Urologist
Belkin
Andrey Ivanovich
20 years of experience
Urologist of the first category, member of the European Association of Urology
Make an appointment
The inflammatory process in the kidneys can be sluggish and practically not manifest itself, but more often the pathology is indicated by a whole set of characteristic symptoms. The disease was called “nephritis”, various types of which have now been studied in detail and described in the medical literature. Inflammation may affect the tissue of one or both kidneys, which is determined during the diagnostic process. Practical experience in the treatment of nephritis allows us to count on stable and long-lasting results. Especially if the patient seeks medical help in a timely manner and strictly follows the specialist’s instructions.
Types of jades
Depending on the location of the inflammatory process, there are:
- Glomerulonephritis is inflammation in the area of the kidney glomeruli. The disease is autoimmune in nature.
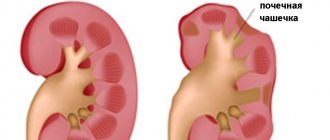
- Pyelonephritis, or kidney nephritis, is a lesion of the kidney tissue and pelvis.
- Hereditary nephritis is a disease whose first symptoms appear in childhood.
- Interstitial nephritis is inflammation in the area of the renal tubules, as a result of which the conductive function of the kidneys is impaired.
- Radiation nephritis is an inflammatory process due to irradiation of the body or undergoing a course of radiation treatment.
A comprehensive diagnosis of the patient’s body allows one to accurately identify the site of inflammation and take measures to slow its spread and gradual extinction.
General information
Nephritis is a group of kidney diseases of an inflammatory nature. There are two main forms in children: hereditary and acquired.
The inflammatory process usually occurs in both kidneys of the child, spreading to the pyelocaliceal system, renal glomeruli and tubules. This disease can appear even in newborns; in medicine there is currently no consensus on what the mechanism of the onset and development of the disease is. Acute tubulointerstitial nephritis is usually provoked in children by a hereditary predisposition, accompanied by infection and allergies. Source: N.I. Khlebovets Tubulointerstitial nephritis in children // Journal of Grodno State University, 2014, No. 1, pp. 94-97
Causes
The main cause of the disease is the penetration of infection into the tissues of the kidneys and urinary tract from the outside or from another organ where an inflammatory process is observed at one stage or another. The infectious process can be started by:
- Recently suffered infectious diseases, the pathogens of which were not completely destroyed.
- Regular hypothermia of the body.
- Malfunctions of the immune system, its depressed state due to surgery or serious illness.
- Disruption of the blood supply to the kidneys.
- Stagnation of urine, the chemical environment of which is favorable for the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
Depending on the duration and nature of the disease, acute and chronic nephritis are distinguished. The first type of disease often occurs as a result of taking “aggressive” medications: antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants and diuretics, analgesics and drugs that suppress pathogens of viral and bacterial diseases. A negative reaction of the kidneys to the drug taken becomes the main cause of inflammation, especially in elderly patients and people with congestion in the body.
Chronic nephritis occurs due to a long course of the acute stage of the disease and the lack of proper treatment. The situation is worsened by uncontrolled use of medications and the presence of foci of cancer in the body. If it is not possible to accurately determine the cause of kidney inflammation, the patient is diagnosed with “idiopathic nephritis”, and the course of treatment is developed on a strictly individual basis.
Symptoms of nephritis
The following signs most likely indicate an inflammatory process in the kidneys:
- increase in body temperature up to 40⁰С;
- muscle aches and lower back pain;
- swelling of the face and limbs;
- darkening of urine;
- decreased number of urinations during the day.
At risk are children and young men, in whom the inflammatory process develops quite quickly and often becomes dangerous.
Advantages of SM-Clinic
Our medical center employs some of the best specialists in the Northern capital: pediatric nephrologists, urologists, pediatricians.
“SM-Clinic” has modern equipment, thanks to which diseases are diagnosed quickly and accurately. This makes it possible to return children to normal life in a short time. We have no queues, the approach to each child is always individual and delicate. If inpatient observation is required, comfortable rooms are provided.
Sources:
- N.I. Khlebovets. Tubulointerstitial nephritis in children // Journal of Grodno State University, 2014, No. 1, pp. 94-97.
- Lechon FC, Espi MT, Abal RP, Peiro JLE. Acute glomerulonephritis associated with pneumonia: review of three cases. Ped. Nephrol. 2010; 25: 161-164.
- G.A. Makovetskaya, L.I. Mazur, V.N. Barinov, E.A. Barannikova, E.M. Romadanova, P.V. Morinets. Lupus nephritis in children: manifestation, diagnosis, treatment // Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics, 2022, No. 62(4), pp. 185-186.
Lavrishcheva Yulia Vladimirovna Clinic
Author of the article
Lavrishcheva Yulia Vladimirovna
Doctor of the first qualification category
Specialty: nephrologist
Experience: 14 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Diagnostics
The similarity of the symptoms of nephritis with the signs of influenza and ARVI forces specialists to resort to methods of differentiated diagnosis. The following methods for diagnosing nephritis can confirm doctors’ assumptions about inflammation in the kidney area:
- general and biochemical blood test;
- bacteriological urine culture;
- general urine analysis, study according to Zimnitsky and Nechiporenko;
- Ultrasound of the kidneys with the effect of contrast illumination (Doppler);
- ECG, blood pressure monitoring;
- immunological studies;
- radioisotope method for diagnosing inflammatory diseases.
