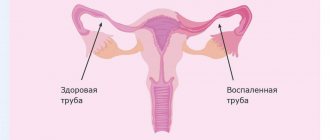
One of the most common diseases of the upper parts of the female reproductive system is adnexitis. It is an inflammatory process in which the uterine appendages are involved. If the disease has spread to both sides, then doctors diagnose bilateral adnexitis. If treated incorrectly or untimely, inflammation can lead to severe purulent-septic lesions or infertility. Therefore, it is very important to immediately undergo a comprehensive examination and begin treatment when the first symptoms occur.
General information
Ovarian adnexitis is a disease that affects the body of the fair sex and is associated with the development of an inflammatory process in the uterine tubes or ovaries.
According to statistics, inflammation of the ovarian appendages or fallopian tubes is detected by gynecologists in every 4th woman. In addition, representatives of the fairer sex need to know about sad statistics. Doctors of gynecological departments call adnexitis in reviews one of the causes of infertility. In 60% of cases, the disease becomes chronic and is practically untreatable. To avoid difficulties with conceiving a child, a woman should pay attention to problems in the genitourinary system in a timely manner.
Advantages of the Mama Papa Ya clinic
Having noticed the symptoms of adnexitis, it is important to contact experienced specialists as soon as possible in order to prevent the disease from developing into a chronic form. We invite women to any of the clinics of the “Mom, Dad, Me” network in Moscow for diagnosis of adnexitis and its effective treatment at any stage. We guarantee that in the comfortable conditions of our departments and under the supervision of the best gynecologists, you will be able to quickly overcome the disease without developing complications or serious consequences.
You can find out more about the prices of services or make an appointment with a gynecologist at the clinic directly on our website or by calling the department nearest to you.
Reviews
Good clinic, good doctor!
Raisa Vasilievna can clearly and clearly explain what the problem is. If something is wrong, she speaks about everything directly, not in a veiled way, as other doctors sometimes do. I don’t regret that I ended up with her. Anna
I would like to express my gratitude to the staff of the clinic: Mom, Dad, and me. The clinic has a very friendly atmosphere, a very friendly and cheerful team and highly qualified specialists. Thank you very much! I wish your clinic prosperity.
Anonymous user
Today I had a mole removed on my face from dermatologist I.A. Kodareva. The doctor is very neat! Correct! Thanks a lot! Administrator Yulia Borshchevskaya is friendly and accurately fulfills her duties.
Belova E.M.
Today I was treated at the clinic, I was satisfied with the staff, as well as the gynecologist. Everyone treats patients with respect and attention. Many thanks to them and continued prosperity.
Anonymous user
The Mama Papa Ya clinic in Lyubertsy is very good. The team is friendly and responsive. I recommend this clinic to all my friends. Thanks to all doctors and administrators. I wish the clinic prosperity and many adequate clients.
Iratyev V.V.
We visited the “Mama Papa Ya” Clinic with our child. A consultation with a pediatric cardiologist was needed. I liked the clinic. Good service, doctors. There was no queue, everything was the same price.
Evgeniya
I liked the first visit. They examined me carefully, prescribed additional examinations, and gave me good recommendations. I will continue treatment further; I liked the conditions at the clinic.
Christina
The doctor carefully examined my husband, prescribed an ECG and made a preliminary diagnosis. She gave recommendations on our situation and ordered additional examination. No comments so far. Financial agreements have been met.
Marina Petrovna
I really liked the clinic. Helpful staff. I had an appointment with gynecologist E.A. Mikhailova. I was satisfied, there are more such doctors. Thank you!!!
Olga
Course of the disease
A woman should especially carefully monitor her health and not delay treatment of adnexitis. She should remember that this disease, if left untreated, leads to infertility.
Understanding the question of what adnexitis is in women, we should talk about the main danger of the pathology. The disease is practically asymptomatic, so it is very difficult to identify it and begin timely treatment. Adnexitis, if left untreated, leads to the development of various complications. These include, for example, adhesions on the fallopian tubes, as well as between them and neighboring organs (uterus, bladder, intestines, omentum).
If adnexitis becomes purulent, purulent masses gradually accumulate in the fallopian tubes. Because of them, sacs are formed filled with pus or serous fluid. Sometimes an infection from the ovary or fallopian tubes penetrates the peritoneum, causing inflammation, the formation of an abscess or peritonitis.
