If the average resident has problems with the kidneys during any examination, then most are sent to a clinic or medical center to see a urologist, since this specialist is always well-known. But few people know that with some problems in this area it is necessary to contact his colleague, a nephrologist. What is the difference and when to whom to run for help? Both doctors, of course, treat kidney diseases. But a urologist is a surgical specialist. In most cases, he considers those diseases that require surgical intervention (for example, tumors, large stones, renal colic, developmental abnormalities, etc.). If necessary, he performs the necessary operation, although, of course, he treats “without a knife.” In addition, the urologist also deals with the treatment of problems of the “lower floors” of the genitourinary sphere (ureters, bladder), “male diseases” (for example, prostatitis or prostate adenoma). The nephrologist tries to cope with some problems conservatively, without surgery. It is connected if, against the background of a urological or other disease, there is renal failure or other significant damage to the kidney.
In general, you need to understand that these two specialists organically complement each other, and if you are redirected from one doctor to another, this is a harmonious optimization of the treatment process. The result is successful assistance to the patient and a solution to many “painful” kidney problems.
So, a nephrologist can help you successfully manage most kidney diseases. He observes and competently guides patients, helping them solve problems to optimize treatment, prescribing the right diet and selecting the optimal medications for impaired renal function, as well as for diseases where the kidneys are affected secondarily.
What does a nephrologist treat?
A nephrologist diagnoses and treats, as well as prevents the following diseases:
- Urolithiasis - the formation of stones from insoluble salts in the bladder, kidneys and ureter;
- Arterial hypertension due to renal pathology - persistently elevated blood pressure is often a symptom of kidney disease.
- Glomerulonephritis is an immune disease that is characterized by inflammation of the renal glomeruli; its symptoms are high blood pressure and swelling;
- Amyloidosis is the excessive formation of the amyloid glycoprotein due to disturbances in protein-carbohydrate metabolism, which in severe cases leads to chronic renal failure (Read also: Causes and symptoms of renal failure);
- Nephritis is an inflammatory disease of the renal pelvis, which affects their vessels, tubules and glomeruli, often develops in children after infectious diseases - tonsillitis, tonsillitis, scarlet fever.
- Pyelonephritis is an acute or chronic disease of the renal pelvis, most often the cause of its development is the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, in particular E. coli;
- Primary or secondary nephropathy;
- Acute or chronic renal failure;
- Drug-induced damage is the occurrence of renal pathologies in connection with taking medications.
Surgical treatment of kidney diseases is carried out by a urologist; surgical intervention is required for the following pathologies:
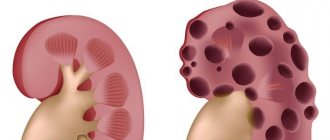
- Polycystic kidney disease, cancer neoplasms;
- Formation of large stones in urolithiasis of the kidneys;
- Tuberculous kidney disease
- Abnormal position of the kidneys, violations of their anatomical structure;
- Complicated pyelophritis;
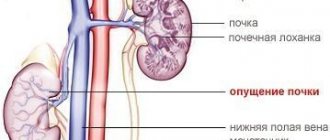
- Nephroptosis.
The symptoms of these diseases are similar to those for which people consult a nephrologist, so additional consultation with a urologist is required to make the correct diagnosis and further treatment.
Instrumental diagnostic methods in nephrology
Nephrologists use several types of imaging techniques to diagnose, monitor, and treat kidney disease. These procedures include:
Ultrasound examination (ultrasound)
An ultrasound uses sound waves to create a picture of the kidneys. This diagnostic test helps detect changes in the size or position of the kidneys, as well as the presence of tumors and other abnormal growths such as cysts or kidney stones.
CT scan
A CT scan uses X-rays to create a picture of the kidneys, sometimes with the help of intravenous contrast dye. However, contrast dyes may cause intolerance in people with kidney disease.
Biopsy
A biopsy involves inserting a thin needle that has a cutting edge to take small samples of kidney tissue that the doctor will examine. Indications for biopsy:
- kidney damage assessment
- determination of the disease process
- understand the complications of transplantation
When to go to a nephrologist?
With an asymptomatic course, kidney diseases can remain undiagnosed for a long time, which leads to a number of serious complications from the urinary and other body systems. The most vulnerable in this case is the cardiovascular system, which suffers first in case of kidney pathologies.
