Pharmacological properties of the drug Naklofen
Diclofenac ([o-(2,6 dichloroanilino)phenyl]acetate sodium salt) is an NSAID with pronounced anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic effects. The mechanism of action is associated with the inhibition of COX and the resulting disruption of prostaglandin synthesis. By blocking the synthesis of prostaglandins, diclofenac eliminates or significantly reduces the severity of symptoms of inflammation. Diclofenac reduces prostaglandin-induced increased sensitivity of nerve endings to mechanical stimuli and biologically active substances that are formed at the site of inflammation. Helps lower body temperature, preventing the effect of prostaglandins on the hypothalamic region of the thermoregulation process, reduces the concentration of prostaglandins in menstrual blood and the intensity of pain during primary dysmenorrhea. During treatment with diclofenac, the concentration of prostaglandins in the urine, gastric mucosa and synovial fluid decreases. During the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, the drug intensively penetrates into the joint cavity, reduces pain at rest and during movement, helps to increase the range of motion in the affected joints, and reduces morning stiffness and swelling of the joints. Naklofen is used to treat rheumatic diseases; to eliminate pain of any localization of various origins. The tablets are coated with an acid-resistant coating and dissolve after entering the intestines. Naklofen Duo contains diclofenac in the form of granules that are resistant to the action of gastric juice and prolonged-release granules, as a result of which the capsules have both rapid and prolonged action. Retard tablets are intended for long-term treatment. After oral administration, diclofenac sodium is rapidly absorbed in the duodenum and small intestine. Over 90% of the drug is absorbed, but due to metabolism during the initial passage through the liver, bioavailability is about 60%. About 99% of diclofenac binds to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. The half-life is 1–2 hours. More than 70% of diclofenac is excreted in the urine in the form of biologically inactive metabolites, only 1% is excreted unchanged. Diclofenac easily penetrates into the synovial fluid, where its concentration reaches 60–70% of the level in the blood serum. After 3–6 hours, the concentration of the drug and its metabolites in the synovial fluid is higher than in the blood serum. Diclofenac is eliminated from synovial fluid much more slowly than from blood serum.
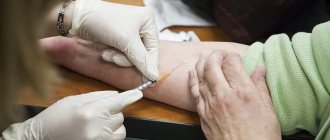
Naklofen injection solution 75 mg/3 ml in 3 ml ampoules in blister No. 5x1
Name
Naklofen solution din. 75mg3ml per amp. 3ml per blister. in pack №5x1
Description
A clear, colorless or light yellow solution, practically free of particles.
Main active ingredient
Release form
The solution for intramuscular administration is transparent, colorless or slightly yellowish, without visible mechanical inclusions.
Dosage
75mg 3ml
special instructions
The drug, when administered intramuscularly, is intended for the treatment of:
- inflammatory and degenerative forms of rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, osteoarthritis, arthrosis, spondyloarthritis, vertebral pain syndrome, extra-articular rheumatism;
- acute attacks of gout;
- renal and hepatic colic;
- inflammation, pain and swelling after injuries and operations;
- severe migraine attacks.
The drug, when administered as an intravenous infusion, is intended for the treatment or prevention of postoperative pain.
Pharmacodynamics
Diclofenac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug with analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. It inhibits the activity of cyclooxygenase and therefore the synthesis of prostaglandins. During treatment with diclofenac, a decrease in prostaglandin levels is observed in urine, gastric mucus and synovial fluid. The drug is used to treat all forms of rheumatic diseases, as well as to reduce pain of various origins.
Pharmacokinetics
Distribution. Maximum plasma concentration is achieved after half an hour. More than 99% of diclofenac is bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. Diclofenac enters the synovial fluid, where it reaches a concentration of 60 to 70% of the plasma value. After a period of time from 3 to 6 hours, the concentration of the active substance and its metabolites in the synovial fluid is higher than in plasma. Diclofenac is eliminated more slowly from synovial fluid than from plasma. Metabolism and excretion. The biological half-life (T1/2) is 1? 2 hours. With mild renal or hepatic dysfunction, it remains unchanged. Diclofenac is almost completely metabolized in the liver, mainly by hydroxylation and methoxylation. About 70% of the drug dose is excreted in the urine in the form of pharmacologically inactive metabolites. Only 1% of diclofenac is excreted unchanged. The remainder of the metabolites are excreted in bile and feces. In elderly patients, absorption, metabolism or excretion of the drug is not significantly altered.
