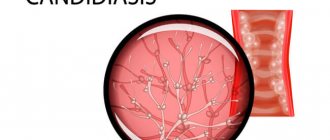
Thrush is an inflammatory disease of the genitourinary system of a fungal nature. It most often occurs in women in the form of vaginal candidiasis. It manifests itself as cheesy or creamy white discharge from the vagina, burning, itching and redness in the genital area, pain during intimacy and during urination. Treatment includes local and systemic use of drugs with antimycotic effects, as well as correction of immunity.
Urogenital candidiasis is a common infectious disease. Thrush occurs mainly in women of reproductive age. In men who are sexual partners of such patients, candidiasis balanoposthitis may occur. A child becomes infected with a fungal infection from a sick mother during childbirth.
Causes
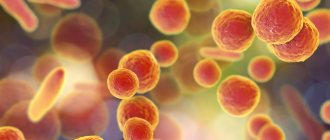
The disease is caused by microorganisms of the genus Candida.
They are part of the opportunistic microflora that constantly lives on the skin and mucous membranes of humans. However, with decreased immunity or hormonal imbalance, fungi begin to actively multiply, suppressing the growth of beneficial bacteria and causing an inflammatory response. The following factors can cause thrush:
- diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, thyroid dysfunction);
- excess weight;
- diseases of the female reproductive system;
- disturbances in the state of the microflora of the mucous membrane of the external genital organs;
- taking antibiotics, hormonal drugs, drugs with cytostatic effects, immunosuppressants;
- radiation and chemotherapy;
- use of tight clothing, underwear made of synthetic fabrics;
- rare change of sanitary pads;
- intrauterine contraception - vaginal diaphragms, douching, spermicides;
- use of intimate deodorants, scented pads and tampons.
An exacerbation of the disease often occurs on the eve of menstruation and after significant stress. Diet is also important - consuming large amounts of carbohydrates contributes to the development of fungal infections.
Sex is one of the causes of candidiasis
Unprotected sexual intercourse is one of the common ways of transmitting thrush to your sexual partner. Most often, this disease passes from a woman to a man, and the latter may not even realize that he has the disease. Being a carrier of the disease, a man, without knowing it, can infect a woman in whom the disease will cause unpleasant symptoms.
During sexual intercourse, the disease is transmitted to a sexual partner, provided that a favorable environment for the development and reproduction of the fungus is established. After sexual contact, especially if ejaculation occurs, the microflora of a woman’s vagina changes significantly, which leads to the occurrence of candidiasis. Moreover, this applies not only to promiscuity, but also to sex with a regular partner.
Best materials of the month
- Coronaviruses: SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Antibiotics for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19: how effective are they?
- The most common "office" diseases
- Does vodka kill coronavirus?
- How to stay alive on our roads?
You should also know that thrush can also be contracted after oral sex. Sex on the beach is also a provoking factor in the occurrence of such an infection. Sand is a strong irritant to the vaginal mucosa, and salt water disrupts its microflora. Having sex in clean, but rather cool water can also lead to the onset of illness.
Therefore, during an illness, it is best to refuse intimacy and wait for a complete recovery.
Classification
Vaginal candidiasis occurs in acute or chronic form.
In the latter case, the symptoms are less pronounced, but the disease has a long course and is more difficult to treat. Chronic thrush can be recurrent, with frequent exacerbations, and persistent, when episodes of deterioration are rare and associated solely with the provoking factor. The formulation of the diagnosis also specifies whether urogenital candidiasis is complicated or uncomplicated, depending on the number of exacerbations of the disease over 12 months and the severity of its manifestations. The congenital form of thrush is observed in children infected during childbirth from a sick mother. Candidiasis of newborns most often affects certain areas - eyes, mouth, respiratory tract, lungs, skin, but fungal sepsis cannot be excluded when a large amount of the pathogen enters the blood.
Is thrush really a problem?
The content of the article
People of all ages suffer from candidiasis, with the peak incidence occurring between 20 and 40 years of age. According to statistics, 60% of women have been diagnosed with thrush at least once in their lives, and in 9%, candidiasis has a recurrent (repeating) course. In reality, this figure is higher, since in many patients the disease does not produce noticeable symptoms and the fungus is detected only when swabs are taken from the vagina.
The main problems of this pathology are self-medication, which leads to the disease becoming chronic, and negligent attitude towards one’s health. Gynecologists at the Diana Medical Center daily encounter cases of thrush, the severity of which is due to the patients’ late seeking of professional medical help.
Symptoms
The acute form of vaginal candidiasis has a clear clinical picture.
