe the skin and help reduce itching and inflammation from rashes, acne and psoriasis.
The plant has the ability to suppress the production of prostaglandins - lipids that are active in the sebaceous glands. Sunburn Remedy
Aloe helps with minor burns due to its cooling and soothing properties.
Indications for the drug Aloe juice
Aloe juice: gastritis, gastroenteritis, enterocolitis, constipation (including spastic and atonic), chronic colitis (inside); acute and chronic purulent diseases (externally).
Aloe syrup with iron: anemia of various origins, iron deficiency in the body due to malabsorption, blood loss, malnutrition, increased need for iron (pregnancy, active growth of children and adolescents).
Aloe liniment: second and third degree burns, prevention and treatment of skin lesions during radiation therapy, dry and moist epidermatitis, kraurosis of the vulva, acute and subacute inflammatory processes (dermatitis, eczema, psoriasis, neurodermatitis, lichen planus) and other skin diseases.
Aloe coated tablets: myopic chorioretinitis, in the complex treatment of progressive myopia.
How to take aloe for immunity
Aloe has anti-inflammatory, antiviral, antifungal and antibacterial properties. The presence of polysaccharides and antioxidants in this plant explains its immunostimulating properties.
Regular consumption of aloe juice is good for the heart: B-sitosterol prevents the absorption of cholesterol and helps reduce triglyceride levels.
The immune system is a complex structure that protects people from external biological influences. When the immune system works properly, it protects the body from bacteria and viral infections by destroying cancer cells and foreign substances.
If the immune system is weakened, its ability to protect the body is also weakened, allowing pathogens that cause colds and flu to develop in the body.
Aloe juice stimulates a part of the immune system called macrophages. Macrophages are cells that engage in phagocytosis and engulf pathogens in the bloodstream. Research on aloe juice shows that the polysaccharides in aloe vera help suppress inflammation.
It is best to take aloe in the form of juice or as part of healthy drinks. Juices and smoothies will support the immune system and help the body in cases where the disease could not be avoided.
Directions for use and doses
Aloe juice: orally, 20–30 minutes before meals, 1 teaspoon 2–3 times a day; externally - in the form of lotions and direct irrigation of wounds. Course - 15–30 days.
Aloe syrup with iron: orally, 1/2–1 teaspoon in 1/4 glass of water for 1 dose. Course - 15–30 days.
Aloe liniment: externally, to prevent skin damage - after each irradiation, lubricate the skin with liniment throughout the course (on average 45 days); for treatment - apply a thin layer to the affected skin surface 2-3 times a day and cover with gauze; in gynecology - morning and evening applied to the affected areas 2 times a day (morning and evening); for acute and subacute inflammatory processes of the skin - apply a thick layer to the affected areas (without subsequent application of a bandage) 2 times a day; for dry skin, lubricate the affected areas of the skin with liniment alternate with lanolin.
Aloe coated tablets: orally, 15 minutes before meals, 1 tablet. 3–4 times a day. The course is 1 month, if necessary, repeat after 3–6 months.
Aloe: recipes
Aloe juice for immunity can be prepared at any time of the year using seasonal products.
Aloe and orange
- 2 tablespoons of gel;
- 1 tablespoon white vinegar (optional);
- 1 glass of water;
- 1 glass of orange juice.
Place the aloe in a blender, add a glass of orange juice and water and blend for several minutes at low speed until the gel is completely dissolved.
Instead of orange juice, you can add any citrus juice. Aloe and watermelon
- 4 glasses of fresh watermelon juice;
- 3 tablespoons of gel.
Place the ingredients in a blender and blend until the gel pieces dissolve.
Add some lemon or lime juice. Store in an airtight container in the refrigerator. Aloe and fruit smoothie
- 1⁄2 cup strawberries or blueberries;
- 1 banana;
- 1.5 glasses of plant milk;
- 4 tablespoons aloe gel.
Beat all ingredients until smooth and creamy.
For a richer flavor, use nut milk or add 1 tablespoon nut butter. Aloe and green smoothie
- 240 ml freshly brewed green tea;
- 1 tablespoon of gel;
- 240 g fresh spinach;
- 1 banana
- 120 g pineapple,
- 1 date without pit.
