Univit Kids instructions
Chewable lozenges in the shape of dinosaurs Dietary supplement
Ingredients: glucose syrup filler, sugar, gelatin filler, ascorbic acid (vitamin C), niacinamide (niacin), tocopherol acetate (vitamin E), pyridoxine hydrochloride (vitamin B6), retinol acetate (vitamin A), folic acid, D -biotin (biotin), cholecalciferol (vitamin D3), cyanocobalamin (vitamin B12), water, acidity regulator citric acid, glazing agent capol (vegetable oil, carnauba wax E903, beeswax E901), natural food coloring “red” ( from fruits and vegetables), natural raspberry flavor, natural orange flavor, natural orange food coloring (paprika emulsion).
% of recommended daily requirement
| Vitamins: | Contents in 1 lozenge (4 g) | Children 3-7 years old | Children 7-11 years old | Boys 11-14 years old | Girls 11-14 years old |
| Niacin (B3)* | 8 mg | 73 | 53 | 44 | 44 |
| Vitamin B12* | 1.25 mcg | 83 | 63 | 42 | 42 |
| Vitamin B6 * | 0.7 mg | 58 | 47 | 41 | 44 |
| Vitamin C * | 40 mg | 80 | 67 | 57 | 67 |
| Vitamin A * | 200 mcg | 40 | 29 | 20 | 25 |
| Vitamin D3* | 5 mcg | 50 | 50 | 50 | 50 |
| Vitamin E* | 6 mg | 86 | 60 | 50 | 50 |
| Biotin* | 15 mcg | 100 | 75 | 60 | 60 |
| Folic acid * | 100 mcg | 50 | 50 | 29 | 29 |
* In accordance with MP 2.3.1.2432-08 “Norms for physiological needs for energy and nutrients for various groups of the population of the Russian Federation.”
Nutritional value of 1 lozenge: carbohydrates – 2.9 g, including sugar – 2 g; protein – 0.32 g; fat – less than 0.01 g.
Energy value of 1 lozenge: 13.1 kcal / 55.6 kJ.
Area of application: Univit® Kids is recommended as a dietary supplement - an additional source of vitamins A, C, E, D, group B (B3, B6, B12, folic acid and biotin).
The activity of Univit® Kids for children is determined by the properties of its constituent components. The provision of vitamins included in the composition is necessary for the normal function of the skin, mucous membranes, vision, processes of protein, fat and carbohydrate metabolism, hematopoiesis, for normal growth and development, functioning of the nervous system and mental development, and an adequate immune response.
Vitamins C, E and A are the most important components of the body's antioxidant defense; play an important role in the functioning of the immune system; increase resistance to various infections; contribute to the proper growth and development of the child’s body.
Vitamin D is necessary for the formation of the child’s musculoskeletal system, the growth of bones and teeth; plays an important role in the functioning of the immune system, helping to increase the body's resistance to viral and bacterial infections.
Vitamin B12 is an important factor in normal growth and hematopoiesis, which determines its role in maintaining the adaptive capabilities of the child’s body.
Recommendations for use: children aged 3–11 years – 1 chewable lozenge once a day; children aged 11–14 years – 1 chewable lozenge 2 times a day with meals. Duration of treatment – 1 month.
Before use, it is recommended to consult a pediatrician.
Contraindications: individual intolerance to the components, diabetes mellitus. Not recommended for overweight or obese persons.
Release form: 30 chewable lozenges in the shape of dinosaurs weighing 4.0 g in a plastic bottle.
Storage conditions: store in original packaging at a temperature not exceeding 25°C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Not a medicine. Sales to the public through the pharmacy chain and specialized departments of the retail chain.
Certificate of state registration: RU.77.99.11.003.E.001902.03.14 dated 03/20/2014.
Shelf life : 18 months from the date of manufacture.
, Am Ochsenwald 3, D-66539, Neunkirchen, Germany (Amapharm GmbH, Am Ochsenwald 3, D-66539 Neunkirchen, Germany).
Organization receiving complaints from consumers: Pharmstandard OJSC, 141700 Russia, Moscow region, Dolgoprudny, Likhachevsky proezd, 5B. www.pharmstd.ru
Importer: Pharmstandard LLC, 121151 Russia, Moscow, Taras Shevchenko embankment, 23 A.
Supradin Kids Junior chewable tablets from 5 years old 30 pcs.
pharmachologic effect
Supradin is a multivitamin complex for the prevention of hypovitaminosis.
