Infections of the genitourinary system are among the most common diseases that are widely encountered in both outpatient and in-hospital medical practice. Their share in the structure of nosocomial infections accounts for more than 40%. There is a certain pattern in the fact that urogenital infections occur much more often in women throughout their lives than in men.
The most common and socially significant infections of the genitourinary organs include gonococcal, chlamydial, mycoureaplasma and trichomonas invasions. The total number of people annually suffering from urogenital infections in the world is hundreds of millions [1, 3, 4, 7, 8].
The difficulty of clinical and laboratory diagnosis of bacterial infection lies in the presence of 2-3 or more pathogenic pathogens at the same time.
The inflammatory process during urogenital infections is a complex vascular-mesenchymal tissue response to the damaging effect of a pathological agent. This reaction is aimed at destroying the infectious agent and restoring damaged tissue. The inflammatory process refers to a protective-adaptive reaction, the outcome of which can very often lead to unfavorable conditions. Thus, urogenital infections can cause ectopic pregnancy, infertility, miscarriage, labor anomalies, placental pathology, antiphospholipid syndrome, autoimmune pathology, anti-CG syndrome, infection of the newborn, stillbirth, pelvic pain, dyspareunia, menstrual irregularities, adhesions , after surgical inflammatory complications, ectopia of the cervix, endometriosis, polyps of the cervical canal and endometrium, uterine fibroids and an increased risk of HIV infection [2, 3, 4, 11].
The most common and serious consequences of urogenital infection are infertility and ectopic pregnancy. Infertility with chlamydia occurs in 50%, with gonococcus - in 30-40%, with ureaplasma - in 30% or more, with trichomonas invasion - in 45-50% of patients.
Urogenital infections are predominantly transmitted sexually. Non-sexual transmission of urogenital infections is facilitated by contamination of hands, toiletries, towels, bed linen, shower arms (bidets), toilet seats, etc. with infectious discharge.
Trichomoniasis is the most common disease of the genitourinary system and ranks first among diseases that are predominantly sexually transmitted. About 200 million cases of trichomoniasis are reported annually around the world. The disease is not seasonal and affects all segments of the population [2, 3, 7, 11].
The incidence of trichomoniasis among women in the general population is 5-10%, among pregnant women - 12.6%, among those seeking vaginal discharge - 18-50%, among prisoners and prostitutes - 50-60%.
The incidence rate of men in the general population has not been determined, as it ranges from 0 to 58%, while at the same time, among those who consulted a dermatovenerologist, it is more than 6% and rises to 10% when modern diagnostic methods are used. In the United States, approximately 3 million new cases of trichomoniasis occur in women each year. Among registered patients, the ratio of men to women is 1: 4 [1, 4, 8, 10].
Trichomoniasis is a protozoal invasion that has pathogenetic, clinical and microecological features. The etiological agent of trichomoniasis is Trichomonas vaginalis, a protozoan parasite with a rather complex structure and peculiar metabolism. According to taxonomy, the unicellular protozoan T. vaginalis belongs to the kingdom of higher procysts Protozoa, the class Flagella, family Trichomonadidae, genus Trichomonas. To date, more than 50 species of Trichomonas are known, most of which are commensals of the digestive canal of mammals and birds. T. vaginalis has five flagella and an intracellular supporting structure that consists of a costa and an axostyle. The axostyle is a very important element of the support system of the protozoan. Passing along the body, the axostyle divides the parasite into two unequal parts, going beyond its limits, it forms a spicule. It is believed that this structure contributes to the primary attachment of the parasite to epithelial cells and the release of “cell uncoupling factor” (CRF) into the external environment. CRF is considered as a means by which the parasite destroys epithelial cells and penetrates the intercellular space [1, 5, 10, 11].
T. vaginalis affects the urethra, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, bladder and renal pelvis in men, the vestibule of the vagina and the vagina itself, ovarian appendages, fallopian tubes, and uterus. With trichomoniasis, an ascending urinary tract infection often develops.
It has been established that urogenital trichomoniasis is most often a multifocal infection, in which the pathogen can affect both the organs of the genitourinary system and other organs and systems. The presence of specific receptors for estradiol and dehydrotestosterone in Trichomonas during chronic infection can serve as factors for the development of hyperplastic processes in hormonally dependent tissues.
A significant proportion of patients (from 25 to 50%) have latent or erased forms without any complaints, so trichomonas are often detected during preventive examinations or the active involvement of sexual partners with trichomoniasis in the examination. In 50% of these women, clinical signs may appear 6 months after infection.
Trichomonas carriage occurs in 40-50% of patients with mixed urogenital infection. The age of women with trichomoniasis and mixed infection is 18-59 years.
