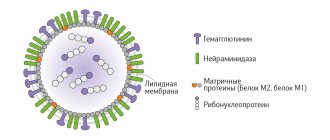
"Algavac-M" - a vaccine for the prevention of hepatitis A
Culture purified inactivated vaccine
, Russia.
Protects against viral disease: hepatitis A.
Try on: for adults and small children from the age of three.
Included in the national calendar of preventive vaccinations in Russia.
IMPORTANT: vaccinations with the Algavac-M vaccine are not carried out in clinics
Advantages of the ALGAVAK-M vaccine:
- A single administration of the vaccine stimulates the rapid development of specific cellular and humoral immunity factors and the production of antibodies to the hepatitis A virus;
- A full course of vaccination, consisting of two vaccinations carried out with an interval of 6-12 months, activates the additional production of virus-neutralizing antibodies in high titers and the creation of long-term intense immunity to the hepatitis A virus;
- Vaccination prevents the spread of infection, since protective antibodies appear in the blood already 15 days after vaccination;
- Unlike many foreign analogues, the drug does not contain antibiotics or preservatives;
- The vaccine is produced according to international GMP production quality standards;
- The vaccination effectiveness rate is 98.6%.
- A full course of vaccination ensures the development of specific immunity for 12-15 years in 90-95% of vaccinated people.
Indications for vaccination "ALGAVAK-M"
Persons who are or will be at risk of contracting viral hepatitis A are subject to vaccination:
- persons living in areas with a high incidence of hepatitis A;
- children and adults traveling on vacation or for work to regions with a high incidence of hepatitis A (military personnel, travelers, etc.);
- children and adults visiting swimming pools;
- children and adults visiting public catering places (restaurants, cafes);
- persons contacted in outbreaks;
- persons at occupational risk of infection: medical personnel and patient care personnel (especially in infectious diseases, gastroenterological and pediatric departments); staff of preschool institutions; sewer and water supply workers; food industry and catering personnel;
- persons from special risk groups (patients with chronic liver disease or an increased risk of liver disease; patients with hemophilia; patients with multiple blood transfusions; drug addicts; homosexuals; persons who are promiscuous).
Indications for use
The vaccine is used to prevent viral hepatitis A in adults, adolescents and children over 3 years of age.
Indications for use:
- living in environmentally unfavorable areas where the risk of contracting hepatitis A is increased;
- planning travel to regions with high incidence rates;
- travel within the country and abroad;
- presence of an occupational risk of contracting hepatitis A: medical staff, social workers, specialists who work in preschool and school institutions, workers of water supply and sewerage systems, public catering establishments;
- entry into a risk group, the presence of chronic liver pathologies, hemophilia, frequent intramuscular and intravenous injections.
Vaccination is also recommended for people who often change sexual partners, use drugs and lead a socially disadvantaged lifestyle.
Instructions for use
Algavac M is used in accordance with special instructions for use. Vaccination is indicated only for healthy people. Before carrying out it, it is necessary to conduct an examination, which includes examination by a specialist, measurement of temperature, pressure, assessment of the condition of the skin and mucous membranes. If necessary, the doctor prescribes certain blood and urine tests.
If you have chronic diseases, additional consultation with specialized specialists is necessary. Allergic patients may suffer from unwanted side reactions in the first days after administration of the drug. To prevent skin itching, inflammation and local swelling, it is necessary to take an antihistamine the day before the procedure.
Vaccination is carried out only in a medical institution, in a specially equipped room where there is a first aid kit for emergency care. The vaccine is administered intramuscularly into the shoulder area. There is no other method of administration provided. The dose for children is 0.5 ml, for adults - 1 ml. Vaccination is carried out in a course, observing a certain interval between administration of the drug.
Main stages of vaccination:
- studying the external condition of the ampoule, checking the expiration date, batch and other important indicators reflected on the ampoule with the drug;
- shaking the ampoule;
- taking the vaccine into a disposable sterile syringe;
- treating the shoulder muscle with an antiseptic;
- administration of a vaccine in a certain dose;
- repeated antiseptic treatment of the injection site.
After vaccination, patients receive detailed advice about possible reactions and their prevention. An opened ampoule can be used within 30 minutes. It is not recommended to rub the injection site so as not to provoke skin inflammation.
