A dry cough in a child is a kind of protective mechanism necessary to cleanse the airways and maintain their patency. It can be a natural reaction to the temporary effect of an irritant or a symptom of a disease, not always associated with the respiratory system.
The cause of a child's dry cough can be viral, bacterial infections, allergic reactions, dirty air, mechanical compression of the respiratory system, for example, by a foreign body or neighboring tissues.
Types of dry cough in children
Dry coughs range from minor coughing to poorly controlled attacks. The following types of cough are distinguished:
- Acute - appears suddenly, most often accompanies viral infections, foreign body entry into the respiratory tract.
- Protracted - may be the result of an acute cough, usually appears during a period of prolonged recovery after ARVI or acute bronchitis, lasting more than 4 weeks
- Chronic - develops after three months (12 weeks) of prolonged cough; it can be a complication after an untreated disease.
- Paroxysmal - appears as an uncontrolled attack, may be a symptom of an allergic reaction or whooping cough.
- Barking is often a symptom of laryngitis, laryngotracheitis, and inflammation of the larynx. It may be a manifestation of false croup, a dangerous condition in children.
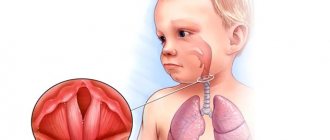
Barking cough
Diphtheria
15360 08 June
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Barking cough: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Cough is a physiological protective reaction of the body in response to irritating substances entering the respiratory system (less often, the digestive tract). The respiratory epithelium, which covers the respiratory tract from the inside, protects the body from the penetration of infectious agents (bacteria, viruses, etc.), retains dust particles inhaled with the air on its surface, and also helps cleanse the respiratory tract from them. The cells of the epithelium of the respiratory tract are adjacent quite tightly to each other, forming a barrier that does not allow microbes to pass through. A secretion (mucus) is produced on the surface of the epithelium, which moisturizes the epithelium and air passing through the respiratory tract, and also creates an additional barrier to infection. The respiratory epithelium has special cilia on its surface that help cleanse the walls of the respiratory tract, “washing out” mucus with dust and microorganisms settled on it in the direction from bottom to top.
The mucous membrane of the respiratory tract is well supplied with blood, which ensures warming of air coming from outside, sufficient mucus production and timely transportation of leukocytes (immune cells) to the area where infectious agents enter.
With the development of inflammatory changes in the wall of the respiratory tract or when they are irritated, for example by dust or caustic gases, the cough center is activated.
Types of cough
Depending on the presence of sputum, dry and wet cough are distinguished. Interestingly, these two types of cough can replace each other during the course of the disease.
Based on timbre, coughs are classified into silent, muffled, hoarse and others, among which the barking cough occupies a special place.
When describing this type of cough, it is appropriate to say that it really is somewhat reminiscent of a dog barking: just as loud and sharp, often with a metallic tint.
Possible reasons for the development of a barking cough
A barking cough usually indicates damage to the larynx.
The larynx with the vocal folds located in it plays a key role in the vocal apparatus. The vocal folds are stretched between cartilaginous structures, the degree of their tension is regulated by the laryngeal apparatus. Between the two vocal folds there is a gap through which the air exhaled from the lungs passes, creating oscillatory movements. The length of the vocal folds and the frequency of vibration determine the characteristics of the voice and cough in people with lesions of the vocal apparatus.
Inflammatory diseases of the larynx are grouped under the general name “laryngitis”. Inflammation of the larynx often develops in connection with an infectious lesion of the upper respiratory tract, and isolated inflammation of the larynx occurs quite rarely; much more often, the infectious process spreads to the larynx from the pharynx or trachea. Other causes of laryngitis are thermal injuries (exposure to gaseous substances that have a high temperature), inhalation injury from gaseous caustic chemicals, and allergic processes. Laryngitis develops when the vocal apparatus is overstrained.
Diseases that cause barking cough
Among infectious lesions of the larynx leading to the development of a barking cough, it is customary to distinguish two groups of diseases:
- Diphtheria of the larynx is an infectious disease of a bacterial nature, characterized by the formation of lamellar plaques in the respiratory tract, which are prone to independent separation from the mucous membrane and lead to blockage of the lumen of the respiratory tract, up to a complete disruption of their patency.
