Stein-Leventhal syndrome occurs in every fifth woman during the fertile period.
Pronounced signs of polycystic disease are most often absent, and problems with conception are often the reason for visiting a doctor. Despite the fact that polycystic ovary syndrome causes a lot of trouble, it is not a death sentence, you just need to take care of your health in time and undergo a course of treatment. With PCOS, there is an increase in luteinizing hormone (LH) and male sex hormones in the blood. The reasons are not well understood; there is a high probability of a hereditary factor in the development of the pathology. Many women, upon learning of their diagnosis, remember that their mother or other relatives also had problems conceiving. The main symptom of PCOS (Stein-Leventhal syndrome) is enlarged, due to the formation of numerous cysts, the so-called polycystic ovaries. They are usually detected during an ultrasound.
Women who are diagnosed with polycystic ovaries are interested in: “How to get pregnant? What treatment is required?”, because due to cystic changes, the normal functioning of the ovary, blood supply and supply of nutrients are disrupted. PCOS is characterized by the fact that the egg matures, but ovulation does not occur. The level of estrogen in the blood increases and the amount of progesterone decreases. This disrupts the normal development of the endometrium of the uterus. It actively grows under the influence of estrogens and thickens. This can cause a delay in menstruation and menstrual irregularities. And menstruation itself becomes profuse, and uterine bleeding may develop.
What is PCOS
Signs and symptoms
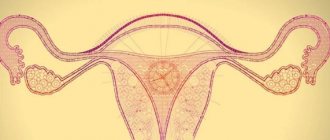
During the menstrual cycle in the reproductive period, folliculogenesis occurs - the maturation of follicles containing eggs. The follicles grow, and before ovulation, one of them ruptures, releasing an egg (ovulation), which, under favorable conditions, can be fertilized. Other follicles undergo the opposite change. This happens normally. If an ultrasound examination reveals more than 10 small underdeveloped follicles in any phase of the cycle, a diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is made. Follicles that have not completed their physiological development are located along the periphery of the ovary, the center is not thickened. There are no cysts themselves in the classical sense on the ovaries.
Polycystic ovary syndrome manifests itself individually, and there is no clear clinical picture for all patients with this disease. Most often there is a combination of symptoms in different variations. Some women may not even have echo signs of the disease (on ultrasound), but the combination of hyperandrogenism with the absence of ovulation gives reason to suspect PCOS. Sometimes polycystic ovary syndrome can occur with ovulation, but echo signs of PCOS and hyperandrogenism must be present to make a diagnosis.
Due to the absence of specific characteristic symptoms, it is impossible to feel that PCOS has developed, but a woman should be alerted to the appearance of the following signs:
- Instability of the menstrual cycle, irregularity, pain, heavy discharge or, conversely, its complete cessation, non-cyclical discharge.
- Increased hair growth in areas unusual for women (face, chest, abdomen).
- Fat deposits on the abdomen and waist.
- Alopecia (hair loss on the scalp).
- Increased oiliness of hair, skin, acne.
These endocrine disorders may indirectly indicate the presence of polycystic ovary syndrome. But to clarify the diagnosis, an examination by a specialist and additional instrumental studies are required.
Hyperandrogenism occurs as a result of intense production of male hormones (testosterone, androstenedione) in the female body. The cause may be genetic predisposition, dysfunction of the pituitary gland and hypothalamus, pituitary tumors. Previously, hyperandrogenism was considered an obligatory and defining sign of PCOS; now the diagnosis is made even with normal levels of male hormones. The situation is similar with obesity. Excess male hormones lead to fat deposition mainly on the waist and abdomen. But today PCOS is also registered in women with normal weight. Although excess body weight is the most important factor in the development of the disease.
This is due to the fact that adipose tissue is capable of producing estrogens, which causes hormonal imbalance. Their excess has an adverse effect on the entire body and hormone-producing cells. The secretion of many hormones is regulated by feedback; in addition, their active effect on the body, transport in the blood, is carried out by binding to proteins of the same type. Therefore, changes in the blood levels of one hormone also affect others.