Beat the mixture until smooth.
Add 1 tablespoon of chia seeds for omega-3 fatty acids. Aloe and tropical fruits
- 4 tablespoons of gel;
- 180 g pineapple,
- 180 g papaya.
Place the ingredients in a blender and blend. If you need to sweeten, add 1 teaspoon of honey.
Side effects and overdose
Failure to comply with the dosage of plant preparations, especially juice, leads to an overdose of antaglycosides and can cause poisoning, the symptoms of which are diarrhea with blood and mucous films, inflammation of the intestines, tenesmus, blood in the urine. Pregnant women may have a miscarriage.
Long-term internal use of the whole leaves, with the peel, is fraught with the development of oncology, since the peel contains aloin, a substance that is a carcinogen in large doses. Thus, in an experiment conducted by American specialists as part of the National Toxicology Program, about half of the rats that were given high doses of a plant extract obtained from the whole leaf developed benign and malignant tumors in the large intestine.
Medicinal properties of aloe
Each therapeutic effect of a plant is determined by a group of beneficial substances contained in aloe.
- Antibacterial, incl. against staphylococci, streptococci, typhoid, intestinal, diphtheria and dysentery bacilli, antiviral and antifungal - due to acemannan, aleolitic, phenylacrylic, chrysophanic and cinnamic acids, vitamin C;
- Anti-inflammatory and antiseptic – salicylic acid, bradykininase enzyme, steroid molecules;
- Antitoxic – acemannan, aloin (a substance from anthraquinone derivatives), phenolic components, catalase enzyme;
- Antioxidant - manganese, copper, vitamins C and E, anthraquinone and phenol molecules;
- Choleretic – zinc, selenium and inositol components;
- Calming – magnesium, manganese, B vitamins;
- Laxative – anthraquinone and phenolic group substances;
- Pain reliever – salicylic acid, bradykininase enzyme;
- Antihyperglycemic - two fractions of acemannan - Erboran A and B;
- Antiallergenic – bradykininase enzyme;
- Anticancer – aloemodin, which is an anthraquinone molecule, acemannan, antioxidant vitamins and minerals;
- Wound healing, incl. in relation to sluggish, long-term processes - vitamin C, the enzyme bradykininase;
- Regenerating – vitamin C, catalase enzyme, anthraquinone;
- Immunomodulatory - due to polysaccharides, magnesium, and the enzyme bradykininase.
The plant enhances the secretory activity of the digestive glands (chrysic acid, sodium), normalizes metabolic processes, has a tonic, nourishing, rejuvenating and moisturizing effect on the skin by activating the growth of fibroblasts, relieves itching and irritation. Promotes regeneration of skin damage without scarring. Reduces blood cholesterol levels and promotes the breakdown of cholesterol plaques. Eliminates inflammation in the biliary tract, normalizes the function of the gallbladder.
Features of the plant leaf
Aloe leaves have an unusual structure and include a gelatinous, gel-like core surrounded by a layer of sap and a thin, tough skin. Leaves can accumulate large amounts of water, increasing significantly in size. To preserve moisture, the leaves close their pores, which prevents the evaporation of water when there is insufficient supply from the outside. During prolonged drought, the size of the leaves visually decreases due to the consumption of moisture reserves. Also, in unfavorable conditions, the plant sheds its lower leaves in order to preserve life.
Chemical composition
The leaves contain many useful components (about 200), which determine the value of the crop:
- water (up to 97% of the mass);
- esters;
- traces of essential oils;
- acids: citric, cinnamic, malic, succinic, chrysophanic, l-coumaric, hyaluronic, isocitric, salicylic, etc.;
- tannins;
- resins;
- flavonoids, incl. catechins;
- beta-carotene;
- enzymes;
- bitterness;
- minerals: phosphorus, potassium, sodium, chlorine, calcium, iron, magnesium, manganese, chromium, zinc, cobalt, etc.;
- amino acids: threonine, methionine, leucine, lysine, valine, isoleucine, phenylalanine;
- simple sugars: fructose, glucose;
- polysaccharides, incl. acemannan;
- vitamins: B1, B2, B3, B6, B9, B12, C, E, retinol, choline;
- steroid molecules: sitosterol, composterol and luteol;
- anthraglycosides: nataloin, emodin, aloin, homonataloin, rabarberone;
- substances of the phenolic group, incl. anthraquinone.