Vaccination during pregnancy and breastfeeding
During pregnancy and while breastfeeding, it is prohibited to vaccinate against hepatitis A. If a woman becomes infected during pregnancy, specialists establish medical supervision over her. Jaundice does not threaten the life of the child or the health of the mother. But with a complicated course, the risk of miscarriage and fetal death increases. Therefore, even when planning a pregnancy, it is worth getting vaccinated, especially if the expectant mother is at risk.
It is important to pay increased attention to personal hygiene, thorough hand washing, and treatment of nipples before and after feeding. In this case, vaccination can be carried out during the lactation period.
Use in children
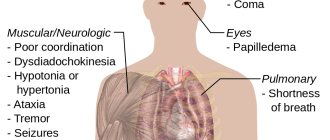
The Algavac M vaccine can be used in cases where the child is already 3 months old. There is no need to get vaccinated before this period, since the newborn receives immunity from the mother. Its effect lasts for approximately 90 days. Pediatricians recommend vaccination before attending kindergarten, where the child will have contact with other children and eat food not prepared at home. Jaundice is difficult for children to tolerate, with clear clinical manifestations. In some children, chronic pathologies of the liver and digestive system progress after the disease.
Contraindications
Only a doctor can decide whether ALGAVAK M is suitable for vaccination
ALGAVAK M is contraindicated if there is a history of an allergic reaction to any component of the vaccine.
Vaccination with ALGAVAK M is contraindicated in the following cases:
- Acute infectious and non-infectious diseases, exacerbations of chronic diseases. The vaccination is carried out no earlier than 1 month after recovery (remission).
- Severe reaction (temperature above 40°C; hyperemia, swelling at the injection site with a diameter of more than 8 cm) with the previous administration of the drug.
- Immunodeficiency conditions, malignant blood diseases and neoplasms.
- Pregnancy.
- Hypersensitivity to any component of the vaccine.
Vaccination against hepatitis A
“Epidemiological surveillance and prevention of viral hepatitis A”
approved by the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation G.G. Onishchenko 28.01. 2011
section 3.3.2. Mechanism, routes and factors of transmission of infection
3.3.2.1. Transmission of the GA virus (HAV) is carried out through the fecal-oral mechanism, which is realized in all ways characteristic of intestinal infections: water, food and household contact.
3.3.2.2. Waterborne transmission may manifest as typical acute or chronic waterborne epidemics. Infection of people occurs when using poor-quality drinking water, bathing in contaminated reservoirs and pools, with intense pollution from water bodies near water intakes, the absence or violation of water treatment regulated by GOST and the rules for disinfecting water supplied to the population, when using technical water pipes, violation of the sanitary and technical condition of the distribution water supply network combined with water shortages and sewerage or contaminated groundwater. The transmission factor can also be water from wells and other non-centralized water supply sources.
With moderate contamination of water supplies with feces, people with high resistance develop predominantly undiagnosed forms of infection, which cause the population to acquire immunity.
3.3.2.3. Food products are a transmission factor in cases of contamination with the virus at food enterprises, catering establishments and trade establishments of any form of ownership. In this case, the sources of the virus are personnel with undiagnosed forms of acute GA (AGA) who violate the rules of personal hygiene. In some cases, virus contamination of food products occurs due to accidents in sewer networks in these institutions.
Berries, vegetables and herbs are contaminated with the virus when they are grown in irrigated fields or agricultural lands where undisinfected wastewater is used as fertilizer. Food products can become contaminated with HAVs during their preparation using poor-quality water during processing and preparation, and washing dishes. Seafood caught in sewage-contaminated coastal waters may be contaminated with HAV.
3.3.2.4. The household route of transmission occurs when sanitary and hygienic rules and personal hygiene rules are violated, which is more often observed in children's groups and families. Transmission factors include hands, as well as all objects contaminated with HAV. In addition, a variant of contact transmission of HAV is its transmission through oral-anal and oral-genital contacts.
