Intestinal dysfunction is one of the most severe functional digestive disorders.
The large and small intestines are responsible for the functions of digestion and assimilation of food, and also remove undigested residues from the body.
Patients often experience intestinal obstruction, the causes of which may be associated with dangerous diseases. This pathology often requires radical treatment measures.
Intestinal obstruction and its types
Intestinal obstruction - as a congenital pathology
Nutrients travel a long way in the body in order to provide all cells with energy and building material. At the same time, the final digestive processes occur in the intestines, including the absorption of food substrates and excretion of feces.
The total length of the human intestine is 4 meters. The appearance of an obstructed area in any part of the intestine can lead to serious consequences.
The intestine has a muscular lining. Wave-like muscle contraction ensures the movement of food and feces into the lumen of the organ. Violation of this intestinal function may be one of the causes of obstruction.
Stagnation of feces only aggravates the condition, since this results in increased absorption of water and hardening of the stool. However, much more often, obstruction is formed due to more serious pathologies.
Intestinal obstruction can be complete or incomplete. With incomplete obstruction, the patient's intestines still produce gas.
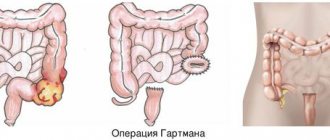
Types of surgery for bowel obstruction include:
- Surgical resection : Removal of the obstruction is necessary when a mass such as a tumor is present.
- Removing adhesions : If you have scar tissue compressing the outside of your intestines, it is often necessary to cut them off, although the scar tissue may return.
- Stent placement : A stent, which is a tube that holds the intestine open, may be placed inside the intestine to allow food and stool to pass through and prevent blockages. This may be necessary when bowel obstruction recurs or when the bowel is severely damaged.
- Colostomy/ileostomy : If your intestines are damaged or inflamed, you may need a permanent or temporary ileostomy or colostomy, which is an artificial opening in the abdomen to remove waste or stool. Sometimes these are temporary structures needed to prevent a severe gastrointestinal infection from spreading throughout the body. However, it is possible that the ends of the intestine cannot be reconnected and these openings may be required for a long time.
- Revascularization . Ischemic colitis may require revascularization, which is the repair of blocked blood vessels that supply blood to the intestines.
Symptoms
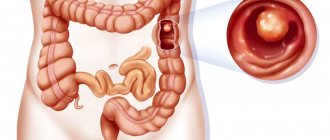
Bowel obstruction may be caused by a tumor
The symptoms of intestinal obstruction will depend on the location and duration of the obstruction. For example, vomiting is an early sign of small intestinal obstruction.
The same symptom may appear with prolonged obstruction of the large intestine. Partial obstruction can cause diarrhea.
What happens to the removed stoma?
Within 2-3 weeks after the operation for acute intestinal obstruction, provided the general condition improves and the consequences of intoxication of the body are eliminated, a repeat operation can be performed to restore the natural passage of food. In such cases, an intestinal anastomosis is performed, which is immersed inside the abdominal cavity.
In other cases, a colostomy bag is attached to the colostomy to collect intestinal contents. Modern types of colostomy bags make it possible to maintain an acceptable quality of life even when used for several months. [2.6]
Diagnosis of the disease
Intestinal obstruction: diverticulosis
Diagnosis of intestinal obstruction includes a physical examination of the patient, laboratory and instrumental studies.
First of all, the doctor learns about the patient’s complaints and conducts a general examination. Already at this stage, characteristic signs of pathology are revealed. In addition, the doctor needs to find out the medical history and also find out whether the patient has had surgical interventions in recent years.
The physical examination will include palpation, percussion, and auscultation using a phonendoscope. The first two methods help detect bloating and signs of pain. When listening, organ motility disorders are often revealed.
If at this stage the doctor does not identify accurate signs of intestinal obstruction, laboratory and instrumental tests will be prescribed.