Directions for use and doses
Side effects can be minimized by using the minimum effective dose for the minimum period necessary to control symptoms (see Precautions section). Naklofen injection solution can be administered intramuscularly, by deep injection into the upper outer quadrate of the gluteus maximus muscle, or as a slow intravenous infusion after dilution, as described in the instructions. Naklofen injection solution (for intramuscular or intravenous administration) should not be used for more than two days; If necessary, treatment can be continued with Naklofen tablets, capsules or suppositories. Each ampoule is intended for single use only. The solution should be used immediately after opening the ampoule. Any unused contents must be discarded. Intramuscular injection In order to prevent damage to nerves or other tissues at the site of intramuscular injection, the following rules must be observed. The dose is usually one 75 mg ampoule per day, by deep injection into the superior outer quadrant of the gluteus maximus muscle. If two injections per day are required, then one injection is given in each buttock. Alternatively, one 75 mg ampoule can be combined with other dosage forms of Naklofen (enteric-coated tablets, extended-release tablets, capsules or suppositories) up to a maximum daily dose of 150 mg. For migraine attacks, available clinical experience is limited to use as follows: treatment begins as early as possible with 1 ampoule of 75 mg, if necessary, treatment is continued with suppositories on the same day at a dose of up to 100 mg. The total dose on the first day should not exceed 175 mg. There is no data on the use of Naklofen for more than 1 day for migraine. If it is necessary to continue treatment in subsequent days, you should limit yourself to the use of suppositories in a daily dose of up to 150 mg, divided into several single doses. Intravenous infusions Naklofen solution for injection should not be administered as an intravenous bolus injection. Immediately before starting the intravenous infusion, Naklofen, depending on the required duration, should be diluted in 100? 150 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution or 5% glucose solution, buffered sodium bicarbonate injection (0.5 ml of 8.4% solution or 1 ml of 4.2%) taken from a freshly opened container; add to this solution the contents of one ampoule of Naklofen. Only clear solutions can be used. If the solution contains crystals or sediment, it cannot be used for infusion. Two alternative dosage regimens for Naklofen, injection solution are recommended. For the treatment of moderate to severe postoperative pain, 75 mg should be administered continuously over 30 minutes to 2 hours. If necessary, treatment can be repeated after a few hours, but the dose should not exceed 150 mg in any 24-hour period. To prevent postoperative pain, a loading dose of 25-50 mg should be administered 15 minutes to 1 hour after surgery, followed by a continuous infusion of approximately 5 mg/hour up to a maximum daily dose of 150 mg. Selected patient groups Elderly patients (65 years and older) The use of the minimum effective dose is recommended. Patients with proven congestive heart failure (NYHA II-IV), coronary artery disease, peripheral arterial disease and/or cerebrovascular disease Diclofenac is contraindicated in patients with proven congestive heart failure (NYHA II-IV), coronary artery disease, peripheral arterial disease and/or cerebral vessels. Patients with impaired renal function Diclofenac is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment. Since specific studies have not been conducted in patients with impaired renal function, specific recommendations for dose adjustment cannot be made. Caution is recommended when using diclofenac in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment. Patients with impaired liver function Diclofenac is contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment. Since specific studies have not been conducted in patients with impaired liver function, specific recommendations for dose adjustment cannot be given. Caution is recommended when using diclofenac in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. Method of administration: Intramuscular or intravenous administration.
Use during pregnancy and lactation
Suppression of prostaglandin synthesis can adversely affect the course of pregnancy and intrauterine development of the fetus. Data from epidemiological studies indicate an increased risk of miscarriage and/or the development of heart defects and gastroschisis after taking prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors in early pregnancy. The absolute risk of cardiovascular disease increases from less than 1% to 1.5%. The risk is believed to increase with increasing dose and duration of therapy. It has been shown that in animals, the administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors leads to disruption of embryo implantation. In addition, in animals receiving a prostaglandin synthesis inhibitor during the period of organogenesis, the incidence of various developmental defects, including developmental disorders of the cardiovascular system, increased. Diclofenac should not be prescribed during the first two trimesters of pregnancy unless the benefit outweighs the risk to the fetus. If, after all, Naklofen is used by a woman in the first or second trimester of pregnancy, then the dose should be minimal, and the duration of treatment should be ? as short as possible. As with other NSAIDs, use of the drug during the third trimester of pregnancy is contraindicated. When taking prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors in the third trimester of pregnancy, the fetus may have: 1) premature closure of the ductus arteriosus and pulmonary hypertension, 2) renal dysfunction, with the progression of which renal failure with oligohydroamnion develops. When taking diclofenac at the end of pregnancy, weak labor may develop and the duration of labor may increase. In the mother and in the fetus/newborn, bleeding time may be prolonged; the antiaggregation effect may occur even after taking very low doses of diclofenac. Therefore, diclofenac is contraindicated during the third trimester of pregnancy. Lactation Like other NSAIDs, small amounts of diclofenac are excreted in breast milk. Therefore, diclofenac should not be used during breastfeeding to avoid unwanted effects in the baby. Effects on fertility The use of diclofenac sodium may impair female fertility and is not recommended for women trying to conceive. In women experiencing difficulty conceiving, or with a suspected diagnosis of infertility, treatment with diclofenac sodium should be discontinued. Effect on the ability to drive vehicles and equipment Naklofen has a slight or moderate effect on the ability to drive vehicles and machines. Patients who experience dizziness and/or other undesirable central nervous system effects while taking diclofenac should not drive or operate hazardous machinery.
