Fallopian tube obstruction is a pathological condition that develops as a result of an inflammatory process in the tube or in the tissues surrounding it. Very often, a woman does not even suspect the existence of the disease until problems arise with conceiving a baby. The causes of obstruction of the fallopian tubes are very different, most often these are infections that are accompanied by an inflammatory process. Also, adhesions can appear after abortion, surgery, or peritonitis. In most cases, the pathology does not affect the woman’s health; the only problem for her is the inability to conceive naturally. Tubal obstruction can be treated conservatively or surgically. If therapy is ineffective, they resort to IVF or other assistive technologies.
Fallopian tube obstruction: infertility
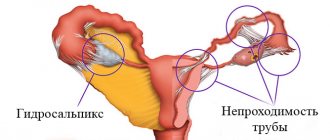
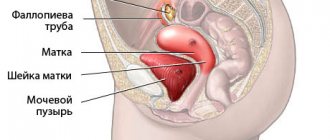
Fallopian tube obstruction is one of the most common causes of infertility. Every month, during ovulation, an egg is released from one of the ovaries. The egg travels through the fallopian tube to the uterus. To fertilize an egg, a sperm passes through the cervix, uterus, and enters the fallopian tubes (where fertilization occurs). Patency of the fallopian tubes allows the egg to travel from the ovary to the uterine cavity, where it can continue its development and give rise to pregnancy.
Options and causes of fallopian tube obstruction
Fallopian tube obstruction varies. The type and degree of blockage of the tube significantly affect the possibility of conception. There are the following options:
- Complete obstruction of the fallopian tubes
- Blockage of one pipe
- Partial gynecological obstruction of the fallopian tubes with movement disorders
- Adhesions around appendages and tubes
- Violation of the motor activity of villi on the funnel of the pipe
The fallopian tubes are paired organs with a diameter of about a centimeter and a length of about 10 centimeters. Inside the tube, the diameter varies, from a millimeter at the entrance to the uterus to a centimeter on the other side. Any inflammatory process in which these organs are involved can cause the formation of adhesions and blockage of the lumen of the tube. So, with one episode of inflammation, the probability of signs of tubal obstruction occurring is 15%, with two – 35%, with three – 75%. Sometimes infectious diseases are practically asymptomatic, which absolutely does not exclude the formation of adhesions. With chronic inflammation with frequent exacerbations, complete obstruction of the fallopian tubes occurs, according to some data, with a probability of 90%.
The most common causes of fallopian tube obstruction resulting from inflammation are chlamydial infection, gonorrhea, mycoplasma, gardnerella, and ureaplasma. Due to the increasing incidence of tuberculosis, this infection cannot be ruled out. Surgery in the pelvis or abdominal cavity can easily provoke obstruction of the fallopian tubes. Pathology often occurs after removal of appendicitis, especially purulent, complicated by peritonitis. Also, signs of obstruction of the fallopian tubes are detected with endometriosis, after abortion or ectopic pregnancies, with tumors or polyps in the uterine cavity and appendages, and abnormal development of these organs.
Different types of pathology
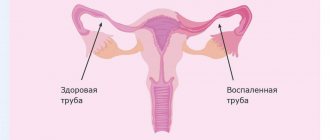
Doctors distinguish several types of fallopian tube lesions. The main type is the number of pipes affected - one or two. A lesion in one tube is called a unilateral lesion. Two pipes – bilateral damage. Closing the lumen of one tube significantly reduces the chances of conception, but the possibility remains. With bilateral damage, pregnancy is impossible.
Further, obstruction is characterized by the degree of closure of the lumen - complete or partial3:
- With partial obstruction, the lumen is narrowed, but is still present. The egg, due to its relatively large size, squeezes through with difficulty or gets stuck, which can lead to an ectopic pregnancy when smaller sperm from the uterus penetrate the fallopian tube.
- Complete obstruction means that the egg cannot move and sperm cannot enter the fallopian tube from the other side. A state of infertility occurs.
Overlapping of the lumen can be formed in different parts of the fallopian tube. The thinnest area is the most sensitive - the isthmus. Even mild inflammation of the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube can lead to its complete closure. The most stable area is the funnel, due to its largest width. It can also be blocked, but in extremely rare cases due to congenital pathologies or injuries3.
The reasons for closing the lumen in the tubes are divided into functional and anatomical. With functional obstruction, the main detrimental effect is on muscle motility and the properties of the mucous membrane of the fallopian tube. The movement of the egg is too slow or completely absent. Anatomical obstruction is characterized by the presence of adhesions, trauma, or the consequences of surgery1.
