Most often, the disease develops against the background of reduced immunity under the influence of external factors: bacteria settle on the surface or in the thickness of the tonsils, causing severe inflammation. Without proper and timely treatment, the disease can lead to serious health problems.
There are secondary sore throats that develop against the background of other infectious diseases, for example, sore throat due to scarlet fever, diphtheria, measles, stomatitis, etc.
But there are other types of tonsillitis, so-called atypical, associated with blood pathologies. These include monocytic tonsillitis and agranulocytic tonsillitis.
What is agranulocytosis
The agranulocytic type of sore throat is one of the manifestations of agranulocytosis, which is quite rare.
Make an appointment right now!
Call us by phone or use the feedback form
Sign up
With agranulocytosis, there is a sharp decrease in the number of granular leukocytes in the blood (up to their complete disappearance). Leukocytes, as we know, are the main defenders of our body from viruses and bacteria that have penetrated it. As soon as the infection enters the body, the immune system receives a signal about the invasion, and increased production of leukocytes begins, which capture the “enemy” and destroy it. Of course, if there are very few white blood cells in the blood, a person becomes much more susceptible to the effects of pathogens.
The manifestation of agranulocytic tonsillitis cannot be considered an independent disease. This is a syndrome that occurs against the background of certain diseases. It is impossible to distinguish this type of tonsillitis from others “by eye”; laboratory tests must be carried out.
Most often, the disease manifests itself in people under the age of forty. Children and young people are diagnosed with this diagnosis quite rarely. It is noteworthy that women suffer from the disease twice as often as men.
The main reason for the development of the disease is the incorrect prescription of antibacterial agents and cytostatics (drugs whose action is aimed at inhibiting and suppressing the process of cell division; most often these drugs are used in the treatment of malignant neoplasms).
Leukopenia and agranulocytosis
The proportion of leukopenic conditions among other diseases of the blood system is quite large. Statistical data indicate an increase in the number of patients with severe leukopenia in recent years. Often the development of this pathology is in some connection with the use of new bacteriostatic agents in medical practice, with exposure to ionizing radiation, as well as with an increase in episodes of allergic diseases. In assessing leukopenic conditions, the doctor should avoid two opposing trends: in some cases, there is no due attention to leukopenia, which is the beginning of a severe pathology of the blood system, and the necessary preventive and therapeutic measures are not taken; in others, any decrease in the number of leukocytes is regarded as a symptom of a severe pathology with unfounded the use of potent leukopoietic drugs (drugs that enhance the intensity of the formation of these blood cells). Therefore, to correctly assess the significance of “individual” leukopenia, it is necessary, if possible, to find out its causes and mechanism of development, since only such a solution to the issue ensures the success of treatment and preventive measures in each individual case. Leukopenias are often combined with a significant decrease in the number of neutrophils in the peripheral blood, therefore, in essence they are neutropenia or granulocytopenia (respectively, a decrease in the number of neutrophils and granulocytes).
The causes of granulocytopenia, with all their diversity, are divided into exogenous (acting from the outside), endogenous (arising in the body itself) and hereditary. The first group of factors includes some substances that have a toxic effect, such as benzene, toluene, arsenic, mercury; some medications; radiation; infectious diseases.
Endogenous causes of neutropenia may be a violation of the endocrine regulation of granulocytopoiesis, i.e., the formation of granulocytes (thyrotoxicosis, adrenal insufficiency, dysfunction of the pituitary gland), increased spleen function, allergic conditions.
The listed leukopenias are classified as functional. But leukopenia and neutropenia can be a manifestation of a violation of bone marrow hematopoiesis in systemic blood pathologies: acute leukemia, hypo- and aplastic conditions. In some cases, it is not possible to identify the causative factor leading to the development of granulocytopenia. Recently, there are fewer and fewer such forms.
In recent years, a special group of hereditary neutropenias (constant and periodic neutropenias) has been identified. In addition, leukopenia can be symptomatic in the form of an unstable hematological sign in some diseases.
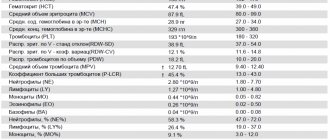
Moderate asymptomatic leukopenia without any clinical manifestations are discovered by chance and are one of the secondary and optional symptoms of various diseases. They are characterized by a moderate decrease in the number of leukocytes (up to 3.0-4.0 H 109/l) and mild granulocytopenia (40-60% of the total number of neutrophils). The functional properties of leukocytes are not changed. Myelopoiesis is not impaired. Bone marrow is normal. There are also no changes in the formation of red blood cells and platelets. Such leuko- and neutropenia are most often purely symptomatic, accompanying a number of diseases not related to the blood system (thyrotoxicosis, gastritis, enterocolitis, cholecystitis, and many others).
Why does agranulocytic sore throat occur?
Factors influencing the lack of leukocytes in the blood are conventionally divided into two types: myelotoxic and autoimmune. In the first case, there is a direct toxic effect on the cells in which leukocytes develop. These cells are called myelocytes. In the second case, under the influence of certain factors, the body begins to consider its own leukocytes as foreign elements and begins to fight against them.
Myelotoxic factors include exposure to ionizing radiation (during radiation therapy, when working with devices that are sources of this type of radiation), improper or uncontrolled use of medications (antibiotics, cytostatics), prolonged exposure to toxins (benzene, petroleum products, mercury, arsenic, insecticides).
Autoimmune causes include some infectious and autoimmune diseases (infectious mononucleosis, typhoid, hepatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus), as well as taking drugs that inhibit the formation of blood cells, including leukocytes (sulfonamides).