Composition and release form Supradin Kids Junior chewable tablets from 5 years old 30 pcs.
Tablets - 1 tablet:
- active ingredients: vitamin A (palmitate) - 300 mcg; vitamin D3 - 2.5 mcg; vitamin E - 5 mg; vitamin B1 (mononitrate) - 0.45 mg; vitamin B2 - 0.45 mg; vitamin B6 (hydrochloride) - 0.45 mg; vitamin B12 (hydrochloride) - 0.5 mcg; vitamin C (ascorbic acid) - 22.5 mg; nicotinamide - 6 mg; pantothenic acid - 2 mg; folic acid - 75 mcg; biotin - 10 mcg; calcium (carbonate) - 120 mg; magnesium (oxide) - 25 mg; iron (fumarate) - 6 mg; copper (citrate) - 0.4 mg; iodine (potassium iodide) - 60 mcg; zinc (citrate) - 4 mg; manganese (sulfate) - 1 mg; selenium (sodium selenate) - 12.5 mcg; chromium (chloride) - 12.5 mcg; choline (bitartrate) - 25 mg;
- excipients: xylitol (“Xylitab” 100); sorbitol; talc; anhydrous citric acid; orange-tangerine flavoring; magnesium stearate; aspartame; iron oxide yellow; sugar.
30 and 50 chewable tablets in a plastic bottle. 1 fl. in a cardboard pack.
Characteristic
Choline is an important element that is necessary for nutrition and brain function, and memory support.
Vitamin C is involved in the functioning of the immune system and has pronounced antioxidant properties.
Directions for use and doses
Inside, during meals. Children 5–11 years old: 1 tablet. chewable per day, children over 11 years old - 2 tablets. chewable per day. Duration of treatment - 1 month. It is recommended to consult a doctor before use.
Indications for use Supradin Kids Junior chewable tablets from 5 years old 30 pcs.
Supradin is recommended for the prevention of hypovitaminosis caused by insufficient intake of vitamins from food and in conditions accompanied by an increased need for vitamins and minerals in the body:
- people leading an active lifestyle;
- athletes;
- with long-term treatment of obesity and diets;
- for gastrointestinal diseases;
- for women to improve the condition of skin, hair and nails;
- with seasonal hypovitaminosis in the winter-spring period;
- during illness, during the recovery period, during an epidemic of influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections to increase the body's resistance to infections;
- when taking antibiotics, hormonal drugs and chemotherapy drugs;
- to compensate for vitamin deficiency in alcohol abusers and smokers.
Contraindications
Individual intolerance to components.
Application of Supradin Kids Junior chewable tablets from 5 years old 30 pcs. during pregnancy and breastfeeding
During pregnancy, Supradin should be taken only under the supervision of a doctor.
special instructions
For the attention of patients with diabetes mellitus: 1 table. chewing corresponds to 0.056 XE.
Overdose
If the instructions are followed, an overdose is unlikely. Treatment: rinse the stomach.
Side effects of Supradin Kids Junior chewable tablets from 5 years old 30 pcs.
If the recommendations for use are followed, serious side effects are usually not observed, even when using the drug for several months. Sometimes allergic reactions and indigestion may occur.
Drug interactions
Concomitant use with other multivitamin preparations is not recommended.
Possibilities of using multivitamin complexes in neuropediatrics
The role of vitamins in maintaining somatic and psychoneurological health has long been known and is beyond doubt [1, 2]. A distinctive feature of many modern multivitamin preparations and vitamin-mineral complexes is the inclusion in their composition of biologically active substances (BAS), characterized by a positive effect on the cognitive and neurological functions of the human body. It is no coincidence that in their monograph O. A. Gromova et al. (2012) call vitamins, lecithin and individual microelements “smart micronutrients,” emphasizing their role in ensuring adequate neuropsychic development of children [3].
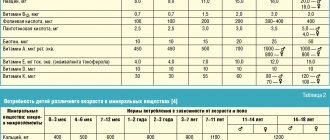
Let me remind you that since 2008, our country has had updated “Norms for physiological needs for energy and nutrients for various groups of the population of the Russian Federation”, which provide for a revision of recommendations for individual nutrients, including those related to the consumption of vitamins, as well as macro- and microelements children and adolescents [4]. These data are presented in table. 1 and 2.
Vitamin lines
The emergence of so-called “vitamin lines” reflects the evolution of ideas about vitamins and the needs for them of various categories of patients and healthy individuals. In this regard, special attention is paid to children of different ages.