Clinical manifestations of ovarian inflammation
The inflammatory process in the uterine appendages is accompanied by vivid clinical manifestations. The pain is localized in the lower abdomen on one or both sides. From this area, pain is projected onto the lower back, labia, anus, tailbone, thigh or perineum. The lymph nodes in the groin often become enlarged (they become painful and visibly protrude above the skin). With purulent forms of adnexitis in women, the temperature rises to 38-39 °C (it normalizes in the morning, and reaches high levels in the late afternoon or at night). Patients with this diagnosis complain of constant nausea or vomiting, experience extreme thirst or dry mouth, they lose their appetite, and if a woman smokes, she develops a persistent aversion to tobacco products against the background of adnexitis. Localization of pain is observed in the lower abdomen, and with body movements it becomes more pronounced. Women with purulent adnexitis experience increased emotionality, they worry and cry for no reason. Consciousness becomes confused, headaches occur, urination is weak and painful, purulent discharge appears from the genitals.
Chronic adnexitis has mild symptoms or occurs without any symptoms. Sometimes women with this pathology complain of aching pain in the lower abdomen, which intensifies before the onset of menstruation. If you turn your torso sharply, the abdominal pain becomes acute. Increased pain also occurs during sexual intercourse, when the partner makes sudden movements.
Adnexitis - ICD code
Inflammatory processes in the uterine appendages are classified into several types. Depending on this, the ICD code for adnexitis is selected from the numbering N70-N77. In the reference book on the international classification of diseases, inflammation of the uterus, ovaries and fallopian tubes belongs to the category of inflammatory diseases of the female pelvic organs. N70 is a code assigned to salpingo-oophoritis in ICD 10. This category in the reference book is called “Salpingitis and oophoritis”. It includes the following subcategories:
- acute adnexitis with ICD 10 code in adults - N70.0;
- chronic adnexitis - in ICD 10 the code for this disease is designated as N70.1;
- unspecified adnexitis - according to ICD 10, the disease is assigned code N70.9.
Code N70.1 corresponds to all types of chronic forms of adnexitis (including unilateral and bilateral salpingoophoritis). If adnexitis is not treated, the disease can provoke the development of complications and diseases of the internal organs located near the uterus. For example, one of the complications of the disease is acute cystitis, which is assigned code N30.0 in ICD 10.
Acute adnexitis according to ICD 10
Acute adnexitis in the international classification of diseases, 10th revision, has the code N70.0. In accordance with this code, the gynecologist determines the duration of the disease (7-10 days), symptoms (severe pain in the lower abdomen, spreading to the sacral region and becoming stronger with strong palpation). In accordance with the classification of adnexitis according to the ICD, acute adnexitis also manifests itself in the form of nausea, frequent vomiting, elevated body temperature, muscle spasms, fever, and purulent vaginal discharge. Women with adnexitis often complain of difficult and painful urination. If the etiology of adnexitis is not clear and the fallopian tube is involved in the process, then acute adnexitis according to the ICD has code N70.9.
Chronic adnexitis and ICD code
If adnexitis becomes chronic, it is assigned code 70.1 in ICD 10. The pathology develops as a result of improper treatment of the acute form of adnexitis or its complete absence. The disease periodically worsens and subsides, but is not completely eliminated. When diagnosing Chronic adnexitis, the ICD code remains the same, regardless of location.
Cost of treatment of chronic bilateral adnexitis
The cost of treating adnexitis at the Healthy Family multidisciplinary clinic depends on the stage of the disease, as well as related factors:
- woman's age;
- pathogen;
- the chosen treatment complex;
- the need for hospitalization.
On average, the cost of treatment ranges from 4,000 to 12,000 rubles.
In the acute form of the disease, doctors first prescribe antibiotics, taking into account the resistance of the pathogen to them. In case of mixed infection, when the pathogen cannot be identified, complex drugs are prescribed. In addition to antibiotics, medications are prescribed to normalize the microflora of the intestines and vagina.
To quickly normalize the body’s condition and eliminate manifestations of intoxication, detoxification therapy is carried out, and pain is relieved with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. In the absence of positive dynamics, the specialist adjusts the therapy.