Precautionary measures
Side effects of the drug can be reduced by using the lowest effective dose for the shortest period necessary to relieve symptoms. Co-administration of Naklofen with other NSAIDs, including selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors, should be avoided due to the lack of evidence of synergistic effects and the occurrence of potentially dangerous additive effects. If there are medical indications, it is recommended to prescribe treatment to elderly patients with caution. In particular, treatment should be started with the lowest effective dose of the drug, especially in frail elderly patients or those with low body weight. As with other NSAIDs, diclofenac may in rare cases cause allergic reactions, including anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions. Like other NSAIDs, due to its pharmacodynamic properties, diclofenac can mask the signs and symptoms of infectious diseases. Effect on the gastrointestinal tract When taking NSAIDs, including diclofenac, gastrointestinal bleeding, ulceration or perforation, sometimes fatal, was observed regardless of the period of treatment and was accompanied or not accompanied by symptoms and a history of serious gastrointestinal disorders. They tend to have more serious consequences in older people. If ulcers or gastrointestinal bleeding occur in patients receiving diclofenac, the drug should be discontinued. As with other NSAIDs, including diclofenac, medical supervision is necessary, and particular caution should be exercised when prescribing diclofenac in patients with symptoms suggestive of gastrointestinal disorders, patients with a history of gastric or intestinal ulcers, bleeding or perforation. The risk of gastrointestinal bleeding increases with increasing dose of NSAIDs, especially in patients with a history of ulcers complicated by hemorrhage or perforation. Elderly patients have a higher incidence of adverse reactions when taking NSAIDs, especially gastrointestinal bleeding and perforation, sometimes fatal. To reduce the risk of gastrointestinal toxicity in patients with a history of peptic ulcers (complicated by bleeding or perforation) and in elderly patients, treatment should begin with the lowest effective dose of the drug. These patients should consider combination therapy with protective agents (for example, misoprostol or proton pump inhibitors), as well as patients taking drugs containing low doses of acetylsalicylic acid (acetylsalicylic acid/aspirin drugs increase the risk of gastrointestinal disorders). Patients, especially older patients, should report any unusual abdominal symptoms (especially bleeding) to their doctor. Caution should be exercised when prescribing Naklofen to patients concomitantly taking medications that may increase the risk of bleeding and ulcers, such as systemic corticosteroids, anticoagulants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors or antiplatelet agents. Careful medical supervision is necessary for patients suffering from ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease, since the course of these diseases may worsen. Effect on the liver Careful medical supervision is necessary for patients with impaired liver function, because. their condition may worsen. During therapy with diclofenac, an increase in the activity of liver enzymes may be observed. Diclofenac should be discontinued immediately if elevated liver enzymes persist or increase, clinical signs suggestive of liver disease, or other manifestations (eg, eosinophilia, rash) appear. With long-term use of diclofenac, regular monitoring of liver function is recommended. When taking diclofenac, hepatitis may occur without previous symptoms. Caution should be exercised when prescribing diclofenac to patients with hepatic porphyria, because this may cause an exacerbation of the disease. Effect on renal function Cases of fluid retention and edema have been reported when taking NSAIDs, including diclofenac. Particular caution should be exercised in patients with impaired cardiac or renal function, in patients with a history of hypertension, in elderly patients receiving concomitant therapy with diuretics or drugs that may significantly affect renal function and in patients with significant extracellular volume depletion. associated with various reasons, for example, before or after major surgery. When prescribing diclofenac, regular monitoring of renal function is recommended. Canceling therapy is usually accompanied by normalization of their functions. Effects on the skin and subcutaneous tissue In rare cases, serious skin reactions, some fatal, have been reported with the use of NSAIDs, including exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis. Patients are at greatest risk at the beginning of therapy: in most cases, reported adverse reactions occurred in the first month of treatment. Treatment with Naklofen should be stopped at the first signs of skin and mucous rashes, as well as other signs of hypersensitivity. Effect on the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems Patients with arterial hypertension and/or mild congestive heart failure require careful monitoring due to the possible development of fluid retention and edema during treatment with non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Results from clinical trials and epidemiological data suggest an increased risk of arterial thromboembolic complications (eg, myocardial infarction or stroke) associated with the use of diclofenac, especially at high doses (150 mg per day) and during long-term treatment. In patients at high risk of cardiovascular events (for example, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, smoking), diclofenac is prescribed only after a thorough examination. The risk of cardiovascular events depends on the dose and duration of treatment with diclofenac; therefore, the lowest effective dose and shortest duration of treatment should be used. Depending on the relief of symptoms and the patient's condition, the dosage of the drug should be periodically reviewed. Hematological effects It is recommended to prescribe diclofenac only for a short period. During long-term therapy, careful monitoring of blood counts is necessary. Like other NSAIDs, diclofenac may temporarily inhibit platelet aggregation. Patients with disturbances in the hemostatic system should be carefully monitored. Pre-existing asthma In patients with asthma, seasonal allergic rhinitis, swelling of the nasal mucosa (ie, nasal polyps), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, or chronic respiratory tract infections (especially those associated with allergic rhinitis or having similar symptoms) more often than other patients, exacerbations of bronchial asthma (so-called analgesic intolerance), Quincke's edema or urticaria occur. Therefore, such patients, as well as patients suffering from allergies to other substances with skin reactions, itching or urticaria, are advised to take special precautions. Information on excipients 3 ml of solution (one ampoule) contains 120 mg of benzyl alcohol. Benzyl alcohol is contraindicated in newborns and children under 3 years of age. In susceptible individuals, especially those with a history of asthma or allergies, metabisulfite may cause allergic-type reactions, including symptoms of anaphylactic reaction and bronchospasm. Naklofen contains less than 1 mmol (23 mg) sodium per dose, i.e. essentially “sodium-free.”
