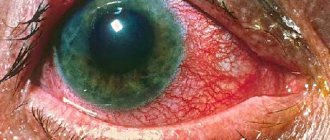
Photo
In the photo you can clearly see what the eye looks like when the blood vessels in it have burst. Given in varying degrees:
Causes of rupture of blood vessels in the eye
There are many reasons that can provoke rupture of the ocular vessels. In general, they can be divided into two large groups - external causes and internal disorders in the body.
Internal disturbances in the functioning of the body
These include:
- hypertension . Increased pressure often causes rupture of the eye vessels. In addition, sometimes, in addition to bleeding in the eye, nosebleeds may occur. This problem requires careful diagnosis and treatment;
- diabetes . The disease affects both small capillaries and fairly large vessels. In this case, hemorrhages can occur quite often;
- blood diseases . Sometimes hemorrhage may indicate diseases such as leukemia or lymphoma;
- lack of vitamins . Important vitamins for the eye vessels are A and C;
- intraocular pressure. In this case, blood circulation is disrupted, and the load on the vessels increases several times. As a result, their walls cannot withstand, and hemorrhage occurs;
- vascular pathologies . These can be both hereditary and congenital pathologies;
- traumatic brain injuries . Hemorrhage may indicate a serious injury requiring immediate medical attention;
- increase in body temperature.
External factors
Among the external factors we can highlight:
- eye strain;
- lack of sleep or severe stress;
- vigorous physical activity, such as lifting weights;
- alcohol abuse;
- wearing contact lenses;
- getting a foreign object into the eye;
- rubbing the eyes with your hands.
Non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis
“Due to the high probability of an unfavorable course of NAFLD, especially in combination with other manifestations of metabolic syndrome, all patients, regardless of the severity of the disease, require dynamic monitoring and treatment”
Chief physician of the State Center "Expert", professor of PSPbSMU named after. acad. I.P. Pavlova Mehdiev S.N.
Treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, NAFLD) is carried out using examination and treatment methods developed by the head physician of the center, Professor Mehdiyev Sabir Nasredinovich , based on Russian and foreign clinical recommendations, as well as our own practical and research experience.
Treatment begins with an examination tailored to the individual characteristics and health status of the patient, which will allow:
- Assess the degree of inflammation in the liver and the risks of developing health-threatening liver diseases (cirrhosis and liver cancer).
- Identify lipid metabolism disorders (fat metabolism) and other metabolic disorders in the body.
- Check for risk of developing cardiovascular diseases.
- To provide a reliable assessment of the condition of the liver tissue without invasive intervention.
Based on the results of the examination, an individual treatment program , which will include:
- dietary recommendations and physical activity regimen;
- drug therapy to help the body return to a healthy state.
Treatment is carried out under the supervision of a gastroenterologist; a second appointment will be required in 1-2 months. Repeated ultrasound and elastography of the liver to assess the success of treatment are carried out no earlier than six months later.
Treatment options for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the absence of complications is carried out on an outpatient basis. To date, there is no single drug to treat this disease, so treatment includes a range of measures, both with and without the use of drug therapy.
The main non-drug measures are proper nutrition, weight loss and sufficient physical activity. Losing body weight if you are overweight should be done gradually, no more than 0.5 - 1 kg per week. Rapid weight loss can cause deterioration and progression of steatohepatitis. It is advisable to select the diet individually, but its main provisions are to reduce the consumption of animal fats, simple carbohydrates and sweets.
Weight loss is the most important condition for success. A 10-14% reduction in weight significantly reduces the amount of fat in liver cells. If you fail to lose at least 1 kg in the first month, you may need the help of a nutritionist who, together with you, will analyze and adjust your diet to speed up weight loss.
In the absence of success of conservative measures to reduce body weight, with a high degree of obesity (BMI >40 kg/m2) and the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, bariatric surgery is used to treat obesity.
Drug therapy for fatty hepatosis and steatohepatitis is considered as an additional means to measures to introduce a healthy lifestyle. Drugs are used to correct metabolic syndrome—lowering the level of triglycerides in the blood, increasing tissue sensitivity to insulin, as well as hepaprotectors and antioxidant agents.
If necessary, drug therapy is adjusted during treatment. The duration of medication depends on the stage of fatty hepatosis and health status, but a diet and daily routine with a sufficient amount of physical activity will need to be followed even after the end of treatment. If a person returns to an unhealthy diet after recovery and gains excess weight again, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease returns.
Non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis can be combined with diseases of the cardiovascular system and pancreas or be the cause of their development.
Treatment of patients with non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis and diseases of the cardiovascular system
Gastroenterologist and cardiologist Olga Aleksandrovna Mekhtieva specializes in the treatment of patients with hypertension and non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis . She uses rhythmocardiography techniques, which detect the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases at an early stage. Simultaneous treatment of hypertension and non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis will help restore liver health, normalize blood pressure and reduce the risks of developing liver and cardiovascular diseases.
Treatment of patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes
Patients with complex cases of a combination of non-alcoholic fatty hepatosis and pancreatitis or type 2 diabetes are managed by the chief physician of our center, Sabir Nasredinovich Mehdiev . Sabir Nasredinovich has been treating people with fatty hepatosis and its complications for more than 12 years, and is also engaged in scientific research on this topic.
For diseases of the pancreas and type 2 diabetes, a gastroenterologist and an endocrinologist in our center treat patients together.
As a result of treatment, the patient will receive
- Stopping the process of fat accumulation in the liver, reducing the rate of disease development.
- Reducing liver fat.
- Reducing the risk of developing steatohepatitis, cirrhosis and liver cancer.
- Reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.
- Improving the quality of life and increasing its duration.