Treatment of the subacute phase of the disease is quite similar to the acute phase. Thus, specialists at the Healthy Family multidisciplinary clinic prescribe a set of medications that are suitable for outpatient treatment. But in particularly difficult cases, the patient may need to be hospitalized.
First of all, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed, which can suppress the activity of the pathogen in the fallopian tube. According to the doctor's decision, the patient may be prescribed a complex of several antimicrobial drugs. Additionally, a decision is made on treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs in the form of suppositories and tablets. Their main task is to provide symptomatic assistance, eliminate pain, as well as fever.
Immunomodulatory drugs may also be prescribed. This is especially true if active viral infections were detected during diagnosis. Vitamin complexes are also prescribed to support all body systems. To restore normal microflora, probiotics and prebiotics are used vaginally. To prevent adhesions, it is recommended to undergo physiotherapy.
If the disease has not been treated in full or on time, then chronic bilateral adnexitis develops. Its treatment is very difficult, because the onset of a period of imaginary well-being is perceived by most women as a victory over the disease. But further progression of the disease and the spread of infection leads to the fact that women are often unable to have children.
In the chronic course of the disease, specialists prescribe complex treatment. It includes:
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- proper diet;
- physical therapy classes.
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by the occurrence of serious complications. If a woman experiences purulent discharge or a very high temperature, treatment is best done in a hospital setting under the supervision of a doctor.
Pain is eliminated with the help of painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. To increase effectiveness, in the first stages of treatment, antibiotics are administered intravenously, and later they are replaced by taking them in tablet form.
Digestive disorders are also one of the common manifestations of the disease. Therefore, it is important for patients to follow a proper diet. The doctor adjusts the diet and fills it with foods high in fiber, vitamins and microelements. Temporarily limited:
- smoked meats;
- pickles;
- spices;
- fatty foods;
- carbonated drinks;
- fast food.
To quickly normalize the condition, the daily diet includes:
- porridge;
- vegetable dishes;
- dairy products;
- lean meat, fish.
Particular attention is paid to the amount of fluid a woman consumes. It should be between 2-2.5 liters.
Classification of the disease
The severity of the symptoms of the inflammatory process depends on the pathogen, the degree of development of the pathology, and the individual characteristics of the patient, the main of which is the state of the immune system.
Depending on the causative agents of the disease, adnexitis is distinguished:
- specific - caused by gonococci, diphtheria and tuberculosis bacteria;
- nonspecific - provoked by opportunistic microflora (streptococci, E. coli) or sexually transmitted infections (chlamydia, trichomonas, mycoplasmas, ureaplasmas).
Depending on the location of inflammation, adnexitis is distinguished:
- right-sided - the right appendages become inflamed, and the pain can be confused with manifestations of appendicitis;
- left-sided - inflammatory processes develop in the appendages located on the left side, symptoms resemble colitis;
- bilateral - both ovaries and both fallopian tubes are affected, the woman feels very severe pain in the lower abdomen, radiating to the vagina and anus.
There are also several types of adnexitis, differing in symptoms:
- acute – a serious condition with chills and severe fever, accumulation of toxins in the blood due to the active activity of the pathogen;
- subacute – the symptoms are mild; in fact, this form of inflammatory disease is a transitional phase between an acute and chronic condition;
- chronic - the disease develops against the background of protracted infections that are not treated effectively, accompanied by chills and fever;
- purulent - the most complex form of acute salpingoophoritis, in which filled cavities form in the inflamed uterine appendages.
Depending on the method of occurrence of the disease, there are:
- endosalpingoophoritis - the causative agent of the disease enters the female genitourinary system through the mucous membranes;
- myosalpingoophoritis is a rare form of pathology in which the pathogen affects the organs of the reproductive system, namely its muscle layer;
- peresalpingo-oophoritis - damage to the body by infection begins in the abdominal cavity and gradually spreads to the organs located in the pelvis.
Causes of adnexitis
The main reason for the development of adnexitis is infection. The causative agents of the disease are pathogenic bacteria - streptococci, staphylococci, enterococci, gonococci, chlamydia, Escherichia coli and tuberculosis bacilli.
The primary form of adnexitis, which is an independent disease, is usually provoked by opportunistic bacteria, which can be activated when the immune system is weakened or when an intrauterine contraceptive is used.