Interaction with other drugs
Lithium: Coadministration may increase plasma concentrations of lithium. Therefore, monitoring serum lithium levels is recommended. Digoxin: Coadministration may increase plasma concentrations of digoxin. Therefore, monitoring serum digoxin levels is recommended. Diuretics and antihypertensive drugs: Like other NSAIDs, co-administration of diclofenac with diuretics or antihypertensive drugs (for example, beta blockers, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACE)) may result in a decrease in their antihypertensive effect. Therefore, when combining these drugs, caution should be exercised, especially in elderly patients, and periodic monitoring of blood pressure is also necessary. After the start of concomitant therapy and periodically during its further continuation due to the increased risk of developing a sufficient amount of fluid while taking diuretics with potassium-sparing drugs in the blood serum. Therefore, frequent monitoring of potassium levels is necessary. Other NSAIDs and corticosteroids: Concomitant use of diclofenac and other systemic NSAIDs or corticosteroids may increase the incidence of adverse gastrointestinal effects. Anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents: It is recommended to use with caution, because coadministration may increase the risk of bleeding. Despite the fact that clinical studies have not revealed the effect of diclofenac on the action of anticoagulants, there are isolated reports of an increased risk of bleeding in patients receiving diclofenac and anticoagulants simultaneously. Such patients should be carefully monitored. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs): Concomitant use of systemic NSAIDs, including diclofenac, and SSRIs may increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding. Antidiabetic drugs: Clinical studies have shown that diclofenac does not interfere with the clinical effects of oral antidiabetic drugs. However, there are isolated reports of hypoglycemic and hyperglycemic effects requiring changes in the dosage of antidiabetic drugs during treatment with diclofenac. Therefore, glucose monitoring is recommended as a precaution during concomitant therapy. Methotrexate: Diclofenac may inhibit tubular renal clearance of methotrexate and thereby increase its levels. During concomitant therapy, it is recommended to use NSAIDs, including diclofenac, with caution. Since diclofenac can increase the concentration and, therefore, the toxicity of methotrexate, this drug is administered at least 24 hours before or after treatment with methotrexate. Cyclosporines: Diclofenac, like other NSAIDs, may increase nephrotoxicity due to its effect on renal prostaglandins. Diclofenac is recommended to be administered in doses lower than those that would be used in patients not receiving cyclosporines. Quinolone antibacterials: There have been isolated reports of seizures, which may have been associated with the concomitant use of quinolones and NSAIDs. Phenytoin: When taking phenytoin together, periodic monitoring of phenytoin plasma concentrations is recommended due to the possible increase in phenytoin. Colestipol and cholestyramine: These substances may delay or reduce the absorption of diclofenac. It is therefore recommended that diclofenac be administered at least one hour before or 4 to 6 hours after colestipol/cholestyramine administration. Potent CYP2C9 inhibitors: It is recommended to use diclofenac with caution with strong CYP2C9 inhibitors (for example, sulfinpyrazone and voriconazole), because Significant increases in maximum plasma concentration and exposure of diclofenac may occur due to inhibition of its metabolism. Use with caution with other drugs known to be hepatotoxic, for example, antibiotics, antiepileptic drugs.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity to diclofenac, sodium metabisulfite, or other components of the drug. Like other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, diclofenac is contraindicated in patients in whom hypersensitivity to salicylates or other prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors manifests itself in the form of bronchial asthma, urticaria or rhinitis. Liver failure (Child - Pugh Class C) (liver cirrhosis and ascites). Renal failure (creatinine clearance
Compound
3 ml of solution (1 ampoule) contains: Active substance: diclofenac sodium 75 mg. Excipients: benzyl alcohol, propylene glycol, sodium metabisulfite, sodium hydroxide, water for injection.
Overdose
Symptoms There is no typical clinical picture for an overdose of diclofenac. Overdose may cause symptoms such as vomiting, gastrointestinal symptoms, diarrhea, dizziness, tinnitus, or seizures. In case of severe poisoning? acute renal failure, possible liver damage. Therapeutic measures Treatment of acute poisoning with NSAIDs, including diclofenac, consists of supportive and symptomatic therapy. Supportive and symptomatic therapy should be carried out for complications such as hypotension, renal failure, convulsions, gastrointestinal disorders, and respiratory depression. Special measures such as forced diuresis, dialysis or hemoperfusion are likely to be ineffective in eliminating NSAIDs, including diclofenac, due to high protein binding and extensive metabolism. Treatment is symptomatic.
Side effect
Side effects that occur during treatment with diclofenac sodium are classified into appropriate groups depending on the frequency of occurrence: very frequent (? 1/10), frequent (? 1/100 to
- Rare: hypersensitivity reactions, anaphylactic and anaphylactoid reactions (including bronchospasm, hypotension, shock);
- Very rare: angioedema (including facial edema).
- Very rare: disorientation, depression, insomnia, nightmares, irritability, psychotic reactions.
Mental disorders
Nervous system disorders
- Frequent: headache, dizziness;
- Rare: dizziness, fatigue;
- Very rare: paresthesia, memory impairment, convulsions, anxiety, tremor, aseptic meningitis, taste disturbance, cerebrovascular accident. Visual disorders
- Very rare: blurred vision, blurred vision, diplopia.
Disorders of the hearing organ and labyrinth system
- Frequent vertigo;
- Very rare: tinnitus, hearing loss.
Heart disorders
- Very rare: palpitations, chest pain, heart failure, myocardial infarction.
Vascular disorders
- Very rare: arterial hypertension, vasculitis.
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders
- Rare: asthma (including shortness of breath);
- Very rare: pneumonia.
