In this section you will learn:
- How often does it occur?
- Causes of miscarriage
- Symptoms
- Stages
- Possible complications
- How to diagnose
- How to treat
- Recovery after treatment
- Prevention
An unexpected termination of pregnancy in the first trimester, accompanied by pain and bleeding, is called spontaneous abortion, or miscarriage. This dangerous condition not only stops the development of the embryo, but also threatens the life of the woman. The consequences of a miscarriage damage the reproductive organs and reduce the chances of becoming pregnant in the future.
What are the signs of a miscarriage?
To understand what's going on, you need to understand what spontaneous miscarriage looks like. The most common symptom is excessive bloody discharge with clots. Sometimes they can be weak at first, and then quite large. You should monitor your condition and if even slight bleeding begins, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Sometimes a miscarriage can start suddenly. But it happens that before this there may be slight nagging pain in the lower abdomen, lower back, and brown spotting.
Women may not immediately realize that they are having a miscarriage. Especially if the delay is only a few days, and the test was not done, then you might think that your period just started.
But usually, a woman who already knows about her pregnancy remembers how a spontaneous miscarriage occurs forever. In most cases, this is heavy bleeding with blood clots, mucus and severe abdominal pain. If measures are not taken immediately, chills, fever, and the skin may become pale. The patient may even lose consciousness. If a woman does not immediately see a doctor or call an ambulance, she may even die from blood loss, since sometimes such bleeding can be incredibly serious.
Spontaneous miscarriage may also have symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, frequent urination, dizziness, weakness,
Genetic testing will give the answer
- First, it is definitely worth doing genetic tests on the miscarriage material.
- Secondly, both partners should also check their karyotype and consult a geneticist.
- After a miscarriage, every woman should also undergo an ultrasound examination, which will evaluate the structure of her reproductive organs.
- The gynecologist will definitely prescribe hormonal and immunological tests.
Genetic testing
One of the most well-known causes of recurrent miscarriages is congenital thrombophilia. This is the body's genetic tendency to form clots in the veins and arteries. This occurs due to a defect in three mechanisms that control blood clotting:
- inhibition of thrombin synthesis;
- factor V inactivation;
- fibrin breakdown.
Undiagnosed and untreated thrombophilia can lead to venous thrombosis, arterial embolism, recurrent miscarriages, severe preeclampsia, HELLP syndrome, liver infarction, thrombocytopenia, intrauterine growth restriction and many other equally serious complications. Therefore, after a miscarriage it is worth getting it diagnosed. It consists of detecting mutations in genes responsible for coagulation processes.
What can cause early miscarriage?
Why does it happen that a miscarriage occurs? Many reasons can be given here, but in each specific case, research is carried out, the patient undergoes tests.
The causes of spontaneous abortion may be as follows in the first trimester:
- Increased contractile activity of the uterus, which literally “pushes out” the embryo.
- Genetic abnormalities in the fetus. Sometimes this happens once in one woman, as a result of genetic “breakdowns”. And it happens that it’s all about the genes of the future father and mother, and therefore it is necessary to look for problems together with a geneticist.
- Lack of the hormone progesterone. This is the so-called “pregnancy hormone”. If it is not enough, then it is prescribed additionally.
- Immunological disorders that prevent the embryo from developing normally.
- Intoxication.
- In the second trimester, the reasons for miscarriage may be slightly different:
- Uterine fibroids.
- Adhesive processes in the pelvic organs.
- Polyps in the uterus that prevent the embryo from developing normally.
- Endometriosis, which causes connective tissue to grow outside the uterus.
- Pathology of the cervix, namely an open cervix, which does not allow you to carry a child to term and give birth to it on time.
- Infections that can cross the placenta and cause fetal death.
- Some chronic diseases of the mother.
But besides this, there may be many other specific reasons that are individual for each woman. For example, hard physical work, work in hazardous enterprises, severe stress and anxiety can also cause spontaneous abortion. Many women are at risk of spontaneous miscarriage, but not everyone can have an abortion. Much depends on the state of health, immunity, even emotional state.
Spontaneous miscarriages in the first trimester
Etiology . The causes of spontaneous abortions are divided into genetic and external. It is believed that 60-80% of spontaneous miscarriages in the first trimester (early spontaneous miscarriages) are associated with chromosomal abnormalities; this rate is actually higher given that termination of an abnormal pregnancy can occur before implantation. The frequency of fetal chromosomal abnormalities during miscarriages is less (30%) in the second trimester; the frequency of chromosomal abnormalities in stillbirths is only 3%.
An increase in the number of spontaneous miscarriages associated with chromosomal abnormalities is observed in women over 35 years of age. The most common type of chromosomal abnormalities (50% of cases) that lead to spontaneous abortion are autosomal trisomies (non-disjunction of chromosomes during meiosis); in 2/3 of cases of trisomy, trisomy 16 occurs. In 10-20% of cases, the cause of spontaneous abortion is monosomy X (45, X0).