Short description
As a member of the Xanthorrhoeaceae family, the aloe plant is a succulent native primarily to Africa and the Arabian Peninsula.
Of the more than 500 varieties of this family, the most commonly cultivated and used is Aloe Vera, a native of the Mediterranean and aloe vera arborescens, commonly referred to as agave.
A characteristic feature is the fleshy leaves of various shades of green, shaped like a sword with spikes along the edges. The roots are superficial, fibrous.
Features of the workpiece
At home, the leaves that are to be harvested are located at the bottom and in the middle part of the stem. The plant must be at least five years old. It was by this time that the beneficial properties of aloe, which made it popular in folk medicine and cosmetology, fully manifest themselves.
Leaves should not be broken off or cut off. They are removed at any time along with the sheaths, which are easily separated from the stem. Before preparing aloe with your own hands in a certain dosage form, you should keep the leaf for 10 - 12 days in the refrigerator. This is due to the fact that at low temperatures, unique biostimulants are produced and accumulated to support the slowing process of life.
If you need to preserve the raw materials longer, then the washed leaves are cut and laid out on white sheets of paper in a ventilated warehouse, balcony or under a canopy, where the burning rays of the sun do not reach. They can be stored in a dry state for up to two years in bags made of thick fabric or paper.
Use in cosmetology
For face
By using aloe juice on your face at home, you can get rid of many problems.
Cosmetologists often recommend using the unique indoor plant aloe for acne, due to its anti-inflammatory and disinfecting properties. It is more convenient to carry out the procedure while lying down, applying cotton pieces moistened with juice to problem areas for 30 minutes. For seven days, this manipulation is done daily in the evening. The next week, 3 procedures are performed, the third - two.
Aloe is beneficial for facial skin if you want to get rid of blackheads. A mixture of the juice of this indoor plant (2 teaspoons), combined with the same amount of lemon juice and egg white, is kept on the face for 15 minutes. This composition is useful for oily skin, as it tightens pores and cleanses them.
Those with rough, dry skin will benefit from an aloe face mask with the addition of sour cream and honey. The ingredients are mixed in equal proportions and distributed over the skin. Wash off after 20 minutes.
When using aloe for wrinkles in the evenings, after cleansing the skin, use your fingertips to pound aloe juice into problem areas. Cosmetic procedures (their total number is 12) are carried out every other day.
For hair
Considering the benefits of aloe for hair, it should be noted that by rubbing the juice of this plant into the scalp before washing your hair, you can get rid of dandruff, enhance the growth and general condition of your hair.
An aloe tincture will help restore the hair structure, for which finely chopped leaves of the plant are placed in a half-liter jar and filled completely with vodka. Keep in a cool place (can be in the refrigerator) for four days. Rub the resulting liquid into the hair roots, cover with film and a warm scarf for 30 minutes. Then they wash their hair. Repeat the procedure for a month every four days.
Well stimulates hair growth, makes it silky and thick, hair mask with aloe. Mix a raw egg with half a teaspoon of garlic juice and a teaspoon of castor oil. Pour in a decoction of nettles (3 tablespoons) and three times less healing aloe juice. Bring the mixture to a homogeneous state while stirring.
The mask should be distributed over the scalp and the entire length of the curls. Cover with film and insulate with a scarf. During the first procedure, the exposure time is 30 minutes. Subsequently, the duration can be 50 minutes. It is enough to make a mask once a week.
Contraindications
When carrying out any procedures based on the use of aloe, you need to know what contraindications there are:
- pregnancy;
- internal bleeding;
- severe pathological disorders in the functioning of the kidneys, heart, liver;
- cystitis;
- allergy;
- haemorrhoids;
- hepatitis;
- malignant neoplasms.
It is not recommended to give aloe vera preparations to children under 14 years of age. In any case, a doctor's prescription is necessary.
Be healthy!