Gastrointestinal disorders
- Frequent: nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, abdominal pain, flatulence, anorexia;
- Uncommon: constipation;
- Rare: Gastritis, gastrointestinal bleeding, hematemesis, melena, hemorrhagic diarrhea, gastrointestinal ulcer with or without bleeding or perforation;
- Very rare: Colitis (including hemorrhagic, exacerbation of ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease), stomatitis (including ulcerative), glossitis, disorders of the esophagus, stricture-like changes in the small intestine, pancreatitis.
Hepatobiliary system disorders
- Frequent: increased transaminase levels;
- Rare: jaundice, asymptomatic hepatitis, acute hepatitis, chronic active hepatitis, hepatocellular necrosis, cholestasis;
Very rare: fulminant hepatitis, liver failure. Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders
- Common: rash;
- Rare: urticaria;
- Very rare: bullous reactions, eczema, erythema, erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome), exfoliative dermatitis, hair loss, photosensitivity reactions, purpura, allergic purpura, itching.
Renal and urinary tract disorders
- Very rare: renal failure, acute renal failure, hematuria, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, papillary necrolysis, proteinuria.
General disorders and disorders at the injection site
- Common: reaction at the injection site, pain at the injection site, hardening at the injection site;
Rare: swelling, necrosis at the injection site. Infections and infestations
- Very rare: abscess at the injection site.
Clinical trial and epidemiological data suggest that the use of diclofenac, especially at high doses (150 mg daily), over long periods of time, may be associated with a modest increase in the risk of arterial thrombosis (eg, risk of myocardial infarction or stroke). . If serious adverse effects occur, treatment should be discontinued.
Storage conditions
Store at a temperature not exceeding 25 °C. Keep out of the reach of children.
Indications for use of the drug Naklofen
Diseases whose treatment requires anti-inflammatory and/or analgesic action:
- inflammatory rheumatic diseases: rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondyloarthritis, chronic juvenile arthritis, arthritis of various etiologies;
- degenerative rheumatism of the joints and spine: arthrosis, spondylosis;
- arthritis caused by metabolic disorders: gout and pseudogout;
- extra-articular manifestations of rheumatism: periarthritis, bursitis, myositis, tendonitis, synovitis;
- other lesions of the musculoskeletal system, accompanied by inflammation and pain;
- as an analgesic for primary and secondary dysmenorrhea, in the postpartum period, for renal and biliary colic, soft tissue injuries, in the postoperative period and after various dental procedures.
Use of the drug Naklofen
For adults with acute pain syndrome, Naklofen is prescribed 3 ml of solution intramuscularly (contents of 1 ampoule) 1–2 times a day for a short time, followed by switching to oral administration or rectal administration of the drug. For patients with pain syndrome due to renal colic, a second injection at a dose of 75 mg can be prescribed 30 minutes after the first. Parenteral administration of the drug to children is not recommended. The tablets are taken orally during or after meals without chewing, with a small amount of water. Adults are prescribed an initial dose of 100–150 mg/day, depending on the severity of the disease; the usual maintenance dose is 100 mg/day. Children over 14 years of age are prescribed a daily dose of 100 mg, which must be divided into 2 doses. If taking Naklofen tablets is combined with the use of other dosage forms, the total daily dose of the drug should be taken into account. The daily dose of diclofenac is 150 mg and depends on the severity of the disease. At the beginning of treatment, 1 capsule of Naklofen Duo is prescribed 1-2 times a day. In case of severe symptoms, especially in the morning, the daily dose (2 capsules) can be taken in one dose or after a short period of time. Maintenance dose - 1 capsule per day. If taking Naklofen Duo capsules is combined with its other pharmaceutical forms, the total daily dose of the drug should be taken into account, which should not exceed 150 mg. Capsules should be swallowed whole with a small amount of liquid during or immediately after meals. Retard tablets are prescribed 1 tablet per day. For patients who do not tolerate oral administration of the drug, it can be prescribed in suppository form. The initial dose is 100–150 mg/day, usually 1 rectal suppository of 50 mg 2–3 times a day. The usual maintenance dose is 1 suppository of 50 mg 2 times a day. Suppositories are not indicated for use in children.
PHARMACHOLOGIC EFFECT
Diclofenac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects.
The main mechanism of its action and associated side effects are the indiscriminate inhibition of the activity of the enzyme cyclooxygenase 1 and 2 (COX1 and COX2), which leads to disruption of the metabolism of arachidonic acid, a decrease in the synthesis of prostaglandins, prostacyclin and thromboxane. The synthesis of prostaglandins in the kidneys, gastric mucosa and synovial fluid is reduced.
Most effective for inflammatory pain. In rheumatic diseases, the anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect of diclofenac helps to significantly reduce the severity of pain, morning stiffness, and swelling of the joints, which improves the functional state of the joints. For injuries, in the postoperative period, diclofenac reduces pain and inflammatory swelling. Like all NSAIDs, diclofenac has antiplatelet activity. In therapeutic doses, diclofenac has virtually no effect on bleeding time. With long-term treatment, the analgesic effect of diclofenac does not decrease.
PHARMACOKINETICS
Suction
Diclofenac is rapidly absorbed after rectal administration. Cmax is reached after 1 hour. When administered rectally, food intake does not affect the absorption of diclofenac.