Vitamin lines for children, developed by domestic and foreign manufacturers, provide an assortment of multivitamin complexes aimed at different ages and, accordingly, differentiated needs for vitamins.
I would like to note that Supradin Kids Gel is nothing more than a direct analogue (and heir) of the multivitamin complex Kinder Biovital Gel, well known to Russian pediatricians and pediatric neurologists. Previously, the experience of its use in neuropediatrics was reported in a series of our publications, as well as in the works of other authors [5–13]. A multivitamin complex with lecithin, which has a pronounced positive effect, was used by T. N. Platonova and S. V. Yarygina (2005) in the treatment of a representative group of children of early, preschool and school age with functional disorders of the nervous system (neurotic reactions, tics, delayed psychomotor development etc.), and N.A. Korovina et al. (2006) - in the therapy of children with emotional disorders in the form of fears [5, 6]. Employees of the Federal State Budgetary Institution “SCHD” of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences used the described multivitamin complex with lecithin in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, as well as in other clinical situations [7–13].
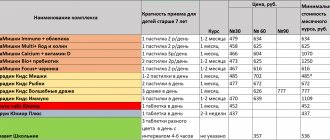
In addition to Supradin Kids gel, the line of vitamin complexes includes Supradin Kids Junior, Supradin Kids with omega-3 and choline (in the form of gummy candies), as well as Supradin Kids Bears (chewable lozenges).
In addition, Supradin is well known to doctors and simply consumers of vitamins in two dosage forms - dragees (coated tablets) and effervescent tablets (quick dissolution). It should be remembered that these forms of the Supradin multivitamin complex are intended not only for adults, but also for children and adolescents over the age of 12 years. The content of vitamins in Supradin dragees and soluble tablets is similar: vitamin A - 3333 IU, vitamin B1 - 20 mg, vitamin B2 - 5 mg, vitamin B6 - 10 mg, vitamin B12 - 5 mcg, vitamin C - 150 mg, vitamin D3 - 500 IU, vitamin E - 10 mg, biotin - 0.25 mg, calcium pantothenate - 11.6 mg, folic acid - 1 mg, nicotinamide - 50 mg. The mineral content in both dosage forms of the Supradin vitamin and mineral complex does not differ for calcium (51.3 mg), manganese (0.5 mg), zinc (0.5 mg) and molybdenum (0.1 mg). A number of other macro- and microelements in Supradin in the form of dragees prevail compared to effervescent tablets: magnesium - 21.2 mg (versus 5 mg), phosphorus - 23.8 mg (versus 47 mg), copper - 1 mg (versus 0. 1 mg), iron - 10 mg (versus 1.25 mg) [14]. What distinguishes Supradin from other multivitamin complexes is the special emphasis placed on the content of B vitamins as the main energy-producing ones. According to research data, in 2010, Supradin became vitamin No. 1 in the recommendations of pharmacists [15].
Separately, I would like to briefly consider the non-vitamin ingredients included in the representatives of the Supradin Kids line. In particular, we are talking about substances such as β-carotene, lecithin, choline and omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids.
Individually and collectively, these substances play a special role in the processes of formation and development of nervous tissue, which is especially important in childhood. During critical periods of development (intense growth, preparation for school, subject learning, physical activity during sports, etc.), the physiological significance of the described nutrients increases significantly.
Beta carotene
One of two isomers of carotene (yellow-orange pigment, which is an unsaturated hydrocarbon from the group of carotenoids). Contained in yellow, orange and green leaves of vegetables and fruits, carrot roots, rose hips, tomatoes, sweet potatoes, etc. Beta-carotene is a provitamin of vitamin A, has antioxidant, adaptogenic and immunomodulatory effects. In the middle of the first decade of the 2000s. The antiepileptic properties of β-carotene have been demonstrated [13].
The unsaturated structure of β-carotene allows its molecules to adsorb light and prevent the production and accumulation of free radicals and reactive oxygen species. Beta-carotene is a natural immunomodulator that increases the body's immune potential regardless of the type of antigen (it acts nonspecifically). Some researchers associate the immunomodulatory activity of β-carotene with its effect on the metabolism of arachidonic acid and its metabolites. It is assumed that β-carotene suppresses the production of arachidonic acid, thereby inhibiting the production of prostaglandin E2 (the latter is a suppressor of NK cells - natural killer cells).
6 mcg of β-carotene is considered to be equivalent to 1 mcg of vitamin A. There is no established upper tolerable intake level for β-carotene. For adults, the physiological requirement is about 5 mg/day (for children it has not yet been specified).