Signs of PCOS
Folliculogenesis is normal and in PCOS
Causes of polycystic ovary syndrome
The pathology develops due to too high levels of male hormones - androgens - in the female body. With normal and stable functioning of the ovaries, every month follicles begin to mature in them, one of them matures completely, and an egg is born in it. As soon as the egg matures, the follicle ruptures and ovulation occurs. However, this happens normally. With polycystic ovary syndrome, the egg does not develop or mature. Which, in fact, leads to a lack of ovulation or menstrual irregularities. This occurs due to malfunctions in the hormonal system - the cyclicity of the well-functioning work of the entire system of the female body is disrupted.
There are some characteristic signs by which one can determine that a woman has polycystic ovary syndrome: her facial features may become masculine, too much hair, acne, and fat deposits (even obesity) appear on the body. PCOS is one of the most common female diseases, affecting 5-10% of women of childbearing age.
Today there is no consensus among doctors regarding the causes of polycystic ovary syndrome. One of the possible causes of PCOS is called heredity, i.e. predisposition to the development of the disease at the gene level, the other is insensitivity to insulin (a pancreatic hormone). The fact is that, according to recent studies, increased production of androgens by the ovaries directly depends on the level of insulin in the body - it is its high concentration that leads to pathology. There are several genes responsible for the biosynthesis of insulin in the female body, and if they do not cope with their job, then insulin is not absorbed properly, and the ovaries react to this in their own way - they begin to produce male hormones in large quantities.
Obesity is considered one of the factors contributing to the development of PCOS. And if it is present in a woman’s family history, then the best method of preventing the syndrome is to maintain normal body weight. In some cases, when the disease is already present, weight loss can lead to relief from the pathology.
Insulin insensitivity can cause the development of type 2 diabetes, so when examining patients with polycystic ovary syndrome, the doctor should pay special attention to this factor. And, conversely, if a woman has diabetes, then it is necessary to diagnose the presence of PCOS.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can manifest itself in a woman with many symptoms, the main ones of which are:
- menstrual irregularities - menstruation is rare or absent (ovarian dysfunction);
- infertility;
- hirsutism - excess hair growth on the back, chest, face, etc.;
- acne - acne on the face;
- enlarged ovaries with small and numerous cysts;
- overweight or obesity, in which fat deposits are concentrated in the abdominal area;
- increased levels of insulin, cholesterol in the blood, level 2 diabetes mellitus;
- arterial hypertension;
- pigmentation of some areas of the skin on the body - neck, elbows, inner thighs;
- disorders of the psycho-emotional state - infertility and unattractive appearance contribute to the development of depressive and anxiety states.
It should be noted that PCOS does not always cause infertility; only 16% of women suffer from it.
Complications of Stein-Leventhal syndrome
PCOS can cause serious complications:
- Menstrual disorder.
- Miscarriage.
- Infertility.
- Oncological diseases of the genital organs.
- Cardiovascular disorders.
- Diabetes mellitus type 2.
Patients with polycystic disease should be informed about this possibility and undergo preventive examinations more often, since they are at risk. With PCOS, the body's sensitivity to insulin (a hormonal substance produced by the pancreas that regulates glucose levels in the bloodstream) decreases. This condition, called insulin resistance, leads to a significant increase in insulin levels in the blood. In turn, high levels of insulin promote excess synthesis of androgens, which lead to changes in the ovaries, reducing their function and changing their structure.
Male hormones interfere with the normal growth of eggs and cause thickening of their outer shell, as a result of which a mature egg is not able to break through the thickened wall of the follicle in order to come out for fertilization. The remaining unruptured follicles become cysts, filling with fluid. Therefore, the ovaries increase in size. Removal, making cuts on the thickened membrane to facilitate the release of the egg, is the basis of surgical treatment for PCOS.
What medications are used to treat polycystic ovary syndrome?