Therefore, you should be attentive to the condition of the body and if the following symptoms appear, immediately contact a nephrologist:
- Anuria is the absence of urination due to insufficient urine flow into the bladder or its complete absence, which can also occur due to impaired renal function. With anuria, urine is either not excreted from the body or is excreted in an amount of no more than 50 ml per day, which leads to venous stagnation, increased load on the heart and intoxication of the body.
- Oliguria – urine is excreted from the body in insufficient quantities (about 400-500 ml with a norm of 1.5 l), this condition is also characterized by an increased load on the cardiovascular system, as well as an increase in diuresis at night.
- Polyuria - frequent urination with the release of large amounts of urine (2-3 liters per day), can occur due to the consumption of drinks that stimulate urine formation, as well as due to disorders of the endocrine system or chronic renal failure.
- Unilateral or bilateral pain localized in the lower back
- Hematuria or proteinuria is the presence of blood or protein in the urine.
A visit to a nephrologist is also necessary; the patient had previously been diagnosed with the following diseases:
- Renal colic;
- Urinary system infections;
- Acute inflammatory processes in the kidneys;
- Chronic or acute renal failure.
High blood pressure can be a symptom of renal pathology, therefore, if there are signs of hypertension, consultation with a nephrologist is necessary.
What symptoms should you see a doctor for?
The kidneys are a kind of filter in the body. They pass through and process harmful substances, which then leave the body naturally. In a healthy body, these functions are performed, but if health is impaired, all toxic substances remain in the body and poison it. This can be very dangerous - in serious cases it can even be fatal.
Therefore, at the first signs of disturbances in the functioning of the urinary system, it is necessary to urgently visit a nephrologist, undergo a full diagnosis and, if necessary, immediately begin treatment. Remember that any pathology is much easier to cure at the initial stage. Whereas in advanced cases, surgical intervention may be necessary for treatment.
When is a child’s nephrologist consultation necessary?
Kidney diseases are often observed in children who have suffered from infectious diseases (tonsillitis, tonsillitis, scarlet fever, acute respiratory infections).
Consultation and treatment with a nephrologist is necessary for the following manifestations:
- An increase or decrease in the volume of urine up to 1/3 of the norm excreted per day;
- Changes in the characteristics of urine - color, smell, consistency;
- Edema syndrome - consultation with a specialist is necessary even if slight swelling appears in the eye area;
- The presence of mucus and blood in the urine, cloudy sediment;
- Redness of the external genital organs, pain when urinating;
- Night urination in children over 4 years of age.
Treatment methods of nephrologists
Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis involves passing blood through an artificial kidney machine called a hemodialyzer to remove waste, excess fluid, and additional chemicals. Blood returns to the body through a catheter into a vessel of the upper, lower limb or sometimes into the vessels of the neck. Hemodialysis is usually used for end-stage renal failure, when the kidneys have lost about 85-90% of normal function and have a GFR of less than 15. 4-hour sessions three times a week are often required. A nephrologist usually oversees these sessions.
Kidney transplant
A transplant involves removing part or all of a damaged kidney and replacing it with a donor organ. Surgeons perform transplant procedures, but nephrologists usually monitor the patient during recovery.
What happens at an appointment with a nephrologist?
During a consultation with a nephrologist, the doctor interviews the patient and determines whether he has symptoms of kidney disease. The nephrologist may ask questions about the presence of urinary system diseases among the patient’s relatives in order to identify a hereditary predisposition to renal pathologies. It is also necessary to inform the specialist about the place and nature of the work (to exclude pathologies associated with intoxication of the body), weight and date of birth (nephrons that make up the kidneys are finally formed in the last stages of pregnancy), data on diuresis and blood pressure level.
Who is a nephrologist
Everyone knows that the human body is a complex, harmonious system of interaction between internal organs and their systems. It should be understood that nephrology problems can be related to neurology, hematology, dermatovenerology, urology, gynecology, etc. In addition, prolonged kidney disease increases the risk of developing diseases of organs that are part of the circulatory system.
A nephrologist is a doctor who treats diseases of important paired organs that are part of the urinary system, diagnoses such diseases, and also develops and implements individual preventive methods. Nephrology is an additional specialization; accordingly, the doctor must have a diploma of higher medical education in the field of pediatrics or in the specialty of general medicine, and only then can he choose an additional, narrower specialization.
If the doctor has previously received education in the specialty of pediatrics, then after receiving additional specialization in the field of nephrology, he will have the specialty of pediatric nephrologist. If a specialist initially received an education in the specialty “general medicine”, and subsequently underwent training in “surgery” and only after that chose a specialization in the field of nephrology, then such a doctor will have the specialty “nephrologist surgeon”. If a doctor, having a basic education in the specialty “general medicine”, completed an internship in the field of surgery, subsequently received residency training in the field of urology and only after that underwent specialization in the field of nephrology, then such a specialist is a urologist-nephrologist.