Tubal patency test
Today, the following methods are used to detect the patency of the fallopian tubes:
- X-ray hysterosalpingography.
This method of diagnosing the condition of the internal female genital organs allows us to determine the shape of the uterus, the degree of lumen, and the structure of the walls. The study involves the introduction of a contrast agent and an x-ray examination of the internal contour of the uterus and tubes. Unpleasant sensations during the procedure are insignificant; Minor bleeding may occur within a few hours after the procedure. - Echohysterosalpingography (hydrosonography).
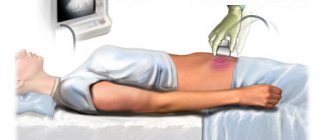
The study is carried out using ultrasound, which diagnoses the condition of the uterine cavity and the patency of the fallopian tubes. This method is less painful than x-ray hysterosalpingography, and therefore is used more widely. During echohysterosalpingography, a catheter is inserted into the uterine cavity, through which a contrast agent is infused in a volume of 10-20 ml. Next, the injected fluid penetrates into the fallopian tubes, then into the abdominal cavity, which further proves the patency of the fallopian tubes. In case of obstruction, the contrast agent accumulates only in the tubes. After the manipulation, patients feel some pain, which, as a rule, goes away quickly. - Fertiloscopy.
The method involves inserting a thin optical device through the posterior vaginal fornix. The examination is performed under intravenous anesthesia and lasts from 10 to 15 minutes. Fertiloscopy allows you to make a visual assessment of the condition of the pelvic organs. To diagnose patency of the fallopian tubes, the doctor injects an antiseptic solution - methylene blue - through the uterine catheter. During fertiloscopy, adhesions are separated simultaneously. - Laparoscopy.
Diagnostics provides high accuracy when checking the patency of the fallopian tubes, and also allows you to identify endometriosis, uterine fibroids and ovarian cysts. If tubal obstruction is detected, during laparoscopy this problem can be eliminated by performing tubal plastic surgery or removal of adhesions.
Diagnosis and treatment
The main diagnostic tool has long been an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity or, more familiar to the ear, ultrasound. In most cases, ultrasound is sufficient to diagnose the problem, especially with the intravaginal method of inserting a diagnostic device. Using ultrasound, you can determine swelling of the fallopian tube, the presence of adhesions or neoplasms1.
Another effective method is endoscopy. A special fiber optic tube with a camera at the end is inserted into the uterine cavity and moves towards the fallopian tubes. Any pathological changes are recorded on a separate monitor4.
A less common method, but especially popular if obstruction is suspected, is hysterosalpingography (HSG). A special contrast agent is injected into the uterine cavity, after which an x-ray of the abdominal cavity is taken. In the image, the uterus is immediately completely visible, and areas of complete obstruction of the tubes are easily identified1.
In addition to the basic methods, doctors take blood, urine and vaginal smears for a general analysis. Typically, the diagnostic process takes place in a gynecologist’s office, but if necessary, a neurologist, oncologist, infectious disease specialist and endocrinologist can be involved in the process.
The choice of treatment method depends entirely on the cause of tubal obstruction and the extent of the lesion2:
- Drug treatment is prescribed for the progression of infectious processes or other failures. The doctor prescribes a specific drug - antibiotics, antiviral drugs, immunostimulants, hormonal drugs and much more.
- Physiotherapy is used after defeating the infection and as a preventive measure. As part of physiotherapy, special baths, massage, electrophoresis and myostimulation are used.
- Surgical treatment is the most effective method and the only one in the presence of adhesions or tumors. Typically, a gentle and modern method of surgery is used - laparoscopy.
If no treatment method produces results, then a diagnosis of infertility is made and the woman should pay attention to artificial methods of insemination. In most cases, the uterus is still functioning, and obstruction of the fallopian tubes is not a contraindication to pregnancy.
Womenfirst
- Abashidze, A. Methods of rehabilitation of reproductive function in women with tubo-peritoneal infertility / A.A. Abashidze // Medical and social examination and rehabilitation – 2014 – No. 2 – pp. 42-46.
- Yakovleva, E. Ways to restore the functional activity of the reproductive organs of women after inflammatory diseases / E.A. Yakovleva // Scientific Gazette - 2013 - No. 25 (168) - Issue 24 - P. 66-72.
- Ayushinova, N. Assessment of the severity of adhesions in the abdominal cavity / N.I. Ayushinova, I.A. Shurygina, M.G. Shurygin, E.V. Glinskaya // Siberian Medical Journal – 2014 – No. 7 – P. 10-14.