Tips and tricks
In order to prevent fatty hepatosis, we recommend that people with a body mass index of more than 25 kg/m2, with abdominal obesity, and diabetes mellitus undergo an ultrasound of the liver and check biochemical blood parameters once a year.
You can learn more about non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and get tips on how to keep your liver healthy from the article by the chief physician of our center S.N. Mehdiyev. “Fat in the liver destroys the heart and leads to diabetes” in Komsomolskaya Pravda.
The diet can be based on a Mediterranean type of diet, including a large amount of fruits and vegetables. It is recommended to start physical activity with walking, swimming or cycling; the main thing is regularity of exercise; daily exercise improves the condition of the liver, even if you cannot lose weight right away.
On the reasons for the development of fatty hepatosis, a fragment of the speech of Professor Sabir Nasredinovich Mehdiev at the scientific and practical seminar “Features of the course of NAFLD in a patient with chronic biliary-dependent pancreatitis”
What to do and how to provide help when a vessel bursts?
Remember! The first step towards successful therapy is to visit an ophthalmologist to identify the root cause of the disease.
Until this point, you can apply a cooling compress to the eye . After making a diagnosis, the specialist selects the most effective treatment and a combination of the best drugs.
Drug treatment
If the hemorrhage is provoked by external factors and is not accompanied by pain , in this case there is no need to take medications.
To speed up the healing process, you can drip the following drops:
Disease prevention
To prevent the problem from developing it is necessary:
- organize good nutrition by including multivitamins and fresh vegetables and fruits in the diet. Vegetables that are dark green in color are especially beneficial for blood vessels;
- organize rest for your eyes . If you have to spend a long time in front of a computer monitor, then every 60 minutes you should do eye exercises or just look into the distance;
- reduce visits to steam rooms and baths . High temperature negatively affects the general condition of blood vessels;
- treat viral diseases in a timely manner , and also regularly visit a therapist and ophthalmologist;
- if you have endocrine or other disorders, take the medications prescribed to you ;
- avoid stress and strong emotions;
- maintain an optimal level of humidity in the room;
- do not refuse the help of an ophthalmologist if you have problems with your eyes.
General principles of treatment
We must remember! Despite the fact that full treatment can be prescribed exclusively by an ophthalmologist, general principles for treating the disease can be identified:
- First of all, measure your blood pressure . Perhaps this is the reason and you need to take the appropriate medications;
- if you have a fever due to the flu or other illness, be sure to take an antipyretic ;
- give your eyes a rest . To do this, avoid heavy exercise for at least 2-3 days and sleep as much as possible.
If your condition does not improve, and concomitant symptoms are added to the hemorrhage, consult a doctor immediately.
Legalon 140
Legalon 140 is a hepatoprotective drug. It interacts with free radicals - kinetically independent particles that have unpaired electrons, and neutralizes their aggressive effect on the body, thereby preventing cell destruction. In damaged liver cells, it activates the formation of protein compounds and phospholipids - complex lipids containing phosphoric acid. Transfers cell membranes to a stable state, prevents the consumption of transaminases, and accelerates the restoration of hepatocytes. Blocks the entry into the cell of substances that have a toxic effect on liver cells. Absorbed slowly in the gastrointestinal tract. In the liver it undergoes metabolic transformations through the formation of conjugates. The half-life averages 6 hours. Elimination from the body is carried out mainly through the gastrointestinal tract. It is not stored in the body. Legalon 140 is indicated for liver intoxication (due to chronic alcoholism, poisoning with halogenated hydrocarbons, heavy metal salts, pharmacological drugs) and for maintaining liver function as a prophylactic agent. The optimal time to take it is after a meal. Single dose – 1 capsule. The frequency of administration is three times a day (as a therapeutic agent), twice a day (as a preventative agent). The drug has a favorable safety profile, is non-toxic and is well tolerated by patients. In rare cases, allergic reactions and diarrhea are possible. The drug is not used in case of individual intolerance to the ingredients, as well as during pregnancy and lactation.
Milk thistle tincture has been used in folk medicine for liver diseases for a long time. Silymarin contained in this plant has confirmed its effectiveness in phytochemical, pharmacological, and histological studies. Based on this biologically active compound, they began to create medicines, the most active of which is Legalon, i.e.
contains twice the dose of silymarin than Silybor, Karsil, etc. Silymarin enters the liver, then, together with bile, into the intestines, after which it is again absorbed and ends up in the liver (enterohepatic circulation), and therefore its content in hepatocytes are one hundred times more than in the bloodstream. Liver cells are renewed every three weeks. Silymarin accelerates this process: it increases the stability of cell membranes, compacts them, and suppresses lipid peroxidation reactions. Legalon 140 is used for hepatitis of viral origin during the recovery period: as a rule, after 2-3 weeks of taking Legalon 140, patients note a decrease or elimination of intoxication phenomena. The drug is also indicated for patients with acute and chronic hepatitis: pharmacotherapy eliminates increased fatigue, discomfort in the right hypochondrium, and normalizes biochemical blood parameters. Legalon has a positive effect on the condition of patients suffering from cirrhosis of the liver: asthenic phenomena are eliminated, the activity of the digestive tract is normalized, the liver decreases in size, and the level of bilirubin in the plasma decreases. According to statistics, the survival rate of patients with liver cirrhosis who took Legalon for more than 40 months is about 60%, while in the control group it was 40%. The drug is effective for drug intoxication (poisoning with antibacterial and psychotropic drugs, paracetamol). The use of Legalon reduces recovery time after liver surgery. The drug shows good results in the treatment of liver diseases associated with excessive alcohol consumption. Cases of pharmacological interactions with other drugs have not been described in the medical literature; none have been noted in post-marketing studies of the drug, which allows the use of Legalon as part of combination drug therapy.