According to medical statistics, every third adult in Russia suffers from one or another allergic disease. About 20% of all diagnosed cases of allergies are due to allergic rhinitis, and this figure is growing every year. Allergic rhinitis is a typical diagnosis for residents of megalopolises and large cities, where unfavorable ecology greatly affects the health of both children and adults.
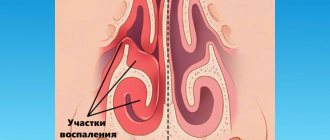
Allergic rhinitis (runny nose) is a disease caused by contact of an irritant (allergen) with the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity.
There are two forms of the disease: seasonal allergic rhinitis (intermittent) and year-round (persistent) rhinitis. From the name of both diagnoses it is clear that in the first case, an exacerbation of allergies occurs at a certain time of the year, usually in spring or summer, when grasses, trees and shrubs are in full bloom, and this condition lasts no more than a month. The second form of the disease is not tied to a specific season, can occur at any time of the year and worries the patient for more than a month. This is a chronic disease, which, in the absence of proper treatment, causes a lot of inconvenience to the patient.
Causes of the disease in adults and children
The list of allergens that provoke allergic rhinitis is quite extensive:
- pollen of flowering plants (ragweed, poplar, alder, birch, etc.);
- house dust;
- fluff;
- pet hair and excretions;
- mold spores;
- insect bites;
- medicines;
- Food;
- spices;
- household chemicals;
- perfumery.
A type of year-round allergic rhinitis is occupational rhinitis, when an adult is allergic to substances with which he is constantly in contact during work: bakers may be allergic to flour dust, veterinarians may be allergic to animal hair and saliva, builders may be allergic to construction materials. dust, etc.
Very often, adult patients do not consult an ENT doctor and try to get rid of allergies on their own, using nasal drops for a long time. And this is a big mistake. Such vasoconstrictor drugs can be used for no more than a week to treat a runny nose and relieve unpleasant symptoms. Constant use of vasoconstrictor drops leads to addiction: the nose stops breathing on its own without a new dose of medicine, and in addition to allergic rhinitis, an adult develops medicinal rhinitis.
A relationship has been established between the development of allergic rhinitis and a hereditary factor: as soon as the ENT doctor begins to collect the patient’s medical history, it turns out that one of the patient’s close relatives is allergic.
Classification and types
Two types of disease with severity and symptoms are indicated in the table
| Name of the disease type | Severity | Features of the flow |
| Intermittent | Lightweight Moderate | The attack develops no more than 4 times in 7 days The illness lasts no more than a month Sleep is not disturbed Symptoms are not pronounced The patient's life goes on as usual |
| Persistent | Moderately Heavy Heavy | Attacks occur more often 4 times every 7 days The disease lasts more than 30 days Symptoms are pronounced Performance is reduced during the day At night, due to nasal congestion and other symptoms, a person cannot get enough sleep |
How to get rid of allergic rhinitis? The doctor will prescribe treatment based on an external examination, age, examination results (form/type of allergic rhinitis, severity and characteristics of the course, the presence of other pathologies in the patient, etc.)
After collecting anamnesis, the treatment algorithm is selected individually for each patient. At the same time, taking special medications for allergic rhinitis is mandatory for all patients. Do not risk your health and consult a doctor on time! Only a specialist can identify competent preventive measures and carry out therapy.
Symptoms of allergic rhinitis
The main symptoms of allergic rhinitis in adults and children: excessive nasal discharge, sneezing attacks, nasal congestion, redness and itching in the eyes, lacrimation.
All these symptoms cause a lot of inconvenience to the patient. Agree, it is very difficult to work, study, and do your usual activities when your nose is not breathing and is constantly leaking.
The first signs of an allergic reaction are similar to the symptoms of colds. How can we understand that we are not dealing with a cold? The characteristic differences between the disease and a cold are as follows:
- with allergic rhinitis, nasal discharge is clear and not thick; with a cold, they are more viscous and have a yellow or greenish tint;
- the classic treatment regimen for colds does not cope with the symptoms, the disease does not recede;
- the allergy occurs without fever;
- Unlike a cold, the reaction after contact with an allergen begins quickly: from a few minutes to hours.
Literature:
- Snegotskaya, M. N. Treatment of allergic rhinitis: the role of topical antihistamines / M. N. Snegotskaya, N. A. Geppe // Attending physician. – 2014. – No. 1.
- Macharadze, D. Sh. Allergic rhinitis: clinic, therapy / D. Sh. Macharadze // Attending physician. - 2022. - No. 10.
- Namazova, L. S. Allergic rhinitis / L. S. Namazova, L. M. Ogorodova // Attending physician. - 2006. - No. 4.
- Vasina, A.A. Differential diagnosis of ARVI and allergic rhinitis in children / A.A. Vasina // Local pediatrician. – 2014. – 02: 7.
