Pharmacodynamics
From Orvirem®, which is a polymer compound of rimantadine with sodium alginate, the active substance is not released immediately, which causes a gradual release of rimantadine into the blood, its prolonged circulation in the body, a constant concentration of the drug in the blood, and a decrease in the toxic effect of rimantadine. Active against strains of influenza A virus. Has an antitoxic effect against ARVI and influenza caused by type B virus.
Orvirem® selectively interacts with the transmembrane viral protein M2, which functions as a proton pump. It prevents a decrease in the pH of endosomes, blocks the fusion of the virus shell with endosome membranes and thus prevents the transfer of viral genetic material into the cell cytoplasm. Inhibits the exit of viral particles from the cell, i.e. interrupts the transcription of the viral genome. Thus, it has a direct antiviral effect. Stabilizes the system of formation of sIgA (secretory immunoglobulin A), as the first level of protection, in the nasopharyngeal mucosa. Promotes the induction of interferon as a second level of protection. Orvirem® helps to normalize the subpopulation composition of immunocompetent cells and, accordingly, improves their functional activity and strengthens the cellular component of immunity. Has a detoxifying effect. Reduces the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-8 and TNF-α, reduces the antigenic load on immunocompetent cells, and quickly stops inflammatory reactions.
ARVI and immunity
According to the World Health Organization, ARVI ranks first in the structure of morbidity among young children. There are a large number of viruses that cause ARVI. These include: influenza viruses, parainfluenza, respiratory syncytial viruses, adenovirus, ECHO viruses, Coxsackie viruses, rhinoviruses, reoviruses, coronaviruses. The high incidence of ARVI is associated with unstable immunity in children after previous ARVI, as well as the high prevalence of these viruses. In unfavorable environmental conditions, acute respiratory viral infections predetermine even greater changes in immunity, especially in young children. This can lead to significant changes in the formation of the baby’s immunity, as well as contribute to the development of chronic diseases of various systems of the child’s body at an older age. Considering the high prevalence of ARVI, the issue of treating children with this pathology remains relevant. We will approach the treatment of colds from the point of view of modern protocols for the treatment of ARVI in children, which were developed by the Russian Union of Pediatricians. Before moving on to considering children's medications for colds and flu, it is necessary to understand the main manifestations of ARVI in children.
It is important to monitor the child’s condition and contact a pediatrician at the first symptoms of a cold.
Directions for use and doses
Inside, after meals, with water, according to the following schemes:
Treatment regimen
| Age | Reception days | |||
| 1st | 2nd | 3rd | 4th | |
| 1–3 years | 2 teaspoons 3 times | 2 teaspoons 2 times | 2 teaspoons 2 times | 2 teaspoons 1 time |
| 3–7 years | 3 teaspoons 3 times | 3 teaspoons 2 times | 3 teaspoons 2 times | 3 teaspoons 1 time |
| 7–14 years | 4 teaspoons 3 times | 4 teaspoons 2 times | 4 teaspoons 2 times | 4 teaspoons 1 time |
Prophylactic scheme
| Age | Daily dose | Reception scheme | Admission deadline |
| 1–3 years | 2 teaspoons | 1 per day | 10–15 days |
| 3–7 years | 3 teaspoons | 1 per day | 10–15 days |
| 7–14 years | 4 teaspoons | 1 per day | 10–15 days |
1 teaspoon = 5 ml.
The maximum daily dose is 5 mg of rimantadine per 1 kg of body weight.
Efficiency
The criteria for assessing the preventive effectiveness of the tested drug was its ability to prevent disease during an outbreak of influenza or ARVI of another etiology in a team.
Preventive effectiveness was also judged by its effect on viral shedding in hospitalized children with influenza and by the frequency of development of nosocomial acute respiratory infections among them.
As a result of the studies, preventive effectiveness: excellent - 71.6%, satisfactory - 11.9%, unsatisfactory - 16.5%. Systematic administration of the drug to prevent influenza reduces the incidence of the disease by 4–5 times in organized groups.
The criteria for assessing the therapeutic effectiveness of the drug were the duration of the main clinical symptoms of the disease (temperature reaction, intoxication and catarrhal symptoms in the nasopharynx), the speed of disappearance of pathological changes in laboratory parameters, if any developed at the onset of the disease, the development or absence of complications, as well as certain adverse reactions in response to his introduction.