Tests prescribed by a nephrologist
- Tests that determine the level of creatinine, urea, calcium and phosphate, blood and urine tests for electrolytes;
- Blood test to determine the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation;
- C-reactive protein test.
Additionally, the following instrumental studies may be needed:
- X-ray examination of the kidneys - angiography;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and abdominal organs;
- Radionuclide examination – scintography;
- CT scan;
- Kidney tissue biopsy.
Treatment of kidney diseases by a nephrologist has two main directions:
- Nephroprotective treatment is a universal option that allows you to restore kidney function in any possible pathologies;
- Specific treatment – therapy is aimed at treating a specific disease.
What does a nephrologist do and what does he do?
The activities of a nephrologist are closely related to such areas of medicine as surgery and urology. Let us note that a nephrologist is, first of all, a general practitioner, and therefore carries out medication or any other treatment not related to surgery.
A nephrologist carries out professional activities in public medical institutions, as well as in private medical institutions, conducting outpatient visits.
What is the difference between a urologist and a nephrologist? A urologist is a doctor with a broader specialization, since the area of medical activity of a urologist includes therapy and diagnosis of diseases of the genitourinary system, as well as individual organs (kidneys, prostate, etc.). It is the urologist who performs surgical operations, if necessary, for diseases of the paired organs included in the urinary system.
What does a nephrologist do during an appointment? The appointment with a nephrologist does not have a specific focus. Initially, the doctor conducts a survey of the patient to collect information and identify complaints. The nephrologist will be interested in previous infectious diseases, rhythm of life, nutrition, systematic use of drugs, hereditary diseases, etc. Subsequently, the nephrologist performs an external examination and palpation, and also, often, taps the kidneys with a finger.
Often, to make an adequate diagnosis, the results of laboratory tests and diagnostic hardware procedures are evaluated. Types of diagnostics that may need to be performed at the discretion of the nephrologist:
- Retrograde pyelography;
- Scintigraphy;
- Biopsy;
- X-ray, as well as a specific X-ray examination, in which a certain substance is injected into a blood vessel;
- Ultrasound examination of the kidneys, as well as (if necessary) abdominal organs;
- Pneumoperitoneum (injection of gas into the abdominal cavity);
- ECG;
- CT scan;
- Radioisotope radiography;
- Study of blood pressure in dynamics;
Our service will select the best nephrologist for you for free when you call our Unified Appointment Center by phone. We will find an experienced doctor near you, and the price will be lower than if you contact the clinic directly.
Necessary tests:
- Daily diuresis;
- Research on Nechiporenko;
- OAM and UAC;
- BAC for creatinine, uric acid and urea levels;
- Analysis for cholesterol and triglycerides;
- Samples of Reberg and Zemnitsky;
- Urine culture for bioflora;
Since many kidney diseases occur due to various disorders and infectious lesions of the body, additional consultation with other specialized specialists may be required.
If diseases are detected, the nephrologist prescribes treatment, which will usually have 2 basic directions:
- Direct treatment of the disease;
- Nephroprotective treatment aimed at protecting this paired organ and normalizing its functioning;
Preparing to see a nephrologist
- Diagnosis by a nephrologist is carried out on an empty stomach; you must abstain from food for 12 hours before visiting a specialist;
- 12 hours before visiting a nephrologist, it is also prohibited to drink alcohol and smoke;
- The day before administration, liquid is limited to a minimum amount;
- It is recommended not to take any medications for 24 hours unless it threatens your health. If the course of the drug cannot be interrupted, you must inform your doctor about this.
Symptoms of kidney disease
- Pain in the lower back and side (sharp or dull, constant or worsened by physical activity, light tapping on the back and ribs);
- change in urine color;
- strong smell of urine;
- the appearance of blood in the urine;
- cloudiness of the urine, the appearance of sediment and sand in it when standing;
- pain and stinging when urinating;
- swelling of the face and other parts of the body, most pronounced in the morning;
- increasing weakness, shortness of breath, increased blood pressure, dry mouth, itchy skin;
- high blood pressure, difficult to correct with antihypertensive drugs;
- a decrease in the amount of urine excreted by a third of the usual daily norm when drinking the same amount of liquid;
- a sharp increase in the amount of urine excreted, its discoloration.
The appearance of one or more symptoms is a reason to contact a nephrologist.