The autumn-winter period traditionally marks the seasonal outbreak of ARVI (acute respiratory viral infection). This is a group of viral diseases that are transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person through personal contact or through surfaces in public places. Many people underestimate the seriousness of ARVI and believe that it is just a cold, which in any case will go away on its own. However, under no circumstances should you allow an infection to occur and leave it untreated, as this is fraught with complications.
At the first symptoms of acute respiratory viral infections and acute respiratory infections, you can make an appointment with a therapist at the Diagnostic and Treatment Center. Under the supervision of a doctor, the disease will pass easier and with fewer risks.
What is ARVI and how does the disease manifest itself?
The cause of ARVI can be any virus from a large group that includes more than 200 types of microorganisms. Among them are adenoviruses, parainfluenza, rhinoviruses and other pathogens. Strictly speaking, these include the influenza virus, but it is usually considered separately, because the course of the disease with influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections differs significantly.
What are the most common symptoms of ARVI in adults and how does the disease progress:
- The virus primarily affects the respiratory tract (that is why the infection is called respiratory). So the disease makes itself felt with a sore throat, runny nose, cough - these manifestations appear almost immediately and gradually increase.
- With ARVI, the body temperature rises to 37-38°C - this is a sign that the immune system is fighting the virus. Due to elevated temperature and viral intoxication, weakness and a feeling of general weakness appear from the first days of the illness.
- Pain syndrome is not uncommon with ARVI. There may be a headache in the forehead area, and often aches in the joints and bones.
- Sometimes ARVI is quite severe, and dizziness, severe pain in the spine, indigestion and other atypical manifestations are added to the usual symptoms.
The disease is transmitted primarily by airborne droplets. The incubation period for ARVI is short: already 2-3 days after contact with the sick person, the first signs of illness appear.
At the same time, the acute phase of the disease does not last long - on average, after 3-4 days the temperature begins to decrease, and other symptoms gradually recede. Full recovery usually occurs within a week after the onset of the acute phase.
About the disease
Acute respiratory viral infection (ARVI) is a large group of pathologies of the upper and middle respiratory tract, which are provoked by pathogenic microorganisms (viruses).
Scientists have identified approximately 200 pathogens that can cause typical clinical signs. This creates difficulties when it comes to accurately verifying the strain of the virus that caused the child’s illness. According to domestic and foreign experts, 3-4 episodes of ARVI per year are the norm for a child. The Americans even make a clarification. They allow an increase in the number of ARVI episodes up to 12 times per year if the child starts going to kindergarten or school. Experts attribute this to a sharp increase in new “acquaintances” with viruses that the baby had not previously been in contact with. Therefore, it is important to understand that you do not always need to panic when the first snot appears in a 3-year-old child who has not been sick before, if he has begun to actively communicate with peers.
Doctors more often use the term “acute respiratory disease (ARI)” than ARVI. This is due to the fact that in order to mention the viral genesis of the disease, this fact must be confirmed in the laboratory. This is often time-consuming and financially disadvantageous for the patient. Therefore, it is easier to indicate the broader term acute respiratory infections, which includes not only bacterial infections, but also viral ones (ARVI). Diagnosis and treatment of children in both cases is carried out according to the same algorithm, which eliminates the risk of reducing the effectiveness of therapy.
How can a doctor help with ARVI?
At the first signs of ARVI during the epidemic season, it is advisable to immediately make an appointment with a therapist. The doctor will determine the severity of the disease and give recommendations on how to treat it at home.
Antiviral, antipyretic and other drugs should be selected by a specialist; you cannot take them uncontrollably and continue normal life with ARVI symptoms. In addition, sometimes a bacterial infection develops against the background of a viral infection. In this case, you will have to select antibiotics, and only a doctor can do this.
During your appointment, the doctor will comprehensively assess your condition:
- Examine inflamed mucous membranes;
- Feels the lymph nodes;
- Measure blood pressure and pulse;
- Listen to breathing and heart rate;
- He will listen carefully and record complaints - how many days the acute phase of the disease lasts, what symptoms of ARVI are bothering you.