Quite often the disease is diagnosed in women during menopause, so scientists do not exclude the influence of hormonal factors on the development of this pathology.
What you need to know about agranulocytosis
Diseases of the blood and blood-forming organs are quite widespread in the world. Blood cells are divided into red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Leukocytes are the main element of the immune system and are heterogeneous in their structure and functions. Morphologically, cells with specific granularity (granulocytes) and cells without it (agranulocytes) are distinguished.
In turn, granulocytes, depending on the color of the inclusions with special staining, are divided into eosinophils, basophils and neutrophils. Typically, neutrophils account for 47 to 70% of all leukocytes. They are the body's main defense against bacteria and fungi. The significant difference in their numbers is due to many factors. On the one hand, these cells have a short life expectancy, on the other hand, too many things affect their numbers: work habits, nervous tension, taking medications, the presence of a bacterial infection. It is with the lack of granulocytes (and primarily neutrophils) that a pathological condition such as agranulocytosis (neutropenia) is associated.
This pathology can extremely rarely be congenital; more often it develops under the influence of external factors. Acquired agranulocytosis can be caused by disorders of the immune system or exposure to toxic substances and other adverse factors on the red bone marrow. Immune damage is characterized by the destruction of leukocytes due to the occurrence of pathological immune reactions in the body, which are associated with external factors and autoimmune processes, such as rheumatoid arthritis or systemic lupus erythematosus. With toxic agranulocytosis, the hematopoietic germ responsible for the production of granulocytes is inhibited. Common causes are poisoning with toxic substances that inhibit hematopoiesis, radioactive radiation, and taking certain medications.
There is a fairly high risk of developing neutropenia during the treatment of cancer, since their therapy widely uses ionizing radiation and cytostatic drugs that have a toxic effect on the red bone marrow.
Immune neutropenia is often associated with the appearance in the body of antibodies to its own leukocytes under the influence of special substances, haptens, which, by binding to proteins, act as antigens. Drugs such as sulfonamides, anti-tuberculosis drugs, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aspirin, analgin, amidopyrine) can act as haptens.
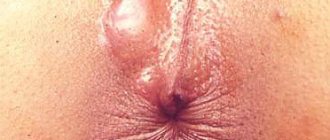
Agranulocytosis is accompanied by the development of various diseases of an infectious nature - tonsillitis, ulcerative stomatitis, pneumonia and other pathological conditions. This is caused by significant contamination of the oral cavity with opportunistic microorganisms, which are activated when immunity decreases. The first manifestations are fever, chills, sweating, and deterioration in general health. The occurrence of ulcerative-necrotic sore throats and stomatitis, which are accompanied by sore throat, increased salivation, and difficulty swallowing, is typical. In severe cases, the intestinal mucosa is affected, which is accompanied by bloating, colic, and diarrhea.
If symptoms are severe, it is necessary to hospitalize the patient as soon as possible in a specialized department, where he will be provided with aseptic conditions. This is necessary to prevent the occurrence of infectious complications. Treatment of agranulocytosis involves eliminating the causes that led to this condition - stopping taking myelotoxic drugs. In the presence of infectious lesions and fever, broad-spectrum antibiotics and antifungal drugs are prescribed. Careful hygienic care of the oral cavity and skin is necessary. If the disease is autoimmune, the use of glucocorticoids is indicated. If the white blood cell count is severely low, a white blood cell transfusion may be required. In each case, the treatment complex is prescribed individually by a hematologist.
Yuri Kuzmenkov, doctor, Republican Scientific and Practical Center "Cardiology"
The doctor's areas of interest are therapy, cardiology, endocrinology.
We are waiting for your questions, friends!
Symptoms of agranulocytosis
The diagnosis can only be confirmed with the help of clinical studies and tests, but some specific signs can indicate the development of the disease. The first symptoms appear within one to two days after infection.
Friends! Timely and correct treatment will ensure you a speedy recovery!
The following symptoms of the disease can be identified:
- rapid onset, a sharp increase in body temperature up to 40°C;
- a symptom of a sore throat is an increasing sore throat, which indicates the spread of infection;
- salivation increases;
- the presence of an unpleasant putrid odor from the oral cavity;
- the appearance of ulcers on the tonsils, then the ulcers spread throughout the mouth; then tissue necrosis occurs at the site of the ulcers;
- nausea;
- signs of inflammation of the oral mucosa and gingivitis are added;
- weakness, lethargy.
If medical assistance is not provided to the patient in time, his condition will rapidly deteriorate: the body temperature rises to 41°C, joints begin to ache, the skin and mucous membranes begin to acquire a jaundiced tint.
Symptoms of a sore throat, signaling that toxic damage to the brain is occurring, are lethargy, immobility of the patient, and the person may begin to become delirious.
If treatment for sore throat is not started in a timely manner, serious complications will begin that can lead to death.
Complications
As we can see, this form of tonsillitis is one of the most dangerous. Delayed treatment can lead to irreversible consequences, including death. The most common consequence of agranulocytic tonsillitis is the transition of the inflammatory process to neighboring organs and tissues with the formation of ulcers on them, followed by tissue necrosis. Perforation of the palate is often observed. There is a high probability of developing sepsis, which entails infectious-toxic shock, diseases of the intestines, genitourinary system, liver, lungs, peritonitis, mediastinitis and other pathologies.
To avoid such complications, it is necessary to consult a doctor promptly when the first signs of the disease appear! The sooner treatment begins, the higher the prognosis for recovery, even in severe cases of the disease. When sepsis occurs, the prognosis is, alas, the most unfavorable.