This condition is called “true croup” - it is characterized by gradual, steady progression, hoarseness with a further decrease in the volume of the cough. - Acute stenosing laryngotracheitis is an infectious inflammation of the trachea and larynx, leading to obstruction of the airways due to severe swelling of the laryngeal mucosa. This disease is also called false croup, because it is not caused by diphtheria bacillus, but by viruses (parainfluenza, influenza, respiratory syncytial virus) and bacteria - for example, mycoplasma.
False croup usually begins on the 1st–3rd day of a cold, acutely, suddenly, often at night.
A barking cough and severe difficulty breathing are the main signs of this condition.
It is worth saying that true croup affects people who were not vaccinated against diphtheria in childhood.
False croup is a condition characteristic of childhood (usually up to 5 years) - this is due to the structural features of the larynx in children (narrow, with soft cartilage, having a good blood supply to the mucous and submucous membranes), as a result of this structure there is a rapid increase in inflammatory edema and development severe airway obstruction. Which doctors should I contact if I develop a barking cough?
Emergency care for a patient with a barking cough and respiratory distress is usually provided by an emergency physician. Further management of such a patient depends on the cause of the development of barking cough. So, if diphtheria is suspected, the patient is hospitalized in an infectious diseases hospital, where an infectious disease specialist will treat him. If false croup develops in a child, therapy is carried out.
Diagnosis and examinations for barking cough
Diagnosis of a barking cough begins with interviewing the patient (or his parents, if the patient is a child) and finding out the circumstances under which the cough developed. Then the doctor conducts a clinical examination, an integral part of which is examining the oral cavity and listening to breathing sounds using a phonendoscope. Based on the data obtained, a presumptive diagnosis is formed, which requires clarification after the acute condition has been relieved and the risk of developing acute respiratory disorders in the patient has been eliminated.
To diagnose diphtheria, material from the throat and respiratory tract is cultured for the presence of the causative agent of the disease - Corynebacterium diphtheria
.
How to recognize a dry cough in a child
children's dry cough cough attacks without sputum production. However, this criterion is not always sufficient to determine the type of cough. In young children, even with the presence of sputum in the bronchi, there may be a lack of secretion when coughing. This is due to insufficient development of the chest muscles and the viscous consistency of the mucus, which makes effective coughing difficult.
Therefore, it is important to take into account another sign: the source of the sound. A wet cough most often comes from deep in the chest, while a dry cough often forms in the larynx. At the same time, a cough coming from the chest can hardly be called dry even when sputum is not released - it is an unproductive cough - a type of wet cough.
Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the posterior wall of the larynx and pharynx leads to a sore feeling, irritation and associated cough. The irritated mucous membrane triggers the cough reflex, while the dry cough itself leads to even greater injury - the circle closes.
Unlike a wet cough, which brings relief, attacks of a dry cough can come one after another and give no result. With a dry cough, there is no phlegm, so its true cause is inflammation, irritation of the mucous membranes and dryness, which means that repeated attacks worsen the condition. Sometimes it is difficult for a child to stop a series of attacks; he may feel difficulty in breathing, a feeling of lack of air.
A dry cough in a child is always a reason to see a doctor. It exhausts, weakens the baby, and does not allow him to regain strength, especially if observed at night.
Comparison criterion 3 - cough timbre
Dry cough is called barking
, similar, as one might imagine, to the loud barking of a dog.
This situation is due to the fact that the sputum becomes viscous and is difficult or impossible to cough up. A hoarse or hoarse cough
with dull and whistling sounds indicates diseases such as laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis or pneumonia.
With laryngitis and tracheitis, the cough is accompanied by a hoarse voice, and with bronchitis and pneumonia - chest wheezing. A silent cough
may be associated with severe inflammation of the vocal cords. It sometimes occurs in patients with extreme malnutrition or heart failure.
Causes of dry cough in children
The main cause of dry cough is acute respiratory viral infections. They begin with this symptom, while children's dry cough persists for up to 3-4 days, after which it goes away or becomes productive. This manifestation is facilitated by viruses that provoke damage and swelling of the mucous membranes, irritation of the back wall of the larynx and throat.