The main instrumental method is scanning the abdominal cavity. In this case, the doctor receives an image of the intestines, on which it is easy to notice signs of obstruction. Scanning also helps to clarify the area of obstruction and the severity of the pathology.
The following scanning methods are used:
Treatment of small intestinal obstruction
As we have already said, treatment of obstruction begins at the stage of examining the patient. Infusions of rehydrating solutions are carried out, the loss of electrolytes is replenished, and the contents accumulated in the adductor section of the intestine are aspirated using a nasogastric tube. If necessary, antibiotics are prescribed. The main stage of treatment for intestinal obstruction is surgery, which should be performed as soon as possible after diagnosis. It is possible to delay the operation for 2-3 hours to stabilize the patient’s condition. Surgical intervention involves laparotomy - opening the abdominal cavity with subsequent revision and elimination of the causes that caused the development of obstruction:
- The adhesions are cut.
- Hernias are sutured.
- Remove stones or intestinal parasites.
During the operation, the viability of the intestine must be assessed. If there are signs of necrosis, resection of the affected area is performed.
The greatest difficulty is intestinal obstruction caused by malignant neoplasms. In this case, the operation is more extensive. If possible, the tumor is removed within healthy tissue. If this is not possible, palliative operations are performed, for example, bypass anastomoses are performed.
In case of extensive neoplasms or carcinomatosis of the peritoneum, anastomoses have a short-term effect and the obstruction recurs. In such cases, a stoma is indicated - the section of the intestine located above the obstruction is brought out onto the abdominal wall. The intestinal contents will be discharged into a special bag, a colostomy bag. This is a psychologically very difficult operation for patients, but only it can save their lives.
In these cases, if possible, antitumor treatment is carried out, and if the results are stable, reconstructive interventions are performed.
Treatment and patient actions
Intestinal obstruction: diverticulosis
In case of intestinal obstruction, pre-medical care is undesirable, since unprofessional manipulations can only aggravate the patient’s condition.
If signs of obstruction are detected, you should go to the hospital emergency room as soon as possible. At the same time, it is strictly forbidden to give an enema, eat solid foods, or induce vomiting.
Treatment depends on the location and type of obstruction. Partial obstruction is often resolved non-surgically. In this case, intravenous infusions of electrolytes are indicated, since a blocked intestine may not provide complete absorption.
Possible medicinal methods:
- Drugs that counteract the effects of opioid painkillers.
- Antibiotics to treat infection.
- Antiemetic drugs.
- Painkillers.
Surgery is indicated for complete obstruction and life-threatening complications. The doctor may resort to laparoscopic or open surgery.
Studies have shown that the small incision approach (laparoscopy) is safer and more effective for most patients. However, open surgery may be required to remove part of the intestine if necrosis occurs.
Intussusception
For a successful outcome, therapy should begin on the first day from the moment signs of intussusception appear. In the hospital, the child is given enemas, and surgical treatment methods are also available in some cases. Treatment methods may be different, depending on the situation, age of the patient, etc.
Air, saline, and barium enemas are effective for treating intussusception. An enema increases the pressure in the baby's intestines, so the intussusception straightens. This procedure is also called reduction. When using enemas to monitor the condition of the intestine, x-rays or ultrasound diagnostics are necessary.
An enema is effective in 75 cases out of 100. There is evidence that an enema with air is more effective than with barium or saline. ). The success of the procedure also depends on the duration of symptoms: the longer signs of intussusception are present, the less likely it is that the enema will be successful.
Bowel perforations occur in 25 out of 1000 cases of liquid enema use. With air enemas, the ratio of the number of perforations to the number of attempts to deliver an enema is 2 to 1000. This procedure is sometimes used again. But repetition more than 3 times is not recommended. This method of treatment is not used if there are signs of inflammatory processes in the abdominal wall, with sepsis (generalized infection), perforation, or gangrene of the intestine.