Distribution
99% of absorbed diclofenac is bound to plasma proteins, mainly albumin. Diclofenac actively penetrates into the synovial fluid, where it reaches 60-70% of serum concentrations. 3-6 hours after application, the concentrations of the active substance and metabolites in the synovial fluid are higher than in the serum. Diclofenac is eliminated from synovial fluid more slowly than from blood serum.
Metabolism and excretion
T1/2 of diclofenac is 1-2 hours. Diclofenac is almost completely metabolized in the liver, mainly by hydroxylation and methoxylation. The enzyme system P450 CYP2C9 takes part in the metabolism of the drug. The pharmacological activity of the metabolites is lower than that of diclofenac.
T1/2 from plasma - 2 hours. About 70% of the administered dose is excreted in the form of pharmacologically inactive metabolites by the kidneys; less than 1% is excreted unchanged, the rest of the dose is excreted as metabolites in the bile.
Pharmacokinetics in special clinical situations
In patients with severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 10 ml/min), the excretion of metabolites in bile increases, but no increase in their concentration in the blood is observed.
In patients with chronic hepatitis or compensated cirrhosis of the liver, as well as in elderly patients, the pharmacokinetic parameters of diclofenac do not change.
INDICATIONS
Diseases that require achieving a rapid anti-inflammatory or analgesic effect:
- inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system (rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondyloarthritis, juvenile chronic arthritis, arthritis of other etiologies);
— degenerative diseases of the musculoskeletal system (osteoarthritis);
- microcrystalline arthritis (gouty arthritis, pseudogouty arthritis);
- rheumatic lesions of soft tissues;
- periarthritis, bursitis, myositis, tendonitis, synovitis;
- other inflammatory diseases of the musculoskeletal system, accompanied by pain.
As an analgesic, Naklofen is used for soft tissue injuries, in dentistry, after surgery, for severe migraine attacks, primary algodismenorrhea, adnexitis, as well as for renal or biliary colic.
Diclofenac is intended for symptomatic therapy and does not affect the progression of the disease.
DOSING REGIME
Rectally. If patients have poor tolerance to oral forms of diclofenac, Naklofen can be administered rectally in the form of suppositories in appropriate doses. When combining several dosage forms (in addition to oral administration of the drug), it should be taken into account that the daily dose of diclofenac should not exceed 150 mg.
For adults, the initial dose is 100-150 mg per day (1 suppository 2-3 times a day), depending on the severity of the disease. For adolescents aged 15 years and older, it is recommended to take 1 suppository no more than 2 times a day. The maintenance dose is usually 100 mg per day (1 suppository 2 times a day).
The minimum effective dose should be used for the shortest possible course.
SIDE EFFECT
Classification of the frequency of side effects (WHO):
very often - >1/10
often - from > 1/100 to < 1/10
uncommon - from > 1/1000 to < 1/100
rarely - from>1/10000 to<1/1000
very rarely - from <1/10000, including individual reports.
From the digestive system: often - epigastric pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, anorexia, increased aminotransferase activity; rarely - gastritis, proctitis, exacerbation of hemorrhoids, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract (vomiting with blood, melena, diarrhea mixed with blood), gastrointestinal ulcers (with or without bleeding or perforation), hepatitis, jaundice, impaired liver function; very rarely - stomatitis, glossitis, dry mucous membranes (including the mouth), damage to the esophagus, diaphragm-like intestinal strictures (nonspecific hemorrhagic colitis, exacerbation of ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease), constipation, pancreatitis, fulminant hepatitis. When using suppositories, local irritation and inflammation are possible.
From the nervous system: often - headache, dizziness; rarely - drowsiness; very rarely - sensory disturbance, incl. paresthesia, memory disorders, tremor, convulsions, anxiety, cerebrovascular disorders, aseptic meningitis, disorientation, depression, insomnia, nightmares, irritability, mental disorders.
From the senses: often - vertigo; very rarely - visual impairment (blurred vision, diplopia), hearing impairment, tinnitus, impaired sense of taste.
From the urinary system: very rarely - acute renal failure, hematuria, proteinuria, interstitial nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, papillary necrosis.
From the hematopoietic organs: very rarely - thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, eosinophilia, hemolytic and aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis.
Allergic reactions: anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, including a pronounced decrease in blood pressure and shock; very rarely - angioedema (including of the face).
From the cardiovascular system: very rarely - palpitations, extrasystole, chest pain, increased blood pressure, vasculitis, heart failure, myocardial infarction.
From the respiratory system: rarely - cough, bronchial asthma (including shortness of breath); very rarely - pneumonitis, laryngeal edema.
From the skin: often - skin rash; rarely - urticaria; very rarely - bullous rashes, eczema, incl. multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome, Lyell's syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis, itching, hair loss, photosensitivity, purpura, incl. allergic.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
— the period after coronary artery bypass grafting;
- erosive and ulcerative changes in the mucous membrane of the stomach or duodenum, active gastrointestinal bleeding;
- inflammatory bowel diseases (UC, Crohn's disease) in the acute phase;
- rectal bleeding, hemorrhoids, trauma or inflammation of the rectum;
- cerebrovascular bleeding;
- hemophilia and other bleeding disorders;
- severe liver failure or active liver disease;
- severe renal failure (creatinine clearance less than 30 ml/min), including confirmed hyperkalemia, progressive kidney disease;
- decompensated heart failure;
- inhibition of bone marrow hematopoiesis;
— III trimester of pregnancy, breastfeeding period;
- children's age (up to 15 years);
- complete or incomplete combination of bronchial asthma, recurrent polyposis of the nose and paranasal sinuses and intolerance to acetylsalicylic acid and other NSAIDs (including a history);
- hypersensitivity to diclofenac.