When treating influenza and acute respiratory viral infections, it reduces the time of manifestation of the main symptoms of the disease by 3.1–3.6 days. The duration of the temperature reaction, symptoms of intoxication, as well as catarrhal symptoms in the nasopharynx are significantly reduced. Peripheral blood counts normalize faster. Indicators of specific and nonspecific immunity improve.
In case of late treatment and relapses of the disease, the use of Orvirem® reduces the duration of the disease by 2 times and prevents the development of complications.
The drug has proven its safety:
— there were no significant changes in the dynamics of peripheral blood parameters in children of the compared groups;
— no pathological changes were detected in the urine;
— there is no increase in allergic mood in both children with high and normal levels of IgE in the blood serum, which confirms clinical data on the absence of any allergic reactions to its administration.
Orvirem
Orvirem is an antiviral drug. Used for prevention and treatment at the initial stage of development of influenza A, incl. in pediatric practice, starting from 1 year. In 1964, an article about the American antiviral drug adamantadine, published in the Soviet magazine Abroad, prompted the Latvian chemist Janis Polis to create a domestic anti-influenza drug. This is how rimantadine was synthesized. However, the side effects of the drug did not allow its use in children under 12 years of age. This is how Orvirem was born - a complex that includes a matrix of low molecular weight sodium alginate polysaccharide and rimantadine fixed in it, where sodium alginate is not only an excipient, but also an adsorbent and a detoxifier rolled into one. Orvirem circulates in the blood longer and diffuses more slowly into tissues, which allows it to be used in lower dosages (unlike regular rimantadine, the drug can be taken once a day instead of 4) and minimize the risk of adverse reactions. Orvirem is a membranotropic drug: rimantadine penetrates the cell membrane of the virus, reaching the viral target protein, which in this case is the matrix (M2) protein of the influenza virus, which ensures the viability of the virus. By irreversibly binding and blocking this protein, rimantadine prevents the development of infection. In addition to this, Orvirem increases the production of the immune protein interferon. Thus, this drug is a modified rimantadine, which has higher antiviral activity and better tolerability compared to the traditional form of this drug. The preventive and therapeutic effectiveness of the drug has been studied in clinical studies.
The main criterion for the effectiveness of Orvirem in the prevention of influenza in the study was a reduction in incidence. The use of the drug among members of organized groups (children's educational institutions, hospitals, etc.) made it possible to reduce the incidence of influenza virus by 4–5 times. The therapeutic effectiveness of the drug was assessed by its ability to reduce the duration of symptoms of influenza (fever, catarrhal manifestations), bring laboratory parameters to physiological norms, and prevent complications of the disease. It was found that the use of Orvirem can reduce the duration of clinical symptoms of influenza by 3-3.5 days. There were no significant changes in peripheral blood parameters during the study. No pathological changes in urine were detected. To effectively prevent influenza, it is enough to use the drug for 2-3 days before the onset of symptoms of the disease. For effective treatment, Orvirem should be taken 6-7 hours after the onset of clinical signs of the disease. Orvirem should not be used for liver diseases in the acute phase, acute and chronic renal failure, persistent hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, individual intolerance to rimantadine and auxiliary components of the drug. Orvirem, when used together with antiepileptic drugs, reduces the effectiveness of the latter. In turn, the effectiveness of Orvirem itself will be reduced by drugs taken together with it that have sorbing, astringent and enveloping properties.
Orvirem syrup for children 2 mg/ml 100 ml fl.
pharmachologic effect
Orvirem is an antiviral drug. Rimantadine is an adamantane derivative; active against various strains of influenza A virus (especially type A2). Being a weak base, rimantadine acts by increasing the pH of endosomes, which have membrane vacuoles and surround viral particles after they enter the cell. Preventing acidification in these vacuoles blocks the fusion of the viral envelope with the endosome membrane, thereby preventing the transfer of viral genetic material into the cell cytoplasm. Rimantadine also inhibits the release of viral particles from the cell, i.e. interrupts transcription of the viral genome. Prescribing rimantadine for 2-3 days before and 6-7 hours after the onset of clinical manifestations of type A influenza reduces the incidence, severity of disease symptoms and the degree of serological response. Some therapeutic effect may also occur if rimantadine is administered within 18 hours of the onset of influenza symptoms.