From the point of view of the morphology of trichomonas, the number of atypical forms has increased. These forms have low mobility and have an amoeboid or spherical shape, which makes bacterioscopic diagnosis difficult, and therefore causes underdiagnosis of trichomoniasis.
One of the most important cofactors of Trichomonas vaginalis is its ability to enhance HIV transmission. According to many foreign authors, Trichomonas vaginalis can influence the epidemiology of HIV. The spread of HIV in trichomoniasis is largely facilitated by damage to the mucous membranes (hemorrhagic punctate), allowing the virus to penetrate the bloodstream.
Trichomonas has a general biological phenomenon of capturing (phagocytosis) and reserving various pathogenic and opportunistic microorganisms, which can cause the persistence of various pathogens and lead to the development of relapses of STIs associated with incomplete phagocytosis of microorganisms and the inaccessibility of antibiotics inside Trichomonas vaginalis.
The absence of pathognomonic clinical manifestations of urogenital trichomoniasis, its frequent course with minimal clinical manifestations makes laboratory research methods the basis for diagnosing the disease. For a higher percentage of detection of Trichomonas invasion, it is necessary to use several laboratory diagnostic methods aimed at identifying the pathogenic agent and antibodies to the pathogen produced by the macroorganism. To diagnose urogenital trichomoniasis, it is necessary to use microscopic, cultural, molecular biological and serological studies [1, 3, 4, 11].
The quality of effective and timely therapy for trichomoniasis largely influences the spread, course and prognosis of the disease. The success of treatment depends on the correct individual selection of the drug, its pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.
Treatment failure is often associated with non-compliance with the recommended treatment regimen or reinfection.
Some cases of unsuccessful therapy for patients with trichomoniasis are explained by the production of proteolytic enzymes and enzymes that inhibit antiprotozoal drugs by trichomonas; inactivation of etiotropic drugs by the accompanying bacterial microbiota cannot be ruled out. Although modern treatment regimens for urogenital trichomoniasis with 5-nitroimidazole isomers are quite effective, the effectiveness reaches 76 and 90%, often even long-term use of trichomonacid drugs does not allow achieving clinical and microbiological cure. Strains of urogenital Trichomonas isolated from different patients may have different sensitivity to anti-Trichomonas drugs. A number of authors have established an increase in the resistance of Trichomonas to metronidazole in those individuals who were treated with it several times. The emergence of relative resistance to metronidazole is associated with taking insufficient doses of the drug [4, 5, 11].
Resistance of Trichomonas vaginalis to treatment may be a consequence of the transformation of aerobic metabolism into anaerobic one. In complex clinical cases in which standard treatment regimens are ineffective, cure can be achieved with higher doses of metronidazole.
Trichomonas with a high level of resistance to metronidazole drugs are difficult to eradicate. In such circumstances, effective treatment requires a very high toxic level of drug concentration, often given simultaneously orally and intravaginally or intravenously.
It is obvious that new protistocidal agents are needed to eradicate resistant strains of Trichomonas. Despite the many antimicrobial drugs, their number is constantly increasing. The development of new drugs is based on expanding the antimicrobial spectrum, increasing activity against certain microorganisms, searching for compounds with high activity against problematic pathogens, improving pharmacokinetic properties, and reducing toxicity.
A promising modern drug for the treatment of diseases caused by Trichomonas vaginalis is secnidazole, an antiprotozoal and antibacterial drug from the nitroimidazole group. Secnidazole is a derivative of 5-nitroimidazole, the latest generation drug has high activity against Trichomonas and other protozoa. Penetrating into the cell of a microorganism, secnidazole is activated as a result of the reduction of the 5-nitro group and interacts with cellular DNA, destroying its structure and leading to the death of the protozoa.
In Ukraine, secnidazole is registered under the subname “Secnidox” [9].
The purpose of the work is to study the effectiveness, tolerability and compliance of Secnidox in the complex treatment of patients with urogenital trichomoniasis (UT).
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Pharmacodynamics
An antiprotozoal drug with an antibacterial effect , belonging to the group of nitroimidazoles, has a bactericidal and amoebicidal effect . Seknidoksos is active especially against trichomonas , dysenteric amoeba , and intestinal lamblia .
Penetrating into the cell of a microorganism, Secnidazole interacts with DNA, destroying its helical structure, inhibiting nucleotide synthesis and cell death. The drug has a teturam-like effect (sensitization to alcohol) and increases the sensitivity of tumors to radiation.