- Kareva, E.N. Choosing an antihistamine: a pharmacologist’s view / E.N. Kareva // RMJ. - 2016. - No. 12. - P. 811–816.
- Fomina, D.S. Choosing an antihistamine from the perspective of evidence-based medicine / D.S. Fomina, L.A. Goryachkina // Effective pharmacotherapy. Allergology and immunology. — No. 1 (1).
- Instructions for use of drugs
- Instructions for use of the drug TIZIN® Alergy.
- Instructions for use Tizin® Classic for children and Tizin® Expert for children.
- A.A. Vasilyeva, R.F. Khakimova. Tactics of management of patients with allergic rhinitis during pregnancy, BULLETIN OF MODERN CLINICAL MEDICINE 2015 Volume 8, no. 2, pp. 82-88.
Phases of disease development
The development of allergic rhinitis occurs in two stages.
The first occurs almost immediately after contact with an irritating substance - within the first minutes and sometimes seconds. The allergen enters the body and provokes the production of antibodies. The leading role in this is played by the so-called mast cells, a type of immune cell. They release inflammatory mediators (the most famous is histamine). They are responsible for the appearance of allergy symptoms.
In two thirds of people prone to allergies, after twelve hours (some less) the second phase of allergic rhinitis begins. The so-called “delayed response”. At this time, immune cells (eosinophils, basophils, etc.) concentrate at the site of inflammation. Other inflammatory mediators—cytokines and leukotrienes—are released into the blood. This provokes chronic allergic inflammation in the nasal mucosa and increased sensitivity of the respiratory tract to various irritants, which are usually contained in the inhaled air.
Who is most at risk
It is not entirely clear why some people become hypersensitive to allergens, although the likelihood of developing allergies is higher if there is a history of allergies in the family. Heredity forms atopy, a genetic tendency to develop allergic conditions. Their heightened immune response to allergens leads to increased production of IgE antibodies.
Environmental factors may also play a role. Research has shown that certain factors can increase a child's chance of developing allergies, such as smoking in the home and early exposure to dust mitesSource: Allergic Rhinitis: What is it? Osipova V.V. Asthma and allergies, 2022. p. 19-20.
When and why should you contact an ENT doctor?
Despite the fact that the symptoms of the disease do not seem dangerous, it is necessary to consult an ENT doctor, since constant, chronic inflammation of the nasal mucosa can lead to serious disorders in the body, for example, otitis media, frequent sinusitis, and the formation of polyps. To prevent the development of these pathological conditions, you must immediately contact an ENT doctor to prescribe treatment.
Several research methods are used to make a diagnosis: rhinoscopy; endoscopic examination of the nasal cavity; skin allergy tests; general blood analysis.
After a confirmed diagnosis, a suitable treatment regimen is prescribed.
4. Treatment of non-allergic rhinitis
There is no specific treatment for non-allergic rhinitis. Injections and many allergy medications are not used to treat nonallergic rhinitis. But you can learn to control the problem:
- You can use seawater-based nasal irrigation sprays;
- You should avoid all those factors that cause a runny nose - smoking, household chemicals, etc.;
- You must tell your doctor if you are taking any medications. Perhaps rhinitis appeared precisely because of them, and the doctor will select other drugs that will not cause rhinitis as a side effect.
- Nasal antihistamines, glucocorticoids, or ipratropium may relieve symptoms;
- Decongestant drops and sprays can relieve nasal congestion, but such drops are usually not recommended for use more than two or three times a day.
In some cases, when treatment does not produce the desired results, surgery to remove nasal polyps or correct a deviated septum may improve the effect of drug therapy for rhinitis. But surgery as a method of treating rhinitis can be considered only when other methods of treating rhinitis do not lead to a reduction in the symptoms of rhinitis.
Complications of allergic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis does not belong to the category of dangerous diagnoses. But it often leads to other unpleasant health consequences. Complications are a consequence of swelling of the nasal mucosa and difficulty in nasal breathing:
- Sinusitis is an inflammatory process in the paranasal sinuses.
- Otitis media is an inflammation in the middle part of the hearing organ.
- Enlarged tonsils.
- The growth of polyps - formations arising from the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity and sinuses, and leading to impaired nasal breathing.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, consultation with an allergist is necessary. Often, a doctor can diagnose allergic rhinitis by symptoms as well as personal and family history, noting seasonality and triggers. He may examine the inside of your nose to look for nasal polyps. Allergic rhinitis is usually confirmed at the beginning of treatment. If a patient responds well to antihistamines, the symptoms are almost certainly caused by an allergy.
If the exact cause of allergic rhinitis is not determined, your doctor may refer you to a clinic for allergy testing.
Two main allergy tests:
- Skin testing - an allergen is placed on the arm and the surface of the skin is pierced with a needle to allow the allergen to affect the immune system. If you are allergic to this substance, a small itchy spot (blister) will appear.
- Blood tests – to check for the presence of immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies in the blood; the immune system produces this antibody in response to a suspected allergen.
