In Russia, there are more than 4 million people diagnosed with osteoarthritis (OA). At the same time, the prevalence of undiagnosed disease can reach 15 million. The incidence of OA is steadily growing, with about 600 thousand new cases of this pathology registered in Russia every year. According to forecasts, by 2022 the number of people suffering from osteoarthritis may increase to 57%, and disability of varying degrees may reach 66%.
With this disease, destruction and disruption of cartilage restoration processes occur, as well as involvement in the pathological process of the bone located under the cartilage and the tissues surrounding the joint: joint capsule, synovial membrane, ligamentous-muscular apparatus.
With age, cartilage tissue loses special substances (type 4 chondroitin sulfates), which are able to retain moisture and maintain the firmness and elasticity of the joint. These processes, in addition to age, are affected by metabolic disorders, excess weight, genetic predisposition, injuries, professional or sports overload, and a violation of the physiological axis of the joints, congenital or acquired. These changes occur both in the peripheral joints, which are subject to maximum load, and in the spine. With osteochondrosis, the intervertebral discs (“spacers” between the vertebrae) lose up to 50% of chondroitin sulfate. Flexibility in the joints and spine disappears, movements in them become limited and are accompanied by crunching, morning and starting stiffness, pain of a mechanical nature (under load), with prolonged stay in one position are disturbing. As the disease progresses, in addition to cartilage, other joint structures are also involved, which leads to local inflammation and severe pain (therefore, one of the names of the disease is osteoarthritis). With increased load on the spine (for example, working in a summer cottage, carrying heavy loads, etc.), cracks and destruction appear in the intervertebral discs. The result is an attack of acute pain, pinching of nerves and vessels along the spine, and the formation of intervertebral hernias.
What is hyaluronic acid for joints?
Hyaluronate is the main component of joint fluid. It gives it the necessary viscosity, thanks to which the cartilage receives the components necessary for metabolism and maintains functionality. Hyaluronic acid is also part of cartilage, and if it is deficient, the formation of chondrocytes (cartilage cells) stops. It is this component that gives cartilage its elasticity and ability to absorb shock. When it is deficient, it becomes brittle, cracks, and arthrosis develops.
The formation and breakdown of hyaluronic acid occurs non-stop in the body. However, with age or against the background of functional disorders, metabolic mechanisms slow down - a deficiency of hyaluronate or defects in its structure is formed. Molecules are still formed, but are no longer able to bind and retain water. Scientists call this process aging of the body.
The worse hyaluronic acid retains moisture, the faster the body ages
Why is the molecular weight of hyaluronic acid important?
The substance is a polymer, a long chain of 10-20 thousand organic and inorganic elements. It can be low- or high-molecular - with a molecular weight from 5 thousand to 20 million Da.
High molecular weight acid, which is a very long chain, penetrates the cell worse than low molecular weight acid. “Hyaluron”, which is part of the synovial fluid, has a molecular weight of 2-3 million Da - the optimal value in order to penetrate between chondrocytes and at the same time maintain lubricity.
Low molecular weight acid penetrates the cartilage, delivering nutrients and fluid to it. High molecular weight - does not penetrate inside, but forms a lubricating layer that performs a shock-absorbing function. Hyaluronate-based injections are done to eliminate friction of cartilage and restore viscosity and volume of synovial fluid.
The synthetic drug Noltrex, whose molecular weight is 10 million Da, copes with this no worse, and even more effectively. The substance adheres to the cartilaginous surfaces without penetrating inside, and effectively performs the function of synovial fluid.
The hyaluronic acid molecule holds up to 300-500 water molecules
Biological value
The biological role of Hyaluronic acid cannot be underestimated. Thanks to hyaluronic acid, the intercellular substance is formed in which the cells of the body function. It is in this environment that their division occurs, where nutrients enter the cells and their waste products are excreted.
About 50% of hyaluronate is found in the skin. Hyaluronic acid is involved in the synthesis of collagen and elastin, maintaining the youth and beauty of the skin. This substance has such a quality as hydrophilicity, thanks to this ability it binds moisture, which prevents its excessive loss by the body.
In addition to beauty, Hyaluronic acid is involved in the healing process of wounds, helps strengthen the immune system, protects tissues from premature aging, blocking the negative effects of free radicals.
If at a young age you notice dry skin, this is the main sign of an acute deficiency of hyaluronic acid. Appropriate measures must be taken as soon as possible.
Benefits for joints and ligaments
Hyaluronic acid is a real salvation for joints and ligaments; being an integral part of synovial fluid, it improves the sliding process of cartilage surfaces.