Surgery
Indications for surgical treatment of intussusception:
- the doctor suspected damage to the intestinal wall - in such cases, surgical treatment should be emergency
- the enema did not help even on the 3rd try
- the intestine has burst, feces penetrate into the abdominal cavity
Stages of surgery to treat intussusception:
- A skin incision is made on the anterior abdominal wall.
- The involved area of intestine is gently stretched to restore the normal shape of the intestine.
- The doctor removes the damaged areas.
- The appendix is also removed, even if it is healthy.
- The required number of stitches is placed on the wound.
If a large amount of intestine is removed or a severe infection develops, an ileostomy must be performed for a certain period. This is an operation to connect the lumen of the small intestine through the abdominal wall with a colostomy bag. Without treatment, intestinal obstruction occurs, and rupture of the intestinal wall is likely, which results in generalization of the infection, which in most cases entails death.
Intussusception can recur, which happens in some cases. If treatment with enemas was carried out, in 10 cases out of 100 a relapse is possible. Then the enema is repeated or surgery is performed. When surgical treatment is used, relapse is recorded in 2-5% of cases. Then the operation is repeated to straighten the intestine and find the causes of the disease. Sometimes the part of the intestine where the pathology occurs is removed.
What to do after surgery
After surgery, you should be careful for about 2-3 weeks to notice possible complications in the child:
- nausea and vomiting
- diarrhea
- temperature increase
- restlessness and frequent crying
You should take care of the seam. Maintain hygiene in this area and check for signs of post-operative wound infection:
- tissue swelling
- pain
- increase in temperature in that area
- redness in and around the suture
Possible complications
Intestinal obstruction
Complications of intestinal obstruction can cause the patient's death. In this case, complications often arise due to untimely or incorrect treatment.
The most dangerous complications:
- Necrosis of a section of the intestine. In this case, the death of organ cells occurs. This pathology can occur if an obstruction interferes with the blood supply to the intestine. This is a common complication of obstruction caused by an abdominal hernia.
- Peritonitis. A strong enlargement of the intestinal area leads to rupture of the organ wall and release of contents into the abdominal cavity. In this case, a severe infectious process occurs.
Other complications:
- Dehydration.
- Electrolyte imbalance.
- Kidney failure.
- Sepsis.
It is important to remember that delay in detecting an obstruction increases the chances of dangerous complications occurring.
Preoperative testing
If you have symptoms of a bowel obstruction, your doctor will do a physical exam to check your stomach and bowel sounds.
Diagnostic evaluation may include an abdominal x-ray, computed tomography (ultrasound) scan, or ultrasound. These tests may or may not include a barium enema, which involves injecting a small amount of contrast material into the rectum to better visualize the structures.
If you have a blockage, you may also need a sigmoidoscopy or colonoscopy, which are invasive diagnostic procedures in which a camera is inserted into the colon to visualize the blockage.
Is it possible to help a patient without surgery?
Often in severe cases and inoperable tumors in critically ill patients with partial intestinal obstruction, decompression of the gastrointestinal tract is achieved by endoscopic placement of a stent in the colon. In this case, the surgical operation is performed through the natural lumen of the intestine - under the control of a colonoscope, a balloon is initially inserted into the lumen of the colon per rectum, expanding the narrowed (stenotic) area, and then a stent is installed.
Timely preventive installation of a stent in the intestinal lumen can prolong life and significantly improve its quality by reducing intoxication, as well as avoid possible surgical intervention in patients with stage 4 cancer. Stenting of areas of the duodenum can be performed in a similar manner. [9,11]
We install stents in the large intestine in patients with intestinal cancer and with a high class of anesthetic risk due to the presence of concomitant diseases, including coronary heart disease, diabetes mellitus and a number of others. This will allow you to maintain intestinal patency for a long time and avoid surgical intervention.
Book a consultation 24 hours a day
+7+7+78
Bibliography:
- Clinical recommendations: Acute intestinal obstruction of tumor etiology. - Moscow, 2014.