Spontaneous miscarriages can also be caused by infections, maternal anatomical abnormalities, immune and endocrine factors. In most cases of early spontaneous abortions, the cause remains unknown.
Diagnostics
Most patients with spontaneous miscarriage complain of bleeding from the vagina. Patients may complain of contractions, pain in the lower abdomen and a decrease in signs of pregnancy (cessation of nausea, softening of the mammary glands, etc.). An objective examination evaluates the state of hemodynamics and the presence of fever. During vaginal examination, differential diagnosis is made with other conditions that may cause bleeding.
Pay attention to the size of the uterus and the dilatation of the cervix. Laboratory testing includes an analysis of hCG levels, a general blood test, determination of blood group and Rh factor; in Rh-negative pregnant women, the titer of anti-Rh antibodies is also determined. Ultrasound examination allows you to determine signs of fetal life or death and features of placentation.
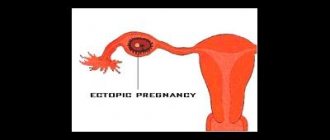
Differential diagnosis of early spontaneous miscarriage from ectopic pregnancy involves monitoring hCG levels. Visualization of fetal cardiac activity by ultrasound or a doubling of hCG levels every 48 hours in early pregnancy indicates a progressive intrauterine pregnancy.
Differential diagnosis for bleeding in the first trimester of pregnancy
- spontaneous abortion
- postcoital bleeding
- ectopic pregnancy
- lesions or trauma to the cervix and vagina
- hydatidiform mole
- bleeding not related to pregnancy
Treatment depends on the type of miscarriage and the patient's desire to continue the pregnancy. The first stage of treatment is hemodynamic stabilization. In case of a complete abortion, monitoring is carried out for the possible occurrence of re-bleeding or an increase in body temperature. Any tissue that is removed from the uterus is subject to mandatory histological examination and chromosomal analysis.
In case of incomplete, inevitable and uncompleted miscarriage, the following treatment options are possible:
1) waiting until the spontaneous completion of the miscarriage (provided that hemodynamics are stable);
2) curettage of the uterine cavity;
3) administration of prostaglandins (misoprostol) to induce uterine contractions and dilation of the cervix.
Patients with a threatened miscarriage who are ready to continue the pregnancy are prescribed bed rest, sexual intercourse and the introduction of any drugs into the vagina are prohibited. Drug treatment often includes progestins (duphaston, utrozhestan), human chorionic gonadotropin preparations (pergonal, prophase).
For bleeding in the early stages of gestation, estrogens are also used to maintain implantation (proginova, microfolin) until the bleeding stops. Spontaneous cessation of bleeding is often observed. Patients with episodes of bleeding during pregnancy are at greater risk of preterm labor and premature rupture of membranes in preterm pregnancy.
Rh-negative patients who have had bleeding episodes during pregnancy should be prescribed anti-Rhesus immunoglobulin. For infected (septic) abortion, febrile treatment begins with an infusion of broad-spectrum antibiotics and metronidazole in combination with intramuscular antibiotics of another class; after normalization of body temperature and vital functions, careful evacuation of the fertilization product is carried out (vacuum aspiration or curettage).
What types of miscarriage can there be?
There are several types of spontaneous abortions:
- Early (up to 12 weeks)
- Late (13-22 weeks).
You can also distinguish some other types:
- Threatening miscarriage. It manifests itself as slight abdominal pain, spotting, and the muscles of the uterus are quite active. But at the same time the cervix is closed.
- Incipient miscarriage. There is a detachment of the ovum, bloody discharge. The cervix is closed, but the internal os is open.
- Abortion is on the move. The fertilized egg leaves the uterus and is located in the cervical canal. Severe pain and bleeding begin.
- Incomplete abortion. Part of the egg may come out of the uterus, and part may still be in it. In this case, there is severe bleeding, abdominal pain, and shock may develop.
- Complete abortion. With it, the fertilized egg is completely released from the uterus. This is a “mini birth”, with some bleeding and abdominal pain.
- Failed abortion. With it, the fertilized egg remains in the uterus. In this case, the fetus is already dead. Such an egg can remain inside a woman for some time, her condition worsens, and signs of pregnancy disappear.
Also, such miscarriages can be divided into several more types:
- Interrupted biochemical pregnancy. It happens within 1-3 weeks. But a woman usually perceives it as the beginning of her period.
- Spontaneous miscarriage (before 22 weeks).
- Premature birth (after 22 weeks).
Diagnosis of miscarriage
To accurately understand that a spontaneous abortion has occurred, it is necessary to correctly diagnose it. To do this you should:
- Analyze the patient's complaints. Usually this is bleeding, pain and cramps in the abdomen, poor general health, pale skin, increased body temperature.
- Conduct a gynecological examination. The uterus is palpated, the cervix and external os are examined.
- Colpocytological examination is carried out.
- They take tests for certain hormones.