The infection can penetrate into the appendages through the blood, lymph, external genitalia, and from other organs (lungs, kidneys, throat). First, the pathogens enter the vaginal mucosa, and then penetrate the fallopian tubes into the ovaries. As a result, adhesions form between the fallopian tubes and the ovaries. In the absence of timely, adequate medical care, the number of adhesions gradually increases, which disrupts the patency of the tubes, which can lead to infertility.
According to statistics, purulent inflammation in the ovaries and fallopian tubes most often develops in women who use an intrauterine device. Infection can also occur during childbirth, during instrumental curettage or abortion.
Increase the risk of developing adnexitis:
- having multiple sexual partners;
- intimate contacts during menstruation;
- refusal of barrier contraceptives;
- hypothermia, especially if it is accompanied by a weakened immune system;
- any intrauterine interventions, regardless of their purpose (hysteroscopy, abortion, instruments)
- lack of hygiene;
- frequent overwork;
- constant stress.
Secondary adnexitis is the result of inflammatory diseases affecting various organs of the abdominal cavity: colitis, diverticulitis, appendicitis. Sometimes syphilis, ureaplasmosis, gonorrhea, and tuberculosis can provoke inflammation of the appendages.
Diagnostic measures
Treatment of salpingoophoritis is performed under the supervision of a gynecologist after confirmation of the diagnosis. The doctor takes into account objective data, the patient’s complaints, and the results of laboratory and instrumental tests. Girls with signs of inflammation of the fallopian tubes and ovaries are prescribed:
- gynecological examination;
- microbiological examination of smears from the urethra, vagina and cervix;
- ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs;
- radiography of the uterus, fallopian tubes and ovaries;
- functional tests.
If there are appropriate indications, the doctor may insist on conducting a diagnostic operation to clarify the location of the abscess and examine the fallopian tubes.
Symptoms
Complaints about adnexitis and all the symptoms can be completely different and depend on the individual characteristics of the female body, as well as the form of the disease. The only common symptom for all types of adnexitis is related to the localization of pain. Discomfortable sensations occur in the lower lateral parts of the abdomen (if bilateral adnexitis develops) or shift to the left or right (if salpingoophoritis is unilateral).
Symptoms of adnexitis are almost always associated with pain. The pain, starting in the abdomen, radiates to:
- coccyx;
- lower back;
- labia;
- anus;
- crotch;
- hips.
Inflammation of the uterine appendages and ovaries is accompanied by pain and swelling of the lymph nodes located in the groin (they become clearly visible, protruding from under the skin).
Pain syndrome with adnexitis is directly related to the entry of an infectious pathogen into the human body. Against the background of infection, the uterine appendages swell greatly, purulent or serous inflammatory fluid appears (sometimes blood impurities are noticeable in it).
The first signs of developing adnexitis:
- elevated temperature;
- stomach ache;
- atypical vaginal discharge;
- uterine bleeding;
- nausea, gagging and vomiting, bloating;
- urinary disorders (emptying the bladder becomes painful and difficult);
- there is strong tension in the abdominal wall;
- sharp pain appears;
- the patient complains of a deterioration in general health;
- sweating;
- temperature rise to high levels (38-39°C);
- pain in the muscles and head (a characteristic sign of intoxication);
- When pressing on the abdomen, pain appears.
Symptoms of adnexitis in women are expressed to varying degrees. The intensity of their manifestation depends on what type of pathogen provoked the disease, how strong the patient’s immunity is, and the extent of the spread of the inflammatory process.
Discharge during adnexitis
The inflammatory process in the uterine appendages is almost always accompanied by the appearance of secretions of various colors that emit an unpleasant odor. In women with adnexitis, the discharge provokes itching, burning and irritation of the vagina. Discomfort in the genital area becomes the first “alarm bell” and a reason to contact a specialist. Discharge from this disease can be:
- scanty;
- abundant;
- yellow;
- green;
- brown;
- bubbling.
The color of the discharge is important in the diagnosis of adnexitis. Based on the shade of vaginal leucorrhoea, the doctor determines the approximate type of pathogen that provoked the disease.
