- Types and types of aneurysms
- Symptoms of an aneurysm
- Causes of damage to the arteries of the brain
- Hemorrhagic stroke and other consequences
- Surgical removal
- Consequences of the operation
- Pregnancy and aneurysm
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of aneurysm
- Taking medications
- Folk remedies for aneurysm
- Recommendations for aneurysm
- Prevention
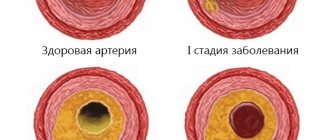
An aneurysm is a pathology of the arteries in which thinning and protrusion of the wall occurs in a certain area. The disease affects the blood vessels in the brain, through which blood circulates under high pressure. This situation poses a serious threat to the health and life of the patient due to deterioration of cerebral circulation and irreversible damage to nervous tissue. With an aneurysm, the vessel increases in size and begins to compress neighboring areas. This causes dysfunction of the central nervous system. A critical condition occurs if a vessel ruptures and cerebral hemorrhage occurs, which often leads to death.
Types and types of aneurysms
The classification of aneurysms is based on their shape and size, causes of occurrence, and number of chambers:
- According to the shape of the protrusion of the walls, they are bag-shaped and spindle-shaped. The first type is more common.
- Depending on the size of the pathology, they are divided into four groups. If the aneurysm is smaller than three millimeters, it is called milliary. A normal size protrusion reaches 15 mm. Large aneurysms grow up to 25 mm; those from 25 mm or more are called giant.
- The pathology can be congenital or acquired as a result of illness or injury.
- Depending on the number of aneurysms, they can be single or multiple. The protrusion may consist of one or more chambers.
Classification of the disease
Experts distinguish between two types of disease: arterial and arteriovenous aneurysm, of which arterial aneurysm is the most dangerous. Aneurysms are classified according to these parameters:
1. By configuration:
- saccular;
- spindle-shaped.
2. By location:
- anterior cerebral artery;
- internal carotid artery;
- vertebrobasilar system;
- middle cerebral artery;
- multiple localizations.
3. By size of education:
- gigantic size;
- large;
- medium size;
- small;
- miliary.
Symptoms of an aneurysm
At the initial stages, the pathology may not manifest itself in any way. We are talking about the so-called asymptomatic aneurysm. As it increases, a characteristic neurological picture appears:
- headache;
- loss of sensation in the lower extremities;
- violation of fine motor skills, diction;
- numbness of the face, weakening of the facial muscles, loss of control over facial expressions.
Impaired cerebral circulation changes character and behavior. The person becomes restless and emotionally unstable.
When an aneurysm ruptures, a severe headache occurs, which is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, and pallor. The patient experiences convulsions and develops photophobia. Due to impaired cerebral circulation, a person loses orientation and falls into an unconscious state. If there are signs of aneurysm rupture, you should urgently call an ambulance and take the victim to the neurological department.
Symptoms of cardiac aneurysms
The cause of the development of cardiac aneurysms is most often the thinning of the muscle wall due to a heart attack. Having a heart attack weakens the tissue, which often causes the damaged area to bulge. The left ventricle of the heart and the interventricular septum are most susceptible to such pathologies. Symptoms in this case can manifest themselves in the form of pressing pain in the heart area, tingling sensations, and shortness of breath. Heart rhythm disturbances and signs of chronic coronary insufficiency may also be observed. Rupture of an acute aneurysm most often leads to death. In this case, the patient experiences severe pallor, loss of consciousness, coldness of the extremities and hoarse breathing. You can learn about treatment methods for cardiac aneurysms here.
Causes of damage to the arteries of the brain
An aneurysm can develop on any vessels. According to statistics, protrusion is most often diagnosed in the arteries at the base of the skull. This is caused by physiological characteristics: in this area the blood pressure is higher than in the rest, so the risk of damage to the vessel walls increases. If one layer is damaged, then the wall protrudes in this area under the pressure of the blood flow.
All aneurysms can be divided into congenital and acquired. Congenital causes are caused by abnormalities in the development of blood vessels, genetic diseases in which connective tissue weakens. Against the background of a burdened heredity, pathology can develop even at a young age, although the disease is very rare in children.
Most aneurysms are acquired. They arise as a result of traumatic brain injuries and brain tumors. The high-risk group includes patients with hypertension, atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, and people who engage in weightlifting or intense physical labor. The likelihood of an aneurysm increases if a person regularly exposes himself to stress or leads an unhealthy lifestyle.