- Yakovleva, N. The importance of endoscopic technologies in the diagnosis and selection of treatment methods for patients with tubo-peritoneal infertility / N.V. Yakovleva // Mother and child in Kuzbass - 2013 - No. 2 (53) - pp. 31-37.
- Dubinskaya, E. Pelvic peritoneal adhesions (endoscopic characteristics) / E.D. Dubinskaya, A.S. Gasparov, S.K. Nazarov, M.F. Dorfman // Bulletin of RUDN University, Medicine. Obstetrics and Gynecology, – 2010 – No. 6 – P. 166-173.
RUDFS183119 dated 10/03/2018
Test for tubal patency: price
The cost of diagnosing tubal patency depends on the chosen method. Only your attending gynecologist can determine which method is optimal in your particular case. In general, the price of the study consists of the cost of the intrauterine catheter (which, in turn, depends on the manufacturer, the price of the echo contrast gel), the cost of consumables and the cost of the specialist’s work. The price is also influenced by the geographical location and prestige of the clinic. In Moscow, the average cost of diagnosing tubal patency varies from 1,500 to 4,500 rubles.
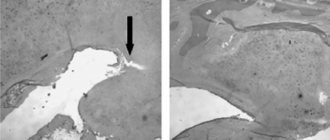
Hysterosalpingography images
The right fallopian tube is obstructed in the ampullary section.
The left fallopian tube is freely patent.
The "R" on the image indicates the patient's right side.
The arrow indicates an obstruction in the ampullary section of the right fallopian tube.
The right and left fallopian tubes are difficult to pass due to the presence of bilateral valve sactosalpinxes.
The image clearly shows dilated and tortuous fallopian tubes.
The arrow shows the fallopian tube on the left with the presence of a valve sactosalpinx.
The "R" on the image indicates the patient's right side.
The left fallopian tube is freely patent.
The right fallopian tube is obstructed in the intramural section.
The arrow indicates the presence of an obstruction at the mouth of the right fallopian tube.
The letter "R" in the image represents the patient's right side.
The left fallopian tube is obstructed in the ampullary section.
The right fallopian tube is difficult to pass due to the presence of a valve sactosalpinx on the right.
The arrow shows the valve sactosalpinx on the right.
The "R" on the image indicates the patient's right side.
Clinical signs of tubal obstruction and diagnosis
Tubal obstruction has scant symptoms. The manifestations are associated with an exacerbation of the inflammatory process; patients are bothered by various types of pain in the lower abdomen, vaginal discharge, and sometimes fever. A woman can live with a problem for many years without knowing about it. Some patients do not even have a history of surgery or inflammatory diseases. By and large, the pathology does not at all affect general well-being and health (except reproductive health), and is not life-threatening. But very often, obstruction of the fallopian tubes causes infertility; the inability to get pregnant forces patients to consult a doctor.
Since fallopian tube obstruction has mild symptoms, additional diagnostic tests must be performed before prescribing treatment. Ultrasound provides little information. To obtain more data, hydrosonography is done.
A more accurate method is x-ray hydrosalpingography, but this type of diagnosis is performed less and less due to its harm to health. X-ray hydrosalpingography has begun to be replaced by diagnostic laparoscopy, which makes it possible to simultaneously diagnose pathology and eliminate it.
Fallopian tube obstruction: what to do?
Having received a diagnosis of “obstruction of the fallopian tubes,” patients are interested in the question of whether it is possible to eliminate the pathology, or is it better to immediately opt for the method of artificial insemination.
Age plays a big role in resolving this issue. Up to 35 years of age, in the absence of other disorders that prevent pregnancy, you can try to restore the patency of the tubes and become pregnant within a year. As for women over the age of 35 who suffer from long-term infertility and tubal obstruction, here it is worth first of all giving preference to IVF. The fact is that over time, the quality of eggs deteriorates, as a result of which the risk of genetic disorders in the fetus increases. Therefore, it is not considered advisable to waste time trying to restore the patency of the tubes.
Clinical prognosis
In addition to oncological diseases that pose a direct threat to a woman’s life, the most severe pathologies of the fallopian tubes include hydrosalpinx, pyosalpinx and salpingitis. These diseases carry a high risk of developing difficult-to-treat forms of female infertility, and therefore the main efforts should be aimed at their prevention.
Other diseases of the fallopian tubes are successfully treated and have favorable clinical prognoses both in terms of recovery and in the matter of preserving the possibility of subsequent childbearing - of course, subject to timely seeking medical help.