A dry cough may be accompanied by the following diseases:
- laryngitis;
- tracheitis;
- laryngotracheitis;
- bronchitis
- sometimes chronic pharyngitis and adenoiditis.
A dry cough can be observed as one of the first symptoms of the disease, as well as at the final stage of recovery - already during the recovery period, as a residual effect. As a rule, it manifests itself in the form of isolated coughs. In some cases, residual cough may be present for up to 4–8 weeks after the cold.
There are also less common causes of dry cough in children:
- whooping cough;
- allergy;
- irritation of the respiratory tract by polluted air, dust, fumes, tobacco smoke, chemical vapors;
- diseases of the digestive system, thyroid gland, heart.
A pediatrician or pediatric pulmonologist can figure out the real reasons. In diagnosis, the accompanying symptoms, nature, frequency, and time of onset of dry cough are of particular importance.
What can you do before the doctor arrives?
- Calm your baby down and distract him with his favorite toy or book.
- Ventilate and humidify the room well. In the absence of a humidifier, you can hang wet laundry in the room or breathe (5-10 minutes) with the baby the steam from hot water drawn into the bath.
- Keep your baby's feet and chest warm.
- Give your child more to drink (milk, juices or hot tea).
- An allergic reaction can be treated with antihistamines.
All these measures are aimed at temporarily relieving symptoms. By removing the symptoms, you cannot get rid of the disease.
Adverse symptoms associated with cough
The treatment regimen for dry cough in children depends on the causes that caused it, so it is important to take into account the accompanying symptoms.
- If a dry cough is barking, hoarse, and occurs when inhaling cold air, the cause may lie in the development of laryngitis or laryngotracheitis. With chronic bronchitis, cough can only be observed in the morning.
- Bronchial asthma is sometimes characterized by the absence of expectorated sputum, accompanied by a suffocating cough and shortness of breath. Obstructive bronchitis also leads to difficulty breathing, whistling, and shortness of breath. Pale skin and increased sweating may occur.
- Dryness, sore throat, rawness, itching, pain when swallowing are common symptoms of pharyngitis.
- The most common accompaniment of a dry cough is elevated body temperature. In this case, we are most likely talking about ARVI or influenza.
It is important to understand that a dry cough in a child is already a reason to visit a doctor or call a specialist at home. However, there are accompanying symptoms that require immediate help: hemoptysis, elevated body temperature, difficulty breathing.
Symptoms of a cough in the throat
The symptoms of a cough in the throat boil down to the fact that a person is bothered by an obsessive, sometimes painful cough. The cough can be dry or wet. A dry cough involves the absence of phlegm, which makes it longer, unproductive and debilitating. A wet cough is characterized by coughing up mucus, causing it to occur intermittently. The cough may go away or weaken after drinking warm drinks or applying warm compresses to the throat.
Any cough may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as:
- Sore throat, redness;
- Sensation of a foreign body or lump in the throat;
- Chest pain;
- Nasal congestion, presence of mucous discharge;
- Increased body temperature;
- Headache;
- Deterioration in general health.
The above symptoms indicate that it is necessary to seek qualified help from an ENT doctor who can select an effective treatment.
Diagnosis of cough
Most often, cough is a symptom of respiratory diseases, the diagnosis of which is not difficult for a doctor. Based on the results of the examination, the specialist will determine the fact of ARVI.
A dry cough in a child without snot and fever requires more extensive diagnostics. A chest x-ray can help here, and if necessary, a specialist will refer you to a CT scan.
Fiberoptic bronchoscopy, or video bronchoscopy, is a method that can be of great importance in identifying complex and hidden causes of cough. It allows you to visually assess the patency of the bronchi, the condition of the mucous membranes, and also obtain tissue and sputum samples for further study in the laboratory.
Spirography is a method for studying the functioning of the respiratory system. It helps to assess the function of external respiration and get an idea of how fully the respiratory system works. Blood gas testing is necessary to diagnose respiratory failure.
Radiopulmonography is used to detect uneven ventilation, which is caused by narrowing of the small bronchi.