β-carotene deficiency in children is more often manifested by impaired twilight vision, slow bone growth, damage to the integumentary epithelium of the skin and mucous membranes, as well as an increased susceptibility to inflammatory diseases.
Lecithin
A group of fatty substances found in animal and plant tissues, as well as egg yolks. Lecithin consists of orthophosphoric acid, choline, fatty acids, glycerol, glycolipids, fats and phospholipids.
When lecithins are broken down, higher fatty acids (palmitic, stearic, oleic and arachidonic) are formed. Lecithin is a powerful antioxidant; it is necessary for the formation of intercellular space, the normal functioning of the nervous system and the activity of neurons, for the transport of essential nutrients and vitamins to cells. Lecithin prevents the production of free radicals. About one third of the insulating and protective tissues of the brain (brain and spinal cord) are composed of lecithin.
Severe lecithin deficiency can lead to decreased intelligence, parkinsonism, and the development of multiple sclerosis.
Food products high in lecithin include eggs (yolk), poultry and fish. On an industrial scale, lecithin is extracted from by-products of the production of soybean flour and oil. Soy lecithin is produced from purified soybean oil using low-temperature processing; it contains oil, phospholipids, vitamin A, vitamin E, etc. (used as a biologically active and flavoring food additive. Lecithin is also obtained from sunflower oil (by extraction); it differs from soybean in composition and fatty acid content.
Lecithin is one of the main sources of nutrition for the nervous system. It promotes better absorption of fat-soluble vitamins, and its inclusion in the composition of Supradin Kids gel allows us to potentiate the utilization and clinical effect of the vitamin ingredients of this dietary supplement.
When lecithin interacts with pantothenic acid, acetylcholine is formed, which is necessary to activate intellectual activity, memory and thought processes [11].
Since it has been proven that lecithin is the most important building element of the peripheral and central nervous systems, its deficiency in childhood is accompanied by a number of undesirable consequences (slow formation of the central nervous system, intracranial hypertension, delayed mental and/or speech development, psycho-emotional instability; impaired memory, attention, behavior, etc.). With severe lecithin deficiency, degenerative processes may occur in the muscles.
Kholin
It is a vitamin-like substance, which is sometimes classified as a water-soluble B vitamin (vitamin B4, vitamin BP). Choline is 2-hydroxyethyltrimethylammonium hydroxide, [(CH3)3N+CH2CH2OH]OH–. The classification of choline as a B vitamin is conditional, since animal microorganisms have the ability to synthesize it.
Acetylcholine (the most important neurotransmitter) is synthesized from choline. Choline is an important substance for the nervous system and improves memory, is part of phospholipids, and is involved in the synthesis of methionine, where it is a supplier of methyl groups.
According to WH Meck et al. (2008), choline received by children during the first years of life is of decisive importance for the development of memory [16].
Nutritional sources of choline include egg yolk, organ meats, cabbage, spinach and soy. These products are not always consumed by children in the required quantities. For this reason, the choline found in Supradin Kids Junior and Supradin Kids Omega-3 and Choline is a valuable addition to these multivitamins.
Choline deficiency interferes with adequate carnitine production, promotes cholesterol metabolism disorders and fat deposition in the liver.
Omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids
These fatty acids, found in seafood and plant fats, are polyunsaturated fatty acids with a double bond (C=C) starting after the third carbon atom from the end of the carbon chain. Fatty acid molecules have two ends - acidic (COOH) and methyl (CH3). The location of the first double bond is measured from the methyl end (called the omega end).
DHA is an essential polyunsaturated fatty acid belonging to the class of omega-3 unsaturated acids. It is part of the lipids of most animal tissues and is one of the main components of complex lipids.
The main sources of DHA are salmon and Atlantic herring fish oils, marine shellfish, zooplankton, dinophyte microalgae, some seaweeds and flaxseed oil.
Along with eicosapentaenoic acid, DHA is one of the most valuable omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids for human health. It plays an important role in the formation of the brain and vision in the early stages of ontogenesis, and also has a beneficial effect on the state of cerebral circulation.
DHA is a conditionally essential nutrient during the period of active brain growth. DHA is a major component of the gray matter of the brain, retina and cell membranes. Its deficiency in some cases is associated with the risk of developing depressive conditions, suicidal behavior, and attention disorders. The latter can hinder successful learning at school.