- An ultrasound of the pelvic organs is performed.
If such miscarriages occur frequently, then it is necessary to find out the reason. To do this, they conduct various studies, consultations with geneticists, endocrinologists and other specialists.
How to carry out treatment?
How to treat a spontaneous miscarriage depends on the type of miscarriage. If it is threatening and has begun, then the following must be taken:
- The woman must be in hospital.
- A diet that contains all the necessary minerals and trace elements.
- The patient must remain in bed.
- Sedative medications and drugs that relax the muscles of the uterus should be prescribed.
- If abortion is “in progress,” then all measures must be taken to stop the bleeding.
- If the abortion is complete and incomplete, then everything “unnecessary” that is in the uterus should be removed. For this purpose, curettage can be used.
- If there is a failed abortion, then sometimes they use expectant tactics, when they wait for everything to “come out of the uterus on its own.” And sometimes they do curettage.
- Also, sometimes during a frozen pregnancy, expectant management can be used, especially for nulliparous women. Then after about 4-6 weeks a spontaneous miscarriage may occur. Sometimes drug treatment is used, in which special pills are used to help complete the pregnancy. And sometimes they do surgical curettage.
In any case, abortion should not be left to chance; you must consult a doctor who will choose a treatment tactic.
What consequences?
Typically, spontaneous miscarriage in early pregnancy carries certain risks. The consequences of spontaneous miscarriage can be different:
- Heavy bleeding, pain.
- Infertility.
- But the most difficult and life-threatening miscarriages are those that a woman causes herself, at home. If they are not treated and the consequences are not eliminated, they can result in the woman’s death.
Usually, if the patient was provided with high-quality medical care, there are practically no complications. After about 10 days, the bleeding stops, and after 4 weeks the woman begins her normal menstruation.
Chances of getting pregnant after a late miscarriage
It should be understood that after a late miscarriage there is always a chance of getting pregnant again. However, it must be remembered that after a miscarriage, the likelihood of terminating a subsequent pregnancy increases by twenty-five percent. Its risks can only be minimized by timely, comprehensive treatment. You need to approach your next pregnancy carefully and responsibly.
First of all, a woman should know that for several weeks after a miscarriage she is not recommended to be sexually active in order to avoid infection of the uterine mucosa. And the uterus should recover after a miscarriage. You can expect your first period only starting from the fifth week after a spontaneous abortion.
It is worth planning a pregnancy after a late miscarriage after six months. At this time, it is necessary to contact the reproductive center to find out the reasons for the termination of pregnancy. It is recommended that the husband also undergo a full examination with a spermogram. It is also necessary, having found out the cause of late-term miscarriage, to undergo a course of treatment. Excellent results are obtained after spa treatment.
It is also necessary to restore the psycho-emotional balance of the spouses, give time to realize what happened and cope with emotions. They may need help from a psychologist. Sometimes women fall into a state of depression, from which they can recover after consulting a psychotherapist.
In some cases, genetic counseling may be necessary. Modern genetics makes it possible not only to identify the causes of miscarriage, but also to predict the risks of subsequent conceptions, as well as to prevent miscarriage. You should discuss with your gynecologist the contraceptive methods that are safest for a woman planning a pregnancy after a late miscarriage.
Is there any prevention?
Pregnancy after a spontaneous miscarriage can occur and be quite successful. But first the cause of the abortion must be established. If these are genetic problems, endocrine pathologies, problems with the blood or the uterus, then it is necessary to undergo special treatment. But there are general recommendations that will help reduce the risk of miscarriages:
- After termination of pregnancy, a woman needs to rest well, gain strength, take a course of vitamins, possibly oral contraceptives, prescribed by the doctor. It is best to plan your next pregnancy after about 6 months.
- You should lead a healthy lifestyle.
- Do not smoke or drink alcohol.
- Exercise regularly.
- Take vitamins and balanced meals.
- Visit your gynecologist regularly.
- Have fewer stressful situations, give up heavy physical activity.
- Reduce work with harmful substances and poisons to a minimum.
- Normalize weight if it is too small or, on the contrary, too large.
- Consultations with a psychologist and psychotherapist are possible.
Spontaneous abortion is an unpleasant phenomenon that can happen to every woman. But it is necessary to carry out treatment correctly and consult a doctor on time. In addition, preventive measures should be taken.
Previous abortions
Getting and maintaining a pregnancy is often complicated by a previous abortion. Even the safest option, termination of pregnancy with the help of special medications, greatly affects the hormonal balance. Among the delayed consequences of these drugs is disruption of the ovaries and adrenal glands, which are responsible for the hormones on which the onset of the next pregnancy depends.
Vacuum cleaning or surgery often injures the walls of the uterus. Injuries lead to inflammation, scar formation, and neoplasms, which increase the risk of miscarriage and reduce the possibility of conception.
What can be done in this case? If a woman has had an artificial termination of pregnancy, then before conception it is advisable to examine the uterus and evaluate its condition.