An ECG is needed to assess the function of the cardiovascular system, since sometimes heart disease is the cause of a dry cough in a child . Also, with pulmonary hypertension accompanied by a cough, there is a risk of developing heart complications.
Laboratory tests are carried out without fail. A general blood test helps the doctor draw conclusions about the activity of the inflammatory process. Since with a dry cough it is impossible to collect sputum for analysis, examination of the contents of the bronchi can only be carried out after bronchoscopy.
Survey
An episodic or constant barking cough is an indication for consultation with a pulmonologist or family doctor. A diagnostic search involves conducting instrumental methods of examining the respiratory system to determine the root cause of the symptom. Various laboratory tests help clarify the diagnosis and the leading etiological factor. The most valuable for diagnosing pathologies of the respiratory tract are:
- X-ray examination
. A survey chest x-ray is aimed at excluding damage to the bronchial tree and pulmonary parenchyma, which is also initially accompanied by a dry, sonorous cough. The method is informative for detecting signs of the tuberculosis process, assessing the condition of the heart and large vessels. - Spirography
. To study the capabilities of external respiration, the total lung volume, forced expiratory rate, and other indicators are measured. Deviation of FEV and Tiffno index values from the norm is observed in various types of shortness of breath. Spirography also helps differentiate organic diseases from functional ones. - Visual inspection
. Since the cough often becomes barking in diseases of the larynx, laryngoscopy is recommended - an instrumental examination of the mucous membrane using a special mirror. During the examination, you can notice hyperemia and swelling, which is most pronounced in the area of the vocal folds. Bronchoscopy is indicated to visualize the tracheobronchial tree. - Blood test
. Standard general and biochemical blood tests are performed to detect nonspecific signs of the inflammatory process. If an infectious origin of cough is suspected, serological reactions (RIF, ELISA) are performed to determine antibodies to specific pathogens.
Patients whose cough is accompanied by exudative diathesis or other manifestations of allergic reactions are prescribed allergy tests, and an extended immunogram is performed to measure the concentration of antibodies of different classes. According to indications, a CT scan of the chest is performed to more clearly visualize the morphological features of the thoracic organs. If sputum is released after coughing attacks, it is collected for microscopic and bacteriological examination.
Inhalations for barking cough should only be carried out as prescribed by a doctor.
Features of the treatment of dry cough in children
Treatment of dry cough in a child is carried out comprehensively. It is important to follow several recommendations that are relevant for any cause and case of dry cough:
- Schedule. The regime can be bed or semi-bed depending on the child’s condition, but it is important to ensure sufficient sleep and rest. It is advisable to go to bed and get up at the same time; if necessary, add a nap during the day.
- Walks. Fresh air is of great importance in recovery. If you are feeling well, it is important to take a walk every day.
- Ventilation and humidification of the air in the room.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Warm drinks moisturize the mucous membranes of the oropharynx, and a sufficient amount of liquid is necessary to remove toxins and change the consistency of sputum.
Drug treatment is aimed mainly at eliminating the causes of dry cough in children, as well as restoring the normal functioning of the respiratory system. Antibiotics are recommended only in cases with an established bacterial infection; they are not prescribed for ARVI.
the child’s dry cough is of an allergic nature, medications with antiallergic effects are prescribed.
Symptomatic therapy
To reduce the frequency of barking cough attacks, it is necessary to eliminate provoking factors as much as possible: regularly ventilate the room, carry out wet cleaning, and avoid strong chemical odors. To reduce subjective discomfort in the throat and moisturize the mucous membrane of the respiratory tract, inhalations with herbal solutions and antiseptics are recommended. It is important to provide plenty of warm drink; instead of tea, it is better to use herbal infusions of elecampane, thyme, and chamomile.
For debilitating cough, medications are used before diagnosis. Expectorants and mucolytics, which stimulate mucus production and cleanse the airways, have a good effect. In the case of an allergic nature of a barking cough, antihistamines are prescribed. Self-use of antitussives is prohibited due to possible side effects. In case of severe cough attacks, accompanied by shortness of breath and cyanosis, it is necessary to consult a doctor as soon as possible to determine the root cause of the symptom and select therapy.