Hyaluronate is also one of the most important nutritional and regenerative components of hyaline cartilage, a type of connective tissue, promoting its mobility. Thanks to its ability to retain moisture, it maintains its balance in cartilage tissues, thereby increasing their elasticity and shock-absorbing ability.
Causes of deficiency
Hyaluronic acid deficiency leads to dry and sagging skin and premature aging of the body. But this is just the tip of the iceberg. Also, the lack of substance affects the quality of life. With a lack of hyaluronate, joint diseases are observed, the cause of which is a violation of the trophism of cartilage tissue, as well as an increase in the viscosity of the synovial fluid, which leads to friction of the joints during movement and entails their destruction.
Hyaluronic acid deficiency can be caused by a number of reasons:
- bad habits (alcohol and tobacco);
- deficiency of rutin, vitamin C and other essential microelements;
- excessive exposure to sunlight without the protection of special creams;
- age-related changes in the body;
- nervous tension, stress;
- systematic lack of sleep;
- negative impact of the environment.
Currently, medicine has not invented drugs that could help increase the production of this polysaccharide by the body, but to compensate for its deficiency, hyaluronic acid tablets have been invented.
How is hyaluronic acid obtained?
In the body, natural hyaluronic acid is produced by special cells. They are found in joints, the joint capsule, and other organs - the substance is universal and has the same structure everywhere. It is biologically compatible and does not cause an immune response, even if obtained from the outside, with rare exceptions.
Hyaluronic acid is extracted in one of two ways:
- Physico-chemical.
The source is biomass - cockscombs, ligaments, cartilage, vitreous body of cattle, umbilical cords. They are treated with alkalis and acids, cleaned and dried. Finished preparations contain residues of animal protein, which can cause allergies.
Many vegetarians refuse to use animal-derived hyaluronic acid.
- Biotechnological.
Wheat substrates are used as raw materials. The bacteria housed in them multiply and synthesize hyaluronic acid, which is separated, cleaned and dried. It is this variety that is considered safer and more effective today.
Hyaluronic acid itself is chemically unstable, so it is used for injection in the form of sodium hyaluronate - sodium salt.
What is the difference between native and modified hyaluronic acid
Native – most closely matches the one that is formed in the body. However, it quickly breaks down under the action of hyaluronidase. This form is used in dietary supplements, which must be taken for a long time before the substance accumulates in the body.
Modified - undergoes additional processing. Its molecules are held together with vitamins, amino acids and other microelements, which makes it difficult to recognize by hyaluronidase and increases the period of cleavage, and therefore the duration of action.
It is this modified acid that is used in orthopedics to treat arthrosis or osteoarthritis. After injection into the joint, it remains there for several months, performing the functions of synovial fluid. The synthetic drug Noltrex works on a similar principle, but takes longer, since the enzyme hyaluronidase does not recognize a substance of artificial origin at all. The effect of intra-articular injections of Noltrex lasts for a year, one and a half, and sometimes two years.
Noltrex is not recognized by hyaluronidase, so it lasts longer than hyaluronic acid
Hyaluronic acid is included in many synovial fluid prostheses, for example in “Hyalur CS”:
Recovery after manipulation
The patient can return home immediately after being injected with hyaluronic acid. But in order to maximize the effect of the procedure, it is recommended to reduce physical activity at least in the first few days after leaving the clinic. Otherwise, there is a risk that the injected hyaluronic acid will not be absorbed as needed.
There are practically no side effects, provided there is no individual intolerance. Preparations containing hyaluronic acid are usually safe and well absorbed. Short-term side effects are usually related to the piercing itself. Patients complain of slight pain at the injection site and a slight accumulation of joint fluid.
Hyaluronic acid can be called a universal substance. Preparations containing polysaccharides are used for both beauty and health.
Is it worth drinking hyaluronic acid in the form of tablets and capsules?
Not all people with joint problems are ready to undergo a course of injections, especially if they have a history of polyosteoarthritis, which means that injections must be given to each joint. In such cases, many resort to tablets or capsules containing hyaluronic acid. How justified is this and does it make sense?
In order for hyaluronate to be absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and enter the blood, it must be low molecular weight. Studies have shown that most of the molecules passing through the esophagus are absorbed and have a positive effect on the body. The body independently distributes “hyaluronic acid” and directs it to the needs of internal organs, joints and connective tissue. It will not be possible to restore the health of skin, nails or hair in this way: the body does not “consider” appearance problems to be the most important.
It takes years to take hyaluronic acid tablets to achieve the effect.