In rare cases, if test results are in doubt, a decision is made to perform a kidney tissue biopsy. Often, third-party specialists from other fields of medicine are involved in the examination: ENT doctor, gynecologist, dentist, infectious disease specialist, etc. Their participation in the examination allows us to accurately identify the cause of the disease and identify the source of infection hidden inside the body.
Terminology
The concept of “tubulointerstitial nephropathies” in the broad sense of the word includes inflammatory, metabolic or toxic diseases of the kidneys, which occur in contrast to glomerular (glomerular) diseases with primary and predominant damage to the tubules and interstitial tissue of the kidneys. In a narrower sense, the term “tubulointerstitial nephropathies” is more often used to refer to metabolic and toxic lesions without a clear inflammatory component, applying the term “tubulointerstitial nephritis” or, equivalently, “interstitial nephritis” to inflammatory, immunoinflammatory lesions of the tubules and interstitium. In addition to tubulointerstitial nephropathies as independent nosological forms, a tubulointerstitial component can be isolated in a number of glomerular kidney lesions, including chronic glomerulonephritis.
The term “interstitial nephritis” (IN) has existed since the mid-nineteenth century, but over the course of a century and a half it included various concepts. The term “chronic interstitial nephritis” for a long time corresponded to the modern understanding of kidney damage in hypertension - nephroangiosclerosis, primary wrinkled kidney, i.e. designated those types of kidney pathology, which are based on vascular damage; this group then began to include secondarily wrinkled kidney, chronic nephritis of the hypertensive type. IN was contrasted with tubular, parenchymal nephritis with edematous syndrome (corresponding to modern nephritis with nephrotic syndrome). In parallel, in the first half of the twentieth century, the term “tubulointerstitial nephritis” existed to refer to acute renal failure (ARF).
IN, corresponding to the modern interpretation of this concept, was first described in 1898 by Councilman in patients who had diphtheria and scarlet fever. However, for a very long time, IN was identified exclusively with pyelonephritis and was the prerogative of study by urologists. And at present, IN remains poorly known to a wide range of doctors, which is due, firstly, to the relative rarity of the disease, and secondly, to the nonspecificity of most symptoms. Poor knowledge of this pathology by doctors is evidenced by the fact that among the 22 patients with acute IN we observed, 20 were admitted with other diagnoses: 12 with a diagnosis of chronic glomerulonephritis, 3 with acute glomerulonephritis, 2 with pyelonephritis, 3 with systemic lupus erythematosus. At the same time, IN is in most cases a disease with an established etiology, promising in terms of treatment and prevention.
The current wave of interest in tubulointerstitial lesions is associated both with the possibilities of treatment and prevention (obviously greater than with glomerular diseases), and with the increasing frequency of iatrogenic pathology in general, as well as with the assumption of the leading role of the interstitium and tubules in the progression of kidney diseases.
Treatment
A patient with signs of nephritis is given strict bed rest, which helps reduce the rate of spread of infection through the circulatory system and internal organs. You can cope with the disease by:
- Taking medications to eliminate the causes of inflammation. A course of antibiotics, antiviral drugs, hemosorption procedures and plasmaphoresis to destroy the pathogen in the patient’s blood gives a good effect.
- Blocking the development of the inflammatory process and its spread throughout the body. The effect is achieved by taking hormonal drugs, antihistamines, and medications to activate blood circulation in the kidney tissues.
- Symptomatic treatment to alleviate the patient's condition. The course includes water-electrolyte drips, monitoring of daily urination, intestinal or hemodialysis, which allows you to remove metabolic products from the body.
A prerequisite for successful treatment is a diet for nephritis, the main requirements of which are reducing the amount of salt in the diet and limiting the volume of fluid to 700-800 ml, depending on the patient’s body weight. Treatment is carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor, and its content is adjusted as monitoring indicators change and signs of recovery appear.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms are usually the same, regardless of the cause of kidney damage, and are also similar for children of any age - from newborns to teenagers:
- swelling;
- decreased appetite;
- general weakness;
- feeling of dry mouth;
- chills;
- skin redness;
- dry skin, hair, nails;
- headache;
- pain in the lumbar area;
- convulsions;
- small volume of daily urine;
- bloating;
- vomiting and other gastrointestinal disorders.
If the disease lasts for a long time, then the death of a large number of renal glomeruli occurs. As a result, kidney failure occurs.
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by:
- intense sweating, increasing at night;
- decreased appetite;
- yellow skin tone;
- frequent urge to urinate;
- pain during urination;
- cloudy urine.
Diagnosis and treatment of nephritis in Moscow
The Clinic of JSC "Medicine" invites patients with suspected nephritis to undergo a comprehensive examination and course of treatment. All necessary services can be obtained at the center, which will save the patient from having to sign up for tests and wait a long time for his turn. Each patient is guaranteed confidentiality, attentive and welcoming treatment, the opportunity to undergo examination and receive advice from other specialized specialists, as well as the quality and safety of the proposed treatment procedures. You can make an initial appointment by calling the specified phone number or through the clinic’s website by filling out the appropriate application.