A woman is worried about intense itching, burning in the genital area and near the anus, pain when urinating, during intimacy, discharge from the genital tract of a white or yellowish color with a cheesy consistency and a sour odor. The latter can be abundant or adherent in moderate quantities on the mucous membrane of the vulva, in the posterior and lateral vaults of the vagina. Also in the affected area there is redness, swelling of the tissues, and possible cracks in the skin and mucous membranes. With persistent thrush, the symptoms are less pronounced. There may only be itching and discharge in small quantities, appearing, for example, only on the eve of menstruation. Recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis may be accompanied by striking manifestations during exacerbations. They leave dryness, atrophy, and lichenification on the skin and mucous membranes.
In newborns, thrush is often accompanied by damage to the oral cavity and tongue. A white coating appears on the mucous membrane; when you try to remove it, areas of redness and swelling are found underneath it. A child suffering from candidiasis from birth is capricious, and has sleep and appetite disturbances.
Thrush in men manifests itself in the form of candidal balanoposthitis and urethritis. The disease is accompanied by burning and itching, redness, and swelling in the area of the head of the penis. It may cause rashes, often covered with a white coating, and cracks. Just like in women, sexual intercourse and the process of urination become painful.
Symptoms of thrush: what a woman feels with candidiasis
Candidiasis is difficult to miss - it is one of the most unpleasant diseases. A woman is worried about incessant itching in the genital area, frequent painful urination (dysuria), pain and discomfort during sexual intercourse (dyspareunia), associated with vaginal dryness and injury. The main sign of fungal activity is a cheesy discharge. Whitish deposits begin to form on the reddened mucosa, which separate and form a cheesy vaginal discharge. In men, thrush manifests itself as redness of the head, a white coating accumulates on it, and red spots may form.
In advanced stages, the infection from the external genitalia spreads to the anal area. Cracks in the mucous membrane occur, accompanied by pain during defecation. If thrush is not treated, it becomes chronic and torments the woman constantly - during hypothermia, menstruation, after bathing, when personal hygiene rules are violated or in the premenstrual period, when hormonal levels change, etc.
Against the background of thrush, due to scratching and weakening of the natural flora of the vagina, a bacterial infection can develop, leading to bacterial vaginitis. Vaginitis quickly spreads to the uterus and its appendages, which in some cases can lead to decreased fertility (the ability to conceive), even to infertility.
If any symptoms of thrush appear, especially during pregnancy or breastfeeding, you should contact your doctor to confirm the diagnosis and prescribe timely treatment. The doctor makes a final diagnosis after receiving the test result (smear). A small amount of fungus does not cause disease and is normal.
Diagnostics
A gynecologist diagnoses and treats thrush in women. If candidal balanoposthitis appears, you should seek help from an andrologist. During the patient’s initial visit, the doctor clarifies the nature of the complaints, the duration and frequency of appearance of signs of thrush, and conducts an external examination of the genital organs. Next, the patient is prescribed laboratory tests:
- a smear from the mucous membrane of the genital organs followed by a microscopic examination of the biomaterial;
- cultural seeding to determine the species of the fungus and its sensitivity to antimycotic drugs;
- detection of pathogen gene material by PCR.
In order to clarify the predisposing factors that contribute to decreased immunity and hormonal disorders, the following is carried out:
- clinical blood test;
- determination of antibodies to HIV;
- blood test for the content of important microelements and vitamins;
- analysis of blood glucose and carbohydrate metabolism metabolites.
For the purpose of differential diagnosis, it is possible to conduct other tests, and if necessary, consultations with other specialists are prescribed - a therapist, gastroenterologist, dentist, immunologist, endocrinologist, infectious disease specialist.
Complications
Most complications of vaginal candidiasis are associated with the spread of the inflammatory process to nearby organs and tissues and the addition of bacterial inflammation. It occurs against the background of a sharp decrease in local immunity. Most often, patients encounter the following problems:
- salpingitis and salpingo-oophoritis (adnexitis): inflammation of the uterine appendages: tubes and ovaries; the process can be unilateral or bilateral, accompanied by pain in the lower abdomen, weakness, fever; without treatment, it can cause infertility due to the development of adhesions;
- urethritis: inflammation of the urethra; classic symptoms are a burning sensation when urinating, changes in the appearance and color of urine, redness and swelling in the area of the external urethral meatus;
- cystitis: inflammation of the bladder that develops as a result of the passage of the pathogen from the urethra; Symptoms of urethritis include frequent urination with a small amount of urine, pain and cramping at the end of the process, increased temperature and pain in the lower abdomen.
In addition to the spread of infection, vaginal candidiasis can threaten the development of stenosis (narrowing) of the vagina. This condition occurs due to chronic inflammation, which leads to the growth of scar tissue and narrowing of the lumen of the organ. This leads to significant difficulty in sexual life.