Protrusion of the artery wall can develop against the background of an inflammatory process - aortitis. It can be caused by a streptococcal or fungal infection. The disease can develop against the background of tuberculosis, syphilis, or after unsuccessful surgery.
Hemorrhagic stroke and other consequences
An aneurysm is a dangerous rupture of the vessel wall, which is subject to constant stress due to blood flow. When a rupture occurs, a hemorrhagic stroke occurs. It is a very serious medical and social problem. Due to hemorrhage, a hematoma is formed, which compresses the brain tissue and puts pressure on neighboring vessels. In the absence of treatment, irreversible changes occur in the affected structures within a few hours.
A hemorrhagic stroke can be suspected by severe headaches, sudden problems with speech and coordination of movements. The person feels disoriented and goes into a state of shock. In this case, you need to urgently contact a medical facility. The pathology requires emergency surgery and long-term treatment. Patients who have suffered a hemorrhagic stroke require long-term rehabilitation.
A complicated aneurysm, which is accompanied by thrombosis, is extremely dangerous. Due to a blood clot, blood circulation in the vessel slows down or stops completely. Another common complication is aneurysm dissection. In this case, a lumen is formed in the inner lining of the vessel through which blood passes.
The presence of an aneurysm significantly impairs the quality of life, especially if the pathology affects an important part of the brain. The larger the protrusion, the stronger the disease manifests itself. Due to neurological symptoms, people are forced to give up their usual activities and constantly take medications for headaches. The patient’s well-being worsens in the presence of cardiovascular diseases, increased stress, and bad habits.
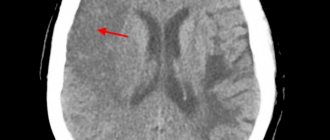
Interpretation of MRI of arterial aneurysm
The result of magnetic resonance imaging is a series of layer-by-layer scans of the area under study. In the process of deciphering images, the radiologist evaluates vascular parameters and identifies deviations from the norm. The data obtained are entered into the research protocol. The attending physician interprets the results, makes a diagnosis, and develops patient management tactics.
A sign of arterial dilatation on standard tomograms is the absence of a signal from rapid blood flow. A cerebral aneurysm appears on MRI as a round formation with a hypointense or heterogeneous signal. Layering of the structure sometimes indicates the formation of a blood clot within the expansion. Due to the vortex blood flow, the MR signal from the center of the sac may be inhomogeneous. A characteristic sign of an aneurysm is the location of the hypointense area in the areas where the arteries pass, somewhat to the side.
On MR angiography images, pathological bulging is defined as dilatation of the vessel, usually near the bifurcation. Large aneurysms are identified by the presence of a mass effect. With slow mural blood flow, visualization of even giant protrusions on MR angiography can be difficult. Thrombosed aneurysms are better visible on T1WI images when performing magnetic resonance imaging of the brain.
Examination of intracranial vessels may reveal signs of recent damage to the aneurysm wall. Up to 2 days from the moment of perforation, the localization of hemorrhages can be determined on scans, since the blood gives a hyperintense signal. The location of the violation of the integrity of the vascular wall is looked for using MR angiography using the phase-contrast technique (if CT is contraindicated).
Surgical removal
After diagnosing and assessing the patient’s condition, the doctor selects a treatment regimen. If the aneurysm is large and there is an increased risk of rupture, surgery to remove the protrusion is recommended. The procedure is performed by a neurosurgeon. It can be planned or emergency if a rupture occurs.
During surgery, the aneurysm is coagulated. It can also be excised or bandaged. The method of eliminating the pathology is selected based on the diagnostic results, depending on the characteristics of the clinical case. The purpose of the operation is to exclude the damaged area of the vessel from the bloodstream. Minimally invasive techniques are used during the procedure.
Treatment
The most effective treatment for cerebral aneurysm
- operation. Only in this case does the patient have a chance to live. The point of the operation is to remove the affected vessel so that its integrity is restored.
Types of surgical interventions:
- Vessel clipping. Performed after craniotomy.
- Endovascular surgery. Trephination is not needed. The procedure is performed through the carotid or femoral artery. The course of the surgical intervention must be carried out under the control of additional imaging methods - CT or MRI.
Today, endovascular techniques are the most popular because they allow manipulation with minimal trauma. The procedure is performed without general anesthesia; the risks with this procedure are much lower. Rehabilitation of patients after surgery occurs in a short time. The patient's chances of life increase significantly. Now you know what an aneurysm is
.
treatment of aneurysm
Take care of your health and contact specialists in a timely manner!