The DHA used in Supradin Kids with Omega-3 and Choline is obtained from seaweed grown on special plantations, which ensures maximum purification and effectiveness of this component of the multivitamin complex [17].
Below we will consider the features of the component composition of multivitamin preparations from the Supradin Kids series, as well as indications for their use and features of their use. All of them are considered as biologically active additives (BAA).
Supradin Kids gel
Multivitamin complex with lecithin and β-carotene, intended for children from 3 years of age.
1 teaspoon (5 g) of Supradin Kids gel contains the following ingredients: β-carotene - 155 mcg ret. eq. (retinol equivalents), vitamin D3 - 3.7 mcg, vitamin E (D, L-α-tocopherol acetate) - 1.9 mg, vitamin B1 (thiamine hydrochloride) - 0.31 mg, vitamin B2 (sodium riboflavin phosphate ) - 0.29 mg, vitamin B6 (pyridoxine hydrochloride) - 0.39 mg, niacin (nicotinamide) - 3.5 mg, pantothenic acid (calcium pantothenate) - 0.42 mg, ascorbic acid (vitamin C) - 13, 5 mg, lecithin - 0.1 g (100 mg) [14].
Children aged 3–6 years Supradin Kids gel are prescribed 1/2 teaspoon (2.5 g) 2–3 per day; for children from 7 years old, 2 teaspoons (10 g) of a multivitamin complex per day are prescribed.
Supradin Kids gel helps optimize the development of the child, including his nervous system. Lecithin, which is part of the Supradin Kids gel, helps increase concentration, and β-carotene not only strengthens vision, but also supports the immune system of children [15].
Supradin Kids Junior
Multivitamin complex with choline in the form of chewable tablets for children aged 5 years and older.
1 tablet of Supradin Kids Junior contains the following substances: vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) - 2.5 mcg (100 IU), vitamin A (retinol) - 300 mcg, vitamin E (α-tocopherol) - 5 mg, ascorbic acid (vitamin C) - 22.5 mg, nicotinamide - 6 mg, vitamin B1 (thiamine) - 0.45 mg, vitamin B2 (riboflavin) - 0.45 mg, vitamin B6 (pyridoxine) - 0.45 mg, vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin ) - 0.5 mcg, pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) - 2 mg, folic acid - 75 mcg, biotin - 10 mcg, choline - 25 mg, calcium (Ca) - 120 mg, magnesium (Mg) - 25 mg, iron (Fe) - 6 mg, zinc (Zn) - 4 mg, manganese (Mn) - 1 mg, copper (Cu) - 0.4 mg, iodine (I) - 60 μg, selenium (Se) - 12.5 μg , chromium (Cr) - 12.5 μg [14].
Dosing of Supradin Kids Junior: aged 5–11 years - 1 tablet 1 time a day, children over 11 years old - 1 tablet 2 times a day.
It is believed that the use of Supradin Kids Junior promotes the harmonious (physical and mental) growth and development of children moving on to subject education.
Supradin Kids with omega-3 and choline
A multivitamin complex enriched with docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and choline - in the form of gummy candies (gummy fish and stars). These chewable lozenges are intended for children from 3 years of age.
1 chewable lozenge contains: vitamin C - 15 mg, niacinamide - 4.5 mg, vitamin B6 - 0.5 mg, vitamin B12 - 0.25 mcg, DKG - 30 mg, choline - 30 mg [14].
Dosage: children aged 3-4 years - 1 lozenge per day, aged 4-14 years - 2 lozenges per day.
The relatively modest presence of vitamins in Supradin Kids with omega-3 and choline is fully compensated by the inclusion of DHA and choline. In this regard, Supradin Kids with omega-3 and choline helps improve memory and mental development of children.
Supradin Kids Bears
Chewable lozenges (4 g each) in the form of gummy bears with various flavors (orange, lemon, raspberry). Intended for children from 11 years of age. As the manufacturers indicate, this general strengthening multivitamin complex promotes the healthy growth and development of school-age children.
One lozenge of Supradin Kids Bears contains the following components: vitamin A - 400 mcg, vitamin E - 5 mg, vitamin D3 - 2.5 mcg, vitamin C - 30 mcg, vitamin B6 - 1 mg, vitamin B12 - 0.5 mcg, nicotinamide - 9 mg, folic acid - 100 mcg, biotin - 75 mcg [14].
Dosing of Supradin Kids Bears involves prescribing 1 chewable lozenge per day to children over 11 years of age.