3.3.2.5. In case of prolonged viremia, parenteral transmission of HAV cannot be excluded. There have been cases of post-transfusion OGA, large-scale outbreaks of OGA among hemophiliacs receiving clotting factor drugs, as well as among people using injectable psychotropic drugs.
section 3.3.4. Epidemiologically significant population groups
3.3.4.1. The following population groups have the greatest risk of developing OGA:
1) persons using poor quality water for drinking purposes:
— surface water bodies;
— sources of decentralized water supply, equipped in violation of the requirements of sanitary rules and regulations;
- sources of centralized water supply that are not subject to reliable cleaning and disinfection, especially in case of accidents in sewer and water supply networks;
— in the area of natural disasters (earthquakes, floods, floods) and other emergency situations;
2) military personnel of military units stationed or conducting combat operations in areas with unsatisfactory sanitary and living conditions or unguaranteed water supply;
3) persons traveling to countries endemic for OGA;
4) children and staff of children's preschool organizations, closed institutions for round-the-clock care of children and adults operating in violation of sanitary and hygienic rules;
5) medical personnel, primarily in infectious diseases and psychiatric departments, in case of non-compliance with the anti-epidemic regime;
6) persons who use injection drugs.
3.3.4.2. Epidemiologically significant professions, whose representatives, in the event of OGA disease, pose a threat of infection to large groups of the population, include:
— employees of food industry enterprises involved in the production, storage, transportation of food products or their sale;
— employees of public catering establishments, as well as organizations directly related to food preparation, service, storage and transportation of food products;
— workers at water supply facilities associated with water treatment and maintenance of water supply networks;
— health care workers;
— employees of children's, educational, health and other organizations (institutions);
— conductors of passenger cars;
- workers of swimming pools or spas;
- trade workers.
9. Vaccinal prevention of acute hepatitis A
9.1. The scope of specific prevention of OGA is determined by specialists from the bodies carrying out state sanitary and epidemiological surveillance in accordance with the epidemiological situation, as well as taking into account the dynamics and trends in the development of the epidemic process of OGA in a specific territory.
9.2. Vaccination of the population against hepatitis A is carried out in accordance with the current calendar of preventive vaccinations for epidemic indications, regional calendars of preventive vaccinations and instructions for the use of medical immunobiological drugs approved for use on the territory of the Russian Federation in the prescribed manner.
9.3. Vaccine prophylaxis is recommended for the following population groups:
— children living in areas with a high incidence of OGA;
— medical workers;
— teachers and staff of preschool organizations;
— workers in the public service sector, primarily those employed in public catering organizations, servicing water supply and sewerage facilities, equipment and networks;
— traveling to hepatitis A endemic regions and countries;
— contacts in outbreaks for epidemic indications;
- military personnel of military units stationed or conducting combat operations in areas with unsatisfactory sanitary conditions or unguaranteed water supply;
- persons with chronic liver diseases or an increased risk of liver diseases (persons with chronic viral hepatitis; chronic carriers of hepatitis B, C and D viruses; persons suffering from chronic hepatitis of alcoholic, autoimmune, toxic, drug and other origin; persons with Wilson-Konovalov disease , hepatoses and hepatopathy, etc.);
- patients with blood diseases and persons on hemodialysis;
— persons with a behavioral risk of becoming infected with HA (men who have sex with other men; persons who are promiscuous; persons who use injection drugs; patients at drug treatment clinics);
— HIV-infected people when they are identified.
9.4. Children are vaccinated against hepatitis A without prior testing for the presence of antibodies to HAV.
9.5. Vaccination of adults without prior examination for the presence of anti-HAV IgG is acceptable in regions free from OGA.
Before vaccinating adults over 30 years of age in regions with high incidence rates of HAV, it is recommended that they be pre-screened for the presence of specific antibodies to HAV, followed by immunization of seronegative individuals.
The conditional protective concentration of specific antibodies to HAV for the population is 22 IU/l, and for special contingents, incl. military personnel - at least 30 IU/l.
9.6. The administration of medical immunobiological preparations is registered in the established medical records, indicating the name, batch number, control number, expiration date, date of administration, dose and nature of the reaction to the administration.
Possible side effects
In isolated cases, vaccinated individuals may experience malaise, headache, and short-term low-grade fever. In rare cases, transient minor soreness or muscle twitching at the site of vaccine administration, as well as slight hyperemia of the skin or mild swelling, which disappear after 1-2 days, are observed.
Considering the theoretical possibility of developing immediate allergic reactions in particularly sensitive individuals, vaccinated individuals must be provided with medical supervision for 30 minutes.
Come get vaccinated at MiracleChildren. A full range of vaccines for children and adults, family vaccinations - at a special price!