In some cases, additional tests may be needed to detect complications, such as nasal polyps or sinusitis. Source: Rhinitis: Differential Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines. Guseva A.L., Derbeneva M.L. Medical Council, 2022. p. 102-108.
Treatment of allergic rhinitis in children and adults
Effective treatment of the disease is selected individually for the patient and includes drug therapy supported by physical procedures.
As drug therapy, the patient may be prescribed:
- antihistamines (Zyrtec, Zodak, Suprastin, etc.);
- local antihistamines in the form of nasal sprays (Azelastine, etc.);
- glucocorticosteroid drugs (“Beclomethasone”, “Mometasone”, etc.);
- cromones - drugs that stabilize the membranes of mast cells that produce histamine (a substance responsible for the reaction when interacting with an allergen) (“Sodium Cromoglycolate”, etc.);
- vasoconstrictor drugs (“Nazivin”, “Otrivin”, etc.);
- saline solutions to rinse the nasal mucosa (“Aquamaris”, “Aqualor”).
The effect of taking medications is enhanced by physical procedures performed in the ENT clinic: infrared laser therapy, vibroacoustic therapy, ultraviolet irradiation sessions, laser photodynamic therapy, ultrasound therapy, magnetotherapy. This comprehensive approach allows you to quickly and safely treat children and adult patients.
If the disease is severe and the prescribed therapy does not provide relief from symptoms, immune therapy is performed, when a small amount of the allergen is injected into the patient’s blood over a certain period of time according to a strict schedule in order to gradually reduce and eliminate the body’s susceptibility to the allergen.
It is very important not to let the disease progress and to consult an ENT doctor in time.
Nasal antihistamines
Currently, the most widely used drugs are levocabastine1. With a mild form of allergy and timely initiation of treatment, they can prevent the appearance and alleviate the symptoms of the seasonal form of the disease. For year-round rhinitis, they are used as part of complex therapy or as an independent symptomatic remedy 1. An example of such drugs is Tizin® Alergy.
Levocabastine is a second-generation antihistamine that acts on histamine H1 receptors and thereby reduces its effect on the mucosa1.
A high safety profile and effect of levobaxtine were observed during clinical trials1. It can be used not only by adults, but also by children over 6 years old. According to the results, it relieves symptoms of the disease after just 5 minutes and can maintain its effect for 12 hours1.
TIZIN® Alergy is available in the form of a spray, which allows you to evenly irrigate the mucous membrane of the nasal cavity.
Up to contents
Prevention of allergic rhinitis
The best method for preventing allergic rhinitis is to avoid contact with the allergen. Of course, it is not always possible to do this completely. But you can minimize contacts.
If a person is allergic to household dust, you need to purchase an air cleaner or vacuum cleaner with an air purification function. It is worth abandoning pillows and blankets made from natural materials in favor of synthetic ones. It is advisable to remove carpets and soft toys from the house, and reduce the number of books stored. Wash curtains often and do wet cleaning.
Allergies to pollen most often occur in spring and summer during the period of active flowering of plants. It is important to know the flowering periods of the plants to which you are allergic, and to go outside at this time as little as possible. Close the windows in your apartment to prevent pollen from flying inside. If you can't avoid walking, wear wide glasses to prevent pollen from coming into contact with your eyes. When you return home, shower and remove your street clothes.
Another common allergen is pet dander and excretions. If it is not possible to take your pet away, keep it outside if you live in a private house, or keep it in one room and keep it out of the bedroom. Wash clothes, clean furniture if your pet has sat on it. Wash your pets frequently. If you are going to visit someone who has a pet, take an antihistamine beforehand.
All allergy sufferers are advised to avoid cigarette smoke, strong odors, exhaust fumes, the most allergenic foods (for example, honey), and also see an allergist.
Prevention and cure forecasts
Most symptoms of allergic rhinitis are manageable. In more severe cases, allergy shots are needed. For some people, especially children, allergies may improve or go away as the immune system becomes less sensitive to the trigger. But if a substance, such as pollen, causes an allergy, it often continues to have long-term effects on the person.
The patient can prevent symptoms by avoiding the pollen to which they are allergic. During pollen season, you should stay indoors with air conditioning if possible. Sleep with the windows closed and drive with the windows closed.
Sources:
- Pharmacotherapy of allergic rhinitis. Palchun V.T., Guseva A.L., Levina Yu.V., Derbeneva M.L. Medical Council, 2022. p. 122-127
- Rhinitis: differential diagnosis and principles of treatment. Guseva A.L., Derbeneva M.L. Medical Council, 2022. p. 102-108
- Allergic rhinitis: what is it? Osipova V.V. Asthma and allergies, 2017. p. 19-20
- Allergic rhinitis from the perspective of an allergist. Sidorovich O.I., Luss L.V. Consilium Medicum, 2022. p. 75-78
- Allergic rhinitis. Ryazantsev S.V., Goncharov O.I. Medical Council, 2022. p. 76-79