With caution: coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular diseases, dyslipidemia/hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus, peripheral arterial disease, smoking, CC less than 60 ml/min; anamnestic data on the development of ulcerative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection, old age, long-term use of NSAIDs, frequent alcohol consumption, severe somatic diseases, pregnancy I-II trimester, concomitant therapy with the following drugs: anticoagulants (for example, warfarin), antiplatelet agents (for example, acetylsalicylic acid, clopidogrel), fibrinolytics, oral glucocorticoids (for example, prednisolone), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (for example, citalopram, fluoxetine, paroxetine, sertraline).
PREGNANCY AND LACTATION
The use of diclofenac in pregnant women is possible only when the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the potential risk to the fetus. Diclofenac should not be used during the last trimester of pregnancy.
Although diclofenac is found in breast milk in small quantities, its use during breastfeeding is not recommended.
SPECIAL INSTRUCTIONS
Patients should inform their physician of any history of chronic diseases, metabolic disorders, or hypersensitivity reactions.
When treating with Naklofen, patients with a history of diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract should be carefully monitored.
The drug should be used with caution in patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease due to a possible exacerbation of the disease.
If signs of liver damage appear (itching, yellowing of the skin, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dark urine, increased levels of liver transaminases), you should stop taking the drug and consult your doctor.
With long-term use (more than 2 weeks) of diclofenac, monitoring of liver function indicators (levels of “liver” transaminases) is necessary.
Diclofenac should be prescribed with caution to patients with severe renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, bleeding disorders, porphyria, epilepsy, as well as patients receiving anticoagulants or fibrinolytics.
The drug should not be used simultaneously with other NSAIDs.
The drug can change the properties of platelets, but does not replace the preventive effect of acetylsalicylic acid in cardiovascular diseases.
The use of the drug may adversely affect female fertility and is not recommended for women planning pregnancy.
In infectious diseases, the anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects of diclofenac sodium can mask the symptoms of these diseases.
In elderly patients, as in the case of other medications, Naklofen should be used in the minimum effective dose.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and other complex mechanisms
During the treatment period, the speed of mental and motor reactions may decrease, so it is necessary to refrain from engaging in potentially hazardous activities that require increased concentration and speed of psychomotor reactions.
OVERDOSE
When using suppositories, an overdose is unlikely.
Symptoms: vomiting, nausea, abdominal pain, bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract, diarrhea, headache, dizziness, tinnitus, increased excitability, hyperventilation with increased convulsive readiness, convulsions, with a significant overdose, acute renal failure, hepatotoxic effect.
Treatment: symptomatic therapy aimed at eliminating increased blood pressure (BP), renal dysfunction, seizures, gastrointestinal irritation, and respiratory depression. Forced diuresis and hemodialysis are ineffective (significant association with proteins and intensive metabolism).
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Increases plasma concentrations of digoxin, methotrexate, lithium and cyclosporine.
Reduces the effect of diuretics; against the background of potassium-sparing diuretics, the risk of developing hyperkalemia increases; against the background of anticoagulants, antiplatelet and thrombolytic drugs (alteplase, streptokinase, urokinase), the risk of bleeding increases (most often in the gastrointestinal tract).
Reduces the effect of antihypertensive and hypnotic drugs. Increases the likelihood of side effects of other NSAIDs and corticosteroids (bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract), the toxicity of methotrexate and the nephrotoxicity of cyclosporine.
Acetylsalicylic acid reduces the concentration of diclofenac in the blood. Concomitant use with paracetamol increases the risk of developing nephrotoxic effects of diclofenac.
When taken simultaneously with hypoglycemic agents, hypo- or hyperglycemia may occur. With this combination of drugs, monitoring of blood glucose concentration is necessary.
Cefamandole, cefoperazone, cefotetan, valproic acid and plicamycin increase the incidence of hypoprothrombinemia.
Cyclosporine and gold preparations increase the effect of diclofenac on the synthesis of prostaglandins in the kidneys, which is manifested by increased nephrotoxicity.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors increase the risk of gastrointestinal bleeding.
Simultaneous administration with ethanol, colchicine, corticotropin and St. John's wort preparations increases the risk of bleeding in the gastrointestinal tract.
Medicines that cause photosensitivity increase the sensitizing effect of diclofenac to ultraviolet radiation.
Drugs that block tubular secretion increase the plasma concentration of diclofenac, thereby increasing its toxicity.
Antibacterial drugs from the quinolone group increase the risk of developing seizures.
CONDITIONS OF VACATION FROM PHARMACIES
On prescription.
CONDITIONS AND DURATION OF STORAGE
At a temperature not higher than 25 °C.
Keep out of the reach of children. Shelf life: 4 years. Attention! The description of the drug on this page is simplified. Before purchasing and using the drug, consult your doctor or pharmacist, and also read the instructions approved by the manufacturer. Information about the drug is provided for informational purposes only and should not be used as a guide to self-medication. ATTENTION! This section is provided for informational purposes only and is not a catalog or price list of our company. To obtain information about the availability of drugs, call + 99871 202 0999 Pharmacy Network Helpline 999.