To diagnose an acute respiratory viral infection, a physician may order laboratory tests to distinguish a viral infection from a bacterial one and prescribe appropriate treatment. Moreover, during a seasonal ARVI epidemic, it most often does not matter which virus from a large group of pathogens entered the body and caused the disease.
Diagnosis of ARVI in adults
In most cases, complex tests are not necessary to confirm the diagnosis. But to find out which pathogen caused the infection, the doctor may prescribe a series of tests1.
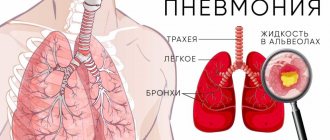
In order to determine the nature of the inflammation, a clinical blood test is performed; to clarify the pathogen, PCR (polymerase chain reaction) or ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay)1 is performed. X-rays are indicated if complications are suspected, such as pneumonia or sinusitis (inflammation of the paranasal sinuses)1.
In the presence of concomitant chronic diseases, additional research methods or specialist consultations may be required1.
Up to contents
Possible complications of ARVI and risk factors
ARVIs are dangerous because they can cause complications in various internal organs. This happens due to a weakened immune system, insufficient treatment and attempts to endure the disease on your feet while continuing to work and live an active life. In this case, a bacterial infection localized in various organs (not necessarily the respiratory system) may be added to the initial disease.
A sign of complications are new symptoms that appear a few days after the onset of the acute phase of ARVI. Also, concomitant diseases may be indicated by a temperature during ARVI, which lasts longer than usual or rises again on days 5-7.
The list of possible complications includes many pathologies, from relatively easy to treat to very dangerous:
- Bronchitis. When the infection penetrates the bronchi, a wet cough and shortness of breath are added to the symptoms of ARVI.
- Pneumonia. In this case, the lung tissue itself becomes inflamed, so the disease is much more severe than bronchitis and often requires hospitalization. Treatment for pneumonia may take several weeks.
- Inflammation of the nasal sinuses - sinusitis, sinusitis. In this case, profuse nasal discharge, congestion, and headache appear. Sinusitis requires special treatment, otherwise it can become chronic.
- Inflammation of the eardrum and middle ear - otitis media. It makes itself felt with severe “shooting” pain and fever; without treatment it can negatively affect hearing and lead to more serious complications.
- Dangerous inflammatory diseases of internal organs: heart (myocarditis), kidneys (pyelonephritis) or even the membranes of the brain (meningitis).
In all cases, you need to urgently consult a doctor and begin treatment, since the listed diseases can pose a threat to life.
If ARVI leads to a complication, the therapist will refer you to a specialized specialist who treats a specific inflammatory process. Some diseases that develop after acute respiratory viral infections are treated in a hospital setting.
Those at risk for complications include adults with chronic diseases, women carrying a child, and pensioners. It is especially important for these people to treat acute respiratory viral infections strictly under the supervision of a doctor and maintain bed rest so that the disease does not lead to more serious consequences for the body.
Treatment of ARVI
Antiviral drugs and basic treatment will be prescribed by a general practitioner. However, you can additionally support your body with effective home remedies and the right regimen to speed up your recovery.
What conditions are important to observe for effective treatment of ARVI:
- Stay in bed at least during the first days of illness, when loss of strength, fever and other symptoms are especially noticeable. If possible, take sick leave. This is important because the human body, when suffering from a viral disease, spends a lot of energy fighting the infection. There is no reserve left for usual activity.
- Drink at least 2 liters of fluid per day. Warm fortified drinks will be especially useful: compote, fruit drink, vitamin decoctions. Instead of black tea, choose herbal tea, and it is better to avoid coffee during an acute period of illness. During an acute respiratory viral infection, the body needs a lot of moisture, because it is constantly excreted through sweat, phlegm, and nasal discharge. Due to this, the body fights the virus.
- Gargle your throat and nose several times a day (a saline solution, for example, is a good gargle). This way you will not only additionally moisturize the mucous membranes, but also wash away pathogens from them, and recovery will come faster.
- Do not lower the temperature below 38 degrees - this is a useful physiological reaction. But if the temperature rises above a critical level and is accompanied by a severe headache, you can take an antipyretic drug - over-the-counter or one prescribed by a doctor.
- Ventilate the room more often so that it is always cool and the contaminated air does not stagnate. There is no need to be afraid of the cold: on the contrary, during illness it is more harmful to be in a dry and warm room.