Consequences of the operation
After the operation, the patient spends from several days to several weeks in the hospital. Rehabilitation consists of taking medications, physiotherapeutic procedures, massage, and therapeutic exercises. Patients with severe neurological disorders are advised to undergo sanatorium-resort treatment, which includes comprehensive rehabilitation programs. They help to fully restore your ability to work.
Complications after surgery include spasms and vascular obstruction. They are more likely to affect older patients and people whose bodies are severely weakened by chronic diseases.
Forecast for life
The prognosis of the disease depends on the location of the vascular protrusion and its size. The initial condition of the patient also has a huge impact. The mortality rate in case of rupture of a cerebral aneurysm exceeds 30-50%. Surviving patients sometimes retain the consequences of the condition in the form of movement restrictions, cognitive impairment and a significant decrease in quality of life. Mortality after recurrent hemorrhage exceeds 70%.
Therefore, it is so important to carry out surgical treatment in time, turning to a qualified neurosurgeon. The operation is postponed only if there are certain medical indications.
Successful neurosurgical operations are carried out at the Burdenko Research Institute. Patients with signs of an aneurysm or suspected aneurysm are admitted here. At the Institute of Neurosurgery, it is possible to carry out comprehensive diagnostics using the latest technology and further treatment of identified diseases.
Pregnancy and aneurysm
Women who are planning to conceive need to be aware of the threat aneurysms pose. During pregnancy, the risks of hemorrhagic stroke for physiological reasons increase. In the second and third trimester, the volume of circulating blood increases and blood pressure rises. The situation may worsen if the patient has concomitant diseases: hypertension, diabetes.
According to statistics, the frequency of hemorrhagic strokes in pregnant women with an aneurysm is 2-5 cases per 10,000. The disease is accompanied by depression of consciousness, profound motor disorders, and respiratory failure. Neurological disorders pose a threat to the life of the expectant mother and child. Due to respiratory failure, the supply of oxygen to organs and tissues is disrupted, and fetal hypoxia develops. Lack of oxygen is a dangerous condition that leads to pathologies of intrauterine development.
A pregnant woman with a ruptured aneurysm requires urgent neurosurgical treatment and oxygen support.
Women of reproductive age who have been diagnosed with a bulging artery wall should consult a neurologist in advance and undergo treatment.
Prevention
Prevention is aimed at treating myocardial infarction, which causes the development of an aneurysm. It is important to take medications as prescribed by your doctor and not to violate the dosage regimen. Visit a cardiologist in a timely manner and do not ignore routine examinations.
Additionally, patients should:
- stick to a diet;
- control blood pressure;
- eliminate psycho-emotional stress;
- do exercises and physical warm-up;
- control weight;
- quit smoking.
Following simple rules of treatment and prevention will help improve your health and prevent relapse and progression of the disease. You can contact our specialist for advice and undergo examination in the cardiology department. Only comprehensive measures can help in the fight against the disease.
Diagnostics
If you suspect an aneurysm, you should make an appointment with a neurologist. The patient is prescribed hardware diagnostics of cerebral vessels. The following procedures are the most informative:
- Computed tomography, which is also indicated for protrusion rupture. A CT image will reveal where the rupture occurred and assess the extent of tissue damage.
- Vascular angiography is the most popular method that doctors use most often. Such diagnostics helps to identify the location and size of the aneurysm.
- MRI and X-ray are a universal way to assess the condition of blood vessels.
- General and biochemical blood tests and urine tests are prescribed to identify changes in the body.
It should be remembered that with small sizes the protrusion may not create discomfort and may not manifest itself in any way. Many clinical cases are identified during preventive examinations and routine medical examinations. This confirms that such activities should not be neglected.
Types of aneurysm by location
Cerebral artery aneurysm
The most common form of this disease. It is characterized by local dilation of the arteries of the brain. In the case of hemorrhage due to a rupture of an aneurysm, a sharp unbearable headache, loss of consciousness, nausea, vomiting, and convulsions are most often noted. In half of the cases, patients die; many of those who survive risk remaining disabled. However, only about 25 percent of patients with an aneurysm experience a headache similar to a migraine before the critical moment. This disease is often misdiagnosed as a brain tumor.
Aortic aneurysm
This type of aneurysm can develop in different areas of this large blood vessel. According to research results, aortic aneurysm is found in 7 percent of those who die for another reason. In the later stages of the disease, patients complain of pressing pain in one or another part of the body.