To treat polycystic ovary syndrome, different types and groups of drugs are used. If a woman is not planning a pregnancy, she may be prescribed oral hormonal contraceptives, which will help regulate the menstrual cycle, reduce the growth of male hormones and cleanse the skin of the face. To prevent excess hair growth, a course of Flutamide, a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with antiandrogenic effects, is usually prescribed. The important point is that no product causes hair loss, it can only stop its growth. And to remove excess vegetation, you should use special techniques.
If PCOS has caused infertility, and a woman wants to get pregnant, a course of treatment with Clomiphene, a drug that stimulates ovulation, is prescribed. To achieve maximum effectiveness in restoring fertility functions, clomiphene is prescribed together with metformin, a drug for the treatment of diabetes. This drug increases the sensitivity of the female body to insulin, which, in turn, leads to a decrease in the production of male sex hormones. Metformin will also help lower blood cholesterol and get rid of excess weight.
And, of course, don’t forget about diet. Only the right diet, eating healthy and low-fat foods, low in carbohydrates will help “curb” insulin and lose extra pounds.
Diagnostics
Despite the fact that women more often turn to a gynecologist about infertility, upon examination they may notice some symptoms that may suggest polycystic ovary syndrome. In the anamnesis, they note irregularity of the menstrual cycle, scanty or heavy menstruation. Upon examination, a woman with PCOS may be diagnosed with hirsutism, excess male-pattern hair growth. Increased weight and acne that cannot be treated are also signs of hormonal imbalance.
PCOS (Stein-Leventhal syndrome) is diagnosed using the following methods:
- Blood test for hormones.
- Ultrasonography.
- An endometrial biopsy is performed using diagnostic laparoscopy - a biopsy sample is taken for morphological examination. Indications include bleeding outside the menstrual cycle.
- Laboratory blood test.
- Glucose tolerance test.
- Sonography (ultrasound examination) of the pelvic organs is performed transvaginally. In PCOS, the study shows the presence of multiple modified follicles (size up to 10 mm), localized on the periphery, a significant increase in ovarian volume (more than 9 cubic cm), thickened stroma, which makes up a quarter of a percent of the total volume of the ovaries.
Blood test for hormones
Ultrasound OMT
Diagnosis of PCOS
To make a diagnosis of polycystic ovary syndrome, it is necessary to conduct a series of studies that should reveal changes in the body. Diagnostics consists of three stages:
- visit to a gynecologist and general examination. The specialist examines the patient’s complaints, her cycle, anamnesis, assesses the body mass index, and the development of the genital organs. Conducts an examination of the uterus and appendages, assesses their size and condition;
- ultrasonography. Pelvic ultrasound is performed in two ways: transabdominal (general examination of the uterus and ovaries) and transvaginally (a sensor is inserted into the vagina and the organs are examined in more detail). This type of study can reveal cysts, follicles, enlarged ovaries, uniformity or heterogeneity of texture, damage to the membranes, etc.;
- laboratory diagnostics. To confirm the diagnosis, if it was detected by ultrasound, blood is donated for sex hormones. The main indicators for identifying PCOS are the hormones LH (luteinizing) and FSH (follicle-stimulating), thanks to which follicles mature and the egg is released. Testosterone and other androgens look the same; their increase indicates the dominance of male sex hormones over female ones, which also affects the normal functioning of the ovaries.
In addition to the above, a general blood test or an analysis for the concentration of thyroid hormones may be prescribed. In some cases, an endometrial biopsy may be prescribed.
How is Stein-Leventhal syndrome treated?
Despite the fact that the exact causes of PCOS are unknown, modern medicine has developed methods for correcting hormonal levels and treating infertility. One of the important factors in restoring hormonal levels is the fight against excess weight. Changes in the sensitivity of insulin receptors cause increased formation of adipose tissue and weight gain. And adipose tissue is capable of synthesizing estrogens, the increased level of which, through feedback, reduces the production of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Therefore, the fight against excess weight plays an important role in the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome complicated by infertility. After all, FSH stimulates the growth of follicles and the full maturation of the egg.