Pharmacokinetics
After oral administration, the drug is completely and quickly absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract, overcomes the blood-brain barrier and passes into breast milk. Cmax in the blood is reached within 4 hours. Bioavailability is about 80%. Secnidoxos is metabolized in the liver. It is excreted by the kidneys within 72 hours.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics.
Secnidox is an antiprotozoal drug from the nitroimidazoles group with an antibacterial effect. secnidox is characterized by a bactericidal (against gram-positive and gram-negative anaerobic bacteria) and amoebicidal (intra- and extraintestinal) effect. Seknidox is especially active against trichomonas vaginalis, entamoeba histolytica, giardia lamblia. penetrating deep into the cell of a microorganism, secnidazole is activated as a result of the reduction of the 5-nitro group, due to which it interacts with cellular DNA. there is a violation of its spiral-like structure and destruction of the threads, inhibition of nucleotide synthesis and cell death. Pharmacokinetics. After oral administration, Seknidox is quickly and completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. Bioavailability is about 80%. Secnidazole penetrates the blood-brain barrier and is excreted into breast milk. T½ of secnidazole is about 25 hours, which makes it possible to simplify the drug dosage regimen, making it more convenient for patients.
Seknidox, instructions for use (Method and dosage)
Secnidox tablets are taken before meals with water.
Doses for adults for various diseases:
Bacterial vaginosis , trichomonas vaginitis and urethritis , acute symptomatic amebiasis - 2 tablets once; asymptomatic amebiasis , including cystic and focal forms: 2 tablets once daily for three days. For liver amebiasis - 1.5 tablets daily for five days. Important: you should not drink alcohol while taking Secnidox!
Doses for children over 12 years of age:
For intestinal amebiasis - asymptomatic amebiasis : 30 mg/kg of child’s weight for three days; acute symptomatic amebiasis and giardiasis : once, at a dose of 30 mg/kg of the child’s weight. For amoebiasis, liver and - separate or single dose daily for 5 days at a dose of 30 mg/kg body weight.
special instructions
The drug should not be prescribed to patients with a history of blood dyscrasia. During treatment with the drug, reversible neutropenia may occur. the number of leukocytes is restored after cessation of treatment. While using the drug, you should avoid drinking alcohol.
Use during pregnancy or breastfeeding. The drug is not used during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
The ability to influence reaction speed when driving vehicles and working with other mechanisms. Does not affect.
Interaction
When taken simultaneously, the drug enhances the effect of Coumarin (indirect anticoagulants).
Simultaneous use of the drug with Disulfiram may provoke paranoid reactions (nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, headache).
When used simultaneously with lithium preparations, increases its concentration in the blood.
Secnidox is not recommended for use with muscle relaxants ( vecuronium bromide ).
Side effects
The drug is easily tolerated, but side effects may occur:
general disorders: general weakness;
from the digestive system: indigestion, nausea, pain in the stomach, metallic taste in the mouth, glossitis, stomatitis.
Less common:
from the hematopoietic system: moderate reversible leukopenia, reversible neutropenia;
allergic reactions: hypersensitivity reactions, including hyperemia, rash, urticaria.
Seknidox price, where to buy
The price of Secnidox No. 2 tablets in the Moscow pharmacy chain is on average 663 rubles per pack. You can purchase the drug without any problems in most pharmacies in Moscow and other Russian cities.
- Online pharmacies in RussiaRussia
- Online pharmacies in UkraineUkraine
- Online pharmacies in KazakhstanKazakhstan
ZdravCity
- Secnidox tablets p.p.o.
1g 2pcs "Bailey-Creat Laboratory", France RUB 815 order
Pharmacy Dialogue
- Seknidox (tab.p.pl/vol. 1g No. 2) Bailey-Creat Laboratory
RUR 521 order
show more
Pharmacy24
- Secnidox 1 g N2 tablets Lab.Bailly-Creat France
143 UAH.order
PaniPharmacy
- Seknidox tablets Seknidox tab 1g No. 2 France, Lab. Bailly-Creat
174 UAH order
show more
Note!
Description of the drug Secnidox table. p/o 1g No. 2 on this page is a simplified author’s version of the apteka911 website, created on the basis of the instructions for use.
Before purchasing or using the drug, you should consult your doctor and read the manufacturer's original instructions (attached to each package of the drug). Information about the drug is provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as a guide to self-medication. Only a doctor can decide to prescribe the drug, as well as determine the dose and methods of its use.
conclusions
The drug "Secnidox" (2 tablets of 1.0 g, film-coated, in a blister produced by World Medicine (France)) has shown high effectiveness in the treatment of patients with urogenital trichomoniasis.
Secnidox was well tolerated by patients; the drug did not cause serious adverse reactions or changes in laboratory parameters of blood and urine.