Adnexitis and brown discharge
Brown vaginal discharge with adnexitis indicates acute inflammation. Often brown leucorrhoea with inflammation of the uterine appendages emit an unpleasant odor and contain purulent inclusions. A characteristic sign of the disease is the acyclic appearance of brown vaginal secretion. Many patients with this symptom of adnexitis suffer from severe pain during menstruation. Against the background of inflammation of the appendages, menstruation becomes abundant. Brown discharge appears regardless of the phase of the menstrual cycle, is spotting and scanty.
Adnexitis and yellow discharge
Adnexitis in women also provokes the appearance of yellow or green discharge with an unpleasant odor. If the inflammatory process is caused by a gonococcal pathogen, the vaginal mucus will be yellow, sometimes mixed with pus. Trichomonas, parasites in the uterine appendages, contribute to the formation of bubbling greenish-yellow discharge. If the disease is in the acute stage, the discharge has a bright yellow color.
Bleeding with adnexitis
Adnexitis and bleeding are dangerous and interconnected pathological conditions. The onset of inflammation is associated with the ingestion of an infectious pathogen, and as the problem worsens, adhesions form, ulcers form in the fallopian tubes, menstrual irregularities are observed, and severe uterine bleeding occurs.
Throughout the entire menstrual cycle (between periods), many women with adnexitis experience severe and prolonged bleeding. This symptom is also associated with menstrual irregularities.
Adnexitis with blood in women is a dangerous condition that requires qualified medical care to eliminate. Uterine bleeding against the background of inflamed appendages can be spontaneous and unexpected. Provoking factors for their appearance are severe stress and a woman lifting heavy objects. Chronic adnexitis is accompanied by spotting bloody discharge from the vagina. If the inflammatory process has become chronic, a woman’s menstruation may stop altogether and be absent for several months in a row.
Local symptoms of inflammation of the appendages:
- Aching, cutting pain of medium duration in the abdominal area;
- Painful periods, dull pain during intimacy;
- Mucous or purulent leucorrhoea, clear discharge, often accompanied by itching and irritation on the skin;
- Changes in the timing, duration of menstruation, cycle shift.
If you note at least one symptom, contact GMS Clinic specialists for diagnosis. It is much easier to cure the disease in the early stages, and the likelihood of avoiding complications and consequences is higher.
Diagnostics
Modern methods of diagnosing adnexitis help to detect the disease in time and treat it before irreversible consequences occur.
Diagnosis of adnexitis in patients is carried out in a hospital setting. An ultrasound is required, a bacterial culture is taken from the vagina, and a general blood test is done. During the differential diagnosis of adnexitis, a specialist separates the disease in question from ailments with similar symptoms (acute appendicitis, endometriosis, diseases of the genital organs, ovarian cyst). In severe cases, consultation with a surgeon is necessary.
To clarify the diagnosis, a medical specialist may conduct the following studies:
- An ultrasound scan of organs located in the pelvis gives a fairly clear picture of the inflammatory process of the appendages;
- general analysis of urine and blood;
- biochemical blood test (sugar, C-reactive protein, total protein);
- a smear of vaginal discharge to determine bacterial culture, the body’s sensitivity to antibiotics and microflora;
- Differential diagnosis of adnexitis is also important. For its purpose, tuberculin tests are carried out (they are taken if there is a suspicion of infection with the tuberculosis bacillus);
- laparoscopy (the procedure is performed in complex cases when difficulties arise with the correct diagnosis of the disease).
Therapeutic course
Treatment of adnexitis in the acute stage is carried out in a hospital setting. The patient receives broad-spectrum antibiotics, painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. If an abscess is detected, surgeons perform surgery, during which the purulent contents are removed and the inflammation site is irrigated with antiseptics and antibiotics. An alternative treatment strategy involves the evacuation of fluid accumulated in the saccular formation through puncture of the vaginal vault. When the appendages melt, signs of renal failure appear and there is an extensive septic process, an adnexectomy is performed - removal of the fallopian tubes and ovaries.
Relapses of pathology in a chronic form allow the use of conservative treatment methods: medication, UV irradiation, electrophoresis, UHF therapy.