Indications
— prevention and early treatment of influenza A in children over 1 year of age. Prevention with rimantadine can be effective during contact with sick people at home, during the spread of infection in closed groups and at a high risk of developing the disease during an influenza epidemic.
Contraindications
- acute liver diseases; — acute and chronic kidney diseases; - thyrotoxicosis; - pregnancy; - lactation period; - children under 1 year of age; - hypersensitivity to the components of the drug Orvirem. The drug should be prescribed with caution for epilepsy (including a history of epilepsy).
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
The drug Orvirem is contraindicated for use during pregnancy and lactation.
special instructions
While taking the drug Orvirem, exacerbation of chronic concomitant diseases is possible. With epilepsy, the risk of developing an epileptic seizure increases. Orvirem syrup contains 60% sucrose, which should be taken into account when prescribing the drug to patients with diabetes. Viruses resistant to the drug may emerge.
Compound
5 ml (1 teaspoon): - rimantadine hydrochloride 10 mg Excipients: sugar, sodium alginate, dye E122, purified water.
Directions for use and doses
For treatment, the drug Orvirem is taken orally (after meals), washed down with water, according to the following scheme: - for children from 1 year to 3 years - on the 1st day, 10 ml (2 teaspoons) of syrup (20 mg) 3 times a day . (daily dose - 60 mg); on days 2 and 3 - 10 ml 2 times a day. (daily dose - 40 mg), on the 4th day - 10 ml 1 time / day. (daily dose - 20 mg); - children from 3 to 7 years old - on the 1st day - 15 ml (3 teaspoons) of syrup (30 mg) 3 times a day. (daily dose - 90 mg); on days 2 and 3 - 3 teaspoons 2 times a day. (daily dose - 60 mg), on the 4th day - 3 teaspoons 1 time / day. (daily dose - 30 mg). For prophylaxis, the drug Orvirem is prescribed: - for children from 1 to 3 years old - 10 ml (2 teaspoons) of syrup (20 mg) 1 time / day; - children from 3 to 7 years old - 15 ml (3 teaspoons) of syrup (30 mg) 1 time / day. within 10-15 days depending on the source of infection. The daily dose of rimantadine should not exceed 5 mg/kg body weight.
Side effects
Orvirem is usually well tolerated. The following adverse reactions are sometimes observed. From the digestive system: nausea, vomiting, epigastric pain, flatulence, anorexia. From the central nervous system: headache, dizziness, insomnia, neurological reactions, impaired concentration. Other: hyperbilirubinemia, allergic reactions (skin rash, itching, urticaria), asthenia.
Drug interactions
When used together, Orvirem® reduces the effectiveness of antiepileptic drugs. When taken simultaneously, adsorbents, astringents and coating agents reduce the absorption of rimantadine. Medicines that acidify urine (acetazolamide, sodium bicarbonate) increase the effectiveness of rimantadine due to a decrease in its excretion by the kidneys. When used together, acetylsalicylic acid and paracetamol reduce the Cmax value of rimantadine by 11%. Cimetidine reduces the clearance of rimantadine by 18%.
Overdose
No cases of overdose have been identified to date.
Active substance
Rimantadine
Conditions for dispensing from pharmacies
On prescription
Dosage form
oral solution
Symptoms of ARVI in children
The child or the child’s parents may notice signs such as:
- Acute onset of the disease, accompanied by a rise in body temperature. Typically, body temperature fluctuates between 37.5-38.0 degrees. Usually the temperature reaction disappears after 2-3 days. A prolonged increase in temperature may indicate influenza or an adenovirus infection. Parents should remember that an increase in temperature over time and increased intoxication in the baby (weakness, lethargy, malaise) may indicate the addition of a bacterial infection. A repeated increase in the baby’s temperature after it has stopped may indicate the development of acute otitis media against the background of a prolonged runny nose.
- Nasal congestion, nasal discharge.
- Burning, pain, tingling, dry throat. Often, an accumulation of mucus, flowing down the back of the throat, can lead to a cough.
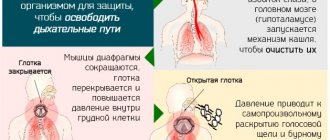
- Noise and pain in the ears, hearing loss, clicking. These symptoms develop when inflammation spreads to the auditory tubes.
- Infants become restless and have difficulty feeding and falling asleep.
- Hoarseness may occur.
- Redness of the eyes.
Signs of ARVI persist for 5-7 days, in some cases reaching 10-14 days.