- Install a humidifier at home. It is important to maintain a sufficient level of humidity in the room so that the mucous membranes of the nose, mouth, and lips do not dry out. Only in this case will they be able to fulfill their protective function and protect against re-infection.
- Use safe home remedies to support your immune system. Ginger, lemon, raspberry jam, turmeric, honey - these products will really strengthen the body's defenses.
How to avoid getting sick during the ARVI epidemic season
There is no vaccine against ARVI, since there are many viruses in this group, and they constantly mutate. However, before the start of the season, you can get vaccinated specifically against influenza (this is also one of the respiratory viruses). The optimal time for vaccination is September-October. But it is important to understand that the vaccine does not provide 100% protection and does not guarantee that you will not get the flu this year. It only reduces the risk and makes the course of the disease easier if infection cannot be avoided.
In general, the human immune system resists infectious agents well, and adults usually do not get sick more than once per season. Simple and accessible measures for the prevention of ARVI will additionally help reduce the risk of the disease.
What to do to avoid getting sick during the cold season:
- Do not go to crowded places unless absolutely necessary. Try to limit yourself to your place of study or work and grocery stores during the period of highest incidence; if you need to visit these places, you should use a medical mask and gloves.
- Wash your hands often with soap, and when this is not possible, use skin disinfectants: wipes, gels, etc.
- Rinse your nose or use seawater sprays every time you return from the street. In order for the nasal mucosa to retain viruses, it must be well moisturized.
- Temper yourself, that is, gradually accustom your body to cold and temperature changes. You can take a contrast shower, douse yourself with cool water, do rubbing and use other methods. The main result of hardening is an organism adapted to stressful external conditions. A seasoned person is at much less risk of hypothermia and getting sick.
- Avoid stress and lead a healthy lifestyle. For strong immunity, it is critically important to get enough sleep, eat a varied and nutritious diet, even in autumn and winter. A healthy routine is the best prevention of seasonal diseases.
- Avoid alcohol. Alcohol attacks the immune system, removes vitamin C and other substances important for protecting against the virus from the body.
- Maintain air humidity in the apartment at a sufficient level. It is important to do this not only during illness, but also all the time the heating radiators are running in the house. A high-quality humidifier device will help achieve air humidity in the house up to 60%, whereas without it in winter this figure usually does not exceed 20%.
Prevention. Is a flu vaccination necessary?
Vaccination is the most important preventive measure against influenza. It is carried out much earlier than the expected epidemic, usually in October–November. The protective effect of the vaccine is one year, so it must be repeated annually. There are practically no contraindications to modern vaccines. Vaccination is indicated for the following population groups (however, you should consult your doctor before undergoing it):
- Children of preschool and school age;
- elderly people (over 65 years old);
- persons with a high probability of infection (military contingents, medical personnel, workers in the sphere of consumer services, transport, educational institutions);
- patients who often suffer from ARVI;
- patients with chronic bronchopulmonary diseases (especially chronic obstructive pulmonary disease);
- patients with chronic heart failure, chronic kidney disease;
- patients with weakened immune systems (diabetes mellitus, HIV infection, spleen removed, or receiving glucocorticoids and cytostatics).
During a flu epidemic, it is too late to administer the vaccine. In this case, it is important to wash your hands with soap and water more often and ventilate the room, wear medical masks in public transport, it is possible to use rimantadine, as well as oxolinic ointment in the nose.
Hardening procedures (rinsing the mouth and nose with cold water, walking barefoot on a cold floor, cold rubbing, dousing, etc.) are important if they are carried out for a long time and systematically. You should not start hardening if a person is sick or in the recovery stage.
Make an appointment with a doctor in Moscow with ARVI symptoms
Get help from a general practitioner for signs of ARVI at the Diagnostic and Treatment Center. With us you can take all the necessary tests within one clinic, quickly receive results and begin treatment. If necessary, the doctor will refer you to another specialist at our multidisciplinary center.
To make an appointment, call us. Registration is available any day, including Saturday and Sunday.
The contents of this article have been checked and confirmed for compliance with medical standards by general practitioner Yulia Vladimirovna Butskikh.