Treatment of adnexitis
Adnexitis is one of the serious pathologies, and therefore requires an integrated approach for its treatment. Therapy is based on the use of antibiotics, antimicrobial drugs, and immunomodulators. The main drug complex is supplemented with a course of vitamin therapy. Vitamins are selected by a gynecologist on an individual basis. They can be administered to the patient by injection or by taking capsules or tablets.
Treatment of the acute form of adnexitis is carried out using conservative methods. An experienced doctor knows well where and how adnexitis hurts in a woman, and based on the examination results, he quickly diagnoses the disease. The course of therapy is carried out using antibiotics. When a tubo-ovarian formation develops, in most cases, patients are recommended to undergo surgery, because conservative treatment is lengthy and may not give a positive result. During surgery, the affected areas of the fallopian tubes are removed.
The chronic form of the disease requires long-term and complex treatment in several stages. As a rule, gynecologists prescribe medications:
- antibacterial;
- anti-inflammatory;
- desensitizing;
- painkillers;
- absorbable.
Immunity enhancing agents can be prescribed as excipients; as a rule, liquid aloe juice is prescribed. In some cases, physiotherapy (laser, magnet) is prescribed.
The acute form of adnexitis, which is accompanied by high body temperature, sharp attacks of pain in the abdominal area, as well as enlargement of the appendages upon palpation, is carried out only under the supervision of highly qualified specialists in a hospital. Bed rest is prescribed. As for drugs, gynecologists prescribe the same group of drugs as in the treatment of chronic adnexitis. After eliminating all pain symptoms, the doctor may prescribe a visit to electrophoresis and ultrasound.
If purulent inflammation is detected, drug treatment becomes insufficient. The drugs are started to be administered near the source of inflammation, and strict bed rest is prescribed. After all purulent foci and pain disappear, standard treatment for this type of disease is prescribed.
As a preventive measure and home treatment, you can resort to traditional medicine recipes, namely:
- treatment with mineral waters and mud;
- ozokerite compresses;
- Spa treatment;
- paraffin compresses.
We draw your attention to the fact that full treatment can only be carried out under the supervision of a highly qualified doctor. Listen to your body, watch for the slightest changes in the menstrual cycle, the amount and type of discharge. Remember that timely treatment, visiting a gynecologist twice a year, maintaining personal hygiene, and proper nutrition will help not only preserve your health, but also experience all the joys of motherhood.
Surgical treatment of adnexitis
For adnexitis, surgical treatment is carried out if, when diagnosing the disease, there is a suspicion of the development of adhesions (formation of scars from connective tissue in the pelvic organs), tubo-ovarian formations (purulent melting of the fallopian tube and ovary), hydrosalpinx (accumulation of fluid in the fallopian tube), as well as or peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum). As a rule, surgical treatment of chronic adnexitis is carried out strictly according to indications, taking into account the clinical picture, general condition, and the presence of concomitant pathology. Surgical intervention is performed using laparoscopy. In the preoperative preoperative period, an IV is prescribed. What is included in infusion therapy? These are antibacterial drugs, such as trichopolum. The use of Trichopolum infusion solution should be started 5-10 minutes before surgery on the pelvic organs. Painkillers for adnexitis are also prescribed in the postoperative period.
If possible, the surgeon tries to eliminate the formations while preserving all organs, but it is possible to remove the tube, uterus or ovary if their condition threatens the patient’s life.
Signs of right-sided adnexitis
Signs that indicate damage to the fallopian tubes and ovaries:
- Severe pain in the abdominal area. As a rule, the right side hurts and women often confuse this with a manifestation of appendicitis.
- Temperature rises to 39 degrees.
- The appearance of purulent vaginal discharge.
- Problems with bowel movements.
- Pain when urinating.
A change in the amount of discharge during menstruation, an increase or decrease in the interval, the appearance of pain, indicates serious health problems. If such a symptom appears, it is best to contact the specialists of the Healthy Family clinic. Doctors will conduct a diagnosis and determine the exact cause of the problem. As a rule, with inflammatory diseases, especially if bilateral adnexitis is chronic, female sex hormones begin to be produced in minimal volumes, which affects menstruation. They can be either too scanty or abundant, and in some cases even the appearance of clots and fragments of the endometrium is observed.