Considering its high efficiency and good tolerability, the drug "Secnidox" can be recommended for wider use in the complex treatment of patients with urogenital trichomoniasis according to treatment regimens depending on the duration of the pathological process.
Results and discussion
Clinical manifestations of Trichomonas infection in the observed men were asymptomatic, with moderate swelling and hyperemia of the urethral sponges and scanty urethral discharge.
In 14 observed patients, a burning sensation on the skin of the glans penis was noted after sexual intercourse. In 20 women examined, the inflammatory process was acute, and clinical manifestations were characterized by copious yellow-green discharge from the genital tract with an unpleasant odor. The prevailing subjective symptoms of trichomoniasis were itching, dysuria, dyspareunia, and in 5 patients - pain in the lower abdomen. During physical examination, hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane were determined, in 14 cases - a small amount of erosive elements in the perineal area. In 13 observed women, the specific inflammatory process was chronic and characterized by moderate hyperemia of the mucous membrane, itching in the external genital area, dyspareunia, while the vaginal discharge was scanty and mucous in nature.
During a colposcopic examination, in 5 patients, pinpoint hemorrhages were detected on the mucous membrane of the vagina and the vaginal part of the cervix. At the same time, the lesions were iodine-negative when stained with 3% Lugol's solution.
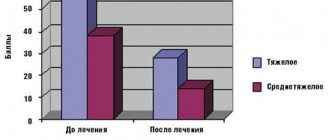
The effectiveness of the use of Secnidox in the complex treatment of patients with UT was indicated by a decrease in the amount of discharge and a change in their nature, as well as the disappearance of subjective sensations.
Of the side effects, taking Seknidox was accompanied by dyspeptic disorders in 3 patients, and a metallic taste in 2 patients, however, these phenomena were insignificantly pronounced and did not require drug withdrawal or additional treatment, and disappeared without a trace after the end of the course of etiotropic therapy. Secnidazole was well tolerated in all patients.
An additional feature of Seknidox is its high bioavailability, which reaches more than 80%, which makes it possible to obtain a high concentration of the active substance in the tissues, and the long half-life (more than 25 hours) makes it possible to simplify the drug dosage regimen as much as possible. Thus, in terms of effectiveness/convenience of use, secnidazole is superior to other drugs of the 5-nitro imidazole group (for example, metronidazole) used to treat trichomoniasis of the genitourinary system.
The immediate and long-term results of the effectiveness of complex treatment of patients with UT using the etiotropic drug “Seknidox” showed complete clinical and microbiological cure in 65 (97.01%) patients.
All patients indicated high compliance with the drug - a one-time dose of the etiotropic drug.
Thus, the results of the study indicate the feasibility and adequacy of using Secnidox for the complex treatment of patients with urogenital trichomoniasis.
This drug is significantly more effective than metronidazole drugs. The high efficiency, safety and compliance of secnidazole is the basis for recommending its wider use as an etiotropic drug in the complex treatment of patients with urogenital trichomoniasis.
Materials and methods
67 patients with UT aged from 18 to 57 years (women - 33, men - 34) were observed. Fresh UT was diagnosed in 21 (31.3%), and chronic UT was diagnosed in 46 (68.7%) of the observed patients. The diagnosis of UT was established on the basis of patient complaints, anamnestic data, clinical manifestations and the detection of T. vaginalis in the studied biological materials. To identify T. vaginalis, bacterioscopic, bacteriological, immunological and molecular biological research methods were used. All patients underwent general clinical examinations before and after treatment.
Complex therapy included the use of Secnidox as an etiotropic drug, as well as hepatoprotectors, adaptogens and local treatment adequate to the topical diagnosis. "Secnidox" was prescribed to patients with fresh UT 2.0 g once, and to patients with chronic UT - 2.0 g on the first, third and fifth days of treatment.
Secnidazole is an antimicrobial and antiprotozoal agent and is a synthetic derivative of 5-nitroimidazole. The drug is active against obligate anaerobic bacteria (spore- and non-spore-forming), causative agents of certain protozoal infections: Trichomonas vaginalis, Giardia lamblia, Entamoeba histolytica. Secnidazole is not active against aerobic bacteria. Secnidazole has a high degree of absorption and bioavailability. The bioavailability of secnidazole is 80% and is metabolized in the liver. The maximum concentration of the drug is achieved 4 hours after a single oral dose (2.0 g). Secnidazole is excreted primarily by the kidneys. Within 72 hours, 16% of the drug dose taken is detected. The drug is also excreted in breast milk and penetrates the placental barrier, which must be taken into account when prescribing the drug to pregnant and lactating women.