- Clinical recommendations: Acute intestinal obstruction of tumor etiology in adults. — Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation. — 2022.
- Intestinal obstruction: educational and methodological manual / P. S. Neverov K46 [and others]. – Minsk: BSMU, 2022. – 42 p.
- Surgical diseases. Educational and methodological manual / Edited by Chernyadyev S.A. – Ekaterinburg, 2019. –29s.
- B. O. Kabeshev, S. L. Zyblev. Acute intestinal obstruction. — A practical guide for doctors. — Gomel, 2022.
- M.Yu. Kabanov, I.A. Solovyov, O.V. Balura. — Results of complex treatment of patients with acute intestinal obstruction of carcinomatous origin. - Bulletin of the Russian Military Medical Academy, 1(37)-2012.
- International Classification of Diseases, 10th Revision (ICD-10) https://mkb-10.com/.
- Barnett A, Cedar A, Siddiqui F, et al. Colorectal cancer emergencies. J Gastrointest Cancer 2013;44(2):132–42.
- National clinical guidelines “acute non-tumor intestinal obstruction”. — Russian Society of Surgeons. — 2015.
- Karakaş DÖ, Yeşiltaş M, Gökçek M, Eğin S, Hot S. Etiology, management, and survival of acute mechanical bowel obstruction: Five-year results of a training and research hospital in Turkey. Ulus Travma Acil Cerrahi Derg 2019;25:268-280.
- Colorectal cancer (update): evidence review for effectiveness of stenting compared with emergency surgery for acute large bowel obstruction. Developed by the National Guideline Alliance part of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. FINAL (January 2020).
- Subramaniyan Ramanathan, Vijayanadh Ojili, Ravi Vassa, and Arpit Nagar. Large Bowel Obstruction in the Emergency Department: Imaging Spectrum of Common and Uncommon Causes. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2017; 7: 15. doi: 10.4103/jcis.JCIS_6_17
Our services
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| X-ray of the abdominal cavity (survey) | 2 400 |
| Diagnostic laparoscopy | 40 000 — 60 000 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Classification
The classification of intestinal obstruction is based on various factors. Accordingly, one or another treatment tactic is selected.
Depending on the cause of the pathological condition, the following types of disease are distinguished:
Dynamic intestinal obstruction (due to spasm or, conversely, decreased tone of the intestinal wall).
Mechanical, which is divided into forms:
- strangulation;
- obstructive;
- ischemic (vascular);
- mixed.
According to the level of localization of the process, the following types of obstruction are distinguished:
- high small intestinal;
- low small intestinal;
- colonic
By severity:
- partial;
- complete.
According to clinical signs:
- spicy;
- subacute;
- chronic course.
Stages of intestinal obstruction:
- It’s not for nothing that the stage of “ileus cry” bears this name. It is characterized by severe abdominal pain and lasts 2-12 hours.
- Intoxication is a period of “light” interval, when the pain syndrome subsides and intestinal peristalsis weakens. The feeling of better health is deceptive. The clinic is characterized by bloating, asymmetry of the abdomen, lack of stool and gas.
- The terminal stage is characterized by poor circulation and the development of peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum). It usually occurs 36 hours after the onset of the disease.
Our doctors
Prokhorov Yuri Anatolievich
Surgeon, head of the surgical service of CELT, candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category
33 years of experience
Make an appointment
Lutsevich Oleg Emmanuilovich
Chief Surgeon of CELT, Honored Doctor of the Russian Federation, Chief Specialist of the Moscow Department of Health in Endosurgery and Endoscopy, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Head of the Department of Faculty Surgery No. 1 of the State Budgetary Educational Institution BPO MGMSU, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Doctor of the Highest Category, Professor
43 years of experience
Make an appointment
Gordeev Sergey Alexandrovich
Surgeon, Candidate of Medical Sciences, doctor of the highest category
42 years of experience
Make an appointment