There are aneurysms of the thoracic aorta and aneurysms of the aortic arch, the peculiarity of which is that it can develop even within 20 years after a chest injury. There is also an abdominal aortic aneurysm, which is often asymptomatic. However, very thin patients may feel throbbing and pain when they place their hand on their abdomen.
Aneurysm of peripheral vessels (blood vessels of the extremities)
Source: tirachardz / ru.freepik.com
Aneurysms of peripheral vessels are less dangerous in comparison with other types. Most often they develop in the vessels of the lower extremities - the popliteal and femoral arteries. Aneurysms of the vessels of the upper extremities are much less common. The clinical course is often asymptomatic, but sometimes patients note coldness and pallor of the limb, pulsation and pain when palpated.
Such aneurysms are subject to rupture much less frequently, but are often a source of thromboembolic complications.
Heart aneurysm
Characterized by a saccular protrusion of the heart wall. Acquired cardiac aneurysm occurs at the site of a myocardial infarction and is detected in 5-20 percent of patients who have suffered it. Over time, a scar is found at the site of the lesion, which gradually protrudes. An aneurysm can develop either immediately after a heart attack or several months after.
When any form of aneurysm is detected, surgical intervention is most often required. The essence of the operation is to exclude the aneurysm from the bloodstream to prevent life-threatening hemorrhages - endovascularly, by clipping, excision of the damaged section of the vessel and replacing it with a plastic prosthesis or a fragment of a blood vessel from another part of the body.
It is not always possible to prevent the development of an aneurysm, but you can reduce your risk of developing one by quitting smoking and reducing high blood pressure. To do this you need:
- Eat a healthy diet - in particular, eat more fruits and vegetables and less salt;
- drink alcohol in moderation or avoid it altogether;
- maintain a healthy weight;
- devote time to regular physical activity - approximately 150-200 minutes of moderate activity per week;
- reduce caffeine consumption to approximately 400 mg per day, which is approximately 2-3 cups of 250 ml.
Treatment of aneurysm
Aneurysm is treated conservatively and surgically. Therapy is selected by the doctor based on the clinical case. The neurologist assesses the condition of the arteries and the degree of their damage. Based on the data obtained, conclusions can be drawn about the possibility or impossibility of using conservative methods. If the protrusion is significant, which is accompanied by severe neurological symptoms, and there is a high risk of aneurysm rupture, the patient is recommended to undergo elective surgery. This is a radical method that helps prevent possible complications. Urgent surgical treatment is required if rupture cannot be avoided and the patient suffers a hemorrhagic stroke.
Taking medications
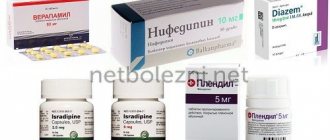
The main method of conservative treatment of an aneurysm is taking medications. The patient is prescribed a complex of drugs:
- drugs to lower cholesterol and prevent atherosclerosis;
- painkillers;
- anticonvulsants;
- drugs to normalize blood pressure: amlodipine, atenolol, anaprilin, enalapril (consultation with a doctor is required, there are contraindications)
Drug therapy is also indicated in the postoperative period. It eliminates neurological symptoms and pain, and reduces the likelihood of disease relapse.
Folk remedies for aneurysm
Herbal medicines are used to treat diseases that contribute to the development of aneurysm. Folk remedies cannot cure an existing pathology, but they will reduce the risk of its occurrence.
First of all, we are talking about herbal medicines with anti-inflammatory and hypotensive effects. They prevent the development of inflammation and help normalize blood pressure. To improve blood circulation and normalize blood pressure, decoctions and infusions of hawthorn and viburnum berries are used.
For the prevention and treatment of blood vessels, herbal preparations with celandine and dill are used. It should be understood that herbal remedies in the treatment of aneurysm are an auxiliary method. Their effectiveness increases if a person leads a healthy lifestyle.
Symptoms of peripheral vascular aneurysms
When aneurysmal enlargements occur in peripheral vessels, the culprit may be atherosclerosis of the lower extremities, vascular erosion, congenital diseases, or trauma. Signs of damage to the blood vessels of the legs are the characteristic symptoms of ischemia of the lower extremities: pain in the legs, pallor and coldness of the skin, pulsation of the vessel, and the possible presence of a protruding formation. Symptoms of an aneurysm in the renal artery are rare urination, weakness, and lower back pain. Aneurysmal formation of the splenic artery rarely manifests itself with any symptoms other than pain in the left hypochondrium.
Timely diagnosis and treatment of an aneurysm allows you to avoid thrombosis and hemorrhage, which are the consequences of this disease. If you observe any of the above symptoms, be sure to consult a doctor!