All components of the Supradin Kids Bears vitamin complex are selected taking into account their interaction and complement each other. A full range of essential vitamins provides the child’s daily needs, helps stimulate mental development and cope with school stress.
Vitamin-mineral and multivitamin complexes are one of the tools in childhood neurodietology [18]. The Supradin Kids vitamin line, in which vitamins are presented in combination with minerals and biologically active substances (lecithin, choline, DCG, β-carotene), fully reflects a progressive view of optimizing the somatic and neuropsychiatric health of children and adolescents.
This approach is intended not only to provide various organs and systems of the body with the necessary vitamins and minerals, but also to resist stress, improve the perception of information, and optimize the cerebral functions of children [19].
Literature
- Vitamins and minerals in nutrition and maintaining the health of children. Chapter 17. In the book: Clinical dietetics of childhood: A guide for doctors / Ed. Borovik T. E., Ladodo K. S. M.: MIA LLC. 2008. pp. 443–471.
- Combs GF Jr. (ed). The vitamins Fundamental aspects in nutrition and health. 4 th ed. London-San Diego. Academic Press/An Imprint of Elsevier. 2012. 570 p.
- Gromova O. A., Torshin I. Yu., Egorova E. Yu. “Smart” micronutrients. Micronutrients and neuropsychic development of the child: monograph. M.: Miklos. 2012. 168 p.
- Norms of physiological needs for energy and nutrients for various groups of the population of the Russian Federation. Method. rec. MP 2.3.1.2432–08.3.2.1. Balanced diet. M., 2008. 40 p.
- Platonova T.N., Yarygina S.V. Efficacy of the multivitamin complex “Kinder Biovital Gel” for minimal neurological dysfunction in preschool children // Consilium medicum. Pediatrics. 2005. T. 7. No. 1. P. 48–49.
- Korovina N. A., Zakharova I. N., Naumenko L. L. Micronutrient deficiency and neuropsychic development of children // Consilium medicum. Pediatrics. 2006. T. 8. No. 2. P. 52–55.
- Studenikin V. M. Multivitamin preparation with lecithin: use in pediatric neurology // Treating Doctor. 2003. No. 6. P. 56–57.
- Studenikin V.M., Balkanskaya S.V., Maslova O.I. Possibilities of using a multivitamin preparation with lecithin in pediatric neurology // Consilium medicum. Pediatrics. 2004. App. No. 1. pp. 16–19.
- The use of a multivitamin preparation with lecithin in neuropediatrics (a manual for doctors). M.: Medical practice. 2005. 20 p.
- Studenikin V.M., Nikolaev A.S., Akoev Yu.S., Balkanskaya S.V. et al. Vitamins and the use of multivitamin preparations in pediatrics // Pediatrician’s Handbook. 2006. No. 6. P. 68–88.
- Studenikin V.M., Balkanskaya S.V., Shelkovsky V.I. Effect of lecithin on the neurological status of children // Treating Doctor. 2009. No. 6. pp. 46–49.
- Studenikin V.M., Balkanskaya S.V., Shelkovsky V.I. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in children: diagnosis and treatment // Attending Physician. 2010. No. 1. P. 31–34.
- Vitamins in neurodietology. Ch. 6. In the book: Neurodietology of childhood (collective monograph) / Ed. Studenikina V.M.M.: Dynasty. 2012. pp. 97–113.
- Register of Medicines of Russia "Encyclopedia of Medicines". Ed. 21st, revised and additional M.: RLS-Media. 2013. 1612 p.
- Alekseev M. Vitamins for the smart // Russian pharmacies. 2011. No. 22 (203). pp. 12–15.
- Meck WH, Williams CL, Cermark JM, Blusztajn JK Developmental periods of choline sensitivity provide an ontogenetic mechanism for regulating memory capacity and age-related dementia // Frontiers Integrate. Neurosci. 2008. Vol. 1 (Art. 7). P. 1–11.
- An ordinary miracle for extraordinary children. Who needs children's vitamins and why // My favorite pharmacy. 2011. No. 8 (80). S. 4.
- Studenikin V.M., Shelkovsky V.I. Vitamin and mineral complexes for children: a tool for neurodietology // Pediatrics. 2008. T. 87. No. 6. P. 105–109.
- Benton D. Vitamins and neural and cognitive developmental outcomes in children // Proc Nutr. Soc. 2012. Vol. 71(1). P. 14–26.
V. M. Studenikin, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Corresponding Member of the RAE
FSBI "NTsZD" RAMS, Moscow
Contact Information