Side effects of the drug Naklofen
Possible side effects from the gastrointestinal tract (nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, dyspepsia and flatulence), headache, dizziness, which, as a rule, do not require cessation of treatment. Very rarely possible: bleeding, ulcers and perforation of the gastrointestinal tract, asymptomatic hepatitis, jaundice, acute hepatitis, chronic active hepatitis, hepatocellular necrosis and cholestasis, skin rash, itching, peripheral edema (swelling of the extremities), depression, insomnia, fatigue, anxiety , irritability or drowsiness, renal failure, hematuria. In isolated cases, the development of nonspecific hemorrhagic colitis, relapse or worsening of ulcerative colitis or the appearance of Crohn's disease, hypersensitivity reactions (bronchospasm, angioedema, anaphylactic shock), photosensitivity, anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia and agranulocytosis are observed.
Special instructions for the use of Naklofen
For patients with a history of gastrointestinal bleeding, diclofenac is prescribed only in urgent cases, under close medical supervision, with the simultaneous use of antiulcer drugs. Caution is also required when prescribing Naklofen to patients with ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease, since diclofenac can cause a relapse or exacerbation of the disease. Diclofenac is prescribed with caution to patients with renal, hepatic or heart failure, patients with epilepsy, porphyria, impaired hemostasis, as well as patients who have been treated with anticoagulants or fibrinolytics. In elderly patients, diclofenac should be prescribed at the minimum effective dose. Although diclofenac has not been experimentally established to have teratogenic properties, the drug should not be prescribed during pregnancy unless the potential benefit to the mother outweighs the possible risk to the fetus. It is especially not recommended to prescribe the drug in the third trimester of pregnancy, since the blockade of prostaglandin synthesis caused by it can lead to premature closure of the ductus arteriosus. It is recommended to stop breastfeeding while taking the drug. The drug may slightly affect the patient’s ability to drive and operate machinery. Patients with dizziness and central nervous system disorders should refrain from driving vehicles and working with potentially dangerous mechanisms.
Naklofen
Naklofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, one of many generics of the “classic” of this group of drugs - diclofenac. It has analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects. Used for diseases and pathological conditions in which it is necessary to achieve a rapid anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect, including rheumatoid arthritis, seronegative spondyloarthropathy, juvenile polyarthritis, osteoarthritis, gout, pyrophosphate arthropathy, rheumatic diseases of the periarticular soft tissues, inflammation of the periarticular tissues, joint capsule, skeletal muscles, tendons, synovial membrane of the joint, other inflammatory diseases accompanied by severe pain. As a pain reliever, Naklofen is in demand for traumatic damage to soft tissues in dental practice, after operations, for severe migraines, painful menstruation, inflammation of the ovaries and fallopian tubes, exacerbations of urinary and cholelithiasis. At the same time, Naklofen only temporarily eliminates pain symptoms, without in any way affecting the cause of the disease (symptomatic treatment). Diclofenac is the most popular NSAID both among doctors (“the title” of the most prescribed NSAID speaks volumes) and among patients, since its over-the-counter status allows one to purchase the drug as part of the concept of responsible self-medication without visiting a clinic or writing a prescription from a doctor. Taking into account all generics, diclofenac is firmly among the ten best-selling drugs in the world, regardless of pharmacological group. The action of this drug is based on the ability to suppress the synthesis of the enzyme cyclooxygenase, which is involved in the formation of mediators of pain and inflammation, prostaglandins.
In addition to this, Naklofen has central analgesic activity due to its effect on opiate receptors. The drug is most effective for pain syndrome of inflammatory origin. For diseases of the joints and periarticular tissues, Naklofen softens or completely relieves pain, eliminates morning stiffness in movements, swelling, and improves the functional characteristics of joints. For traumatic injuries and after surgery, Naklofen eliminates pain and swelling associated with inflammation. With prolonged drug courses, the analgesic effect of the drug does not decrease. Naklofen is not used for individual intolerance to the active or auxiliary components, ulcerative-erosive lesions of the stomach and duodenum, severe liver and kidney diseases, severe heart failure, inflammation of the rectum, bronchial asthma in the acute phase. In pediatrics, the drug is used starting from the age of 15. It is allowed to take Naklofen in minimal dosages in the 1st and 2nd trimester of pregnancy. In the third trimester of pregnancy, taking the drug is contraindicated, as well as during breastfeeding. The risk of developing unwanted side effects (a comprehensive list of them can be found in the instructions for use) can be reduced by using Naklofen in the minimum effective dosage and a course of the shortest possible duration. Particular caution should be observed when prescribing the drug to elderly patients: in this case, pharmacotherapy must be carried out under strict medical supervision. The combined use of Naklofen with other NSAIDs is contraindicated.
Drug interactions Naklofen
Simultaneous administration of Naklofen with lithium salts or digoxin may cause an increase in their concentration in the blood serum. Naklofen may reduce the diuretic effect of some diuretics; its simultaneous administration with potassium-sparing diuretics can lead to the development of hyperkalemia. When administered simultaneously with acetylsalicylic acid or other NSAIDs, the risk of side effects increases. May enhance the nephrotoxic effect of cyclosporine and the toxic effects of methotrexate, reduce the effectiveness of antihypertensive drugs. Diclofenac generally does not affect the activity of oral hypoglycemic agents.