Development of follicles under the influence of hormones
If you are diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome, in addition to drug treatment, it is recommended to play sports or exercise, and walk in the fresh air more often. Physical activity increases muscle sensitivity to insulin. You also need to eat right. If all this does not help, you may have to resort to liposuction.
In many cases of PCOS, a reduction diet is prescribed during treatment, which helps not only to cope with excess weight, but also to normalize lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. The diet consists of reducing daily caloric intake. Of the required 2000 kilocalories, carbohydrates make up 52%, fats - 32% (of which a third are unsaturated fats), proteins - 16%. The intake of hot, spicy, salty foods, marinades, and liquids is limited. Fasting days are observed. You should not starve, this negatively affects glucogenesis.
Often, with PCOS, treatment for which is selected strictly individually, patients are prescribed oral contraceptives, this helps to temporarily normalize cycle disorders and reduce the severity of symptoms, but they can be used up to 35 years of age, in addition, they are not recommended if the woman smokes.
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome
The doctor decides how to treat polycystic ovary syndrome in a patient, based on the diagnosis, severity of symptoms and her well-being. First, it is necessary to accurately identify the cause of the disease and direct efforts to eliminate it.
This pathology is associated not only with gynecology, but also closely with endocrinology, since the root cause is hormonal imbalance, so treatment is often carried out by endocrinologists.
To completely cure polycystic ovary syndrome, you need to go through several stages.
- Bringing the patient's weight back to normal if it does not suit her. It is also necessary to develop a balanced diet, which must be adhered to throughout the entire period of treatment, and better yet, after it. Establishing water metabolism in the body, setting the daily intake of clean water. It is also necessary to introduce regular physical activity into the patient’s life. Normalize sleep (at least 7-8 hours a day), protect yourself from stressful situations. Such a change in lifestyle will have a beneficial effect on the human body and well-being, and will also prepare the ground for further treatment.
- Next, treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome with hormone-containing drugs is prescribed. Most often, combined oral contraceptives are used, which are selected individually for a person, based on his tests and characteristics of the body. The drugs are taken in courses of at least three months (the number of courses is determined by the doctor based on the success of treatment), throughout the entire period it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination of the pelvic organs to monitor treatment
- Combating insulin resistance, including prescribing special medications.
Usually, after hormone therapy, the condition improves, but some cases require surgical intervention, and for women planning pregnancy, methods are used to stimulate the onset of ovulation.
Surgical methods for treating PCOS in gynecology
Today, ovarian surgeries are performed laparoscopically. It leaves minimal marks on the patient's body. Main types of surgical intervention:
- wedge resection of the ovaries – a maximum of 2/3 of the cortex and medulla of the ovary is removed, thus stimulating ovulation;
- endothermocoagulation of the ovaries - consists of point cauterization of the hypertrophied stroma.
If the operation is successful, the woman can become pregnant within a year. Often, after surgery, it is necessary to undergo additional drug therapy to obtain the best result.
Relapse
Since today it is not known exactly why some women experience polycystic ovary syndrome and others do not, some relapse after treatment. Therefore, after the first effective treatment, it is necessary to adhere to the correct lifestyle as much as possible. In some cases, to preserve reproductive function, a woman may be prescribed combination hormonal therapy before menopause.
It is necessary to regularly visit a gynecologist and endocrinologist, and also donate blood for sex hormones and thyroid hormones.
Pregnancy and polycystic disease
You can get pregnant with polycystic disease without treatment, you just have less chance of getting pregnant. Moreover, every year the number of cysts increases, this adversely affects the ovarian tissue, so treatment in order to become pregnant must be carried out as early as possible, since with age the likelihood of conceiving a child becomes even less.
Treatment consists of hormonal correction and ovarian stimulation. If a woman experiences menstrual irregularities, she is prescribed oral contraceptives to normalize it. After their use, periods begin regularly and conception is possible. If pregnancy still does not occur, you can try ovarian stimulation. It is carried out according to various schemes, only under the supervision of a doctor. You cannot take ovulation-stimulating drugs on your own, as this can lead to hyperstimulation, which is dangerous for a woman’s health.