Of course, tablets and capsules are not enough to treat osteoarthritis, just as one remedy is not enough. Sometimes joints continue to deteriorate even after a course of intra-articular injections of Noltrex, if a person does not follow the basic rules of work and rest, does not receive vitamin C from food, for example, or has an extra 20 kg of weight. Listen to the advice of experienced orthopedists, choose reliable therapeutic methods - and may your joints be healthy!
How to treat sore joints?
With osteoarthritis, it is extremely important to reduce the load on the joints, which is achieved by using various devices. You should wear shoes with low, wide heels and soft elastic soles, which helps absorb the shock that spreads along the leg when walking and injures the cartilage. Shoes should be wide enough and soft on top. If the knee joints are affected, it is recommended to wear knee pads, which fix the joints, reduce their instability, and slow down the progression of the disease. In addition, to reduce the load, it is recommended to walk with a stick, which reduces the load on the hip joint by almost 50%. The cane should be held in the hand opposite the affected joint. In case of bilateral severe damage to the hip or knee joints, walking with the help of Canadian-type crutches is recommended. If you have flat feet, it is recommended to constantly wear special shoes (at home and on the street) with arch supports (insoles that support the arch of the foot and reduce the load on the joint), and in certain cases, custom-made insoles.
Physiotherapy (magnetic therapy, ultrasound, laser therapy) is prescribed only by a physiotherapist if there are no contraindications for these treatment methods. Acupuncture helps relax tense muscles around the joint and helps reduce pain. Massage relieves painful muscle spasms and improves blood circulation in the joint, but this method is used only outside of exacerbation, and it is not the joint itself that is massaged, but the tissues surrounding it. Among other physiotherapeutic methods, electrophoresis using gels containing anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, nimulide, hydrocortisone) has worked well.
Drug treatment
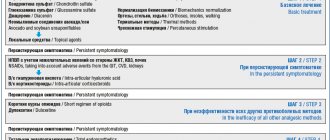
For osteoarthritis, fast-acting drugs (analgesics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - NSAIDs) are used to reduce pain and inflammation, symptomatic slow-acting drugs (chondroprotectors) that can slow the progression of the disease, as well as local hyaluronic acid preparations (hyalgan, hialubrix, etc.), which help reduce pain and improve joint mobility for a long period.
For moderate joint pain, it is better to start treatment with the so-called simple analgesic - paracetamol, since it relatively rarely causes side effects. If its effectiveness is insufficient, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ibuprofen, etc.) are prescribed. However, one should remember the possibility of a negative effect of these drugs on the gastrointestinal mucosa: ulcers, bleeding. A higher incidence of complications is possible in females over 65 years of age with chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract. In recent years, new representatives of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (meloxicam, Celebrex, Airtal, artrosilene, etc.) have been created, which have sufficient effectiveness but less pronounced side effects. However, the question of prescribing anti-inflammatory drugs and the duration of their use should be decided by the doctor. The general principles of using NSAIDs for OA are to use the minimum effective dose, take no more than one NSAID at a time, discontinue the drug if there is no pain, and evaluate the effectiveness of treatment after 2-4 weeks from the start of use. The use of local forms in the form of a gel and spray based on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is recommended for patients with limited joint damage, when it is impossible to take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs orally, when osteoarthritis is combined with concomitant diseases for which many other drugs are taken, which requires taking into account drug interactions. It should be remembered that the local use of these drugs is effective only when applied to the joints 3–4 times, and the course of use should not exceed 10–14 days.
Quite often, with OA of the knee joints, severe inflammation develops in the joint, which is manifested by swelling, hyperthermia, the presence of effusion, increased pain and morning stiffness. In these cases, if NSAIDs and local use of NSAID gels are ineffective, intra-articular steroid administration is indicated, which is prescribed by a rheumatologist. The number of intra-articular injections into the same joint during the year should not be more than two. Prescribing intra-articular or periarticular steroid injections as a “course” of treatment is unacceptable!
In recent years, drugs have been created that are highly effective and have a lower risk of side effects. These are symptomatic, slow-acting drugs (piascledine, alflutop, arthra, teraflex, dona, etc.), which, on the one hand, have a pronounced effect on pain and the functional state of joints, like NSAIDs, and on the other hand, have chondroprotective properties, i.e. slow down the progression of osteoarthritis. Our country has accumulated extensive experience in the use of these drugs. Their distinctive feature is the later onset of the effect, usually 4–8–12 weeks from the start of treatment, and its rather long persistence—for 2–3 months after cessation of treatment. It should be noted that the structure-modifying effect of these drugs (i.e., slowing the progression of OA) is observed 2–3 years after the start of treatment.