The beneficial properties of formic acid were known to the ancient Chinese. They used powder made from ants and mixed with egg and honey as a rejuvenating and healing agent.
Formic acid (methanoic acid) is an organic compound, a saturated monobasic substance found in fruits, plants, human sweat, and urine. In addition to ants, bees secrete acid when they sting.
It was believed that by consuming a few teaspoons of the composition per day, you could live much longer. Currently, a substance with bactericidal, anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties is used in medicine, cosmetology, and the food industry.
Chemical properties
Chemical formula of formic acid: HCOOH. This is one of the first representatives of single-base carbon compounds. The substance was first isolated in 1670 from the forest (red) ant. In the natural environment it is found in the venom of bees, nettles and needles of coniferous trees, secretions of jellyfish, and fruits.
Physical properties
Racemic formula of methanoic acid: CH2O2. The substance under normal conditions appears as a colorless liquid, which is highly soluble in glycerol , acetone , toluene and benzene . Molar mass = 46.02 grams per mole. Esters (ethyl ether and methyl ether) and methane salts are called formates .
Chemical properties
Based on the structural formula of Formic acid, conclusions can be drawn about its chemical properties. Formic acid is capable of exhibiting the properties of acids and some of the properties of aldehydes (reduction reactions).
When formic acid is oxidized, for example, with potassium permanganate , carbon dioxide is actively released. The substance is used as a preservative (code E236). Formic acid reacts with acetic acid (concentrated) and decomposes into carbon monoxide and ordinary water, releasing heat. The chemical compound reacts with sodium hydroxide . The substance does not interact with hydrochloric acid, silver, sodium sulfate, and so on.
Preparation of formic acid
The substance is formed as a by-product during the oxidation of butane and the production of acetic acid . It can also be obtained by hydrolysis of formamide and methyl formate (with excess water); during the hydration of CO in the presence of any alkali. A qualitative reaction for the detection of methanoic acid can be a reaction to algedigs . An ammonia solution of silver oxide and Cu(OH)2 can act as an oxidizing agent. The silver mirror reaction is used.
Applications of formic acid
The substance is used as an antibacterial agent and preservative when preparing feed for long-term storage; the product significantly slows down the processes of decay and rotting. The chemical compound is used in the process of dyeing wool; as an insecticide in beekeeping; during certain chemical reactions (acts as a solvent). In the food industry, the product is labeled E236. In medicine, acid is used in combination with hydrogen peroxide (“pervomur” or performic acid ) as an antiseptic to treat joint diseases.
Side effects and interactions with alcohol
When treating leather with preparations based on formic acid, be careful and follow the manufacturer's instructions. Since saturated solutions of 10% and higher cause a painful reaction, they are characterized by corrosive properties. Accidental ingestion of such a substance burns the mucous membrane of the esophagus and stomach, and contributes to the appearance of severe necrotic inflammation. The vapors of the chemical compound corrode the tissues of the respiratory organs and cause burns to the cornea of the eyes.
If a concentrated solution of formic acid gets on an area of skin, immediately treat the area with an alkaline solution (baking soda - sodium bicarbonate).
Methane compound and its formaldehyde are metabolites formed during the breakdown of methanol in the human body. These substances are toxic and damage the optic nerve, leading to partial or complete blindness. If methanol enters the body, in order to avoid the formation of formic acid under the influence of alcohol dehydrogenase, you should immediately drink a solution of ethyl alcohol. This way you can prevent a reaction from occurring, the consequence of which is loss of vision.
Ethyl alcohol is a kind of antidote that prevents formic acid poisoning.
Narrow-profile use
Certain industries cannot imagine their existence without formic acid. Its reaction, molecular density and unique acidity are unmatched. Therefore, some industries use the substance in several different ways. For example, in food production it is not only a good preservative. Possessing excellent disinfectant properties, it allows you to prepare containers for further use.
In medicine, the element is an excellent antiseptic. However, the range of its action is not limited to this. If the concentration is correct, it can be used in other ways:
- Improves metabolic processes on the surface of the skin.
- Has a positive effect on tissue nutrition.
- Dilates blood vessels so that medications begin to act faster and more effectively.
This opens up wide possibilities for treatment. The substance has proven itself well in eliminating bruises, fighting fungal diseases, and varicose veins. It is used to cleanse the surface of the skin and get rid of acne, so it is also in demand in cosmetology. There is only one contraindication - it should not be applied to open damage, since the product will quickly corrode sensitive tissue, even with minimal concentration.
How it is used in medicine
The remedy is most widely used in medicine due to its vasodilating, antirheumatic, antiarthritic and warming properties. It is recommended to use the acid externally in the form of an alcohol solution for joint pain, muscle pain, and neuralgia. Thanks to the ethanol in the product, an additional cooling and local anesthetic effect is created.
Formic acid is also included in ointments, balms, and gels, which have anti-inflammatory and regenerating properties. These drugs are used for diseases such as rheumatism, radiculitis, and varicose veins. The products promote rapid recovery from injuries, dislocations, sprains, and bruises. They reduce swelling and relieve pain.