Scheme for ovulation stimulation with letrozole
If ovarian stimulation does not help, laparoscopic surgery is possible, during which the cysts are dissected and the dense lining of the ovary is removed, which helps restore blood circulation and normal functioning. Of course, this is a temporary measure, since the cystic changes will form again, but while this happens, the woman’s chances of becoming pregnant increase.
Polycystic ovary syndrome can be eliminated using the following surgical techniques:
- Wedge resection is the excision of androgen-producing ovarian tissue.
- Electrocautery is a low-traumatic procedure that involves destroying tissues that excessively synthesize androgens.
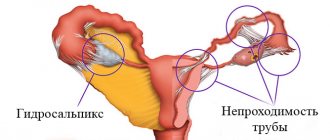
Such operations are now performed using an endoscopic technique - laparoscopy. This is a low-traumatic method of surgical intervention, which is used for both diagnosis and treatment. If polycystic disease is suspected, diagnostic laparoscopy is prescribed. If during the inspection of the abdominal cavity specific changes are detected in the ovaries, the membrane and cystic formations are dissected. The advantages of laparoscopy are that it reduces the risk of formation of adhesions in the abdominal cavity and shortens the rehabilitation period. Often, PCOS is accompanied by adhesions and obstruction of the fallopian tubes. These pathological conditions can be eliminated during laparoscopy.
After a successful operation, ovulation is restored after six months to a year, then the reproductive organs are ready for conception. If pregnancy does not occur after this time, then additional drug therapy is performed. If there is no effect in this case, the best way to get pregnant is to resort to IVF (Read more about in vitro fertilization in this material - note altravita-ivf.ru).
It should be taken into account that when a long-awaited pregnancy occurs after treatment and stimulation, a relapse of polycystic ovary syndrome is possible over a five-year period. Therefore, it is advisable to prevent PCOS after pregnancy, which consists of taking hormonal drugs.
Treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome during pregnancy
Polycystic ovary syndrome is a whole complex of diseases and disorders, which includes a number of different pathologies from ovarian dysfunction to uterine cancer. And among other things, there is infertility. But if a woman has been diagnosed with PCOS, this does not mean that she will never be able to have children. The main cause of impaired fertility in women with this syndrome is the lack of ovulation. And therefore, the doctor’s main goal will be to direct treatment towards stimulating or restoring ovulation. The most common course of therapeutic treatment is taking Clomiphene in combination with Metformin. The first remedy will stimulate the growth of follicles and egg maturation, and the second will help cope with the level of insulin in the blood. If we talk about stronger drugs to stimulate ovulation, then these are gonadotropins, which can also be prescribed to the patient, only in lower doses.
This approach to drug therapy, as well as careful monitoring and supervision by specialists throughout the entire stage of pregnancy, usually allows a woman to successfully conceive and give birth to a healthy child.
In cases where conservative treatment does not give the desired result, the doctor may advise the woman to undergo IVF. But in both cases, the first recommendation of any specialist will be weight loss. Since it is obesity that leads to complications in polycystic ovary syndrome, such as arterial hypertension, miscarriages, gestational diabetes, and premature birth. And this in no way contributes to a normal pregnancy and the birth of a healthy child.
Treatment methods can be either therapeutic or surgical
Surgical intervention for the purpose of surgical manipulation of polycystic ovaries often gives positive results and restores the patient's fertility. But when surgery is not possible, then conservative treatment is resorted to. But the decision about surgery is made taking into account the patient’s age. If an ovarian cyst is detected in a young nulliparous girl, then conservative methods should first be applied that can prevent the development of polycystic disease and preserve fertility.
For treatment, an integrated approach is used, which involves restoring hormonal levels and metabolism, normalizing body weight through diet and physical activity, prescribing pharmacological drugs that increase the effectiveness of deficient hormones and improve the HOMA index (with the development of type 2 diabetes).