Indications for the use of Secnidox are: trichomonas urethritis and vaginitis, bacterial vaginosis, intestinal amebiasis, liver amebiasis, giardiasis. "Seknidox" is taken orally: for adults the dose is 2 g, for children - 30 mg/kg/in one or several doses. The course of treatment is from 1 to 5 days.
Undesirable side effects of the drug manifest themselves in the form of dyspeptic symptoms (nausea, pain in the epigastric region), metallic taste in the mouth, glossitis, stomatitis, moderate reversible leukopenia, allergic reactions. Very rarely, dizziness, loss of coordination, ataxia, paresthesia, and polyneuropathy may occur.
Experimental studies did not reveal the teratogenic effect of secnidazole.
During the period of use of secnidazole, it is necessary to avoid drinking alcohol. When secnidazole is taken simultaneously with anticoagulants (coumarin or indanedione derivatives), the effect of the latter may be enhanced, so the prothrombin time should be periodically monitored and, if necessary, the dose of anticoagulants should be adjusted. Concomitant use of secnidazole with disulfiram may be accompanied by the development of paranoid reactions and psychosis; with ethanol - effects similar to those of disulfiram are possible (abdominal cramps, nausea, vomiting, headache, sudden rush of blood to the face). It is not recommended to combine with non-depolarizing muscle relaxants (vecuronium bromide). When taken simultaneously with lithium drugs, secnidazole increases its concentration in plasma.
Contraindications for the use of secnidazole are organic lesions of the central nervous system, pathological changes in the peripheral blood picture (including history), pregnancy, lactation (breastfeeding), hypersensitivity to imidazole derivatives.
The effectiveness of treatment was assessed based on the positive dynamics of the pathological process, subsequently the absence of clinical manifestations of urogenital trichomoniasis, as well as analysis of the results of a set of laboratory research methods.
The tolerability of the drugs was judged by the patients’ subjective feelings and objective data during a medical examination. The frequency and severity of adverse events were assessed throughout the entire period of clinical observation.
Statistical processing of the obtained data was carried out using parametric methods using computer statistical programs [6].
Bibliography
- Vasiliev M.M. Modern problems of diagnosis and treatment of gonorrheal and trichomonas infections // Vestn. dermatol. and Venerol. - 1998. - No. 4. - P. 39-42.
- Dermatovenerology: Textbook / Ed. V.P. Fedotova, A.D. Dyudyuna, V.I. Stepanenko. Publishing house 2.rus. - Dnepropetrovsk - Kyiv: publishing house "Svidler A.L.", 2011. - 652 p.
- Dudun A.D. Clinical manifestations and overcoming illnesses that are transmitted by state methods // Medical Perspectives. - 2000. - T. 5, No. 5. - P. 103-105.
- Kisina V.I. Urogenital trichomoniasis: problems and ways to solve them // STIs.- 2001.- No. 6.- P. 14-17.
- Compendium 2003—medicinal products // Ed. V.N. Kovalenko, A.P. Viktorova.— K.: Morion, 2003.— 1388 p.
- Lapach S.N., Chubenko A.V., Babich P.N. Statistical methods in biomedical research using Exel. - K.: Morion, 2000. - 320 p.
- Bowden FJ, Garnett GP Trichomonas vaginalis epidemiology: parameters and analyzing a model of treatment interventions // Sex Transm Inf. - 2000. - Vol. 76.— P. 248—256.
- Bowden FJ, Garnett GP Why is Trichomonas vaginalis ignored? // Sex Transm Inf. - 1999. - Vol. 75 (6).—P. 372—374.
- Gillis JC Secnidazole. A review of its antimicrobial activity, pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic use in the management of protozoal infections and bacterial vaginosis / JC Gillis, LR Wiseman // Drugs. - 1996. - Vol. 51 (4).—P. 621-638.
- Guaschino S., De Santo D., De Seta F. New perspective in antibiotic prophylaxis for obstetric and gynecological surgery // J. Hosp. Inf.—2002.—Vol. 50 (suppl. A).—S13—S16.
- Sackett DL, Rosenberg MC, Gray YAM et al. Evidence based medicine: what it is and what it isn’t // BMJ.— 1996.— Vol. 13.— S. 312 (7023).— P. 71-72.
HELL. Dyudyun1, N.M. Polion1, I.O. Babyuk2, V.V. Gorbuntsov1, D.G. Bashmakov1 1 DU “Dnipropetrovsk Medical Academy of the Ministry of Health of Ukraine” 2 DU “Donetsk Institute of Advanced and Advanced Surgery named after V.K. Gusakova"