Obstetrician-gynecologist of the highest category. Kosolapova Ekaterina Vitalievna
Fallopian tube obstruction - treatment
Treatment is mainly carried out when blockage of the fallopian tubes causes infertility. Conservative medicinal methods or surgical ones are used. If there is minor tubal obstruction, treatment includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, resolving therapy with streptokinase or hyaluronidase. If there is an infection, therapy necessarily includes taking antibiotics or antiviral drugs. Physiotherapeutic procedures give good results.
If tubal obstruction has more severe symptoms, treatment may be invasive. Techniques such as blowing and flushing pipes are now a thing of the past. They too often caused complications, and their effect was questionable. The main method of invasive therapy now is an operation called “laparoscopy”.
Symptoms, signs of tubal obstruction
If the fallopian tubes are obstructed, there may be no symptoms or signs; this pathology may not affect the general state of health and well-being in any way. There are cases when a young woman uses contraception in order not to become pregnant during periods of life when they are not planning to have children, and when the desire to have a child comes, the absence of pregnancy and the diagnosis indicated serious problems with the fallopian tubes. This happens, unfortunately, not uncommonly . The woman did not even know about such a pathology, because there were no symptoms of obstruction of the fallopian tubes and no serious health problems either. However, with chronic recurrent inflammatory diseases, as well as with hydrosalpinx, many women experience the following signs of tubal obstruction, which can occur with other pathological processes of the female genital organs:
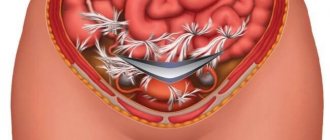
Laparoscopy for tubal obstruction
Laparoscopy for obstruction of the fallopian tubes is prescribed from the 7th day of the cycle and no later than the 10th before the onset of ovulation. However, if there are urgent indications, removal of tubes or adhesions can be performed on any day of the cycle. The operation is performed under general anesthesia.
Manipulations are carried out through several holes in the anterior abdominal wall, 5-7 mm in diameter. A laparoscope equipped with a mini-camera at the end is inserted into one such hole, thanks to which the image is displayed on the screen. A manipulator is inserted into the second puncture, with the help of which the surgeon can move the organs and perform other necessary manipulations. The abdominal cavity is first filled with carbon dioxide in order to improve visibility by raising the abdominal wall.
As a rule, the patient stays in the hospital for no more than a day. Doctors are monitoring her condition and performing ultrasounds. After 2-3 days you can return to work. Drinking alcohol and heavy food is not recommended for 2-3 weeks after surgery. Sexual contacts should also be postponed during this period. As for physical activity, it needs to be increased evenly. It is better to start with walking, gradually increasing their duration.
Please note: if there is significant obstruction of the fallopian tubes, surgery is not always successful. According to statistics, in the first six months after its implementation, only about half of the patients become pregnant. Then this percentage drops, as adhesions can form again.
Fallopian tube obstruction: how to get pregnant
When fallopian tube obstruction is found, what should you do to get pregnant? These questions are often heard in doctors' offices and on online forums. It should be noted that a diagnosis is not a death sentence. Pregnancy with one fallopian tube - healthy, or with partial obstruction - is quite likely. But cases of pregnancy without fallopian tubes naturally have not been recorded. Here we have to resort to assisted reproductive techniques.
The easiest is intrauterine insemination with the sperm of the husband or donor. It will bring results if at least one pipe is in normal condition. Intrauterine insemination is carried out by injecting specially prepared sperm into the uterine cavity. To increase the likelihood of a positive result, ovulation is stimulated. It is necessary that the eggs mature in the ovary on the side where the patent tube is located. This is determined by ultrasound.
Intrauterine insemination costs little and is much cheaper than IVF. The probability of conception with it ranges from 3% to 20%. The procedure is sometimes prescribed after adhesion surgery to increase its effectiveness. Intrauterine insemination, its price may also depend on whether hormonal stimulation of ovulation is carried out. If yes, then the cost will also include the price of the drugs. In most clinics it is 20,000-40,000 rubles.
How to choose the best method?
Many patients are lost in the abundance of diagnostic methods and often do not know what is best to choose for a given study. It is important to understand that you should always consult your doctor. For some, hysterosalpingoscopy is better suited, while others need to additionally remove the cyst from the ovary. In this case, laparoscopy becomes the method of choice. It turns out that the selection of a diagnostic method in most cases is quite individual.
The main criteria that doctors use to evaluate a particular procedure remain:
- Potential reliability of diagnostic information. In this case, laparoscopy often “wins”, since the doctor will be able to see with his own eyes what is happening inside.
- Safety for the patient.
- The need to use additional medications (anesthesia).
- Duration of the procedure.
- The severity of the patient's condition.
By assessing all these criteria, the most appropriate diagnostic method can be selected.