Effect on the human body, daily requirement
The substance is not vital for the human body, so the daily requirement has not been established. It is important not to exceed the daily dose of acid, which is 3 mg. In those quantities in which the substance is present in products or added to them as a preservative, it is harmless to the body. High concentrations of acid may be harmful to health due to their corrosive effects. In the permitted dosage, the substance is a good stimulant for the body. But it does not act directly, but indirectly, that is, it provokes reactions that contribute to healing.
OH group substitution reactions
| Carboxylic acids are characterized by nucleophilic substitution reactions of the OH group with the formation of functional derivatives of carboxylic acids: esters, amides, anhydrides and acid halides. |
2.1. Formation of acid halides
Under the influence of mineral acid hydroxide halides (phosphorus penta- or trichloride), the OH group is replaced by a halogen.
| For example, acetic acid reacts with phosphorus pentachloride to form acetic acid chloride |
2.2. Interaction with ammonia
When ammonia reacts with carboxylic acids, ammonium salts are formed:
When heated, ammonium carbonate salts decompose into amide and water:
2.3. Esterification (formation of esters)
Carboxylic acids react with monohydric and polyhydric alcohols to form esters.
| For example, ethanol reacts with acetic acid to form ethyl acetate (ethyl acetate): |
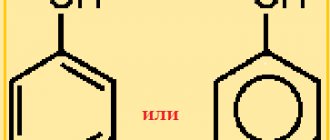
In this case, phenol does not enter into an esterification reaction with carboxylic acids. Phenol esters are obtained by indirect methods.
2.4. Preparation of anhydrides
With the help of phosphorus oxide (V), it is possible to dehydrate (that is, remove water from) a carboxylic acid - as a result, a carboxylic acid anhydride is formed.
| For example, when acetic acid is dehydrated by phosphorus oxide, acetic anhydride is formed |
Classification according to the structure of the hydrocarbon radical
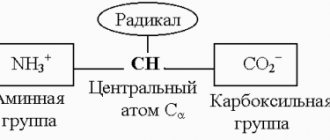
- Saturated carboxylic acids - the carboxyl group COOH is connected to a saturated radical. For example, ethanoic acid CH3–COOH.
- Unsaturated carboxylic acids - the carboxyl group COOH is connected to an unsaturated radical. For example, acrylic acid: CH2=CH–COOH.
- Aromatic acids - the carboxyl group COOH is connected to an unsaturated radical. For example, benzoic acid: C6H5COOH.
- Cyclic acids - the carboxyl group COOH is connected to a hydrocarbon ring. For example, cyclopropanecarboxylic acid: C3H5COOH.
General information
In nature, methanoic acid is found in the following products:
- strawberries;
- raspberries;
- apples;
- avocado;
- wild yam;
- papaya;
- nettle;
- quinoa;
- Chinese lychee;
- dragon fruit (pitaya).
In addition, the compound contains soft drinks, pickled/pickled vegetables, apple cider vinegar, bee secretions, and canned fruit/fish.
According to its organic structure, the substance (HCOOH) belongs to the group of fatty acids and exhibits a strong antimicrobial effect. Its danger depends on concentration. Based on the classification data of the European Union, it has been established that a liquid 10% solution upon contact with skin is irritating, 15% and higher is corrosive, and 100% leaves severe chemical burns and can cause anaphylactic shock.
To enhance the taste and increase the shelf life of canned products, livestock feed, formic acid and its salts are used in the food industry as additives (E236 - E238).
Despite the fact that the compound belongs to the group of protozoa, its role in human life cannot be underestimated. Methanoic acid is involved in metabolic processes. In animals, it ensures the synthesis of purine bases, methion, and nucleic acids.
Application
Sodium and potassium salts of higher fatty acids are effective in South Africa and are used as soaps. Sodium salts of fatty acids are usually solid (standard baby, bath or laundry soap), while potassium salts are liquid.
In the food industry, fatty acids are registered as food additives E570, as foam stabilizer, glazing agent and defoamer.
Distilled fatty acids are raw materials for the manufacture of toilet soap, rubber products, cotton fabrics, emulsifiers, cosmetics, etc. The liquid fraction of fatty acids containing at least 75% oleic acid (olein) is used in the production of chemical fibers. Technical stearic acid (stearin) is used in the manufacture of car wraps, photographic films, impact-resistant polystyrene, stabilizers for polymers, short-chain fatty acids (SCFA) are flavoring agents.
Recipes with formic acid for treating joints
The beneficial properties of formic acid can be used at home for joint ailments. Traditional medicine offers simple algorithms for use.
Pain relieving balm
For rheumatism and arthritis, you can use the following balm:
- 10 ml of formic alcohol is mixed with an equal amount of pepper tincture;
- add 10 g of Menovazin ointment;
- mix the components until a semi-liquid product with a pungent odor is obtained.