Vaginal candidiasis is very dangerous for pregnant women, since without treatment, infection of the fetus is possible, which can lead to its death.
In the postpartum period, women may develop candidal endometritis.
Treatment
Since fungi of the genus Candida belong to the opportunistic flora, treatment is required only in cases of vaginal candidiasis or balanoposthitis proven in laboratory studies, which have characteristic symptoms.
In case of uncomplicated course of the disease and early contact with a gynecologist, it is possible to prescribe only topical medications - vaginal suppositories and tablets for thrush, antifungal ointments, creams. In case of their ineffectiveness, as well as in case of chronic urogenital candidiasis, systemic antimycotics are prescribed - fluconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole.
Drug therapy for thrush during pregnancy is limited to topical antimycotic drugs for intravaginal administration. Children are prescribed systemic antifungal agents for thrush in a dosage adjusted based on body weight.
Local and general drugs are also used to treat balanoposthitis. To achieve greater effect from the use of ointments and creams, the head of the penis is first washed with a weak soda solution. If a man has a regular sexual partner, she also needs to undergo an examination by a gynecologist and, if necessary, a course of antifungal therapy, since infection with thrush is possible during intimate intimacy.
Is thrush contagious?
Keep in mind that candidiasis is a contagious disease and is easily transmitted to a sexual partner, so you will have to be treated together. The disease is often confused with an STD. In fact, thrush does not belong to this group, but contact with a man suffering from candidiasis will provoke the development of infection. A woman also transmits Candida to her partner. In men, thrush occurs more easily, this is due to good access of air to the mucous membrane of the head, but even without obvious signs, a once infected man becomes a carrier of the infection.
Prevention
Prevention of thrush consists of maintaining immunity, eliminating factors that provoke its decline or hormonal imbalance.
It is important to use antibiotics reasonably and only as prescribed by a doctor, and after completing the course of treatment with such drugs, restore the microflora with pro- and prebiotics. The following measures will also help to avoid the development of fungal infections:
- maintaining personal hygiene;
- timely treatment of endocrine and urogenital pathologies;
- normalization of weight and nutrition;
- use of barrier contraceptives;
- having a permanent sexual partner;
- wearing underwear made from natural fabrics;
- refusal of scented personal hygiene products, intimate deodorants, and douches.
Important points in the treatment of oral candidiasis -
There are several problems in treating candidiasis of any location. The first problem is that fungi of the genus Candida can be located not only on the surface of epithelial cells of the mucous membrane, but are also capable of germinating inside epithelial cells. In this case, the mucopolysaccharide membrane of the host cell will protect the fungi not only from phagocytes (which must find, absorb and digest infectious agents), but also, to a certain extent, from antifungal drugs. In this case, higher dosages of drugs and longer courses of treatment (including suppressive therapy) may be required.
Another problem may be an insufficient immune response (for example, incomplete phagocytosis of Candida fungi). In the absence of immunocorrection with the help of immunomodulators, this sharply increases the risk of developing chronic candidiasis and subsequent relapses. Among the immunomodulators, we can recommend the prescription drug "Cycloferon" (in the form of intramuscular injections), but it should be used only after the recommendation of a doctor. If a slight correction of the immune status is necessary, you can use Cycloferon tablets.
It is very important to carry out treatment while sanitation of the oral cavity, i.e. it is necessary to cure all carious teeth, foci of chronic inflammation in the oral cavity, and remove dental deposits. If soft microbial plaque and hard dental deposits have not been removed, this means that a new relapse of oral candidiasis will occur very soon. In addition, for patients with removable dentures, it is important to teach them to regularly disinfect dentures, as well as replace them if their service life has expired. It will be futile to treat oral candidiasis in patients whose dentures continue to be a source of infection.
For smokers, it is very important to reduce the frequency of nicotine consumption in this case, or better yet, give it up. If candidiasis occurs during the use of inhaled steroids (in asthmatics), the patient should be told about the need to rinse the mouth with water after spraying the steroid. During treatment, it is also very important to reduce the amount of carbohydrates consumed, and it is advisable to completely give up sweets and sugar-containing drinks. For patients with dry mouth, it is important to start using special medications to keep the oral mucosa hydrated.
Toothpastes containing lactoferrin, lactoperoxidase, lysozyme, and glucose oxidase can be of great help in the treatment and prevention of candidiasis and stomatitis. Such pastes increase local immunity in the oral cavity and reduce the risk of developing stomatitis and candidiasis. For example, such pastes are included in the SPLAT line of toothpastes.