The presence of an inflammatory process in the appendages provokes the appearance of purulent discharge. They appear during urination, as well as involuntarily. In some cases, it is greenish or yellow mucus. Due to the appearance of uncharacteristic discharge, the vaginal walls become irritated, which leads to severe itching and burning. Experienced specialists at the Healthy Family clinic can make a preliminary diagnosis and identify the pathogen based on the color of the discharge. Thus, under the influence of gonorrhea, clots of a yellowish tint appear, and with trichomoniasis, green-yellow clots appear.
Adnexitis is characterized by frequent bleeding, which can lead to the development of anemia. This makes a woman feel weak and depressed. The appearance of prolonged bleeding indicates that the disease is becoming chronic.
Additionally, women experience symptoms of general intoxication of the body:
- weakness;
- severe headaches;
- decreased appetite.
With a long course of the disease, health deteriorates significantly. Severe inflammation can cause problems with consciousness or disability. As a rule, this occurs due to the pain radiating to the spine.
If the disease progresses and peritonitis develops, the abdominal muscles become very tense, the pain spreads to the entire peritoneal area, and the woman’s condition worsens.
Subacute bilateral adnexitis is characterized by less striking clinical manifestations. The disease develops gradually. The pain is not so pronounced, and the temperature does not rise much. This progression of adnexitis leads to many women delaying treatment, and the disease becomes chronic.
Prolonged course without proper treatment leads to the fact that the inflammatory process spreads not only to the tubes, but also to the uterus. This form of the disease has its own name, salpingoophoritis. Its chronicity has a strong impact on the female body. The following functions are affected:
- menstrual;
- sexual;
- reproductive.
Often, problems with ovulation in combination with obstruction of the fallopian tubes lead to the development of infertility or the occurrence of an ectopic pregnancy. This is due to hormonal instability and the impossibility of normal functioning of internal organs. Even if fertilization proceeds normally and the egg is implanted into the wall of the uterus, then with adnexitis there is still a high probability of miscarriage or miscarriage.
A long-term inflammatory process in the body causes damage to the nervous and endocrine systems. A decrease in the body's protective functions, combined with constant mood swings caused by unstable hormonal levels, provokes the development of depression.
Complications
If adnexitis is untimely or improperly treated, an adhesive process develops in the pelvis. Pain may occur after treatment of adnexitis, which may indicate the formation of adhesions. Adhesions prevent the normal movement of the egg and sperm through the tube. Also, adhesions can form in the uterus, ovaries, intestinal loops, which leads to infertility, tubal obstruction, ectopic pregnancy, intestinal obstruction, inflammation of neighboring organs (pyelonephritis, colitis).
Pelvioperitonitis is also a serious complication. This process is secondary and begins with a sharp and rapid increase in body temperature to 39-40 ° C, the appearance of severe pain in the lower abdomen, tachycardia, bloating, and painful urination. In order to identify microbial agents, a bacteriological examination of the vaginal discharge and cervical canal and ELISA diagnostics are carried out. This complication is treated with infusion, analgesic and antibacterial therapy.
Prevention of adnexitis
It is known that the disease is easier to prevent than to treat, so gynecologists recommend that every woman follow a number of simple rules:
- do not have promiscuous sex life;
- visit a gynecologist every six months;
- avoid abortion;
- maintain personal hygiene;
- dress according to the weather;
- Do not self-medicate, but consult a doctor at the first symptoms of the disease.
Also, prevention of adnexitis in women is based on fulfilling the requirements from the following list:
- Work on strengthening the immune system. Go out into nature more often (in the forest, to bodies of water), and take daily walks.
- Maintaining a daily routine. Sleep at least 8 hours a day.
- Proper, balanced nutrition.
- Proper rest, avoiding stress and unfavorable factors.
- Wear clothes according to the season, avoiding hypothermia.
- Attracting positive emotions into life. They create a kind of barrier to disease.
Prevention of inflammation of the appendages:
- Timely implementation of hygiene procedures to protect against infection entering internal cavities;
- If possible, avoid unprotected sexual intercourse;
- Protect yourself from surgical termination of pregnancy. The easiest way to do this is by using barrier methods of contraception;
- Regular visits to the gynecologist and a smear test for internal flora analysis.
Most often, a visit to a specialist helps to identify the disease and prevent its development in time. In addition, you can contact a herbalist who will create for you a personal collection of herbs that protect the body and help it fight infections.