Homemade ointment is rubbed into the muscles and joints in small quantities and covered with a compress and a woolen scarf. You need to keep the compress for several hours, then the skin is gently washed with warm water.
Rubbing for osteochondrosis
Formic alcohol diluted with water has a good effect on joint ailments. Preparing the rub is very simple:
- 20 ml of pharmaceutical formic alcohol is poured into a small container;
- add 20 ml of clean water;
- stir the solution.
Gently rub the sore areas with the liquid or apply the product to a gauze bandage and apply it as a compress. In case of severe pain, treatment can be carried out up to three times a day.
Since formic alcohol dries the skin, after it it is recommended to moisturize the epidermis with a nourishing cream
Advice! The product is used for severe hematomas; it not only relieves pain, but also promotes the resorption of the bruise.
Acidity
Acids with a short hydrocarbon tail, such as formic and acetic acids, are completely miscible with water and dissociate to form fairly acidic solutions (pKa 3.77 and 4.76, respectively). Fatty acids with a longer tail do not differ significantly in acidity. For example, the pKa of nonanoic acid is 4.96. But as the tail length increases, the solubility of fatty acids in water decreases very quickly; as a result, the acids little change the pH of the solution. The pKa value for each acid is acquired only in the reactions in which these acids are capable of participating. Acids that are insoluble in water can be dissolved in warm ethanol, and titrated with sodium hydroxide solution, using phenolphthalein as an indicator, to a pale pink color. This analysis allows you to determine the fatty acid content in a portion of triglycerides after hydrolysis.
Structural isomerism
Saturated carboxylic acids are characterized by structural isomerism—carbon skeleton isomerism and interclass isomerism.
Structural isomers are compounds with the same composition that differ in the order of bonding of atoms in the molecule, i.e. the structure of molecules.
Carbon skeleton isomers are characteristic of carboxylic acids that contain at least four carbon atoms.
| For example. The formula C4H8O2 corresponds to butanoic and 2-methylpropanoic acid |
| Butanoic (butyric) acid | Isobutyric (2-methylpropanoic) acid |
Interclass isomers are substances of different classes with different structures, but the same composition. Carboxylic acids are isomers of esters. The general formula of both alcohols and ethers is CnH2nO2.
| For example. Interclass isomers with the general formula C2H4O2: acetic acid CH3–COOH and methyl formate H–COOCH3 |
| Acetic acid | Formic acid methyl ester |
| CH3–COOH | HCOOCH3 |
Many other polyfunctional compounds can also have the general formula CnH2nO2, for example: aldehyde alcohols, unsaturated diols, cyclic diesters, etc.
Hair removal with methanic acid
The compound is used not to get rid of unwanted hair, but to slow down hair growth after the hair removal procedure. Formic acid is used as a powerful antiseptic, only in diluted form. It is added to the oil base or purchased ready-made product immediately. After the first application to the shaved area, oil with formic acid increases the time between epilations, prolonging the effectiveness of the procedure, then with regular use it blocks the activity of the follicle. As a result, hair fiber is not formed and vegetation growth slows down.
Sequence of the procedure:
- remove hair from the problem area (using an epilator, wax, tweezers);
- rinse and dry the skin;
- Apply a thin layer of the product to this area for 15 minutes;
- wash off the oil composition with non-hot water;
- examine the skin area for the presence of an allergic reaction, discomfort (if itching, roughness, or redness occurs, applying oil with formic acid is strictly prohibited; if these phenomena are not observed, the procedure can be continued);
- reapply the product to the selected area for another 15 minutes, gradually the duration can be increased and increased to 4 hours;
- Wash off the oil thoroughly with soapy water.
Repeat this procedure as new hairs grow. To achieve a lasting result, be patient; you will need 7–10 epilations using ant oil. If there are damage to the skin (scratches, abrasions, wounds, cracks), you should refrain from the procedure until they are completely healed. In addition, for safety reasons, it is not recommended to apply the product during pregnancy and lactation.
For more delicate hair removal, 10 drops of ant oil should be added to baby cream; the resulting mixture can be applied daily to problem areas. In addition to slowing down hair growth, you will receive nourishment.
Does formic acid help against mosquitoes?
Formic acid is effective against blood-sucking insects - mosquitoes, midges and ticks. Before going into the forest, it is recommended to rub exposed areas of the body with a diluted pharmaceutical substance. The use of an alcohol solution of formic acid is indicated for existing bites. They can be treated with a product to relieve itching and irritation.
You can use mosquito repellent acid even if you don’t have a ready-made alcohol solution at hand. It is enough to find an anthill in the forest, lightly pat it with your hands, and then shake off the stuck insects and quickly rub your neck, face and other open areas with your palms. A natural remedy applied to the skin in minute quantities will help prevent mosquito bites.
To protect against mosquitoes, you can throw a cloth on the anthill, then clean it from insects and wipe the skin
Attention! Formic acid from an anthill is useful only in the absence of allergies. If the skin is prone to irritation, it is better to use mild products against blood-sucking insects.